線上 K8s 集群性能評(píng)估、基礎(chǔ)服務(wù)部署調(diào)優(yōu)
原文鏈接:http://arthurchiao.art/blog/k8s-reliability-list-data-zh/
對(duì)于非結(jié)構(gòu)化的數(shù)據(jù)存儲(chǔ)系統(tǒng)來說,LIST 操作通常都是非常重量級(jí)的,不僅占用大量的 磁盤 IO、網(wǎng)絡(luò)帶寬和 CPU,而且會(huì)影響同時(shí)間段的其他請(qǐng)求(尤其是響應(yīng)延遲要求極高的 選主請(qǐng)求),是集群穩(wěn)定性的一大殺手。
例如,對(duì)于 Ceph 對(duì)象存儲(chǔ)來說,每個(gè) LIST bucket 請(qǐng)求都需要去多個(gè)磁盤中撈出這個(gè) bucket 的全部數(shù)據(jù);不僅自身很慢,還影響了同一時(shí)間段內(nèi)的其他普通讀寫請(qǐng)求,因?yàn)?IO 是共享的,導(dǎo)致響應(yīng)延遲上升乃至超時(shí)。如果 bucket 內(nèi)的對(duì)象非常多(例如用作 harbor/docker-registry 的存儲(chǔ)后端),LIST 操作甚至都無法在常規(guī)時(shí)間內(nèi)完成( 因而依賴 LIST bucket 操作的 registry GC 也就跑不起來)。
又如 KV 存儲(chǔ) etcd。相比于 Ceph,一個(gè)實(shí)際 etcd 集群存儲(chǔ)的數(shù)據(jù)量可能很小(幾個(gè) ~ 幾十個(gè) GB),甚至足夠緩存到內(nèi)存中。但與 Ceph 不同的是,它的并發(fā)請(qǐng)求數(shù)量可能會(huì)高 幾個(gè)量級(jí),比如它是一個(gè) ~4000 nodes 的 k8s 集群的 etcd。單個(gè) LIST 請(qǐng)求可能只需要 返回幾十 MB 到上 GB 的流量,但并發(fā)請(qǐng)求一多,etcd 顯然也扛不住,所以最好在前面有 一層緩存,這就是 apiserver 的功能(之一)。K8s 的 LIST 請(qǐng)求大部分都應(yīng)該被 apiserver 擋住,從它的本地緩存提供服務(wù),但如果使用不當(dāng),就會(huì)跳過緩存直接到達(dá) etcd,有很大的穩(wěn)定性風(fēng)險(xiǎn)。
本文深入研究 k8s apiserver/etcd 的 LIST 操作處理邏輯和性能瓶頸,并提供一些基礎(chǔ)服務(wù)的 LIST 壓力測(cè)試、 部署和調(diào)優(yōu)建議,提升大規(guī)模 K8s 集群的穩(wěn)定性。
kube-apiserver LIST 請(qǐng)求處理邏輯:
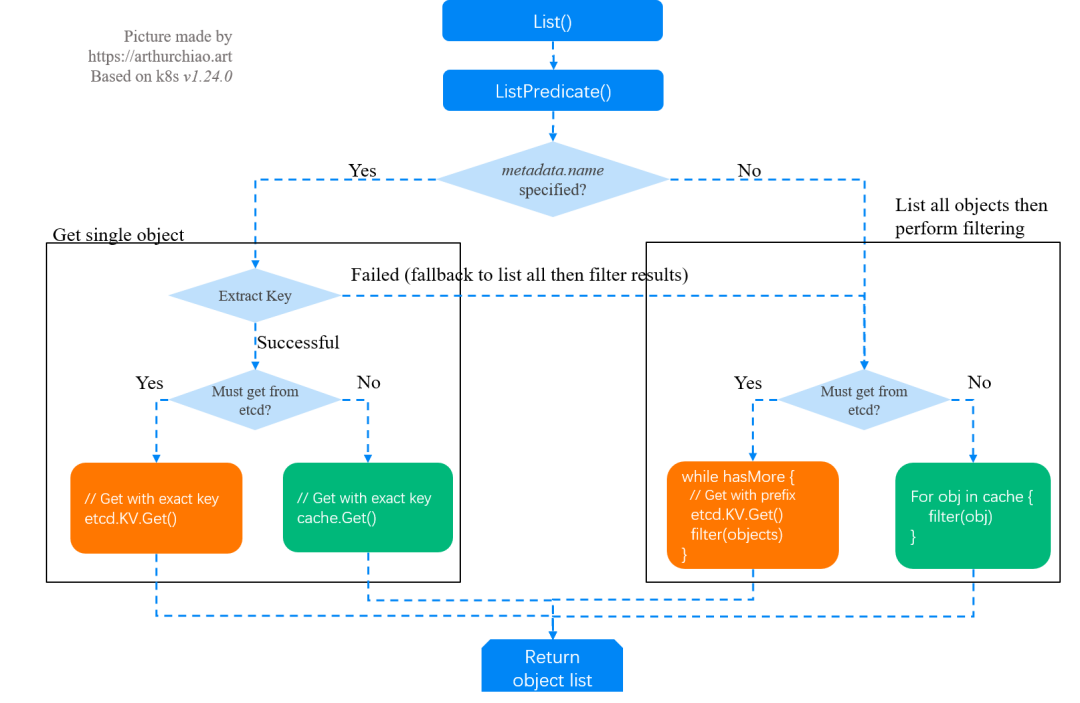
代碼基于 v1.24.0,不過 1.19~1.24 的基本邏輯和代碼路徑是一樣的,有需要可對(duì)照參考。
1 引言
1.1 K8s 架構(gòu):環(huán)形層次視圖
從架構(gòu)層次和組件依賴角度,可以將一個(gè) K8s 集群和一臺(tái) Linux 主機(jī)做如下類比:
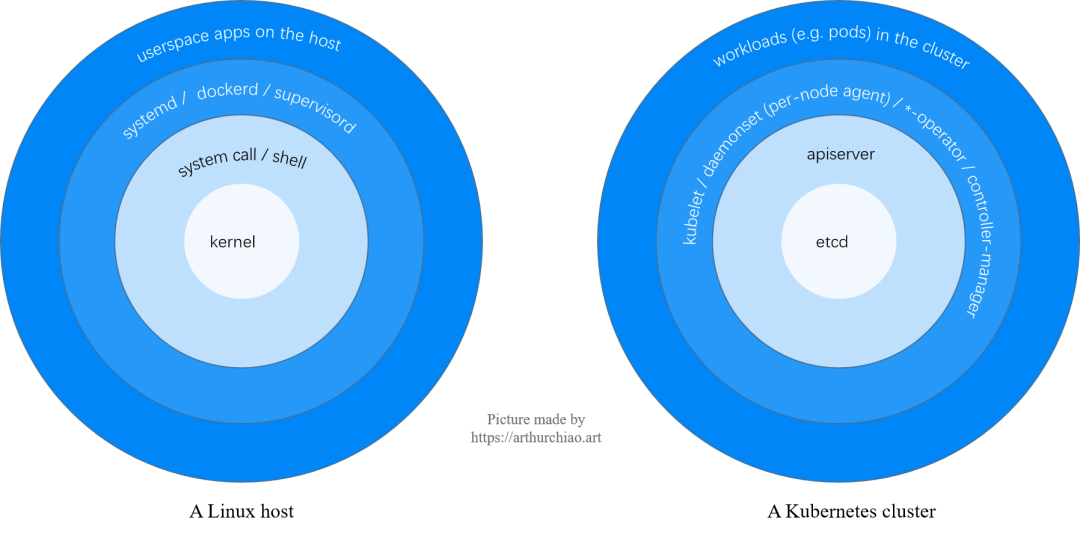
對(duì)于 K8s 集群,從內(nèi)到外的幾個(gè)組件和功能:
etcd:持久化 KV 存儲(chǔ),集群資源(pods/services/networkpolicies/…)的唯一的權(quán)威數(shù)據(jù)(狀態(tài))源; apiserver:從 etcd 讀取( ListWatch)全量數(shù)據(jù),并緩存在內(nèi)存中;無狀態(tài)服務(wù),可水平擴(kuò)展;各種基礎(chǔ)服務(wù)(e.g. kubelet、*-agent、*-operator):連接 apiserver,獲取(List/ListWatch)各自需要的數(shù)據(jù);集群內(nèi)的 workloads:在 1 和 2 正常的情況下由 3 來創(chuàng)建、管理和 reconcile,例如 kubelet 創(chuàng)建 pod、cilium 配置網(wǎng)絡(luò)和安全策略。
1.2 apiserver/etcd 角色
以上可以看到,系統(tǒng)路徑中存在兩級(jí) List/ListWatch(但數(shù)據(jù)是同一份):
apiserver List/ListWatch etcd 基礎(chǔ)服務(wù) List/ListWatch apiserver
因此,從最簡(jiǎn)形式上來說,apiserver 就是擋在 etcd 前面的一個(gè)代理(proxy),
+--------+ +---------------+ +------------+
| Client | -----------> | Proxy (cache) | --------------> | Data store |
+--------+ +---------------+ +------------+
infra services apiserver etcd
絕大部分情況下,apiserver 直接從本地緩存提供服務(wù)(因?yàn)樗彺媪思喝繑?shù)據(jù));
某些特殊情況,例如,
客戶端明確要求從 etcd 讀數(shù)據(jù)(追求最高的數(shù)據(jù)準(zhǔn)確性), apiserver 本地緩存還沒建好
apiserver 就只能將請(qǐng)求轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)給 etcd —— 這里就要特別注意了 —— 客戶端 LIST 參數(shù)設(shè)置不當(dāng)也可能會(huì)走到這個(gè)邏輯。
1.3 apiserver/etcd List 開銷
1.3.1 請(qǐng)求舉例
考慮下面幾個(gè) LIST 操作:
LIST apis/cilium.io/v2/ciliumendpoints?limit=500&resourceVersion=0這里同時(shí)傳了兩個(gè)參數(shù),但
resourceVersion=0會(huì)導(dǎo)致 apiserver 忽略limit=500, 所以客戶端拿到的是全量 ciliumendpoints 數(shù)據(jù)。一種資源的全量數(shù)據(jù)可能是比較大的,需要考慮清楚是否真的需要全量數(shù)據(jù)。后文會(huì)介紹定量測(cè)量與分析方法。
LIST api/v1/pods?filedSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1這個(gè)請(qǐng)求是獲取
node1上的所有 pods(%3D是=的轉(zhuǎn)義)。根據(jù) nodename 做過濾,給人的感覺可能是數(shù)據(jù)量不太大,但其實(shí)背后要比看上去復(fù)雜:
這種行為是要避免的,除非對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)準(zhǔn)確性有極高要求,特意要繞過 apiserver 緩存。
