一文詳解 Ansible 自動化運維
? 開源Linux
一個執(zhí)著于技術(shù)的公眾號
一、Ansible 概述
1、Ansible 特點
Ansible 基于 Python 開發(fā),運維工程師對其二次開發(fā)相對比較容易; Ansible 豐富的內(nèi)置模塊,幾乎可以滿足一切要求; 管理模式非常簡單,一條命令可以影響上千臺主機; 無客戶端模式,底層通過 SSH 通信; Ansible發(fā)布后,也陸續(xù)被 AWS、Google Cloud Platform、Microsoft Azure、Cisco、HP、VMware、Twitter 等大公司接納并投入使用;
二、Ansible的角色
使用者:如何使用 Ansible 實現(xiàn)自動化運維? Ansible 工具集:Ansible 可以實現(xiàn)的功能? 作用對象:Ansible 可以影響哪些主機?
1、使用者
CMDB:CMDB 存儲和管理者企業(yè)IT架構(gòu)中的各項配置信息,是構(gòu)建 ITIL 項目的核心工具,運維人員可以組合 CMDB 和 Ansible,通過 CMDB 直接下發(fā)指令調(diào)用Ansible 工具集完成操作者所希望達到的目標(biāo); PUBLIC/PRIVATE 方式:Ansible 除了豐富的內(nèi)置模塊外,同時還提供豐富的 API語言接口,如PHP、Python、PERL 等多種流行語言,基于 PUBLIC/PRIVATE,Ansible 以 API 調(diào)用的方式運行; Ad-Hoc 命令集:Users直接通過Ad-Hoc命令集調(diào)用Ansible工具集來完成任務(wù); Playbooks:Users 預(yù)先編寫好 Ansible Playbooks,通過執(zhí)行 Playbooks 中預(yù)先編排好的任務(wù)集,按序執(zhí)行任務(wù);
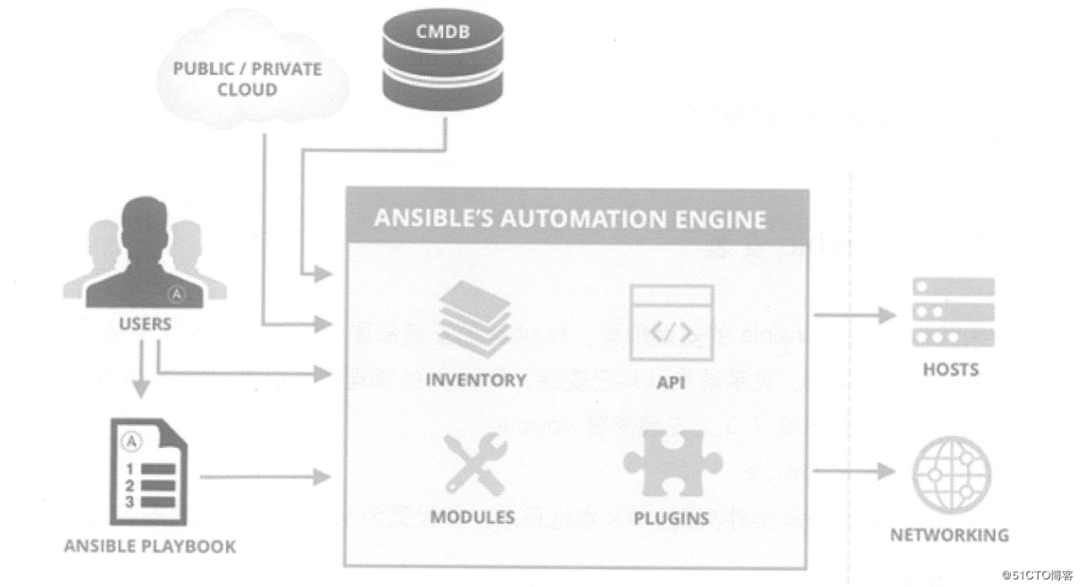
2、Ansible 工具集
Ansible Playbooks:任務(wù)腳本,編排定義Ansible任務(wù)的配置文件,由Ansible按序依次執(zhí)行,通常是JSON格式的YML文件;
Inventory:Ansible 管理主機清單;
Modules:Ansible 執(zhí)行命令功能模塊,多數(shù)為內(nèi)置的核心模塊,也可自定義;
Plugins:模塊功能的補充,如連接類型插件、循環(huán)插件、變量插件、過濾插件等,該功能不太常用;
API:供第三方程序調(diào)用的應(yīng)用程序編程接口;
Ansible:該部分圖中表現(xiàn)得不太明顯,組合 Inventory、API、Modules、Plugins可以理解為是 Ansible 命令工具,其為核心執(zhí)行工具;
3、作用對象
三、Ansible的配置
1、Ansible安裝
1)通過YUM安裝Ansible
[root@centos01 ~]# cd /mnt/ansiblerepo/ansiblerepo/repodata/
[root@centos01 ansiblerepo]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/local.repo
[local]
name=centos
baseurl=file:///mnt/ansiblerepo/ansiblerepo
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
[root@centos01 ~]# yum -y install ansible
2)驗證安裝結(jié)果
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible --version
ansible 2.3.1.0
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = Default w/o overrides
python version = 2.7.5 (default, Nov 6 2016, 00:28:07) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-11)]
3)創(chuàng)建 SSH 免交互登錄
[root@centos01 ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:cJz6NRTrvMDxX+Jpce6LRnWI3vVEl/zvARL7D10q9WY root@centos01
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| . . .|
| . . + oo|
| . = o o. oo|
| = * o..+ *|
| . S *.=+=*+|
| . o =+XooE|
| . ..=.++.|
| ..o ..|
| .. o. |
+----[SHA256]-----+
[root@centos01 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i .ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]
[root@centos01 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i .ssh/id_rsa.pub [email protected]
2、Ansible 配置
-i或—inventory-file來指定 Inventory。[root@centos01 ~]# ansible -i /etc/ansible/hosts web -m ping
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m ping
[root@centos01 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
............
[web]
192.168.100.20
192.168.100.30
[test]
www.benet.com:222
[mail]
yj1.kgc.cn
yj[2:5].kgc.cn
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m command -a "systemctl status httpd" --limit "192.168.100.20"
192.168.100.20 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible 192.168.100.20 -m command -a "systemctl status httpd"
192.168.100.20 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible 192.168.1.* -m command -a "systemctl status httpd"
