使用ZooKeeper實(shí)現(xiàn)分布式隊(duì)列、分布式鎖和選舉詳解

ZooKeeper源碼的zookeeper-recipes目錄下提供了分布式隊(duì)列、分布式鎖和選舉的實(shí)現(xiàn)(GitHub地址:https://github.com/apache/zookeeper/tree/master/zookeeper-recipes)。本文主要對(duì)這幾種實(shí)現(xiàn)做實(shí)現(xiàn)原理的解析和源碼剖析:
1、分布式隊(duì)列
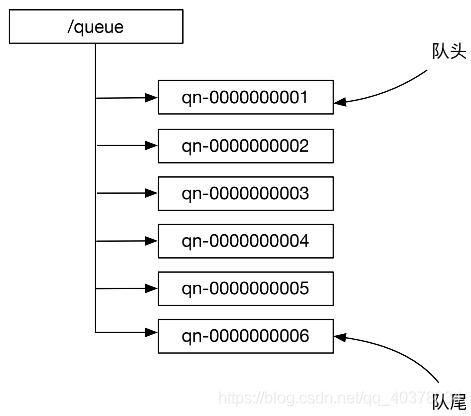
使用路徑為/queue的znode下的節(jié)點(diǎn)表示隊(duì)列中的元素。/queue下的節(jié)點(diǎn)都是順序持久化znode。這些znode名字的后綴數(shù)字表示了對(duì)應(yīng)隊(duì)列元素在隊(duì)列中的位置。znode名字后綴數(shù)字越小,對(duì)應(yīng)隊(duì)列元素在隊(duì)列中的位置越靠前
1)、offer方法
offer方法在/queue下面創(chuàng)建一個(gè)順序znode。因?yàn)閦node的后綴數(shù)字是/queue下面現(xiàn)有znode最大后綴數(shù)字加1,所以該znode對(duì)應(yīng)的隊(duì)列元素處于隊(duì)尾
public class DistributedQueue {
public boolean offer(byte[] data) throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
for (; ; ) {
try {
zookeeper.create(dir + "/" + prefix, data, acl, CreateMode.PERSISTENT_SEQUENTIAL);
return true;
} catch (KeeperException.NoNodeException e) {
zookeeper.create(dir, new byte[0], acl, CreateMode.PERSISTENT);
}
}
}
2)、element方法
public class DistributedQueue {
public byte[] element() throws NoSuchElementException, KeeperException, InterruptedException {
Map<Long, String> orderedChildren;
while (true) {
try {
//獲取所有排好序的子節(jié)點(diǎn)
orderedChildren = orderedChildren(null);
} catch (KeeperException.NoNodeException e) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
if (orderedChildren.size() == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
//返回隊(duì)頭節(jié)點(diǎn)的數(shù)據(jù)
for (String headNode : orderedChildren.values()) {
if (headNode != null) {
try {
return zookeeper.getData(dir + "/" + headNode, false, null);
