使用 Go 語(yǔ)言實(shí)現(xiàn)二叉搜索樹(shù)
二叉樹(shù)是一種常見(jiàn)并且非常重要的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu),在很多項(xiàng)目中都能看到二叉樹(shù)的身影。
它有很多變種,比如紅黑樹(shù),常被用作 std::map 和 std::set 的底層實(shí)現(xiàn);B 樹(shù)和 B+ 樹(shù),廣泛應(yīng)用于數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)系統(tǒng)中。
本文要介紹的二叉搜索樹(shù)用的也很多,比如在開(kāi)源項(xiàng)目 go-zero 中,就被用來(lái)做路由管理。
這篇文章也算是一篇前導(dǎo)文章,介紹一些必備知識(shí),下一篇再來(lái)介紹具體在 go-zero 中的應(yīng)用。
二叉搜索樹(shù)的特點(diǎn)
最重要的就是它的有序性,在二叉搜索樹(shù)中,每個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)的值都大于其左子樹(shù)中的所有節(jié)點(diǎn)的值,并且小于其右子樹(shù)中的所有節(jié)點(diǎn)的值。
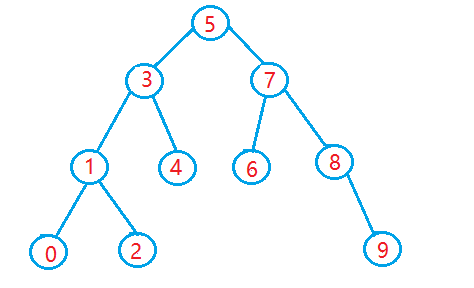
這意味著通過(guò)二叉搜索樹(shù)可以快速實(shí)現(xiàn)對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)的查找和插入。
Go 語(yǔ)言實(shí)現(xiàn)
本文主要實(shí)現(xiàn)了以下幾種方法:
-
Insert(t):插入一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn) -
Search(t):判斷節(jié)點(diǎn)是否在樹(shù)中 -
InOrderTraverse():中序遍歷 -
PreOrderTraverse():前序遍歷 -
PostOrderTraverse():后序遍歷 -
Min():返回最小值 -
Max():返回最大值 -
Remove(t):刪除一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn) -
String():打印一個(gè)樹(shù)形結(jié)構(gòu)
下面分別來(lái)介紹,首先定義一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn):
type Node struct {
key int
value Item
left *Node //left
right *Node //right
}
定義樹(shù)的結(jié)構(gòu)體,其中包含了鎖,是線程安全的:
type ItemBinarySearchTree struct {
root *Node
lock sync.RWMutex
}
插入操作:
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) Insert(key int, value Item) {
bst.lock.Lock()
defer bst.lock.Unlock()
n := &Node{key, value, nil, nil}
if bst.root == nil {
bst.root = n
} else {
insertNode(bst.root, n)
}
}
// internal function to find the correct place for a node in a tree
func insertNode(node, newNode *Node) {
if newNode.key < node.key {
if node.left == nil {
node.left = newNode
} else {
insertNode(node.left, newNode)
}
} else {
if node.right == nil {
node.right = newNode
} else {
insertNode(node.right, newNode)
}
}
}
在插入時(shí),需要判斷插入節(jié)點(diǎn)和當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn)的大小關(guān)系,保證搜索樹(shù)的有序性。
中序遍歷:
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) InOrderTraverse(f func(Item)) {
bst.lock.RLock()
defer bst.lock.RUnlock()
inOrderTraverse(bst.root, f)
}
// internal recursive function to traverse in order
func inOrderTraverse(n *Node, f func(Item)) {
if n != nil {
inOrderTraverse(n.left, f)
f(n.value)
inOrderTraverse(n.right, f)
}
}
前序遍歷:
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) PreOrderTraverse(f func(Item)) {
bst.lock.Lock()
defer bst.lock.Unlock()
preOrderTraverse(bst.root, f)
}
// internal recursive function to traverse pre order
func preOrderTraverse(n *Node, f func(Item)) {
if n != nil {
f(n.value)
preOrderTraverse(n.left, f)
preOrderTraverse(n.right, f)
}
}
后序遍歷:
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) PostOrderTraverse(f func(Item)) {
bst.lock.Lock()