192.168.100.20 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
.......
192.168.100.30 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
.......
3、Ansible 命令
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible
ansible ansible-console-2 ansible-galaxy ansible-playbook-2.7 ansible-vault-2
ansible-2 ansible-console-2.7 ansible-galaxy-2 ansible-pull ansible-vault-2.7
ansible-2.7 ansible-doc ansible-galaxy-2.7 ansible-pull-2
ansible-connection ansible-doc-2 ansible-playbook ansible-pull-2.7
ansible-console ansible-doc-2.7 ansible-playbook-2 ansible-vault
1)ansible
非固化需求; 臨時一次性操作; 二次開發(fā)接口調(diào)用;
Ansible [options]
-v(—verbose):輸出詳細的執(zhí)行過程信息,可以得到執(zhí)行過程所有信息; -i PATH(—inventory=PATH):指定inventory信息,默認為/etc/ansible/hosts; -f NUM(—forks=NUM):并發(fā)線程數(shù),默認為5個線程; —private-key=PRIVATE_KEY_FILE:指定密鑰文件; -m NAME,—module-name=NAME:指定執(zhí)行使用的模塊; -M DIRECTORY(—module-path=DIRECTORY) :指定模塊存放路徑,默認為/usr/share/ansible; -a ARGUMENTS(—args=ARGUMENTS):指定模塊參數(shù); -u USERNAME(—user=USERNAME):指定遠程主機以USERNAME運行命令; -l subset(—limit=SUBSET):限制運行主機;
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible all -f 5 -m ping
192.168.100.20 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.100.30 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web --list
hosts (2):
192.168.100.20
192.168.100.30
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m command -a "df -hT"
192.168.100.30 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
文件系統(tǒng) 類型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 掛載點
/dev/mapper/cl-root xfs 17G 4.4G 13G 26% /
devtmpfs devtmpfs 897M 0 897M 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 912M 84K 912M 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 912M 0 912M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 xfs 1014M 173M 842M 18% /boot
tmpfs tmpfs 183M 16K 183M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs tmpfs 183M 0 183M 0% /run/user/0
192.168.100.20 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
文件系統(tǒng) 類型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 掛載點
/dev/mapper/cl-root xfs 17G 4.3G 13G 26% /
devtmpfs devtmpfs 897M 0 897M 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 912M 84K 912M 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 912M 0 912M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 xfs 1014M 173M 842M 18% /boot
tmpfs tmpfs 183M 16K 183M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs tmpfs 183M 0 183M 0% /run/user/0
/dev/sr0 iso9660 4.1G 4.1G 0 100% /mnt
紅色:表示執(zhí)行過程出現(xiàn)異常; 橘黃顏色:表示命令執(zhí)行后目標(biāo)有狀態(tài)變化; 綠色:表示執(zhí)行成功且沒有目標(biāo)機器做修改;
2)Ansible-doc
ansible-doc [options] [module……]
[root@centos01 ~]#ansible-doc -l
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible-doc ping
> PING (/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible/modules/system/ping.py)
A trivial test module, this module always returns `pong' on successful contact. It
does not make sense in playbooks, but it is useful from `/usr/bin/ansible' to verify
the ability to login and that a usable python is configured. This is NOT ICMP ping,
this is just a trivial test module.
