求求你們了,別再寫滿屏的 try catch 了!!
關(guān)注我們,設(shè)為星標(biāo),每天7:30不見不散,架構(gòu)路上與您共享 回復(fù)"架構(gòu)師"獲取資源
try {...} catch {...} finally {...} 代碼塊,不僅有大量的冗余代碼,而且還影響代碼的可讀性。

Controller層,如果是在Service層,可能會(huì)有更多的try catch代碼塊。這將會(huì)嚴(yán)重影響代碼的可讀性、“美觀性”。什么是統(tǒng)一異常處理
Spring在3.2版本增加了一個(gè)注解@ControllerAdvice,可以與@ExceptionHandler、@InitBinder、@ModelAttribute 等注解注解配套使用。@ExceptionHandler,從字面上看,就是 異常處理器 的意思,其實(shí)際作用也是:若在某個(gè)Controller類定義一個(gè)異常處理方法,并在方法上添加該注解,那么當(dāng)出現(xiàn)指定的異常時(shí),會(huì)執(zhí)行該處理異常的方法,其可以使用springmvc提供的數(shù)據(jù)綁定,比如注入HttpServletRequest等,還可以接受一個(gè)當(dāng)前拋出的Throwable對(duì)象。Controller類都定義一套這樣的異常處理方法,因?yàn)楫惓?梢允歉鞣N各樣。這樣一來(lái),就會(huì)造成大量的冗余代碼,而且若需要新增一種異常的處理邏輯,就必須修改所有Controller類了,很不優(yōu)雅。BaseController的基類,這樣總行了吧。Controller,我為啥非得繼承這樣一個(gè)類呢,萬(wàn)一已經(jīng)繼承其他基類了呢。大家都知道Java只能繼承一個(gè)類。Controller耦合,也可以將定義的 異常處理器 應(yīng)用到所有控制器呢?所以注解@ControllerAdvice出現(xiàn)了,簡(jiǎn)單的說(shuō),該注解可以把異常處理器應(yīng)用到所有控制器,而不是單個(gè)控制器。@ControllerAdvice,統(tǒng)一對(duì) 不同階段的、不同異常 進(jìn)行處理。這就是統(tǒng)一異常處理的原理。Controller前的異常 和 Service 層異常,具體可以參考下圖: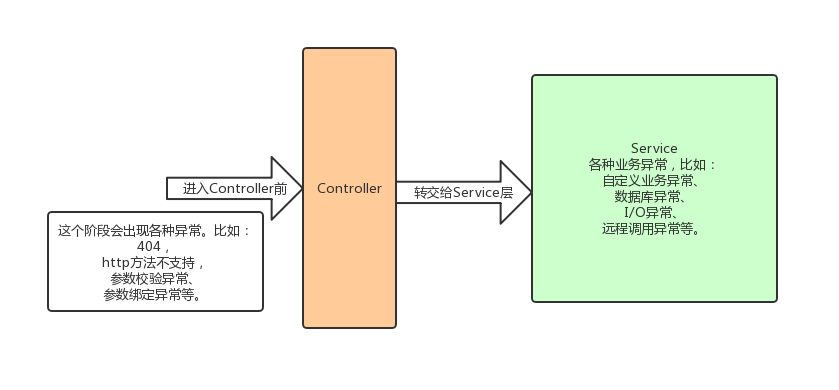
目標(biāo)
try catch 代碼塊,以優(yōu)雅的 Assert(斷言) 方式來(lái)校驗(yàn)業(yè)務(wù)的異常情況,只關(guān)注業(yè)務(wù)邏輯,而不用花費(fèi)大量精力寫冗余的 try catch 代碼塊。統(tǒng)一異常處理實(shí)戰(zhàn)
用 Assert(斷言) 替換 throw exception
Assert(斷言) 大家都很熟悉,比如 Spring 家族的 org.springframework.util.Assert,在我們寫測(cè)試用例的時(shí)候經(jīng)常會(huì)用到,使用斷言能讓我們編碼的時(shí)候有一種非一般絲滑的感覺,比如:@Test
public void test1() {
...
User user = userDao.selectById(userId);
Assert.notNull(user, "用戶不存在.");
...
}
@Test
public void test2() {
// 另一種寫法
User user = userDao.selectById(userId);
if (user == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("用戶不存在.");
}
}
if {...} 代碼塊。那么
神奇的 Assert.notNull() 背后到底做了什么呢?下面是 Assert 的部分源碼:public abstract class Assert {
public Assert() {
}
public static void notNull(@Nullable Object object, String message) {
if (object == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(message);
}
}
}
Assert 其實(shí)就是幫我們把 if {...} 封裝了一下,是不是很神奇。雖然很簡(jiǎn)單,但不可否認(rèn)的是編碼體驗(yàn)至少提升了一個(gè)檔次。那么我們能不能模仿org.springframework.util.Assert,也寫一個(gè)斷言類,不過斷言失敗后拋出的異常不是IllegalArgumentException 這些內(nèi)置異常,而是我們自己定義的異常。下面讓我們來(lái)嘗試一下。Assert
public interface Assert {
/**
* 創(chuàng)建異常
* @param args
* @return
*/
BaseException newException(Object... args);
/**
* 創(chuàng)建異常
* @param t
* @param args
* @return
*/
BaseException newException(Throwable t, Object... args);
/**
* <p>斷言對(duì)象<code>obj</code>非空。如果對(duì)象<code>obj</code>為空,則拋出異常
*
* @param obj 待判斷對(duì)象
*/
default void assertNotNull(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) {
throw newException(obj);
}
}
/**
* <p>斷言對(duì)象<code>obj</code>非空。如果對(duì)象<code>obj</code>為空,則拋出異常
* <p>異常信息<code>message</code>支持傳遞參數(shù)方式,避免在判斷之前進(jìn)行字符串拼接操作
*
* @param obj 待判斷對(duì)象
* @param args message占位符對(duì)應(yīng)的參數(shù)列表
*/
default void assertNotNull(Object obj, Object... args) {
if (obj == null) {
throw newException(args);
}
}
}
Assert斷言方法是使用接口的默認(rèn)方法定義的,然后有沒有發(fā)現(xiàn)當(dāng)斷言失敗后,拋出的異常不是具體的某個(gè)異常,而是交由2個(gè)newException接口方法提供。null,此時(shí)拋出的異常可能為UserNotFoundException,并且有特定的異常碼(比如7001)和異常信息“用戶不存在”。所以具體拋出什么異常,有Assert的實(shí)現(xiàn)類決定。善解人意的Enum
BaseException有2個(gè)屬性,即code、message,這樣一對(duì)屬性,有沒有想到什么類一般也會(huì)定義這2個(gè)屬性?沒錯(cuò),就是枚舉類。且看我如何將 Enum 和 Assert 結(jié)合起來(lái),相信我一定會(huì)讓你眼前一亮。如下:public interface IResponseEnum {
int getCode();
String getMessage();
}
/**
* <p>業(yè)務(wù)異常</p>
* <p>業(yè)務(wù)處理時(shí),出現(xiàn)異常,可以拋出該異常</p>
*/
public class BusinessException extends BaseException {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public BusinessException(IResponseEnum responseEnum, Object[] args, String message) {
super(responseEnum, args, message);
}
public BusinessException(IResponseEnum responseEnum, Object[] args, String message, Throwable cause) {
super(responseEnum, args, message, cause);
}
}
public interface BusinessExceptionAssert extends IResponseEnum, Assert {
@Override
default BaseException newException(Object... args) {
String msg = MessageFormat.format(this.getMessage(), args);
return new BusinessException(this, args, msg);
}
@Override
default BaseException newException(Throwable t, Object... args) {
String msg = MessageFormat.format(this.getMessage(), args);
return new BusinessException(this, args, msg, t);
}
}
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public enum ResponseEnum implements BusinessExceptionAssert {
/**
* Bad licence type
*/
BAD_LICENCE_TYPE(7001, "Bad licence type."),
/**
* Licence not found
*/
LICENCE_NOT_FOUND(7002, "Licence not found.")