首先,這里沒有指定 resourceVersion=0,導(dǎo)致 apiserver 跳過緩存,直接去 etcd 讀數(shù)據(jù); 其次,etcd 只是 KV 存儲(chǔ),沒有按 label/field 過濾功能(只處理 limit/continue),所以,apiserver 是從 etcd 拉全量數(shù)據(jù),然后在內(nèi)存做過濾,開銷也是很大的,后文有代碼分析。 LIST api/v1/pods?filedSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1&resourceVersion=0跟 2 的區(qū)別是加上了
resourceVersion=0,因此 apiserver 會(huì)從緩存讀數(shù)據(jù),性能會(huì)有量級(jí)的提升。但要注意,雖然實(shí)際上返回給客戶端的可能只有幾百 KB 到上百 MB(取決于 node 上 pod 的數(shù)量、pod 上 label 的多少等因素), 但 apiserver 需要處理的數(shù)據(jù)量可能是幾個(gè) GB。后面會(huì)有定量分析。
以上可以看到,不同的 LIST 操作產(chǎn)生的影響是不一樣的,而客戶端看到數(shù)據(jù)還有可能只 是 apiserver/etcd 處理數(shù)據(jù)的很小一部分。如果基礎(chǔ)服務(wù)大規(guī)模啟動(dòng)或重啟, 就極有可能把控制平面打爆。
1.3.2 處理開銷
List 請(qǐng)求可以分為兩種:
List 全量數(shù)據(jù):開銷主要花在數(shù)據(jù)傳輸; 指定用 label 或字段(field)過濾,只需要匹配的數(shù)據(jù)。
這里需要特別說明的是第二種情況,也就是 list 請(qǐng)求帶了過濾條件。
大部分情況下,apiserver 會(huì)用自己的緩存做過濾,這個(gè)很快,因此耗時(shí)主要花在數(shù)據(jù)傳輸; 需要將請(qǐng)求轉(zhuǎn)給 etcd 的情況, 前面已經(jīng)提到,etcd 只是 KV 存儲(chǔ),并不理解 label/field 信息,因此它無法處理過濾請(qǐng)求。實(shí)際的過程是:apiserver 從 etcd 拉全量數(shù)據(jù),然后在內(nèi)存做過濾,再返回給客戶端。因此除了數(shù)據(jù)傳輸開銷(網(wǎng)絡(luò)帶寬),這種情況下還會(huì)占用大量 apiserver CPU 和內(nèi)存。
1.4 大規(guī)模部署時(shí)潛在的問題
再來看個(gè)例子,下面這行代碼用 k8s client-go 根據(jù) nodename 過濾 pod,
podList, err := Client().CoreV1().Pods("").List(ctx(), ListOptions{FieldSelector: "spec.nodeName=node1"})
看起來非常簡(jiǎn)單的操作,我們來實(shí)際看一下它背后的數(shù)據(jù)量。以一個(gè) 4000 node,10w pod 的集群為例,全量 pod 數(shù)據(jù)量:
etcd 中:緊湊的非結(jié)構(gòu)化 KV 存儲(chǔ),在 1GB 量級(jí); apiserver 緩存中:已經(jīng)是結(jié)構(gòu)化的 golang objects,在 2GB 量級(jí)( TODO:需進(jìn)一步確認(rèn)); apiserver 返回:client 一般選擇默認(rèn)的 json 格式接收, 也已經(jīng)是結(jié)構(gòu)化數(shù)據(jù)。全量 pod 的 json 也在 2GB 量級(jí)。
可以看到,某些請(qǐng)求看起來很簡(jiǎn)單,只是客戶端一行代碼的事情,但背后的數(shù)據(jù)量是驚人的。指定按 nodeName 過濾 pod 可能只返回了 500KB 數(shù)據(jù),但 apiserver 卻需要過濾 2GB 數(shù)據(jù) —— 最壞的情況,etcd 也要跟著處理 1GB 數(shù)據(jù) (以上參數(shù)配置確實(shí)命中了最壞情況,見下文代碼分析)。
集群規(guī)模比較小的時(shí)候,這個(gè)問題可能看不出來(etcd 在 LIST 響應(yīng)延遲超過某個(gè)閾值 后才開始打印 warning 日志);規(guī)模大了之后,如果這樣的請(qǐng)求比較多,apiserver/etcd 肯定是扛不住的。
1.5 本文目的
通過深入代碼查看 k8s 的 List/ListWatch 實(shí)現(xiàn),加深對(duì)性能問題的理解,對(duì)大規(guī)模 K8s 集群的穩(wěn)定性優(yōu)化提供一些參考。
2 apiserver List() 操作源碼分析
有了以上理論預(yù)熱,接下來可以看代碼實(shí)現(xiàn)了。
2.1 調(diào)用棧和流程圖
store.List
|-store.ListPredicate
|-if opt == nil
| opt = ListOptions{ResourceVersion: ""}
|-Init SelectionPredicate.Limit/Continue fileld
|-list := e.NewListFunc() // objects will be stored in this list
|-storageOpts := storage.ListOptions{opt.ResourceVersion, opt.ResourceVersionMatch, Predicate: p}
|
|-if MatchesSingle ok // 1. when "metadata.name" is specified, get single obj
| // Get single obj from cache or etcd
|
|-return e.Storage.List(KeyRootFunc(ctx), storageOpts) // 2. get all objs and perform filtering
|-cacher.List()
| // case 1: list all from etcd and filter in apiserver
|-if shouldDelegateList(opts) // true if resourceVersion == ""
| return c.storage.List // list from etcd
| |- fromRV *int64 = nil
| |- if len(storageOpts.ResourceVersion) > 0
| | rv = ParseResourceVersion
| | fromRV = &rv
| |
| |- for hasMore {
| | objs := etcdclient.KV.Get()
| | filter(objs) // filter by labels or filelds
| | }
|
| // case 2: list & filter from apiserver local cache (memory)
|-if cache.notready()
| return c.storage.List // get from etcd
|
| // case 3: list & filter from apiserver local cache (memory)