EXAMPLES:
# Test we can logon to 'webservers' and execute python with json lib.
ansible webservers -m ping
MAINTAINERS: Ansible Core Team, Michael DeHaan
METADATA:
Status: ['stableinterface']
Supported_by: core
3)Ansible-playbook
Ansible-playbook playbook.yml
4)Ansible-console
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible-console
Welcome to the ansible console.
Type help or ? to list commands.
root@all (2)[f:5]$ cd web
root@web (2)[f:5]$ list
192.168.100.20
192.168.100.30
4、Ansible模塊
1)command模塊
chdir:在遠程主機上運行命令前要提前進入的目錄; creates:在命令運行時創(chuàng)建一個文件,如果文件已存在,則不會執(zhí)行創(chuàng)建任務(wù); removes:在命令運行時移除一個文件,如果文件不存在,則不會執(zhí)行移除任務(wù); executeable:指明運行命令的shell程序;
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m command -a "chdir=/ ls ./"
2)shell模塊
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m shell -a "echo hello world "
192.168.100.20 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
hello world
192.168.100.30 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
hello world
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m shell -a "echo hello world > /1.txt"
192.168.100.20 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
192.168.100.30 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
3)copy模塊
dest:指出復(fù)制文件的目標(biāo)目錄位置,使用絕對路徑。如果源是目錄,則目標(biāo)也要是目錄,如果目標(biāo)文件已存在,會覆蓋原有內(nèi)容; src:指出源文件的路徑,可以使用相對路徑和絕對路徑,支持直接指定目錄。如果源是目錄,則目標(biāo)也要是目錄; mode:指出復(fù)制時,目標(biāo)文件的權(quán)限,可選; owner:指出復(fù)制時,目標(biāo)文件的屬主,可選; group:指出復(fù)制時目標(biāo)文件的屬組,可選; content:指出復(fù)制到目標(biāo)主機上的內(nèi)容,不能和src一起使用,相當(dāng)于復(fù)制content指明的數(shù)據(jù)到目標(biāo)文件中;
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m copy -a "src=/etc/hosts
dest=/root/a1.hosts mode=777 owner=root group=root"
4)hostname模塊
name: 指明主機名;
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible 192.168.100.20 -m hostname -a "name=test"
5)yum模塊
name:程序包名稱,可以帶上版本號。若不指明版本,則默認為最新版本; state=present|atest|absent:指明對程序包執(zhí)行的操作:present表明安裝程序包,latest表示安裝最新版本的程序包,absent表示卸載程序包; disablerepo:在用yum安裝時,臨時禁用某個倉庫的ID; enablerepo:在用yum安裝時,臨時啟用某個倉庫的ID; conf_file:yum運行時的配置文件,而不是使用默認的配置文件; disable_gpg_check=yes|no:是否啟用完整性校驗功能;
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m shell -a "/usr/bin/rm -rf
/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-*"
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m shell -a "/usr/bin/mount
/dev/cdrom /mnt"
[WARNING]: Consider using mount module rather than running mount
192.168.100.20 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
mount: /dev/sr0 寫保護,將以只讀方式掛載
192.168.100.30 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
mount: /dev/sr0 寫保護,將以只讀方式掛載
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m yum -a "name=httpd
state=present"
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m shell -a "rpm -qa | grep httpd"
[WARNING]: Consider using yum, dnf or zypper module rather than running rpm