;
/**
* 返回碼
*/
private int code;
/**
* 返回消息
*/
private String message;
}
BAD_LICENCE_TYPE、LICENCE_NOT_FOUND,分別對(duì)應(yīng)了BadLicenceTypeException、LicenceNotFoundException兩種異常。LicenceService有校驗(yàn)Licence是否存在的方法,如下:/**
* 校驗(yàn){@link Licence}存在
* @param licence
*/
private void checkNotNull(Licence licence) {
ResponseEnum.LICENCE_NOT_FOUND.assertNotNull(licence);
}
private void checkNotNull(Licence licence) {
if (licence == null) {
throw new LicenceNotFoundException();
// 或者這樣
throw new BusinessException(7001, "Bad licence type.");
}
}
Assert,只需根據(jù)特定的異常情況定義不同的枚舉實(shí)例,如上面的BAD_LICENCE_TYPE、LICENCE_NOT_FOUND,就能夠針對(duì)不同情況拋出特定的異常(這里指攜帶特定的異常碼和異常消息),這樣既不用定義大量的異常類,同時(shí)還具備了斷言的良好可讀性,當(dāng)然這種方案的好處遠(yuǎn)不止這些,請(qǐng)繼續(xù)閱讀后文,慢慢體會(huì)。注:上面舉的例子是針對(duì)特定的業(yè)務(wù),而有部分異常情況是通用的,比如:服務(wù)器繁忙、網(wǎng)絡(luò)異常、服務(wù)器異常、參數(shù)校驗(yàn)異常、404等,所以有 CommonResponseEnum、ArgumentResponseEnum、ServletResponseEnum,其中ServletResponseEnum會(huì)在后文詳細(xì)說(shuō)明。
定義統(tǒng)一異常處理器類
@Slf4j
@Component
@ControllerAdvice
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(UnifiedExceptionHandler.class)
public class UnifiedExceptionHandler {
/**
* 生產(chǎn)環(huán)境
*/
private final static String ENV_PROD = "prod";
@Autowired
private UnifiedMessageSource unifiedMessageSource;
/**
* 當(dāng)前環(huán)境
*/
@Value("${spring.profiles.active}")
private String profile;
/**
* 獲取國(guó)際化消息
*
* @param e 異常
* @return
*/
public String getMessage(BaseException e) {
String code = "response." + e.getResponseEnum().toString();
String message = unifiedMessageSource.getMessage(code, e.getArgs());
if (message == null || message.isEmpty()) {
return e.getMessage();
}
return message;
}
/**
* 業(yè)務(wù)異常
*
* @param e 異常
* @return 異常結(jié)果
*/
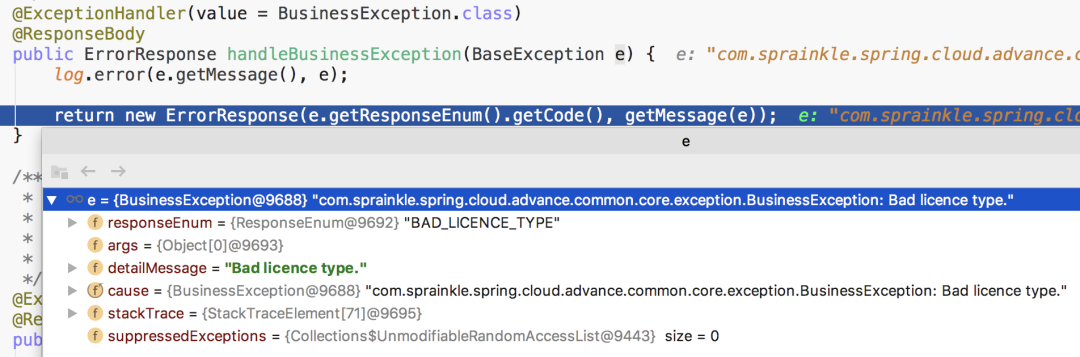
@ExceptionHandler(value = BusinessException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleBusinessException(BaseException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
