Condition實(shí)現(xiàn)原理
點(diǎn)擊上方藍(lán)色字體,選擇“標(biāo)星公眾號(hào)”
優(yōu)質(zhì)文章,第一時(shí)間送達(dá)
Condition接口提供了與Object阻塞(wait())與喚醒(notify()或notifyAll())相似的功能,只不過Condition接口提供了更為豐富的功能,如:限定等待時(shí)長(zhǎng)等。Condition需要與Lock結(jié)合使用,需要通過鎖對(duì)象獲取Condition。
一、基本使用
基于Condition實(shí)現(xiàn)生產(chǎn)者、消費(fèi)者模式。代碼基本與Object#wait()和Object#notify()類似,只不過我們使用Lock替換了synchronized關(guān)鍵字。
生產(chǎn)者
public class Producer implements Runnable {
private Lock lock;
private Condition condition;
private Queue<String> queue;
private int maxSize;
public Producer(Lock lock, Condition condition, Queue<String> queue, int maxSize) {
this.lock = lock;
this.condition = condition;
this.queue = queue;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
for (; ; ) {
lock.lock();
// 如果滿了,則阻塞
while (queue.size() == maxSize) {
System.out.println("生產(chǎn)者隊(duì)列滿了,等待...");
try {
condition.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
queue.add("一個(gè)消息:" + ++i);
System.out.printf("生產(chǎn)者%s生產(chǎn)了一個(gè)消息:%s\n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), i);
condition.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
消費(fèi)者
public class Consumer implements Runnable {
private Lock lock;
private Condition condition;
private Queue<String> queue;
private int maxSize;
public Consumer(Lock lock, Condition condition, Queue<String> queue, int maxSize) {
this.lock = lock;
this.condition = condition;
this.queue = queue;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (; ; ) {
lock.lock();
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("消費(fèi)者隊(duì)列為空,等待...");
try {
condition.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String obj = queue.remove();
System.out.printf("消費(fèi)者%s消費(fèi)一個(gè)消息:%s\n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), obj);
condition.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
測(cè)試類
public class ConditionProducerConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
int maxSize = 10;
Producer producer = new Producer(lock, condition, queue, maxSize);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(lock, condition, queue, maxSize);
new Thread(producer).start();
new Thread(consumer).start();
}
}
二、源碼分析
上述示例中使用的Lock是ReentrantLock,關(guān)于它的lock方法與unlock方法的原理詳見ReentrantLock實(shí)現(xiàn)原理。上述示例中的Condition對(duì)象是調(diào)用了Lock#newCondition()方法,源碼如下:
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
...
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
...
final ConditionObject newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
...
}
...
}
上述的ConditionObject定義在AQS中,如下:
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
implements java.io.Serializable {
...
public class ConditionObject implements Condition, java.io.Serializable {
...
}