|-obj := watchCache.WaitUntilFreshAndGet
|-for elem in obj.(*storeElement)
| listVal.Set() // append results to listOjb
|-return // results stored in listObj
對(duì)應(yīng)的流程圖:

2.2 請(qǐng)求處理入口:List()
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/v1.24.0/staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/registry/generic/registry/store.go#L361
// 根據(jù) PredicateFunc 中指定的 LabelSelector 和 FieldSelector 過濾,返回一個(gè)對(duì)象列表
func (e *Store) List(ctx, options *metainternalversion.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
label := labels.Everything()
if options != nil && options.LabelSelector != nil
label = options.LabelSelector // Label 過濾器,例如 app=nginx
field := fields.Everything()
if options != nil && options.FieldSelector != nil
field = options.FieldSelector // 字段過濾器,例如 spec.nodeName=node1
out := e.ListPredicate(ctx, e.PredicateFunc(label, field), options) // 拉取(List)數(shù)據(jù)并過濾(Predicate)
if e.Decorator != nil
e.Decorator(out)
return out, nil
}
2.3 ListPredicate()
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/v1.24.0/staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/registry/generic/registry/store.go#L411
func (e *Store) ListPredicate(ctx , p storage.SelectionPredicate, options *metainternalversion.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
// Step 1: 初始化
if options == nil
options = &metainternalversion.ListOptions{ResourceVersion: ""}
p.Limit = options.Limit
p.Continue = options.Continue
list := e.NewListFunc() // 返回結(jié)果將存儲(chǔ)在這里面
storageOpts := storage.ListOptions{ // 將 API 側(cè)的 ListOption 轉(zhuǎn)成底層存儲(chǔ)側(cè)的 ListOption,字段區(qū)別見下文
ResourceVersion: options.ResourceVersion,
ResourceVersionMatch: options.ResourceVersionMatch,
Predicate: p,
Recursive: true,
}
// Step 2:如果請(qǐng)求指定了 metadata.name,則應(yīng)獲取單個(gè) object,無需對(duì)全量數(shù)據(jù)做過濾
if name, ok := p.MatchesSingle(); ok { // 檢查是否設(shè)置了 metadata.name 字段
if key := e.KeyFunc(ctx, name); err == nil { // 獲取這個(gè) object 在 etcd 中的 key(唯一或不存在)
storageOpts.Recursive = false
e.Storage.GetList(ctx, key, storageOpts, list)
return list
}
// else 邏輯:如果執(zhí)行到這里,說明沒有從 context 中拿到過濾用的 key,則 fallback 到下面拿全量數(shù)據(jù)再過濾
}
// Step 3: 對(duì)全量數(shù)據(jù)做過濾
e.Storage.GetList(ctx, e.KeyRootFunc(), storageOpts, list) // KeyRootFunc() 用來獲取這種資源在 etcd 里面的 root key(即 prefix,不帶最后的 /)
return list
}
1.24.0 中 case 1 & 2 都是 調(diào)用
e.Storage.GetList(),之前的版本有點(diǎn)不同:
Case 1 中的 e.Storage.GetToList Case 1 中的 e.Storage.List 不過基本流程是一樣的。
如果客戶端沒傳
ListOption,則初始化一個(gè)默認(rèn)值,其中的ResourceVersion設(shè)置為空字符串, 這將使 apiserver 從 etcd 拉取數(shù)據(jù)來返回給客戶端,而不使用本地緩存(除非本地緩存還沒有建好);
Docker+K8s+Jenkins 主流技術(shù)全解視頻資料【干貨免費(fèi)分享】
舉例,客戶端設(shè)置
ListOption{Limit: 5000, ResourceVersion: 0}list ciliumendpoints 時(shí),發(fā)送的請(qǐng)求將為/apis/cilium.io/v2/ciliumendpoints?limit=500&resourceVersion=0。ResourceVersion為空字符串的行為,后面會(huì)看到對(duì)它的解析。用 listoptions 中的字段分別初始化過濾器(SelectionPredicate)的 limit/continue 字段;
初始化返回結(jié)果,
list := e.NewListFunc();將 API 側(cè)的 ListOption 轉(zhuǎn)成底層存儲(chǔ)的 ListOption,字段區(qū)別見下文
metainternalversion.ListOptions 是 API 側(cè)的結(jié)構(gòu)體,包含了
// staging/src/k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/internalversion/types.go
// ListOptions is the query options to a standard REST list call.