return new ErrorResponse(e.getResponseEnum().getCode(), getMessage(e));
}
/**
* 自定義異常
*
* @param e 異常
* @return 異常結(jié)果
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = BaseException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleBaseException(BaseException e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
return new ErrorResponse(e.getResponseEnum().getCode(), getMessage(e));
}
/**
* Controller上一層相關(guān)異常
*
* @param e 異常
* @return 異常結(jié)果
*/
@ExceptionHandler({
NoHandlerFoundException.class,
HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class,
HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException.class,
MissingPathVariableException.class,
MissingServletRequestParameterException.class,
TypeMismatchException.class,
HttpMessageNotReadableException.class,
HttpMessageNotWritableException.class,
// BindException.class,
// MethodArgumentNotValidException.class
HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException.class,
ServletRequestBindingException.class,
ConversionNotSupportedException.class,
MissingServletRequestPartException.class,
AsyncRequestTimeoutException.class
})
@ResponseBody
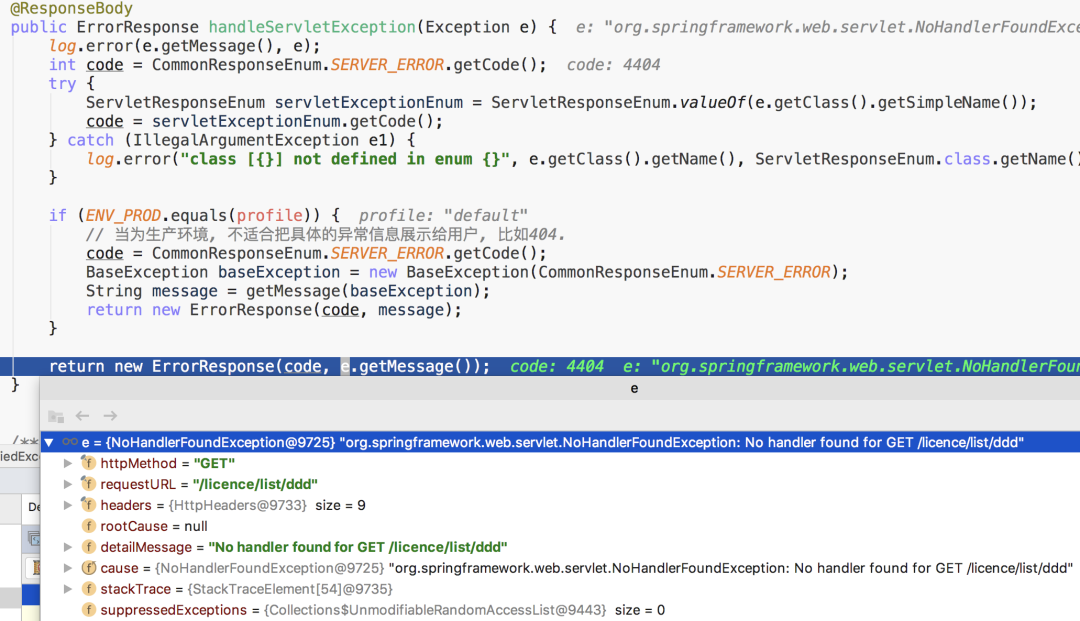
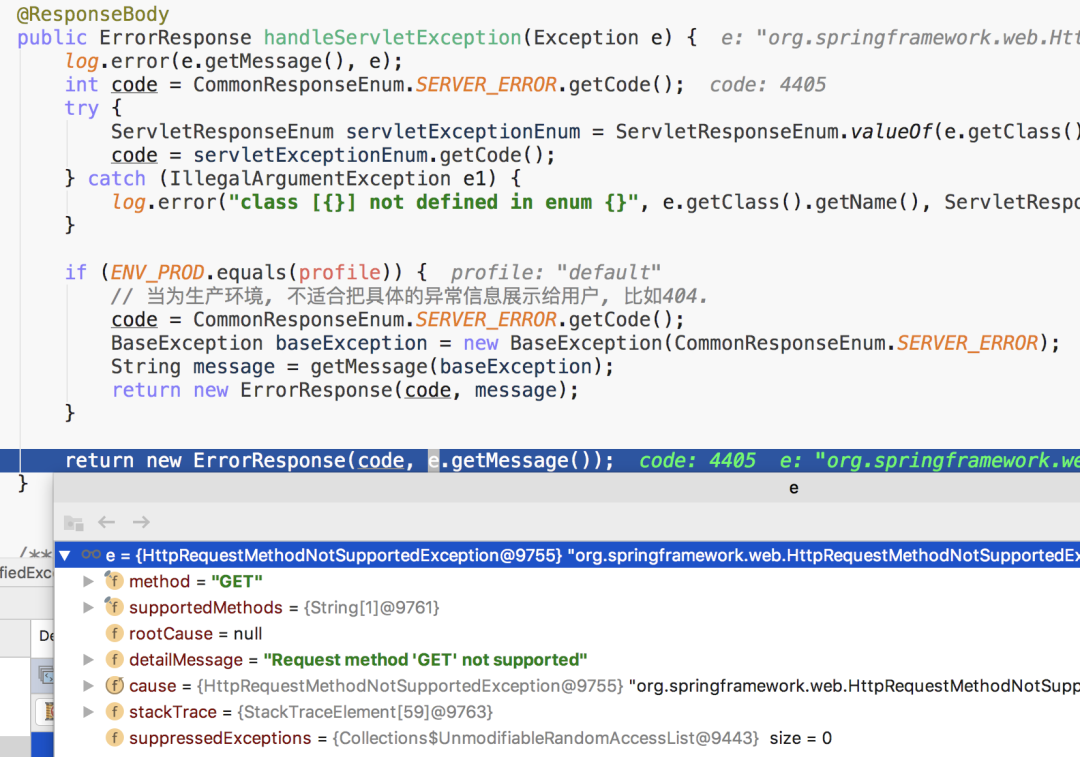
public ErrorResponse handleServletException(Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
int code = CommonResponseEnum.SERVER_ERROR.getCode();
try {
ServletResponseEnum servletExceptionEnum = ServletResponseEnum.valueOf(e.getClass().getSimpleName());
code = servletExceptionEnum.getCode();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e1) {
log.error("class [{}] not defined in enum {}", e.getClass().getName(), ServletResponseEnum.class.getName());
}
if (ENV_PROD.equals(profile)) {
// 當(dāng)為生產(chǎn)環(huán)境, 不適合把具體的異常信息展示給用戶, 比如404.