192.168.100.20 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
httpd-2.4.6-67.el7.centos.x86_64
httpd-tools-2.4.6-67.el7.centos.x86_64
192.168.100.30 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
httpd-2.4.6-67.el7.centos.x86_64
httpd-tools-2.4.6-67.el7.centos.x86_64
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m shell -a "systemctl start httpd"
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m shell -a "netstat -anptu | grep httpd"
192.168.100.20 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 2072/httpd
192.168.100.30 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 3098/httpd
6)service模塊
name:被管理的服務(wù)名稱; state=started|stopped|restarted:動作包含啟動,關(guān)閉或重啟; enable=yes|no:表示是否設(shè)置該服務(wù)開機自啟動; runlevel:如果設(shè)定了enabled開機自啟動,則要定義在哪些運行目標(biāo)下自動啟動;
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m service -a "name=httpd
enabled=yes state=restarted"
7)user模塊
name:必選參數(shù),賬號名稱; state=present|absent:創(chuàng)建賬號或者刪除賬號,present表示創(chuàng)建,absent表示刪除; system=yes|no:是否為系統(tǒng)賬戶; uid:用戶UID; group:用戶的基本組 groups:用戶的附加組; shell:默認使用的shell; home:用戶的家目錄; mve_home=yes|no: 如果設(shè)置的家目錄已經(jīng)存在,是否將已存在的家目錄進行移動; pssword:用戶的密碼,建議使用加密后的字符串; comment: 用戶的注釋信息; remore=yes|no: 當(dāng)state=absent時,是否要刪除用戶的家目錄;
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible web -m user -a "name=user01
system=yes uid=502 group=root groups=root shell=/etc/nologin
home=/home/user01 password=pwd@123"
四、playbook配置文件
1、執(zhí)行配置文件
[root@centos01 ~]# grep -v ^# /etc/ansible/hosts | grep -v ^$
[web1]
192.168.100.20
[web2]
192.168.100.30
[root@centos01 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/a.yml
---
- hosts: web1
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: adduser
user: name=user1 state=present
tags:
- aaa
- name: addgroup
group: name=root system=yes
tags:
- bbb
- hosts: web2
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: copy file to web
copy: src=/etc/passwd dest=/home
tags:
- ccc
...

hosts:任務(wù)的目標(biāo)主機,多個主機用冒號分隔,一般調(diào)用/etc/ansible/hosts中的分組信息; remote_user:遠程主機上,運行此任務(wù)的默認身份為root; tasks:任務(wù),即定義的具體任務(wù),由模塊定義的操作列表; handlers:觸發(fā)器,類似tasks,只是在特定的條件下才會觸發(fā)的任務(wù)。 某任務(wù)的狀態(tài)在運行后為changed時,可通過“notify”通知給相應(yīng)的handlers進行觸發(fā)執(zhí)行; roles:角色,將hosts剝離出去,由tasks、handlers等所組成的一種特定的結(jié)構(gòu)集合;
ansible-playbook [option] /PATH/TO/PLAYBOOK.yaml
—syntax-check:檢測yaml文件的語法; -C(—check):預(yù)測試,不會改變目標(biāo)主機的任何設(shè)置; —list-hosts:列出yaml文件影響的主機列表; —list-tasks:列出yaml文件的任務(wù)列表; —list-tags:列出yaml文件中的標(biāo)簽; -t TAGS(—tags=TAGS):表示只執(zhí)行指定標(biāo)簽的任務(wù); —skip-tags=SKIP_TAGS:表示除了指定標(biāo)簽的任務(wù),執(zhí)行其他任務(wù); —start-at-task=START_AT:從指定的任務(wù)開始往下運行;
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check /etc/ansible/a.yml
playbook: /etc/ansible/a.yml
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible-playbook -C /etc/ansible/a.yml
.................