defer bst.lock.Unlock()
postOrderTraverse(bst.root, f)
}
// internal recursive function to traverse post order
func postOrderTraverse(n *Node, f func(Item)) {
if n != nil {
postOrderTraverse(n.left, f)
postOrderTraverse(n.right, f)
f(n.value)
}
}
返回最小值:
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) Min() *Item {
bst.lock.RLock()
defer bst.lock.RUnlock()
n := bst.root
if n == nil {
return nil
}
for {
if n.left == nil {
return &n.value
}
n = n.left
}
}
由于樹(shù)的有序性,想要得到最小值,一直向左查找就可以了。
返回最大值:
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) Max() *Item {
bst.lock.RLock()
defer bst.lock.RUnlock()
n := bst.root
if n == nil {
return nil
}
for {
if n.right == nil {
return &n.value
}
n = n.right
}
}
查找節(jié)點(diǎn)是否存在:
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) Search(key int) bool {
bst.lock.RLock()
defer bst.lock.RUnlock()
return search(bst.root, key)
}
// internal recursive function to search an item in the tree
func search(n *Node, key int) bool {
if n == nil {
return false
}
if key < n.key {
return search(n.left, key)
}
if key > n.key {
return search(n.right, key)
}
return true
}
刪除節(jié)點(diǎn):
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) Remove(key int) {
bst.lock.Lock()
defer bst.lock.Unlock()
remove(bst.root, key)
}
// internal recursive function to remove an item
func remove(node *Node, key int) *Node {
if node == nil {
return nil
}
if key < node.key {
node.left = remove(node.left, key)
return node
}
if key > node.key {
node.right = remove(node.right, key)
return node
}
// key == node.key
if node.left == nil && node.right == nil {
node = nil
return nil
}
if node.left == nil {
node = node.right
return node
}
if node.right == nil {
node = node.left
return node
}
leftmostrightside := node.right
for {
//find smallest value on the right side
if leftmostrightside != nil && leftmostrightside.left != nil {
leftmostrightside = leftmostrightside.left
} else {
break
}
}
node.key, node.value = leftmostrightside.key, leftmostrightside.value
node.right = remove(node.right, node.key)
return node
}
刪除操作會(huì)復(fù)雜一些,分三種情況來(lái)考慮:
-
如果要?jiǎng)h除的節(jié)點(diǎn)沒(méi)有子節(jié)點(diǎn),只需要直接將父節(jié)點(diǎn)中,指向要?jiǎng)h除的節(jié)點(diǎn)指針置為 nil即可 -
如果刪除的節(jié)點(diǎn)只有一個(gè)子節(jié)點(diǎn),只需要更新父節(jié)點(diǎn)中,指向要?jiǎng)h除節(jié)點(diǎn)的指針,讓它指向刪除節(jié)點(diǎn)的子節(jié)點(diǎn)即可 -
如果刪除的節(jié)點(diǎn)有兩個(gè)子節(jié)點(diǎn),我們需要找到這個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)右子樹(shù)中的最小節(jié)點(diǎn),把它替換到要?jiǎng)h除的節(jié)點(diǎn)上。然后再刪除這個(gè)最小節(jié)點(diǎn),因?yàn)樽钚」?jié)點(diǎn)肯定沒(méi)有左子節(jié)點(diǎn),所以可以應(yīng)用第二種情況刪除這個(gè)最小節(jié)點(diǎn)即可
最后是一個(gè)打印樹(shù)形結(jié)構(gòu)的方法,在實(shí)際項(xiàng)目中其實(shí)并沒(méi)有實(shí)際作用:
func (bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) String() {
bst.lock.Lock()
defer bst.lock.Unlock()
fmt.Println("------------------------------------------------")