} catch (KeeperException.NoNodeException e) {
//另一個(gè)客戶端已經(jīng)移除了隊(duì)頭節(jié)點(diǎn),嘗試獲取下一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)
}
}
}
}
}
private Map<Long, String> orderedChildren(Watcher watcher) throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
Map<Long, String> orderedChildren = new TreeMap<>();
List<String> childNames;
childNames = zookeeper.getChildren(dir, watcher);
for (String childName : childNames) {
try {
if (!childName.regionMatches(0, prefix, 0, prefix.length())) {
LOG.warn("Found child node with improper name: {}", childName);
continue;
}
String suffix = childName.substring(prefix.length());
Long childId = Long.parseLong(suffix);
orderedChildren.put(childId, childName);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
LOG.warn("Found child node with improper format : {}", childName, e);
}
}
return orderedChildren;
}
3)、remove方法
public class DistributedQueue {
public byte[] remove() throws NoSuchElementException, KeeperException, InterruptedException {
Map<Long, String> orderedChildren;
while (true) {
try {
//獲取所有排好序的子節(jié)點(diǎn)
orderedChildren = orderedChildren(null);
} catch (KeeperException.NoNodeException e) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
if (orderedChildren.size() == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
//移除隊(duì)頭節(jié)點(diǎn)
for (String headNode : orderedChildren.values()) {
String path = dir + "/" + headNode;
try {
byte[] data = zookeeper.getData(path, false, null);
zookeeper.delete(path, -1);
return data;
} catch (KeeperException.NoNodeException e) {
