Spring 框架中使用的設(shè)計模式
作者|icoding91
blog.csdn.net/caoxiaohong1005
1. 簡單工廠(非23種設(shè)計模式中的一種)
實現(xiàn)方式:
讀取bean的xml配置文件,將bean元素分別轉(zhuǎn)換成一個BeanDefinition對象。 然后通過BeanDefinitionRegistry將這些bean注冊到beanFactory中,保存在它的一個ConcurrentHashMap中。 將BeanDefinition注冊到了beanFactory之后,在這里Spring為我們提供了一個擴展的切口,允許我們通過實現(xiàn)接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor 在此處來插入我們定義的代碼。 典型的例子就是:PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,我們一般在配置數(shù)據(jù)庫的dataSource時使用到的占位符的值,就是它注入進去的。
各種的Aware接口 ,比如 BeanFactoryAware,對于實現(xiàn)了這些Aware接口的bean,在實例化bean時Spring會幫我們注入對應(yīng)的BeanFactory的實例。 BeanPostProcessor接口 ,實現(xiàn)了BeanPostProcessor接口的bean,在實例化bean時Spring會幫我們調(diào)用接口中的方法。 InitializingBean接口 ,實現(xiàn)了InitializingBean接口的bean,在實例化bean時Spring會幫我們調(diào)用接口中的方法。 DisposableBean接口 ,實現(xiàn)了BeanPostProcessor接口的bean,在該bean死亡時Spring會幫我們調(diào)用接口中的方法。
設(shè)計意義:

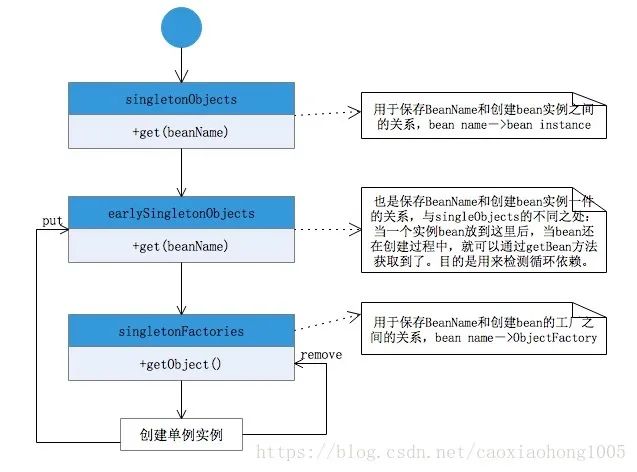
public Object getSingleton(String beanName){//參數(shù)true設(shè)置標(biāo)識允許早期依賴return getSingleton(beanName,true);}protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {//檢查緩存中是否存在實例Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {//如果為空,則鎖定全局變量并進行處理。synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {//如果此bean正在加載,則不處理singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {//當(dāng)某些方法需要提前初始化的時候則會調(diào)用addSingleFactory 方法將對應(yīng)的ObjectFactory初始化策略存儲在singletonFactoriesObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);if (singletonFactory != null) {//調(diào)用預(yù)先設(shè)定的getObject方法singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();//記錄在緩存中,earlysingletonObjects和singletonFactories互斥this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);}}}}return (singletonObject != NULL_OBJECT ? singletonObject : null);}
getSingleton()過程圖
5. 裝飾器模式
實現(xiàn)方式:Spring中用到的包裝器模式在類名上有兩種表現(xiàn):一種是類名中含有Wrapper,另一種是類名中含有Decorator。
實質(zhì):動態(tài)地給一個對象添加一些額外的職責(zé)。就增加功能來說,Decorator模式相比生成子類更為靈活。
6. 代理模式
實現(xiàn)方式:AOP底層,就是動態(tài)代理模式的實現(xiàn)。
動態(tài)代理:在內(nèi)存中構(gòu)建的,不需要手動編寫代理類
靜態(tài)代理:需要手工編寫代理類,代理類引用被代理對象。
實現(xiàn)原理:切面在應(yīng)用運行的時刻被織入。一般情況下,在織入切面時,AOP容器會為目標(biāo)對象創(chuàng)建動態(tài)的創(chuàng)建一個代理對象。SpringAOP就是以這種方式織入切面的。
7. 觀察者模式
實現(xiàn)方式:spring的事件驅(qū)動模型使用的是 觀察者模式 ,Spring中Observer模式常用的地方是listener的實現(xiàn)。
具體實現(xiàn):
事件機制的實現(xiàn)需要三個部分,事件源,事件,事件監(jiān)聽器
public abstract class ApplicationEvent extends EventObject {private static final long serialVersionUID = 7099057708183571937L;private final long timestamp;public ApplicationEvent(Object source) {super(source);this.timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();}public final long getTimestamp() {return this.timestamp;}}
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener {void onApplicationEvent(E event);}
ApplicationContext接口[事件源]
職責(zé):