code = CommonResponseEnum.SERVER_ERROR.getCode();
BaseException baseException = new BaseException(CommonResponseEnum.SERVER_ERROR);
String message = getMessage(baseException);
return new ErrorResponse(code, message);
}
return new ErrorResponse(code, e.getMessage());
}
/**
* 參數(shù)綁定異常
*
* @param e 異常
* @return 異常結(jié)果
*/
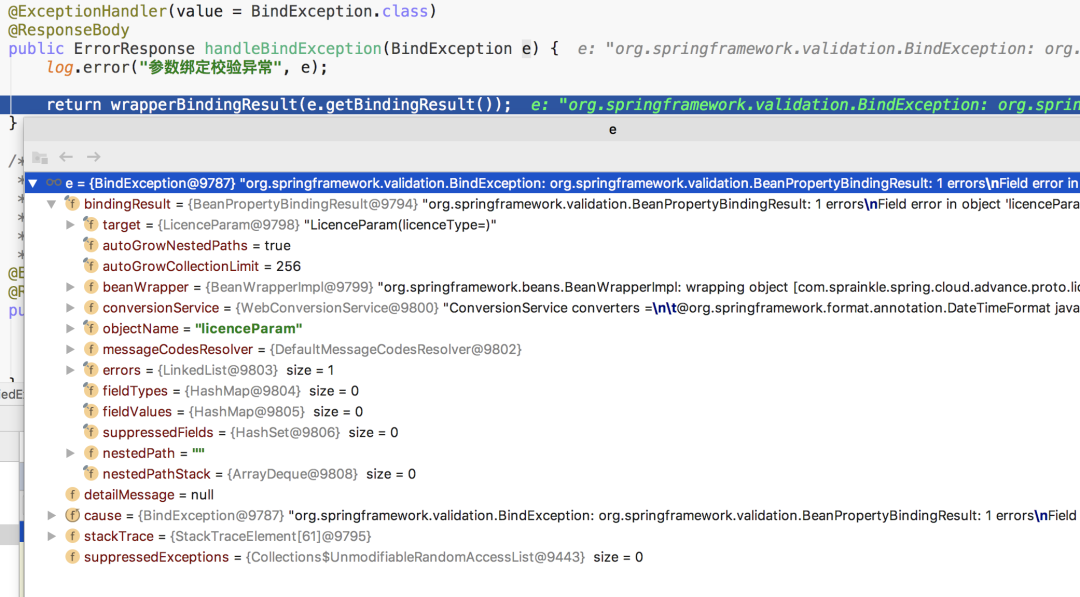
@ExceptionHandler(value = BindException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleBindException(BindException e) {
log.error("參數(shù)綁定校驗(yàn)異常", e);
return wrapperBindingResult(e.getBindingResult());
}
/**
* 參數(shù)校驗(yàn)異常,將校驗(yàn)失敗的所有異常組合成一條錯(cuò)誤信息
*
* @param e 異常
* @return 異常結(jié)果
*/
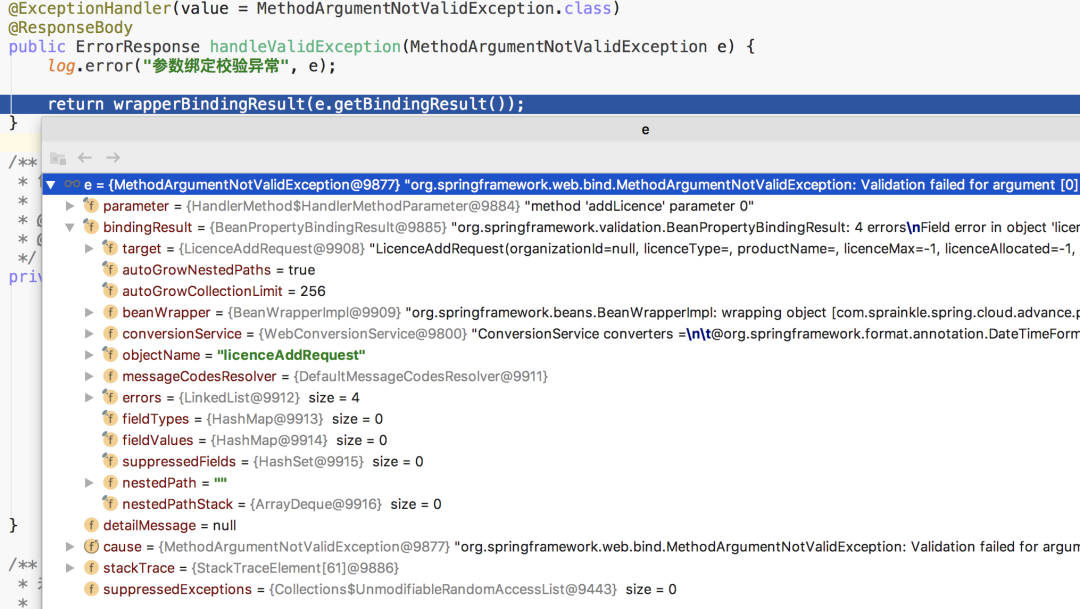
@ExceptionHandler(value = MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) {
log.error("參數(shù)綁定校驗(yàn)異常", e);
return wrapperBindingResult(e.getBindingResult());
}
/**
* 包裝綁定異常結(jié)果
*
* @param bindingResult 綁定結(jié)果
* @return 異常結(jié)果
*/
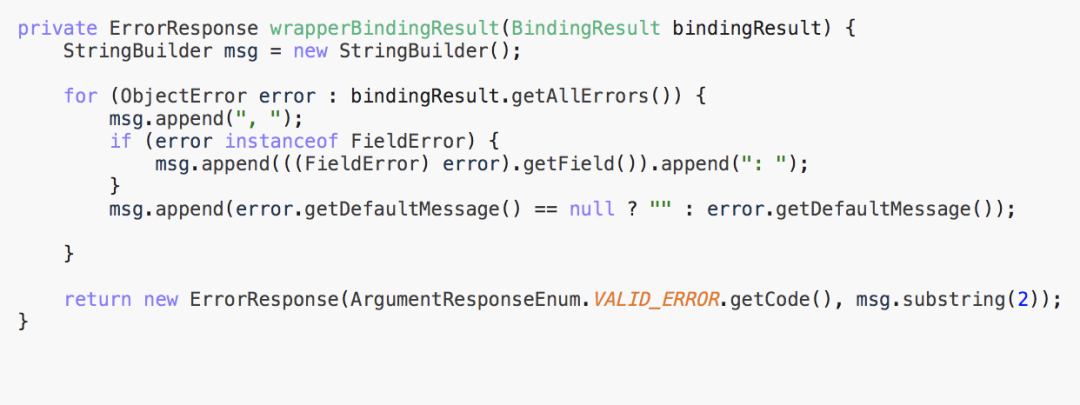
private ErrorResponse wrapperBindingResult(BindingResult bindingResult) {
StringBuilder msg = new StringBuilder();
for (ObjectError error : bindingResult.getAllErrors()) {
msg.append(", ");
if (error instanceof FieldError) {
msg.append(((FieldError) error).getField()).append(": ");
}
msg.append(error.getDefaultMessage() == null ? "" : error.getDefaultMessage());
}
return new ErrorResponse(ArgumentResponseEnum.VALID_ERROR.getCode(), msg.substring(2));
}
/**
* 未定義異常
*
* @param e 異常
* @return 異常結(jié)果
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public ErrorResponse handleException(Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
if (ENV_PROD.equals(profile)) {
// 當(dāng)為生產(chǎn)環(huán)境, 不適合把具體的異常信息展示給用戶, 比如數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)異常信息.