//另一個(gè)客戶端已經(jīng)移除了隊(duì)頭節(jié)點(diǎn),嘗試移除下一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)
}
}
}
}
2、分布式鎖
1)、排他鎖
排他鎖的核心是如何保證當(dāng)前有且僅有一個(gè)事務(wù)獲取鎖,并且鎖被釋放后,所有正在等待獲取鎖的事務(wù)都能夠被通知到
定義鎖
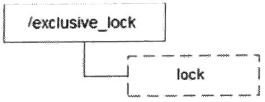
通過(guò)在ZooKeeper上創(chuàng)建一個(gè)子節(jié)點(diǎn)來(lái)表示一個(gè)鎖,例如/exclusive_lock/lock節(jié)點(diǎn)就可以被定義為一個(gè)鎖
獲取鎖
在需要獲取排他鎖時(shí),所有的客戶端都會(huì)試圖通過(guò)調(diào)用create()接口,在/exclusive_lock節(jié)點(diǎn)下創(chuàng)建臨時(shí)子節(jié)點(diǎn)/exclusive_lock/lock。ZooKeeper會(huì)保證在所有的客戶端中,最終只有一個(gè)客戶能夠創(chuàng)建成功,那么就可以認(rèn)為該客戶端獲取了鎖。
同時(shí),所有沒(méi)有獲取到鎖的客戶端就需要到/exclusive_lock節(jié)點(diǎn)上注冊(cè)一個(gè)子節(jié)點(diǎn)變更的watcher監(jiān)聽(tīng),以便實(shí)時(shí)監(jiān)聽(tīng)到lock節(jié)點(diǎn)的變更情況
釋放鎖
/exclusive_lock/lock是一個(gè)臨時(shí)節(jié)點(diǎn),因此在以下兩種情況下,都有可能釋放鎖
當(dāng)前獲取鎖的客戶端機(jī)器發(fā)生宕機(jī),那么ZooKeeper上的這個(gè)臨時(shí)節(jié)點(diǎn)就會(huì)被移除 正常執(zhí)行完業(yè)務(wù)邏輯后,客戶端就會(huì)主動(dòng)將自己創(chuàng)建的臨時(shí)節(jié)點(diǎn)刪除
無(wú)論在什么情況下移除了lock節(jié)點(diǎn),ZooKeeper都會(huì)通知所有在/exclusive_lock節(jié)點(diǎn)上注冊(cè)了子節(jié)點(diǎn)變更watcher監(jiān)聽(tīng)的客戶端。這些客戶端在接收到通知后,再次重新發(fā)起分布式鎖獲取,即重復(fù)獲取鎖過(guò)程
2)、羊群效應(yīng)
上面的排他鎖的實(shí)現(xiàn)可能引發(fā)羊群效應(yīng):當(dāng)一個(gè)特定的znode改變的時(shí)候ZooKeeper觸發(fā)了所有watcher的事件,由于通知的客戶端很多,所以通知操作會(huì)造成ZooKeeper性能突然下降,這樣會(huì)影響ZooKeeper的使用
改進(jìn)后的分布式鎖實(shí)現(xiàn)
獲取鎖
首先,在Zookeeper當(dāng)中創(chuàng)建一個(gè)持久節(jié)點(diǎn)ParentLock。當(dāng)?shù)谝粋€(gè)客戶端想要獲得鎖時(shí),需要在ParentLock這個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)下面創(chuàng)建一個(gè)臨時(shí)順序節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock1
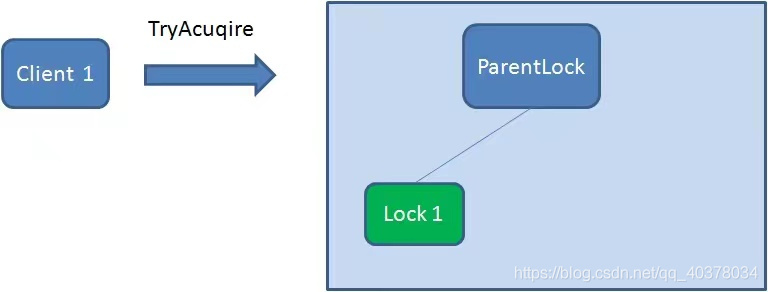