192.168.100.20 : ok=3 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
192.168.100.30 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible-playbook --list-hosts /etc/ansible/a.yml
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible-playbook --list-tasks /etc/ansible/a.yml
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible-playbook --list-tags /etc/ansible/a.yml
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible-playbook /etc/ansible/a.yml
[root@centos01 ~]# ssh 192.168.100.20 tail -1 /etc/passwd
user1:x:1001:1001::/home/user1:/bin/bash
[root@centos01 ~]# ssh 192.168.100.30 ls -ld /home/passwd
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2342 7月 23 16:06 /home/passwd
2、觸發(fā)器
handlers是Ansible提供的條件機制之一。
handlers和task很類似,但是它只在被task通知的時候才會觸發(fā)執(zhí)行。
handlers只會在所有任務(wù)執(zhí)行完成后執(zhí)行。
而且即使被通知了很多次,它也只會執(zhí)行一次。
handlers按照定義的順序依次執(zhí)行。
[root@centos01 ~]# ssh 192.168.100.20 netstat -anpt | grep 80
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 94858/httpd
[root@centos01 ~]# vim /etc/ansible/httpd.yml
---
- hosts: web1
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: change port
command: sed -i 's/Listen\ 80/Listen\ 8080/g' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify:
- restart httpd server
handlers:
- name: restart httpd server
service: name=httpd state=restarted
...
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible-playbook -C /etc/ansible/httpd.yml
[root@centos01 ~]# ansible-playbook /etc/ansible/httpd.yml
[root@centos01 ~]# ssh 192.168.100.20 netstat -anpt | grep 8080
tcp6 0 0 :::8080 :::* LISTEN 103594/httpd
3、角色
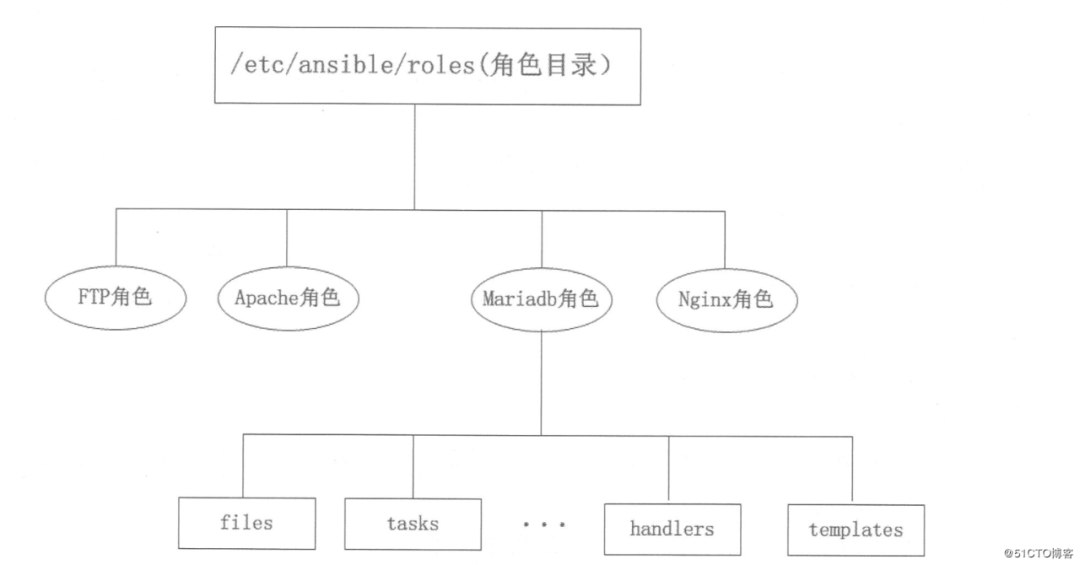
mariadb:mysql角色; Apache:httpd角色; Nginx:Nginx角色;
files:存放由copy或script等模塊調(diào)用的文件; templates:存放template模塊查找所需要的模板文件的目錄,如mysql配置文件模板; tasks:任務(wù)存放的目錄; handlers:存放相關(guān)觸發(fā)執(zhí)行的目錄; vars:變量存放的目錄; meta:用于存放此角色元數(shù)據(jù); default:默認變量存放的目錄,文件中定義了此角色使用的默認變量;
- hosts: web
remote_user: root
roles:
- mysql
- httpd
要求被管理主機上自動安裝mariadb,安裝完成后上傳提前準備好的配置文件至遠端主機,重啟服務(wù),然后新建testdb數(shù)據(jù)庫,并允許test用戶對其擁有所有權(quán)限。
被管理主機配置yum倉庫,自行配置,若被管理端可以連接互聯(lián)網(wǎng),那么直接將yum倉庫指向互聯(lián)網(wǎng)即可。
來源:
https://blog.51cto.com/14156658/2461907
關(guān)注「開源Linux」加星標(biāo),提升IT技能
好文章,分享、點贊、在看三連哦??↓↓↓