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher {void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event);}public void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Publishing event in " + getDisplayName() + ": " + event);}getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(event);if (this.parent != null) {this.parent.publishEvent(event);}}
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoaderimplements ConfigurableApplicationContext, DisposableBean {private ApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster;protected void registerListeners() {// Register statically specified listeners first.for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);}// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);for (String lisName : listenerBeanNames) {getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(lisName);}}}
8. 策略模式
實現(xiàn)方式:
Resource 接口介紹
getInputStream():定位并打開資源,返回資源對應(yīng)的輸入流。每次調(diào)用都返回新的輸入流。調(diào)用者必須負責(zé)關(guān)閉輸入流。 exists():返回 Resource 所指向的資源是否存在。 isOpen():返回資源文件是否打開,如果資源文件不能多次讀取,每次讀取結(jié)束應(yīng)該顯式關(guān)閉,以防止資源泄漏。 getDescription():返回資源的描述信息,通常用于資源處理出錯時輸出該信息,通常是全限定文件名或?qū)嶋H URL。 getFile:返回資源對應(yīng)的 File 對象。 getURL:返回資源對應(yīng)的 URL 對象。
UrlResource:訪問網(wǎng)絡(luò)資源的實現(xiàn)類。 ClassPathResource:訪問類加載路徑里資源的實現(xiàn)類。 FileSystemResource:訪問文件系統(tǒng)里資源的實現(xiàn)類。 ServletContextResource:訪問相對于 ServletContext 路徑里的資源的實現(xiàn)類. InputStreamResource:訪問輸入流資源的實現(xiàn)類。 ByteArrayResource:訪問字節(jié)數(shù)組資源的實現(xiàn)類。
9. 模版方法模式
經(jīng)典模板方法定義:
抽象方法:父類中的是抽象方法,子類必須覆蓋 鉤子方法:父類中是一個空方法,子類繼承了默認也是空的
Spring 模板方法模式實質(zhì):
具體實現(xiàn):
public abstract class JdbcTemplate {public final Object execute(String sql){Connection con=null;Statement stmt=null;try{con=getConnection();stmt=con.createStatement();Object retValue=executeWithStatement(stmt,sql);return retValue;}catch(SQLException e){...}finally{closeStatement(stmt);releaseConnection(con);}}protected abstract Object executeWithStatement(Statement stmt, String sql);}
引入回調(diào)原因:
public interface StatementCallback{Object doWithStatement(Statement stmt);
public class JdbcTemplate {public final Object execute(StatementCallback callback){Connection con=null;Statement stmt=null;try{con=getConnection();stmt=con.createStatement();Object retValue=callback.doWithStatement(stmt);return retValue;}catch(SQLException e){...}finally{closeStatement(stmt);releaseConnection(con);}}...//其它方法定義}
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate=...;final String sql=...;StatementCallback callback=new StatementCallback(){public Object=doWithStatement(Statement stmt){return ...;}}jdbcTemplate.execute(callback);
END
順便給大家推薦一個GitHub項目,這個 GitHub 整理了上千本常用技術(shù)PDF,絕大部分核心的技術(shù)書籍都可以在這里找到,
GitHub地址:https://github.com/javadevbooks/books
Gitee地址:https://gitee.com/javadevbooks/books
電子書已經(jīng)更新好了,你們需要的可以自行下載了,記得點一個star,持續(xù)更新中..
評論
圖片
表情