type ListOptions struct {
metav1.TypeMeta
LabelSelector labels.Selector // 標(biāo)簽過濾器,例如 app=nginx
FieldSelector fields.Selector // 字段過濾器,例如 spec.nodeName=node1
Watch bool
AllowWatchBookmarks bool
ResourceVersion string
ResourceVersionMatch metav1.ResourceVersionMatch
TimeoutSeconds *int64 // Timeout for the list/watch call.
Limit int64
Continue string // a token returned by the server. return a 410 error if the token has expired.
}
storage.ListOptions 是傳給底層存儲(chǔ)的結(jié)構(gòu)體,字段有一些區(qū)別:
// staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/interfaces.go
// ListOptions provides the options that may be provided for storage list operations.
type ListOptions struct {
ResourceVersion string
ResourceVersionMatch metav1.ResourceVersionMatch
Predicate SelectionPredicate // Predicate provides the selection rules for the list operation.
Recursive bool // true: 根據(jù) key 獲取單個(gè)對(duì)象;false:根據(jù) key prefix 獲取全量數(shù)據(jù)
ProgressNotify bool // storage-originated bookmark, ignored for non-watch requests.
}
2.4 請(qǐng)求指定了資源名(resource name):獲取單個(gè)對(duì)象
接下來根據(jù)請(qǐng)求中是否指定了 meta.Name 分為兩種情況:
如果指定了,說明是查詢單個(gè)對(duì)象,因?yàn)? Name是唯一的,接下來轉(zhuǎn)入查詢單個(gè) object 的邏輯;如果未指定,則需要獲取全量數(shù)據(jù),然后在 apiserver 內(nèi)存中根據(jù) SelectionPredicate 中的過濾條件進(jìn)行過濾,將最終結(jié)果返回給客戶端;
代碼如下:
// case 1:根據(jù) metadata.name 獲取單個(gè) object,無需對(duì)全量數(shù)據(jù)做過濾
if name, ok := p.MatchesSingle(); ok { // 檢查是否設(shè)置了 metadata.name 字段
if key := e.KeyFunc(ctx, name); err == nil {
e.Storage.GetList(ctx, key, storageOpts, list)
return list
}
// else 邏輯:如果執(zhí)行到這里,說明沒有從 context 中拿到過濾用的 key,則 fallback 到下面拿全量數(shù)據(jù)再過濾
}
e.Storage 是一個(gè) Interface,
// staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/interfaces.go
// Interface offers a common interface for object marshaling/unmarshaling operations and
// hides all the storage-related operations behind it.
type Interface interface {
Create(ctx , key string, obj, out runtime.Object, ttl uint64) error
Delete(ctx , key string, out runtime.Object, preconditions *Preconditions,...)
Watch(ctx , key string, opts ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error)
Get(ctx , key string, opts GetOptions, objPtr runtime.Object) error
// unmarshall objects found at key into a *List api object (an object that satisfies runtime.IsList definition).
// If 'opts.Recursive' is false, 'key' is used as an exact match; if is true, 'key' is used as a prefix.
// The returned contents may be delayed, but it is guaranteed that they will
// match 'opts.ResourceVersion' according 'opts.ResourceVersionMatch'.
GetList(ctx , key string, opts ListOptions, listObj runtime.Object) error
e.Storage.GetList() 會(huì)執(zhí)行到 cacher 代碼。
不管是獲取單個(gè) object,還是獲取全量數(shù)據(jù),都經(jīng)歷類似的過程:
優(yōu)先從 apiserver 本地緩存獲取(決定因素包括 ResourceVersion 等), 不得已才到 etcd 去獲取;
獲取單個(gè)對(duì)象的邏輯相對(duì)比較簡(jiǎn)單,這里就不看了。接下來看 List 全量數(shù)據(jù)再做過濾的邏輯。
2.5 請(qǐng)求未指定資源名,獲取全量數(shù)據(jù)做過濾
2.5.1 apiserver 緩存層:GetList() 處理邏輯
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/v1.24.0/staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/cacher/cacher.go#L622
// GetList implements storage.Interface
func (c *Cacher) GetList(ctx , key string, opts storage.ListOptions, listObj runtime.Object) error {
recursive := opts.Recursive
resourceVersion := opts.ResourceVersion
pred := opts.Predicate
// 情況一:ListOption 要求必須從 etcd 讀
if shouldDelegateList(opts)
return c.storage.GetList(ctx, key, opts, listObj) // c.storage 指向 etcd
// If resourceVersion is specified, serve it from cache.