...
}
首先來分析下Condition#await()方法
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
int interruptMode = 0;
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
LockSupport.park(this);
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
}
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}
private Node addConditionWaiter() {
Node t = lastWaiter;
// If lastWaiter is cancelled, clean out.
if (t != null && t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) {
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
t = lastWaiter;
}
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION);
if (t == null)
firstWaiter = node;
else
t.nextWaiter = node;
lastWaiter = node;
return node;
}
根據(jù)AQS隊(duì)列的特性,若有多個(gè)線程執(zhí)行lock#lock()方法,會(huì)將處于阻塞狀態(tài)的線程維護(hù)到一個(gè)雙向鏈表中,如下: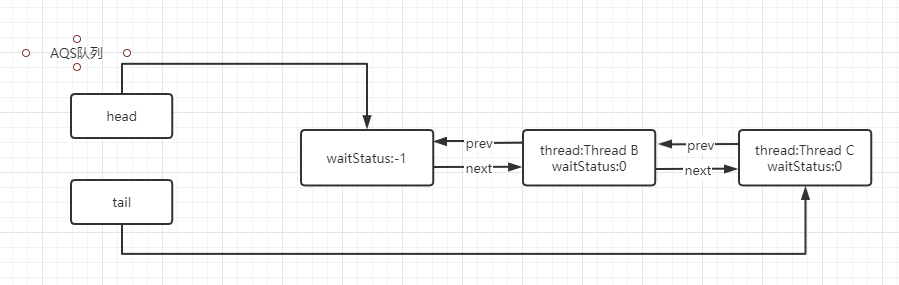
假設(shè)當(dāng)前是線程A獲取到鎖,其他線程執(zhí)行lock#lock()方法時(shí),將會(huì)構(gòu)建成一個(gè)上述鏈表。
若獲取鎖的線程(線程A)執(zhí)行Condition#await()方法,則會(huì)將當(dāng)前線程添加至Condition隊(duì)列中,如下: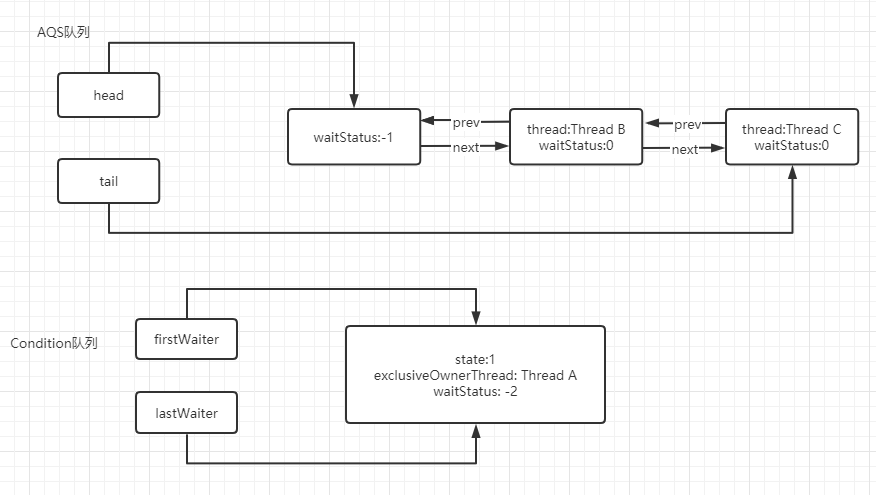
然后在調(diào)用fullyRelease()方法時(shí)會(huì)釋放當(dāng)前線程的鎖,然后喚醒處于阻塞隊(duì)列中的下一個(gè)線程: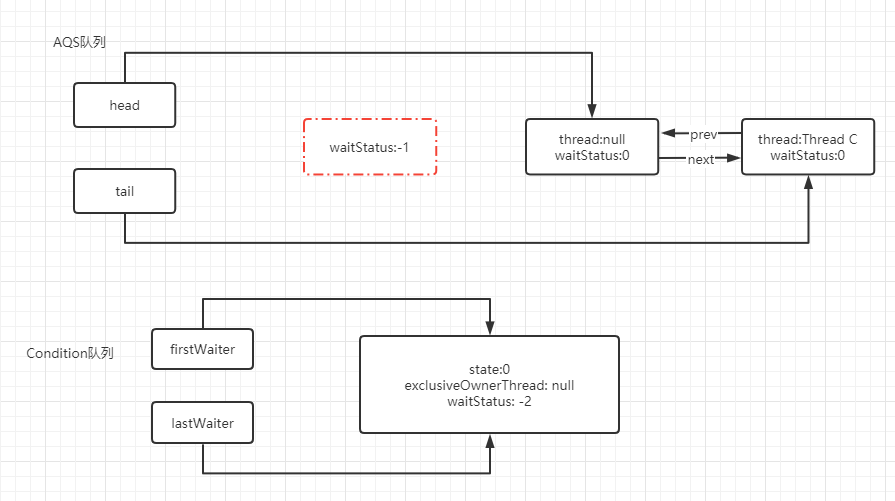
在調(diào)用isOnSyncQueue()方法時(shí)會(huì)檢查當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn)是否在同步隊(duì)列中,若不存在,則會(huì)調(diào)用LockSupport.park()進(jìn)行阻塞。
假設(shè)當(dāng)前線程A是生產(chǎn)者線程,調(diào)用await()方法后,會(huì)釋放鎖,并且將當(dāng)前線程加入到Condition隊(duì)列中。此時(shí),消費(fèi)者能獲取到鎖資源,然后繼續(xù)執(zhí)行。假設(shè)線程B是消費(fèi)者線程,當(dāng)添加一個(gè)元素后會(huì)調(diào)用condition#signal()方法,定義如下:
public final void signal() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null)
doSignal(first);
}
private void doSignal(Node first) {
do {
if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null)
lastWaiter = null;
first.nextWaiter = null;
} while (!transferForSignal(first) &&
(first = firstWaiter) != null);
}
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
/*
* If cannot change waitStatus, the node has been cancelled.
*/
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
/*
* Splice onto queue and try to set waitStatus of predecessor to
* indicate that thread is (probably) waiting. If cancelled or
* attempt to set waitStatus fails, wake up to resync (in which
* case the waitStatus can be transiently and harmlessly wrong).
*/
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);
return true;
}
執(zhí)行signal()方法,會(huì)將Condition隊(duì)列中的第一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)移除,將其變?yōu)橥疥?duì)列中的尾結(jié)點(diǎn),如下:
至此,完成了Condition隊(duì)列轉(zhuǎn)換為同步隊(duì)列的過程。后續(xù)流程基本就是重復(fù)以上操作。
本文詳細(xì)介紹了單個(gè)Condition隊(duì)列的執(zhí)行流程,其實(shí)一個(gè)Lock中可以有多個(gè)Condition隊(duì)列,比如:JUC中提供的LinkedBlockingDeque、ArrayBlockingQueue等
作者 | 生活咖啡
來源 | cnblogs.com/vielat/p/15022895.html