int code = CommonResponseEnum.SERVER_ERROR.getCode();
BaseException baseException = new BaseException(CommonResponseEnum.SERVER_ERROR);
String message = getMessage(baseException);
return new ErrorResponse(code, message);
}
return new ErrorResponse(CommonResponseEnum.SERVER_ERROR.getCode(), e.getMessage());
}
}
ServletException、ServiceException,還記得上文提到的 按階段分類 嗎,即對(duì)應(yīng) 進(jìn)入Controller前的異常 和 Service 層異常;然后 ServiceException 再分成自定義異常、未知異常。對(duì)應(yīng)關(guān)系如下:進(jìn)入 Controller前的異常: handleServletException、handleBindException、handleValidException自定義異常: handleBusinessException、handleBaseException 未知異常: handleException
異常處理器說(shuō)明
handleServletException
http請(qǐng)求,在到達(dá)Controller前,會(huì)對(duì)該請(qǐng)求的請(qǐng)求信息與目標(biāo)控制器信息做一系列校驗(yàn)。這里簡(jiǎn)單說(shuō)一下:Url查找有沒有對(duì)應(yīng)的控制器,若沒有則會(huì)拋該異常,也就是大家非常熟悉的404異常;http方法不同,如:Get、Post等),則嘗試將請(qǐng)求的http方法與列表的控制器做匹配,若沒有對(duì)應(yīng)http方法的控制器,則拋該異常;content-type請(qǐng)求頭,若控制器的參數(shù)簽名包含注解@RequestBody,但是請(qǐng)求的content-type請(qǐng)求頭的值沒有包含application/json,那么會(huì)拋該異常(當(dāng)然,不止這種情況會(huì)拋這個(gè)異常);/licence/{licenceId},參數(shù)簽名包含@PathVariable("licenceId"),當(dāng)請(qǐng)求的url為/licence,在沒有明確定義url為/licence的情況下,會(huì)被判定為:缺少路徑參數(shù);HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException舉的例子完全相反,即請(qǐng)求頭攜帶了"content-type: application/json;charset=UTF-8",但接收參數(shù)卻沒有添加注解@RequestBody,或者請(qǐng)求體攜帶的 json 串反序列化成 pojo 的過程中失敗了,也會(huì)拋該異常;handleBindException
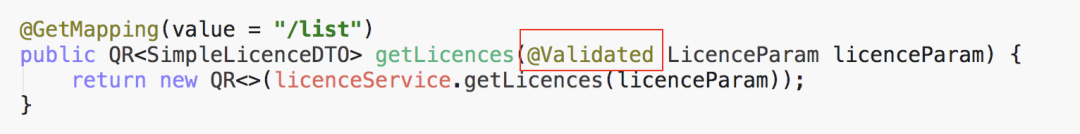
handleValidException
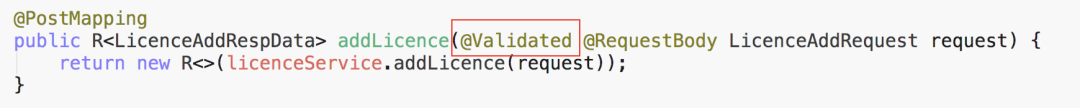
handleBusinessException、handleBaseException
handleBaseException處理的是除了 BusinessException 意外的所有業(yè)務(wù)異常。就目前來(lái)看,這2個(gè)是可以合并成一個(gè)的。handleException
注:上面的 handleServletException、handleException這兩個(gè)處理器,返回的異常信息,不同環(huán)境返回的可能不一樣,以為這些異常信息都是框架自帶的異常信息,一般都是英文的,不太好直接展示給用戶看,所以統(tǒng)一返回SERVER_ERROR代表的異常信息。
異于常人的404
NoHandlerFoundException異常,但其實(shí)默認(rèn)情況下不是這樣,默認(rèn)情況下會(huì)出現(xiàn)類似如下頁(yè)面: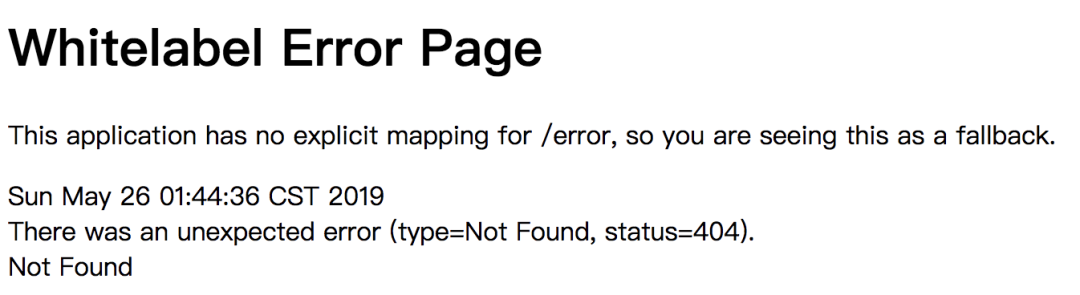
forward跳轉(zhuǎn)到/error控制器,spring也提供了默認(rèn)的error控制器,如下: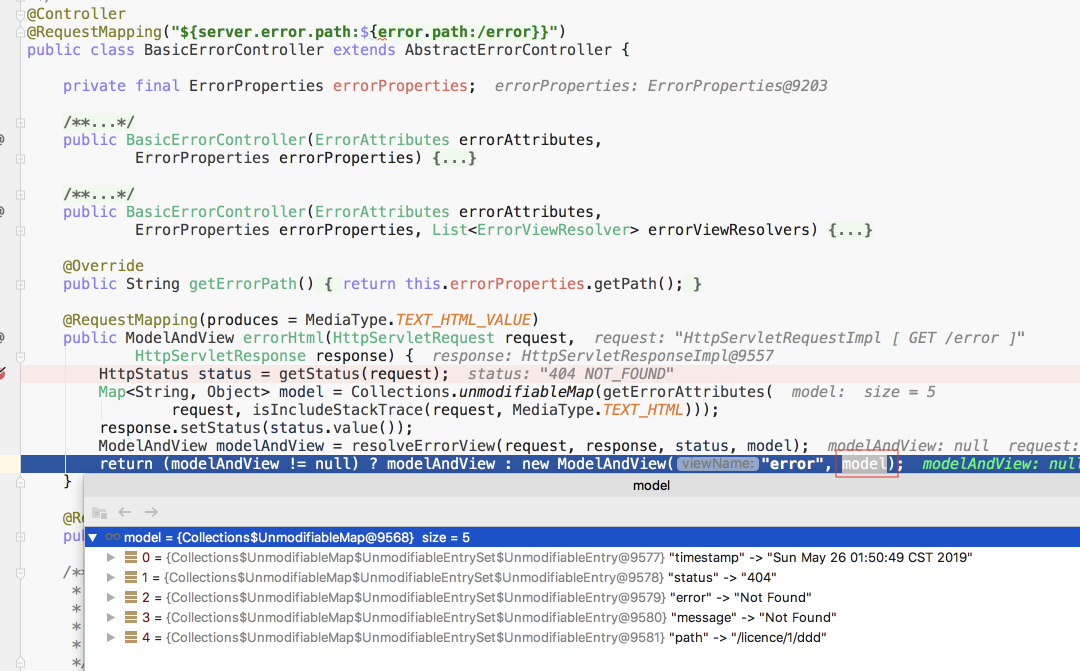
properties文件中加入如下配置即可:spring.mvc.throw-exception-if-no-handler-found=true
spring.resources.add-mappings=false
統(tǒng)一返回結(jié)果