listRV := c.versioner.ParseResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
// 情況二:apiserver 緩存未建好,只能從 etcd 讀
if listRV == 0 && !c.ready.check()
return c.storage.GetList(ctx, key, opts, listObj)
// 情況三:apiserver 緩存正常,從緩存讀:保證返回的 objects 版本不低于 `listRV`
listPtr := meta.GetItemsPtr(listObj)
listVal := conversion.EnforcePtr(listPtr)
filter := filterWithAttrsFunction(key, pred) // 最終的過濾器
objs, readResourceVersion, indexUsed := c.listItems(listRV, key, pred, ...) // 根據(jù) index 預(yù)篩,性能優(yōu)化
for _, obj := range objs {
elem := obj.(*storeElement)
if filter(elem.Key, elem.Labels, elem.Fields) // 真正的過濾
listVal.Set(reflect.Append(listVal, reflect.ValueOf(elem))
}
// 更新最后一次讀到的 ResourceVersion
if c.versioner != nil
c.versioner.UpdateList(listObj, readResourceVersion, "", nil)
return nil
}
2.5.2 判斷是否必須從 etcd 讀數(shù)據(jù):shouldDelegateList()
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/v1.24.0/staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/cacher/cacher.go#L591
func shouldDelegateList(opts storage.ListOptions) bool {
resourceVersion := opts.ResourceVersion
pred := opts.Predicate
pagingEnabled := DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.APIListChunking) // 默認(rèn)是啟用的
hasContinuation := pagingEnabled && len(pred.Continue) > 0 // Continue 是個(gè) token
hasLimit := pagingEnabled && pred.Limit > 0 && resourceVersion != "0" // 只有在 resourceVersion != "0" 的情況下,hasLimit 才有可能為 true
// 1. 如果未指定 resourceVersion,從底層存儲(chǔ)(etcd)拉去數(shù)據(jù);
// 2. 如果有 continuation,也從底層存儲(chǔ)拉數(shù)據(jù);
// 3. 只有 resourceVersion != "0" 時(shí),才會(huì)將 limit 傳給底層存儲(chǔ)(etcd),因?yàn)?nbsp;watch cache 不支持 continuation
return resourceVersion == "" || hasContinuation || hasLimit || opts.ResourceVersionMatch == metav1.ResourceVersionMatchExact
}
這里非常重要:
問:客戶端未設(shè)置 ListOption{} 中的
ResourceVersion字段,是否對(duì)應(yīng)到這里的resourceVersion == ""?答:是的,所以第一節(jié)的 例子 會(huì)導(dǎo)致從 etcd 拉全量數(shù)據(jù)。
問:客戶端設(shè)置了
limit=500&resourceVersion=0是否會(huì)導(dǎo)致下次hasContinuation==true?答:不會(huì),resourceVersion=0 將導(dǎo)致 limit 被忽略(
hasLimit那一行代碼),也就是說, 雖然指定了 limit=500,但這個(gè)請(qǐng)求會(huì)返回全量數(shù)據(jù)。問:ResourceVersionMatch 是什么用途?
答:用來告訴 apiserver,該如何解讀 ResourceVersion。官方有個(gè)很復(fù)雜的 表格 ,有興趣可以看看。
接下來再返回到 cacher 的 GetList() 邏輯,來看下具體有哪幾種處理情況。
2.5.3 情況一:ListOption 要求從 etcd 讀數(shù)據(jù)
這種情況下,apiserver 會(huì)直接從 etcd 讀取所有 objects 并過濾,然后返回給客戶端, 適用于數(shù)據(jù)一致性要求極其高的場(chǎng)景。當(dāng)然,也容易誤入這種場(chǎng)景造成 etcd 壓力過大,例如 第一節(jié)的例子。
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/v1.24.0/staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/etcd3/store.go#L563
// GetList implements storage.Interface.
func (s *store) GetList(ctx , key string, opts storage.ListOptions, listObj runtime.Object) error {
listPtr := meta.GetItemsPtr(listObj)
v := conversion.EnforcePtr(listPtr)
key = path.Join(s.pathPrefix, key)
keyPrefix := key // append '/' if needed
newItemFunc := getNewItemFunc(listObj, v)
var fromRV *uint64
if len(resourceVersion) > 0 { // 如果 RV 非空(客戶端不傳時(shí),默認(rèn)是空字符串)
parsedRV := s.versioner.ParseResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
fromRV = &parsedRV
}
// ResourceVersion, ResourceVersionMatch 等處理邏輯
switch {
case recursive && s.pagingEnabled && len(pred.Continue) > 0: ...
case recursive && s.pagingEnabled && pred.Limit > 0 : ...
default : ...
}
// loop until we have filled the requested limit from etcd or there are no more results
for {
getResp = s.client.KV.Get(ctx, key, options...) // 從 etcd 拉數(shù)據(jù)
numFetched += len(getResp.Kvs)
hasMore = getResp.More
for i, kv := range getResp.Kvs {
if limitOption != nil && int64(v.Len()) >= pred.Limit {
hasMore = true
break
}
lastKey = kv.Key
data := s.transformer.TransformFromStorage(ctx, kv.Value, kv.Key)
appendListItem(v, data, kv.ModRevision, pred, s.codec, s.versioner, newItemFunc) // 這里面會(huì)做過濾
numEvald++
}
key = string(lastKey) + "\x00"
}
// instruct the client to begin querying from immediately after the last key we returned
if hasMore {
// we want to start immediately after the last key
next := encodeContinue(string(lastKey)+"\x00", keyPrefix, returnedRV)
return s.versioner.UpdateList(listObj, uint64(returnedRV), next, remainingItemCount)
}
// no continuation
return s.versioner.UpdateList(listObj, uint64(returnedRV), "", nil)
}
client.KV.Get()就進(jìn)入 etcd client 庫(kù)了,感興趣可以繼續(xù)往下挖。appendListItem()會(huì)對(duì)拿到的數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行過濾,這就是我們第一節(jié)提到的 apiserver 內(nèi)存過濾操作。
2.5.4 情況二:本地緩存還沒建好,只能從 etcd 讀數(shù)據(jù)
具體執(zhí)行過程與情況一相同。
2.5.5 情況三:使用本地緩存
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/v1.24.0/staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/storage/cacher/cacher.go#L622
// GetList implements storage.Interface
func (c *Cacher) GetList(ctx , key string, opts storage.ListOptions, listObj runtime.Object) error {
// 情況一:ListOption 要求必須從 etcd 讀
...
// 情況二:apiserver 緩存未建好,只能從 etcd 讀
...
// 情況三:apiserver 緩存正常,從緩存讀:保證返回的 objects 版本不低于 `listRV`
listPtr := meta.GetItemsPtr(listObj) // List elements with at least 'listRV' from cache.