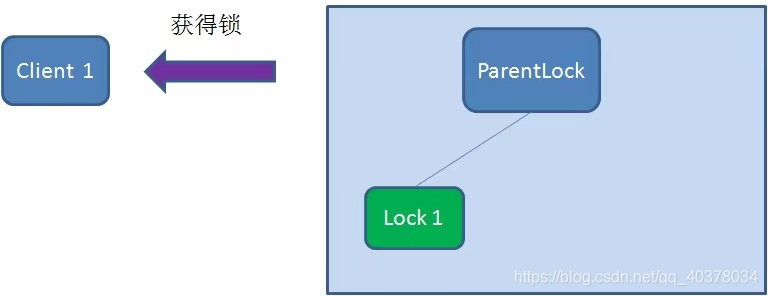
之后,Client1查找ParentLock下面所有的臨時(shí)順序節(jié)點(diǎn)并排序,判斷自己所創(chuàng)建的節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock1是不是順序最靠前的一個(gè)。如果是第一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn),則成功獲得鎖
這時(shí)候,如果再有一個(gè)客戶端Client2前來(lái)獲取鎖,則在ParentLock下再創(chuàng)建一個(gè)臨時(shí)順序節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock2
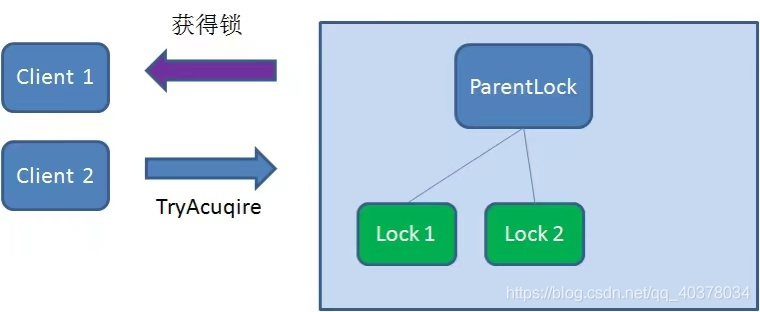
Client2查找ParentLock下面所有的臨時(shí)順序節(jié)點(diǎn)并排序,判斷自己所創(chuàng)建的節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock2是不是順序最靠前的一個(gè),結(jié)果發(fā)現(xiàn)節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock2并不是最小的
于是,Client2向排序僅比它靠前的節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock1注冊(cè)watcher,用于監(jiān)聽(tīng)Lock1節(jié)點(diǎn)是否存在。這意味著Client2搶鎖失敗,進(jìn)入了等待狀態(tài)
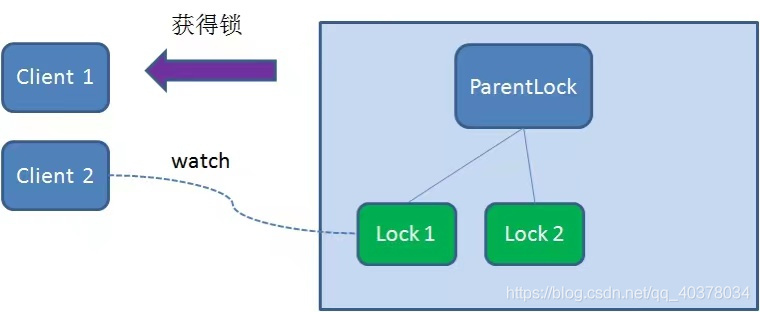
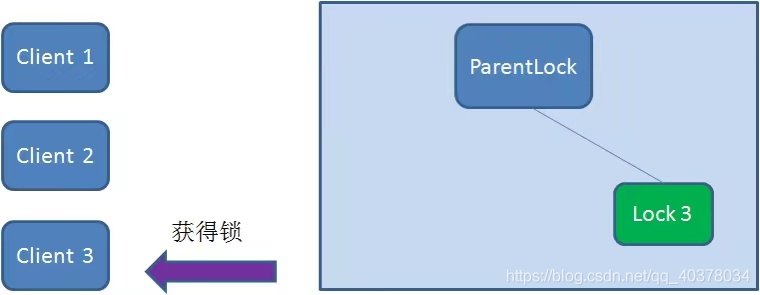
這時(shí)候,如果又有一個(gè)客戶端Client3前來(lái)獲取鎖,則在ParentLock下再創(chuàng)建一個(gè)臨時(shí)順序節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock3
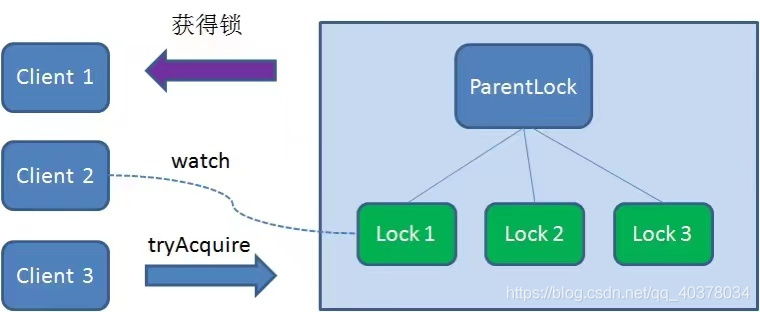
Client3查找ParentLock下面所有的臨時(shí)順序節(jié)點(diǎn)并排序,判斷自己所創(chuàng)建的節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock3是不是順序最靠前的一個(gè),結(jié)果同樣發(fā)現(xiàn)節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock3并不是最小的
于是,Client3向排序僅比它靠前的節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock2注冊(cè)watcher,用于監(jiān)聽(tīng)Lock2節(jié)點(diǎn)是否存在。這意味著Client3同樣搶鎖失敗,進(jìn)入了等待狀態(tài)
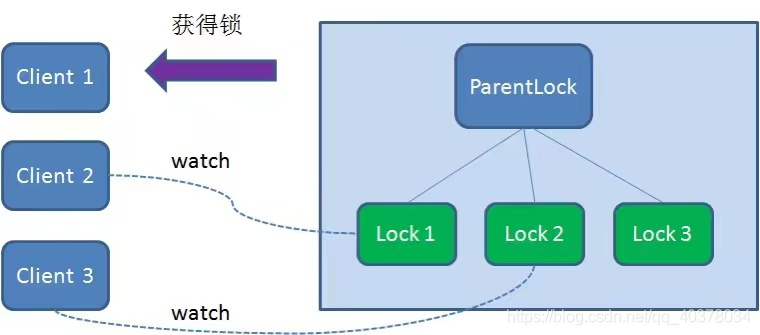
這樣一來(lái),Client1得到了鎖,Client2監(jiān)聽(tīng)了Lock1,Client3監(jiān)聽(tīng)了Lock2。這恰恰形成了一個(gè)等待隊(duì)列,很像是Java當(dāng)中ReentrantLock所依賴的AQS