code、message 是所有返回結(jié)果中必有的字段,而當(dāng)需要返回?cái)?shù)據(jù)時(shí),則需要另一個(gè)字段 data 來(lái)表示。BaseResponse 來(lái)作為所有返回結(jié)果的基類;CommonResponse,繼承 BaseResponse,而且多了字段 data;ErrorResponseQueryDataResponse,該類繼承自 CommonResponse,只是把 data 字段的類型限制為 QueryDdata,QueryDdata中定義了分頁(yè)信息相應(yīng)的字段,即totalCount、pageNo、 pageSize、records。CommonResponse 和 QueryDataResponse,但是名字又賊鬼死長(zhǎng),何不定義2個(gè)名字超簡(jiǎn)單的類來(lái)替代呢?于是 R 和 QR 誕生了,以后返回結(jié)果的時(shí)候只需這樣寫:new R<>(data)、new QR<>(queryData)。驗(yàn)證統(tǒng)一異常處理
common包,以后每一個(gè)新項(xiàng)目/模塊只需引入該包即可。所以為了驗(yàn)證,需要新建一個(gè)項(xiàng)目,并引入該 common包。主要代碼
@Service
public class LicenceService extends ServiceImpl<LicenceMapper, Licence> {
@Autowired
private OrganizationClient organizationClient;
/**
* 查詢{@link Licence} 詳情
* @param licenceId
* @return
*/
public LicenceDTO queryDetail(Long licenceId) {
Licence licence = this.getById(licenceId);
checkNotNull(licence);
OrganizationDTO org = ClientUtil.execute(() -> organizationClient.getOrganization(licence.getOrganizationId()));
return toLicenceDTO(licence, org);
}
/**
* 分頁(yè)獲取
* @param licenceParam 分頁(yè)查詢參數(shù)
* @return
*/
public QueryData<SimpleLicenceDTO> getLicences(LicenceParam licenceParam) {
String licenceType = licenceParam.getLicenceType();
LicenceTypeEnum licenceTypeEnum = LicenceTypeEnum.parseOfNullable(licenceType);
// 斷言, 非空
ResponseEnum.BAD_LICENCE_TYPE.assertNotNull(licenceTypeEnum);
LambdaQueryWrapper<Licence> wrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq(Licence::getLicenceType, licenceType);
IPage<Licence> page = this.page(new QueryPage<>(licenceParam), wrapper);
return new QueryData<>(page, this::toSimpleLicenceDTO);
}
/**
* 新增{@link Licence}
* @param request 請(qǐng)求體
* @return
*/
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Throwable.class)
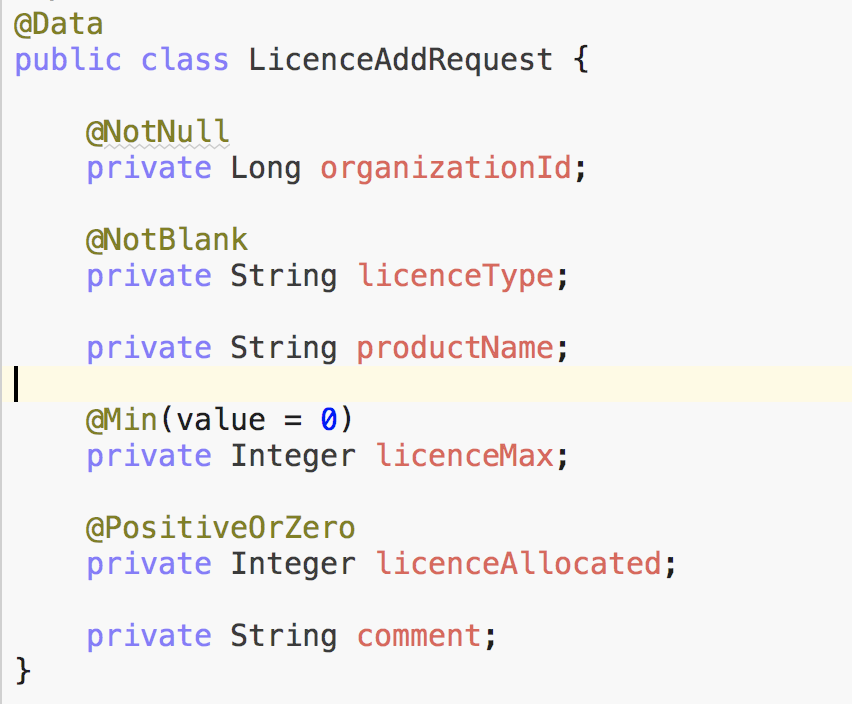
public LicenceAddRespData addLicence(LicenceAddRequest request) {
Licence licence = new Licence();
licence.setOrganizationId(request.getOrganizationId());
licence.setLicenceType(request.getLicenceType());
licence.setProductName(request.getProductName());
licence.setLicenceMax(request.getLicenceMax());
licence.setLicenceAllocated(request.getLicenceAllocated());
licence.setComment(request.getComment());
this.save(licence);
return new LicenceAddRespData(licence.getLicenceId());
}
/**
* entity -> simple dto
* @param licence {@link Licence} entity