listVal := conversion.EnforcePtr(listPtr)
filter := filterWithAttrsFunction(key, pred) // 最終的過濾器
objs, readResourceVersion, indexUsed := c.listItems(listRV, key, pred, ...) // 根據(jù) index 預(yù)篩,性能優(yōu)化
for _, obj := range objs {
elem := obj.(*storeElement)
if filter(elem.Key, elem.Labels, elem.Fields) // 真正的過濾
listVal.Set(reflect.Append(listVal, reflect.ValueOf(elem))
}
if c.versioner != nil
c.versioner.UpdateList(listObj, readResourceVersion, "", nil)
return nil
}
3 LIST 測(cè)試
為了避免客戶端庫(kù)(例如 client-go)自動(dòng)幫我們?cè)O(shè)置一些參數(shù),我們直接用 curl 來測(cè)試,指定證書就行了:
$ cat curl-k8s-apiserver.sh
curl -s --cert /etc/kubernetes/pki/admin.crt --key /etc/kubernetes/pki/admin.key --cacert /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt $@
使用方式:
$ ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "https://localhost:6443/api/v1/pods?limit=2"
{
"kind": "PodList",
"metadata": {
"resourceVersion": "2127852936",
"continue": "eyJ2IjoibWV0YS5rOHMuaW8vdjEiLCJ...",
},
"items": [ {pod1 data }, {pod2 data}]
}
3.1 指定 limit=2:response 將返回分頁(yè)信息(continue)
3.1.1 curl 測(cè)試
$ ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "https://localhost:6443/api/v1/pods?limit=2"
{
"kind": "PodList",
"metadata": {
"resourceVersion": "2127852936",
"continue": "eyJ2IjoibWV0YS5rOHMuaW8vdjEiLCJ...",
},
"items": [ {pod1 data }, {pod2 data}]
}
可以看到,
確實(shí)返回了兩個(gè) pod 信息,在 items[]字段中;另外在 metadata中返回了一個(gè)continue字段,客戶端下次帶上這個(gè)參數(shù),apiserver 將繼續(xù)返回剩下的內(nèi)容,直到 apiserver 不再返回continue。
3.1.2 kubectl 測(cè)試
調(diào)大 kubectl 的日志級(jí)別,也可以看到它背后用了 continue 來獲取全量 pods:
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces --v=10
# 以下都是 log 輸出,做了適當(dāng)調(diào)整
# curl -k -v -XGET -H "User-Agent: kubectl/v1.xx" -H "Accept: application/json;as=Table;v=v1;g=meta.k8s.io,application/json;as=Table;v=v1beta1;g=meta.k8s.io,application/json"
# 'http://localhost:8080/api/v1/pods?limit=500'
# GET http://localhost:8080/api/v1/pods?limit=500 200 OK in 202 milliseconds
# Response Body: {"kind":"Table","metadata":{"continue":"eyJ2Ijoib...","remainingItemCount":54},"columnDefinitions":[...],"rows":[...]}
#
# curl -k -v -XGET -H "Accept: application/json;as=Table;v=v1;g=meta.k8s.io,application/json;as=Table;v=v1beta1;g=meta.k8s.io,application/json" -H "User-Agent: kubectl/v1.xx"
# 'http://localhost:8080/api/v1/pods?continue=eyJ2Ijoib&limit=500'
# GET http://localhost:8080/api/v1/pods?continue=eyJ2Ijoib&limit=500 200 OK in 44 milliseconds
# Response Body: {"kind":"Table","metadata":{"resourceVersion":"2122644698"},"columnDefinitions":[],"rows":[...]}
第一次請(qǐng)求拿到了 500 個(gè) pods,第二次請(qǐng)求把返回的 continue 帶上了:GET http://localhost:8080/api/v1/pods?continue=eyJ2Ijoib&limit=500,continue 是個(gè) token, 有點(diǎn)長(zhǎng),為了更好的展示這里把它截?cái)嗔恕?/p>
3.2 指定 limit=2&resourceVersion=0:limit=2 將被忽略,返回全量數(shù)據(jù)
$ ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "https://localhost:6443/api/v1/pods?limit=2&resourceVersion=0"
{
"kind": "PodList",
"metadata": {
"resourceVersion": "2127852936",
"continue": "eyJ2IjoibWV0YS5rOHMuaW8vdjEiLCJ...",
},
"items": [ {pod1 data }, {pod2 data}, ...]
}
items[] 里面是全量 pod 信息。
3.3 指定 spec.nodeName=node1&resourceVersion=0 vs. spec.nodeName=node1"
結(jié)果相同
$ ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "https://localhost:6443/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods?fieldSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1" | jq '.items[].spec.nodeName'
"node1"
"node1"
"node1"
...
$ ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "https://localhost:6443/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods?fieldSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1&resourceVersion=0" | jq '.items[].spec.nodeName'
"node1"
"node1"
"node1"
...
結(jié)果是一樣的,除非是 apiserver 緩存和 etcd 數(shù)據(jù)出現(xiàn)不一致,這個(gè)概率極小,我們這里不討論。
速度差異很大
用 time 測(cè)量以上兩種情況下的耗時(shí),會(huì)發(fā)現(xiàn)對(duì)于大一些的集群,這兩種請(qǐng)求的響應(yīng)時(shí)間就會(huì)有明顯差異。
$ time ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh <url> > result
對(duì)于 4K nodes, 100K pods 規(guī)模的集群,以下數(shù)據(jù)供參考:
不帶 resourceVersion=0(讀 etcd 并在 apiserver 過濾): 耗時(shí)10s帶 resourceVersion=0(讀 apiserver 緩存): 耗時(shí)0.05s
差了 200 倍。
全量 pod 的總大小按 2GB 計(jì)算,平均每個(gè) 20KB。
4 LIST 請(qǐng)求對(duì)控制平面壓力:量化分析
本節(jié)以 cilium-agent 為例,介紹定量測(cè)量它啟動(dòng)時(shí)對(duì)控制平面壓力。
4.1 收集 LIST 請(qǐng)求
首先獲取 agent 啟動(dòng)時(shí),都 LIST k8s 哪些資源。有幾種收集方式:
在 k8s access log,按 ServiceAccount、verb、request_uri 等過濾; 通過 agent 日志; 通過進(jìn)一步代碼分析等等。
假設(shè)我們收集到如下 LIST 請(qǐng)求:
1. api/v1/namespaces?resourceVersion=0
2. api/v1/pods?filedSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1&resourceVersion=0
3. api/v1/nodes?fieldSelector=metadata.name%3Dnode1&resourceVersion=0
4. api/v1/services?labelSelector=%21service.kubernetes.io%2Fheadless%2C%21service.kubernetes.io%2Fservice-proxy-name
5. apis/discovery.k8s.io/v1beta1/endpointslices?resourceVersion=0
6. apis/networking.k8s.io/networkpolicies?resourceVersion=0
7. apis/cilium.io/v2/ciliumnodes?resourceVersion=0
8. apis/cilium.io/v2/ciliumnetworkpolicies?resourceVersion=0