釋放鎖
釋放鎖分為兩種情況:
1.任務(wù)完成,客戶端顯示釋放
當(dāng)任務(wù)完成時(shí),Client1會(huì)顯示調(diào)用刪除節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock1的指令
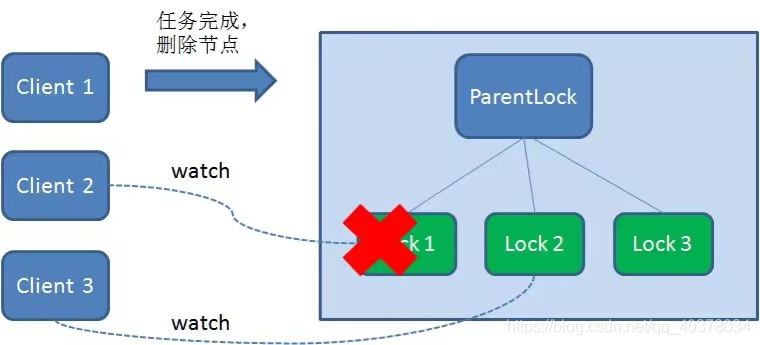
2.任務(wù)執(zhí)行過(guò)程中,客戶端崩潰
獲得鎖的Client1在任務(wù)執(zhí)行過(guò)程中,如果客戶端崩潰,則會(huì)斷開(kāi)與Zookeeper服務(wù)端的連接。根據(jù)臨時(shí)節(jié)點(diǎn)的特性,相關(guān)聯(lián)的節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock1會(huì)隨之自動(dòng)刪除
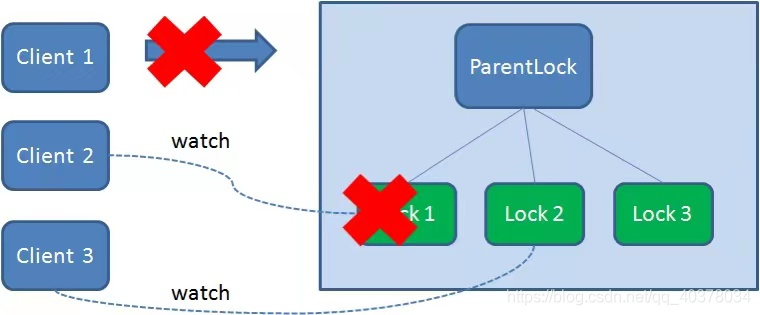
由于Client2一直監(jiān)聽(tīng)著Lock1的存在狀態(tài),當(dāng)Lock1節(jié)點(diǎn)被刪除,Client2會(huì)立刻收到通知。這時(shí)候Client2會(huì)再次查詢ParentLock下面的所有節(jié)點(diǎn),確認(rèn)自己創(chuàng)建的節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock2是不是目前最小的節(jié)點(diǎn)。如果是最小,則Client2獲得了鎖
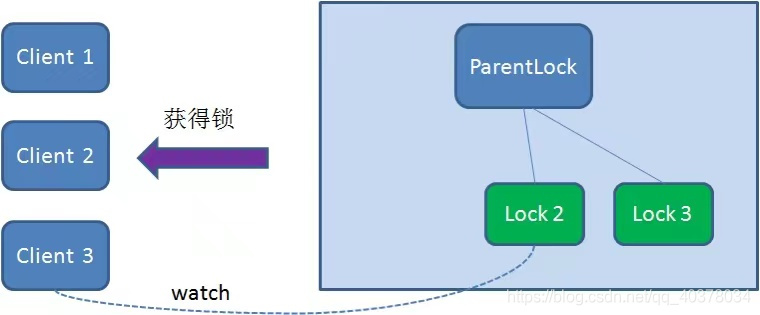
同理,如果Client2也因?yàn)槿蝿?wù)完成或者節(jié)點(diǎn)崩潰而刪除了節(jié)點(diǎn)Lock2,那么Client3就會(huì)接到通知
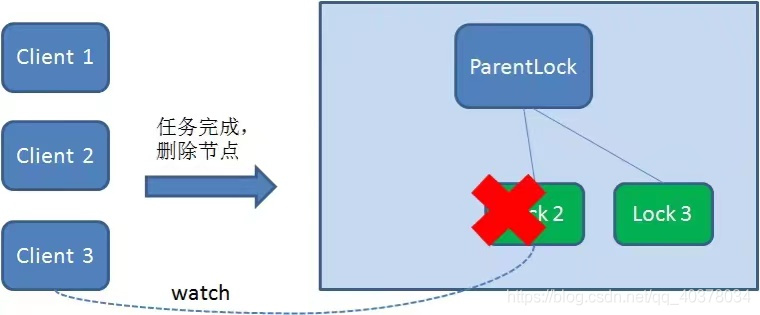
最終,Client3成功得到了鎖
3)、共享鎖
共享鎖又稱為讀鎖,在同一時(shí)刻可以允許多個(gè)線程訪問(wèn),典型的就是ReentrantReadWriteLock里的讀鎖,它的讀鎖是可以被共享的,但是它的寫鎖確實(shí)每次只能被獨(dú)占
定義鎖
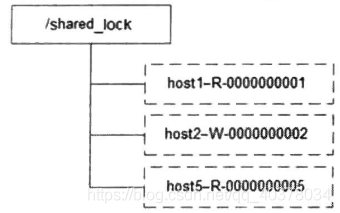
和排他鎖一樣,同樣是通過(guò)ZooKeeper上的數(shù)據(jù)節(jié)點(diǎn)來(lái)表示一個(gè)鎖,是一個(gè)類似于/shared_lock/[Hostname]-請(qǐng)求類型-序號(hào)的臨時(shí)順序節(jié)點(diǎn),例如/shared_lock/192.168.0.1-R-0000000001,那么,這個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)就代表了一個(gè)共享鎖,如下圖所示:
獲取鎖
在需要獲取共享鎖時(shí),所有客戶端都會(huì)到/shared_lock這個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)下面創(chuàng)建一個(gè)臨時(shí)順序節(jié)點(diǎn),如果當(dāng)前是讀請(qǐng)求,那么就創(chuàng)建例如/shared_lock/192.168.0.1-R-0000000001的節(jié)點(diǎn);如果是寫請(qǐng)求,那么就創(chuàng)建例如/shared_lock/192.168.0.1-W-0000000001的節(jié)點(diǎn)