* @return {@link SimpleLicenceDTO}
*/
private SimpleLicenceDTO toSimpleLicenceDTO(Licence licence) {
// 省略
}
/**
* entity -> dto
* @param licence {@link Licence} entity
* @param org {@link OrganizationDTO}
* @return {@link LicenceDTO}
*/
private LicenceDTO toLicenceDTO(Licence licence, OrganizationDTO org) {
// 省略
}
/**
* 校驗(yàn){@link Licence}存在
* @param licence
*/
private void checkNotNull(Licence licence) {
ResponseEnum.LICENCE_NOT_FOUND.assertNotNull(licence);
}
}
mybatis-plus。啟動(dòng)時(shí),自動(dòng)插入的數(shù)據(jù)為:-- licence
INSERT INTO licence (licence_id, organization_id, licence_type, product_name, licence_max, licence_allocated)
VALUES (1, 1, 'user','CustomerPro', 100,5);
INSERT INTO licence (licence_id, organization_id, licence_type, product_name, licence_max, licence_allocated)
VALUES (2, 1, 'user','suitability-plus', 200,189);
INSERT INTO licence (licence_id, organization_id, licence_type, product_name, licence_max, licence_allocated)
VALUES (3, 2, 'user','HR-PowerSuite', 100,4);
INSERT INTO licence (licence_id, organization_id, licence_type, product_name, licence_max, licence_allocated)
VALUES (4, 2, 'core-prod','WildCat Application Gateway', 16,16);
-- organizations
INSERT INTO organization (id, name, contact_name, contact_email, contact_phone)
VALUES (1, 'customer-crm-co', 'Mark Balster', '[email protected]', '823-555-1212');
INSERT INTO organization (id, name, contact_name, contact_email, contact_phone)
VALUES (2, 'HR-PowerSuite', 'Doug Drewry','[email protected]', '920-555-1212');
開始驗(yàn)證
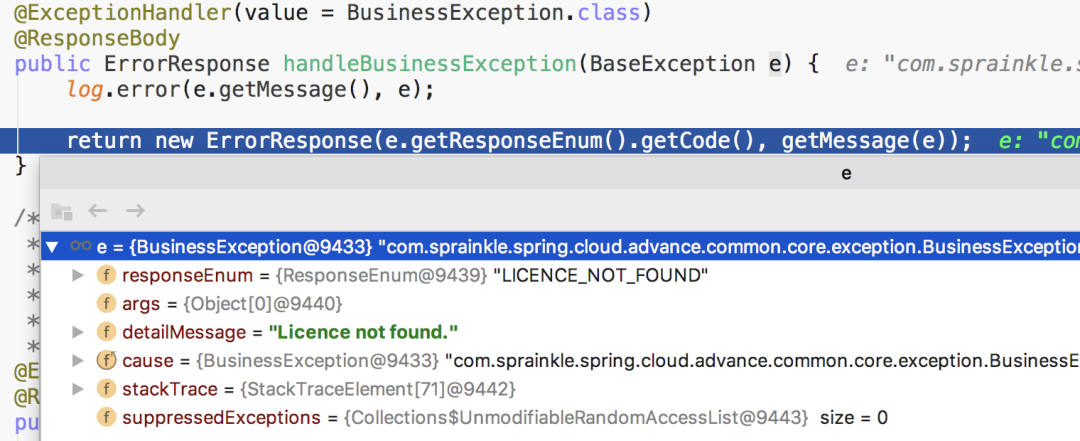
捕獲自定義異常
licence 詳情:http://localhost:10000/licence/5。成功響應(yīng)的請(qǐng)求:licenceId=1

licence type 獲取 licence 列表:http://localhost:10000/licence/list?licenceType=ddd。可選的 licence type 為:user、core-prod 。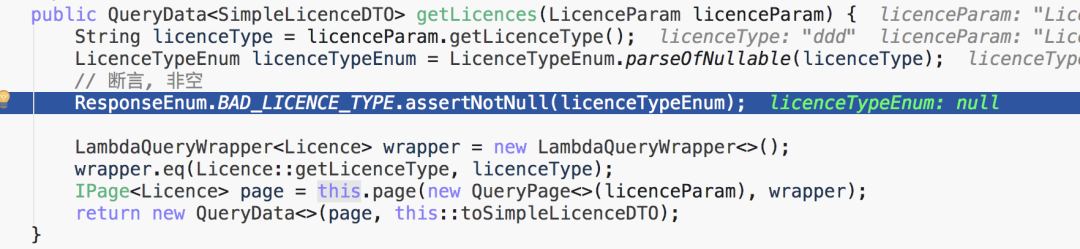




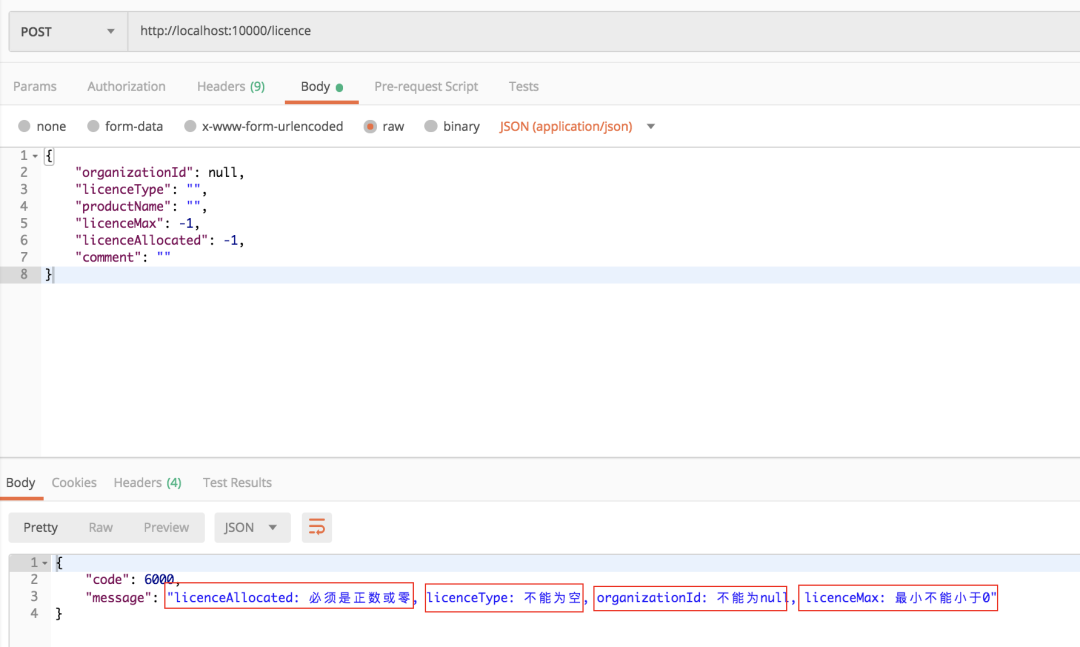
捕獲未知異常
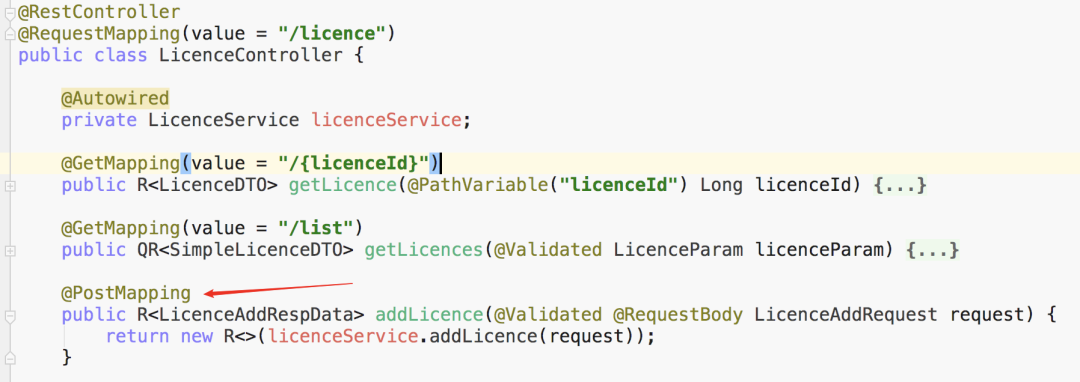
Licence 新增一個(gè)字段 test,但不修改數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)表結(jié)構(gòu),然后訪問:http://localhost:10000/licence/1。
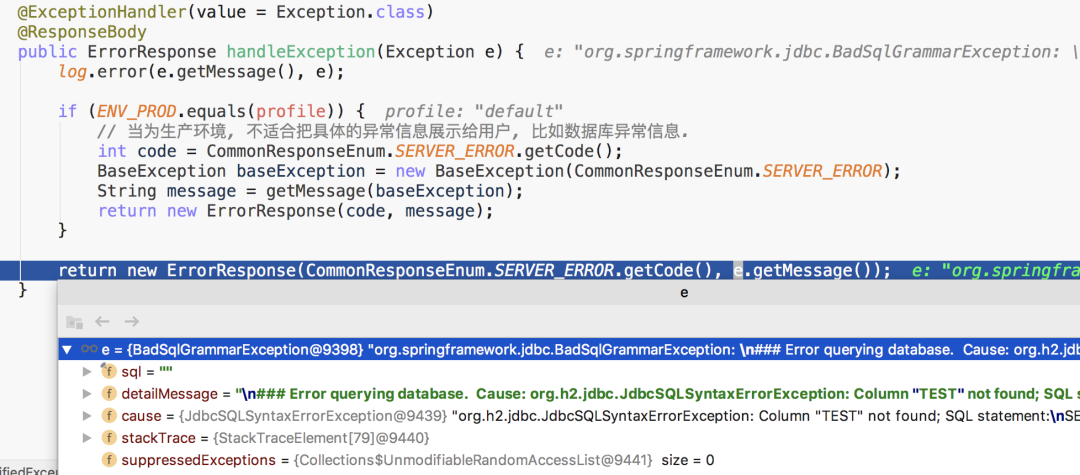

小結(jié)
code、message 的形式返回。每一個(gè)項(xiàng)目/模塊,在定義業(yè)務(wù)異常的時(shí)候,只需定義一個(gè)枚舉類,然后實(shí)現(xiàn)接口 BusinessExceptionAssert,最后為每一種業(yè)務(wù)異常定義對(duì)應(yīng)的枚舉實(shí)例即可,而不用定義許多異常類。使用的時(shí)候也很方便,用法類似斷言。ServletException,因?yàn)槎际且婚L(zhǎng)串的異常信息,若直接展示給用戶看,顯得不夠?qū)I(yè),于是,我們可以這樣做:當(dāng)檢測(cè)到當(dāng)前環(huán)境是生產(chǎn)環(huán)境,那么直接返回 "網(wǎng)絡(luò)異常"。