9. apis/cilium.io/v2/ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicies?resourceVersion=0
2.2 測(cè)試 LIST 請(qǐng)求數(shù)據(jù)量和耗時(shí)
有了 LIST 請(qǐng)求列表,接下來就可以手動(dòng)執(zhí)行這些請(qǐng)求,拿到如下數(shù)據(jù):
請(qǐng)求耗時(shí)
請(qǐng)求處理的數(shù)據(jù)量,這里分為兩種:
apiserver 處理的數(shù)據(jù)量(全量數(shù)據(jù)),評(píng)估對(duì) apiserver/etcd 的性能影響應(yīng)該以這個(gè)為主 agent 最終拿到的數(shù)據(jù)量(按 selector 做了過濾)
用下面這個(gè)腳本(放到真實(shí)環(huán)境 k8s master 上)來就可以執(zhí)行一遍測(cè)試,
$ cat benchmark-list-overheads.sh
apiserver_url="https://localhost:6443"
# List k8s core resources (e.g. pods, services)
# API: GET/LIST /api/v1/<resources>?<fileld/label selector>&resourceVersion=0
function benchmark_list_core_resource() {
resource=$1
selectors=$2
echo "----------------------------------------------------"
echo "Benchmarking list $2"
listed_file="listed-$resource"
url="$apiserver_url/api/v1/$resource?resourceVersion=0"
# first perform a request without selectors, this is the size apiserver really handles
echo "curl $url"
time ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "$url" > $listed_file
# perform another request if selectors are provided, this is the size client receives
listed_file2="$listed_file-filtered"
if [ ! -z "$selectors" ]; then
url="$url&$selectors"
echo "curl $url"
time ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "$url" > $listed_file2
fi
ls -ahl $listed_file $listed_file2 2>/dev/null
echo "----------------------------------------------------"
echo ""
}
# List k8s apiextension resources (e.g. pods, services)
# API: GET/LIST /apis/<api group>/<resources>?<fileld/label selector>&resourceVersion=0
function benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource() {
api_group=$1
resource=$2
selectors=$3
echo "----------------------------------------------------"
echo "Benchmarking list $api_group/$resource"
api_group_flatten_name=$(echo $api_group | sed 's/\//-/g')
listed_file="listed-$api_group_flatten_name-$resource"
url="$apiserver_url/apis/$api_group/$resource?resourceVersion=0"
if [ ! -z "$selectors" ]; then
url="$url&$selectors"
fi
echo "curl $url"
time ./curl-k8s-apiserver.sh "$url" > $listed_file
ls -ahl $listed_file
echo "----------------------------------------------------"
echo ""
}
benchmark_list_core_resource "namespaces" ""
benchmark_list_core_resource "pods" "filedSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1"
benchmark_list_core_resource "nodes" "fieldSelector=metadata.name%3Dnode1"
benchmark_list_core_resource "services" "labelSelector=%21service.kubernetes.io%2Fheadless%2C%21service.kubernetes.io%2Fservice-proxy-name"
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "discovery.k8s.io/v1beta1" "endpointslices" ""
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "apiextensions.k8s.io/v1" "customresourcedefinitions" ""
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "networking.k8s.io" "networkpolicies" ""
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "cilium.io/v2" "ciliumnodes" ""
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "cilium.io/v2" "ciliumendpoints" ""
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "cilium.io/v2" "ciliumnetworkpolicies" ""
benchmark_list_apiexternsion_resource "cilium.io/v2" "ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicies" ""
執(zhí)行效果如下:
$ benchmark-list-overheads.sh
----------------------------------------------------
Benchmarking list
curl https://localhost:6443/api/v1/namespaces?resourceVersion=0
real 0m0.090s
user 0m0.038s
sys 0m0.044s
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 69K listed-namespaces
----------------------------------------------------
Benchmarking list fieldSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1
curl https://localhost:6443/api/v1/pods?resourceVersion=0
real 0m18.332s
user 0m1.355s
sys 0m1.822s
curl https://localhost:6443/api/v1/pods?resourceVersion=0&fieldSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1
real 0m0.242s
user 0m0.044s
sys 0m0.188s
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2.0G listed-pods
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 526K listed-pods-filtered
----------------------------------------------------
...
說明:凡是帶了 selector 的 LIST,例如 LIST pods?spec.nodeName=node1,這個(gè)腳本會(huì)先執(zhí)行一遍不帶 selector 的請(qǐng)求,目的是測(cè)量 apiserver 需要處理的數(shù)據(jù)量,例如上面的 list pods:
agent 真正執(zhí)行的是 pods?resourceVersion=0&fieldSelector=spec.nodeName%3Dnode1,所以請(qǐng)求耗時(shí)應(yīng)該以這個(gè)為準(zhǔn)額外執(zhí)行了 pods?resourceVersion=0,這樣是為了測(cè)試 1 的請(qǐng)求到底需要 apiserver 處理多少數(shù)據(jù)量
注意:list all pods 這樣的操作會(huì)產(chǎn)生 2GB 的文件,因此謹(jǐn)慎使用這個(gè) benchmark 工具,首先理解你寫的腳本在測(cè)什么,尤其不要自動(dòng)化或并發(fā)跑,可能會(huì)把 apiserver/etcd 打爆。
4.3 測(cè)試結(jié)果分析
以上輸出有如下關(guān)鍵信息:
LIST 的資源類型,例如 pods/endpoints/services LIST 操作耗時(shí) LIST 操作涉及的數(shù)據(jù)量 apiserver 需要處理的數(shù)據(jù)量(json 格式):以上面 list pods 為例,對(duì)應(yīng)的是 listed-pods文件,共 2GB;agent 收到的數(shù)據(jù)量(因?yàn)?agent 可能指定了 label/field 過濾器):以上面 list pods 為例,對(duì)應(yīng) listed-pods-filtered文件,共計(jì)526K
按以上方式將所有 LIST 請(qǐng)求都收集起來并排序,就知道了 agent 一次啟動(dòng)操作,對(duì) apiserver/etcd 的壓力。