stringify(bst.root, 0)
fmt.Println("------------------------------------------------")
}
// internal recursive function to print a tree
func stringify(n *Node, level int) {
if n != nil {
format := ""
for i := 0; i < level; i++ {
format += " "
}
format += "---[ "
level++
stringify(n.left, level)
fmt.Printf(format+"%d\n", n.key)
stringify(n.right, level)
}
}
單元測(cè)試
下面是一段測(cè)試代碼:
func fillTree(bst *ItemBinarySearchTree) {
bst.Insert(8, "8")
bst.Insert(4, "4")
bst.Insert(10, "10")
bst.Insert(2, "2")
bst.Insert(6, "6")
bst.Insert(1, "1")
bst.Insert(3, "3")
bst.Insert(5, "5")
bst.Insert(7, "7")
bst.Insert(9, "9")
}
func TestInsert(t *testing.T) {
fillTree(&bst)
bst.String()
bst.Insert(11, "11")
bst.String()
}
// isSameSlice returns true if the 2 slices are identical
func isSameSlice(a, b []string) bool {
if a == nil && b == nil {
return true
}
if a == nil || b == nil {
return false
}
if len(a) != len(b) {
return false
}
for i := range a {
if a[i] != b[i] {
return false
}
}
return true
}
func TestInOrderTraverse(t *testing.T) {
var result []string
bst.InOrderTraverse(func(i Item) {
result = append(result, fmt.Sprintf("%s", i))
})
if !isSameSlice(result, []string{"1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "11"}) {
t.Errorf("Traversal order incorrect, got %v", result)
}
}
func TestPreOrderTraverse(t *testing.T) {
var result []string
bst.PreOrderTraverse(func(i Item) {
result = append(result, fmt.Sprintf("%s", i))
})
if !isSameSlice(result, []string{"8", "4", "2", "1", "3", "6", "5", "7", "10", "9", "11"}) {
t.Errorf("Traversal order incorrect, got %v instead of %v", result, []string{"8", "4", "2", "1", "3", "6", "5", "7", "10", "9", "11"})
}
}
func TestPostOrderTraverse(t *testing.T) {
var result []string
bst.PostOrderTraverse(func(i Item) {
result = append(result, fmt.Sprintf("%s", i))
})
if !isSameSlice(result, []string{"1", "3", "2", "5", "7", "6", "4", "9", "11", "10", "8"}) {
t.Errorf("Traversal order incorrect, got %v instead of %v", result, []string{"1", "3", "2", "5", "7", "6", "4", "9", "11", "10", "8"})
}
}
func TestMin(t *testing.T) {
if fmt.Sprintf("%s", *bst.Min()) != "1" {
t.Errorf("min should be 1")
}
}
func TestMax(t *testing.T) {
if fmt.Sprintf("%s", *bst.Max()) != "11" {
t.Errorf("max should be 11")
}
}
func TestSearch(t *testing.T) {
if !bst.Search(1) || !bst.Search(8) || !bst.Search(11) {
t.Errorf("search not working")
}
}
func TestRemove(t *testing.T) {
bst.Remove(1)
if fmt.Sprintf("%s", *bst.Min()) != "2" {
t.Errorf("min should be 2")
}
}
上文中的全部源碼都是經(jīng)過(guò)測(cè)試的,可以直接運(yùn)行,并且已經(jīng)上傳到了 GitHub,需要的同學(xué)可以自取。
以上就是本文的全部?jī)?nèi)容,如果覺(jué)得還不錯(cuò)的話歡迎點(diǎn)贊,轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)和關(guān)注,感謝支持。
源碼地址:
-
https://github.com/yongxinz/go-example
推薦閱讀:
參考文章:
-
https://flaviocopes.com/golang-data-structure-binary-search-tree/