總結(jié)
spring cloud security 后,還會(huì)有認(rèn)證/授權(quán)異常,網(wǎng)關(guān)的服務(wù)降級(jí)異常、跨模塊調(diào)用異常、遠(yuǎn)程調(diào)用第三方服務(wù)異常等,這些異常的捕獲方式與本文介紹的不太一樣,不過限于篇幅,這里不做詳細(xì)說(shuō)明,以后會(huì)有單獨(dú)的文章介紹。
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
/**
* 沒有登錄
* @param request
* @param response
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(NoLoginException.class)
public Object noLoginExceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,Exception e)
{
log.error("[GlobalExceptionHandler][noLoginExceptionHandler] exception",e);
JsonResult jsonResult = new JsonResult();
jsonResult.setCode(JsonResultCode.NO_LOGIN);
jsonResult.setMessage("用戶登錄失效或者登錄超時(shí),請(qǐng)先登錄");
return jsonResult;
}
/**
* 業(yè)務(wù)異常
* @param request
* @param response
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(ServiceException.class)
public Object businessExceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,Exception e)
{
log.error("[GlobalExceptionHandler][businessExceptionHandler] exception",e);
JsonResult jsonResult = new JsonResult();
jsonResult.setCode(JsonResultCode.FAILURE);
jsonResult.setMessage("業(yè)務(wù)異常,請(qǐng)聯(lián)系管理員");
return jsonResult;
}
/**
* 全局異常處理
* @param request
* @param response
* @param e
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public Object exceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,Exception e)
{
log.error("[GlobalExceptionHandler][exceptionHandler] exception",e);
JsonResult jsonResult = new JsonResult();
jsonResult.setCode(JsonResultCode.FAILURE);
jsonResult.setMessage("系統(tǒng)錯(cuò)誤,請(qǐng)聯(lián)系管理員");
return jsonResult;
}
}
文章來(lái)源:https://cnblogs.com/jurendage/p/11255197.html
到此文章就結(jié)束了。如果今天的文章對(duì)你在進(jìn)階架構(gòu)師的路上有新的啟發(fā)和進(jìn)步,歡迎轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)給更多人。歡迎加入架構(gòu)師社區(qū)技術(shù)交流群,眾多大咖帶你進(jìn)階架構(gòu)師,在后臺(tái)回復(fù)“加群”即可入群。
這些年小編給你分享過的干貨2.ERP系統(tǒng),自帶進(jìn)銷存+財(cái)務(wù)+生產(chǎn)功能,拿來(lái)即用
3.帶工作流的SpringBoot后臺(tái)管理項(xiàng)目快速開發(fā)解決方案
4.最好的OA系統(tǒng),拿來(lái)即用,非常方便5.SpringBoot+Vue完整的外賣系統(tǒng),手機(jī)端和后臺(tái)管理,附源碼!
轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)在看就是最大的支持??
評(píng)論
圖片
表情