$ ls -ahl listed-*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 222 listed-apiextensions.k8s.io-v1-customeresourcedefinitions
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5.8M listed-apiextensions.k8s.io-v1-customresourcedefinitions
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2.0M listed-cilium.io-v2-ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicies
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 193M listed-cilium.io-v2-ciliumendpoints
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 185 listed-cilium.io-v2-ciliumnetworkpolicies
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6.6M listed-cilium.io-v2-ciliumnodes
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 42M listed-discovery.k8s.io-v1beta1-endpointslices
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 69K listed-namespaces
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 222 listed-networking.k8s.io-networkpolicies
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 70M listed-nodes # 僅用于評(píng)估 apiserver 需要處理的數(shù)據(jù)量
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 25K listed-nodes-filtered
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2.0G listed-pods # 僅用于評(píng)估 apiserver 需要處理的數(shù)據(jù)量
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 526K listed-pods-filtered
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 23M listed-services # 僅用于評(píng)估 apiserver 需要處理的數(shù)據(jù)量
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 23M listed-services-filtered
還是以 cilium 為例,有大致這樣一個(gè)排序(apiserver 處理的數(shù)據(jù)量,json 格式):
| List 資源類型 | apiserver 處理的數(shù)據(jù)量(json) | 耗時(shí) |
|---|---|---|
| CiliumEndpoints (全量) | 193MB | 11s |
| CiliumNodes (全量) | 70MB | 0.5s |
| … | … | … |
5 大規(guī)模基礎(chǔ)服務(wù):部署和調(diào)優(yōu)建議
5.1 List 請(qǐng)求默認(rèn)設(shè)置 ResourceVersion=0
前面已經(jīng)介紹,不設(shè)置這個(gè)參數(shù)將導(dǎo)致 apiserver 從 etcd 拉全量數(shù)據(jù)再過濾,導(dǎo)致
很慢 規(guī)模大了 etcd 扛不住
因此,除非對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)準(zhǔn)確性要求極高,必須從 etcd 拉數(shù)據(jù),否則應(yīng)該在 LIST 請(qǐng)求時(shí)設(shè)置 ResourceVersion=0 參數(shù), 讓 apiserver 用緩存提供服務(wù)。
如果你使用的是 client-go 的 ListWatch/informer 接口, 那它默認(rèn)已經(jīng)設(shè)置了 ResourceVersion=0。
5.2 優(yōu)先使用 namespaced API
如果要 LIST 的資源在單個(gè)或少數(shù)幾個(gè) namespace,考慮使用 namespaced API:
Namespaced API: /api/v1/namespaces/<ns>/pods?query=xxxUn-namespaced API: /api/v1/pods?query=xxx
5.3 Restart backoff
對(duì)于 per-node 部署的基礎(chǔ)服務(wù),例如 kubelet、cilium-agent、daemonsets,需要 通過有效的 restart backoff 降低大面積重啟時(shí)對(duì)控制平面的壓力。
例如,同時(shí)掛掉后,每分鐘重啟的 agent 數(shù)量不超過集群規(guī)模的 10%(可配置,或可自動(dòng)計(jì)算)。
5.4 優(yōu)先通過 label/field selector 在服務(wù)端做過濾
如果需要緩存某些資源并監(jiān)聽變動(dòng),那需要使用 ListWatch 機(jī)制,將數(shù)據(jù)拉到本地,業(yè)務(wù)邏輯根據(jù)需要自己從 local cache 過濾。這是 client-go 的 ListWatch/informer 機(jī)制。
但如果只是一次性的 LIST 操作,并且有篩選條件,例如前面提到的根據(jù) nodename 過濾 pod 的例子, 那顯然應(yīng)該通過設(shè)置 label 或字段過濾器,讓 apiserver 幫我們把數(shù)據(jù)過濾出來。LIST 10w pods 需要幾十秒(大部分時(shí)間花在數(shù)據(jù)傳輸上,同時(shí)也占用 apiserver 大量 CPU/BW/IO), 而如果只需要本機(jī)上的 pod,那設(shè)置 nodeName=node1 之后,LIST 可能只需要 0.05s 就能返回結(jié)果。另外非常重要的一點(diǎn)時(shí),不要忘記在請(qǐng)求中同時(shí)帶上 resourceVersion=0。
5.4.1 Label selector
在 apiserver 內(nèi)存過濾。
5.4.2 Field selector
在 apiserver 內(nèi)存過濾。
5.4.3 Namespace selector
etcd 中 namespace 是前綴的一部分,因此能指定 namespace 過濾資源,速度比不是前綴的 selector 快很多。
5.5 配套基礎(chǔ)設(shè)施(監(jiān)控、告警等)
以上分析可以看成,client 的單個(gè)請(qǐng)求可能只返回幾百 KB 的數(shù)據(jù),但 apiserver(更糟糕的情況,etcd)需要處理上 GB 的數(shù)據(jù)。因此,應(yīng)該極力避免基礎(chǔ)服務(wù)的大規(guī)模重啟,為此需要在監(jiān)控、告警上做的盡量完善。
5.5.1 使用獨(dú)立 ServiceAccount
每個(gè)基礎(chǔ)服務(wù)(例如 kubelet、cilium-agent 等),以及對(duì) apiserver 有大量 LIST 操作的各種 operator, 都使用各自獨(dú)立的 SA, 這樣便于 apiserver 區(qū)分請(qǐng)求來源,對(duì)監(jiān)控、排障和服務(wù)端限流都非常有用。
5.5.2 Liveness 監(jiān)控告警
基礎(chǔ)服務(wù)必須覆蓋到 liveness 監(jiān)控。
必須有 P1 級(jí)別的 liveness 告警,能第一時(shí)間發(fā)現(xiàn)大規(guī)模掛掉的場(chǎng)景。然后通過 restart backoff 降低對(duì)控制平面的壓力。
5.5.3 監(jiān)控和調(diào)優(yōu) etcd
需要針對(duì)性能相關(guān)的關(guān)鍵指標(biāo)做好監(jiān)控和告警:
內(nèi)存 帶寬 大 LIST 請(qǐng)求數(shù)量及響應(yīng)耗時(shí)
比如下面這個(gè) LIST all pods 日志:
{
"level":"warn",
"msg":"apply request took too long",
"took":"5357.87304ms",
"expected-duration":"100ms",
"prefix":"read-only range ",
"request":"key:\"/registry/pods/\" range_end:\"/registry/pods0\" ",
"response":"range_response_count:60077 size:602251227"
}
部署和配置調(diào)優(yōu):
K8s events 拆到單獨(dú)的 etcd 集群 其他。
6 其他
6.1 Get 請(qǐng)求:GetOptions{}
基本原理與 ListOption{} 一樣,不設(shè)置 ResourceVersion=0 會(huì)導(dǎo)致 apiserver 去 etcd 拿數(shù)據(jù),應(yīng)該盡量避免。
- END - 推薦閱讀 Go+Vue DevOps 從入門到項(xiàng)目實(shí)戰(zhàn) 頂級(jí) DevOps 工具鏈大盤點(diǎn) 某外企從 0 建設(shè) SRE 運(yùn)維體系經(jīng)驗(yàn)分享 Nginx+Redis:高性能緩存利器 主流監(jiān)控系統(tǒng) Prometheus 學(xué)習(xí)指南 基于 eBPF 的 Kubernetes 問題排查全景圖發(fā)布 一文掌握 Ansible 自動(dòng)化運(yùn)維 Linux的10個(gè)最危險(xiǎn)命令 Kubernetes網(wǎng)絡(luò)難懂?可能是沒看到這篇文章 24 個(gè) Docker 常見問題處理技巧 Shell分析日志文件,全面解鎖新姿勢(shì)! 這篇文章帶你全面掌握 Nginx ! 基于Nginx實(shí)現(xiàn)灰度發(fā)布與AB測(cè)試 一文搞懂 Kubernetes 網(wǎng)絡(luò)通信原理 SRE本質(zhì)就是一個(gè)懂運(yùn)維的資深開發(fā) 搭建一套完整的企業(yè)級(jí) K8s 集群(v1.22,二進(jìn)制方式) 點(diǎn)亮,服務(wù)器三年不宕機(jī)