判斷讀寫順序
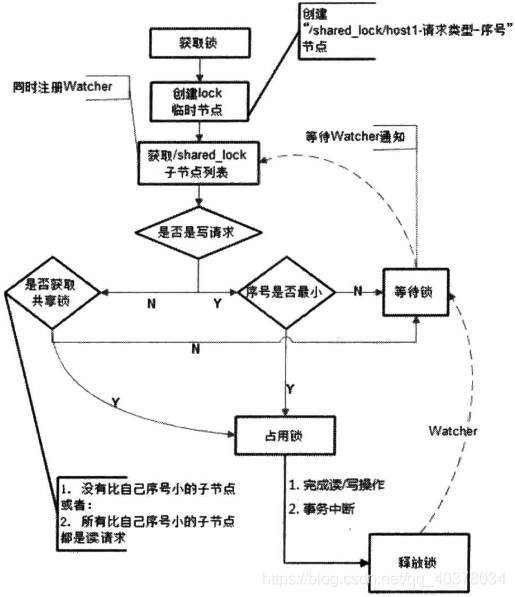
每個(gè)鎖競(jìng)爭(zhēng)者,只需要關(guān)注/shared_lock節(jié)點(diǎn)下序號(hào)比自己小的那個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)是否存在即可,具體實(shí)現(xiàn)如下:
1)客戶端調(diào)用create()方法創(chuàng)建一個(gè)類似于/shared_lock/[Hostname]-請(qǐng)求類型-序號(hào)的臨時(shí)順序節(jié)點(diǎn)
2)客戶端調(diào)用getChildren()接口來(lái)獲取所有已經(jīng)創(chuàng)建的子節(jié)點(diǎn)列表
3)判斷是否可以獲取共享鎖:
讀請(qǐng)求:沒(méi)有比自己序號(hào)小的節(jié)點(diǎn)或者所有比自己序號(hào)小的節(jié)點(diǎn)都是讀請(qǐng)求 寫請(qǐng)求:序號(hào)是否最小
4)如果無(wú)法獲取共享鎖,那么就調(diào)用exist()來(lái)對(duì)比自己小的那個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)注冊(cè)watcher
讀請(qǐng)求:向比自己序號(hào)小的最后一個(gè)寫請(qǐng)求節(jié)點(diǎn)注冊(cè)watcher監(jiān)聽(tīng) 寫請(qǐng)求:向比自己序號(hào)小的最后一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)注冊(cè)watcher監(jiān)聽(tīng)
5)等待watcher通知,繼續(xù)進(jìn)入步驟2
釋放鎖
釋放鎖的邏輯和排他鎖是一致的
整個(gè)共享鎖的獲取和釋放流程如下圖:
4)、排他鎖源碼解析
1)加鎖過(guò)程
public class WriteLock extends ProtocolSupport {
public synchronized boolean lock() throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
if (isClosed()) {
return false;
}
//確認(rèn)持久父節(jié)點(diǎn)是否存在
ensurePathExists(dir);
//真正獲取鎖的邏輯 調(diào)用ProtocolSupport的retryOperation()方法
return (Boolean) retryOperation(zop);
}
class ProtocolSupport {
protected Object retryOperation(ZooKeeperOperation operation)
throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
KeeperException exception = null;
for (int i = 0; i < RETRY_COUNT; i++) {
try {
//調(diào)用LockZooKeeperOperation的execute()方法
return operation.execute();
} catch (KeeperException.SessionExpiredException e) {
LOG.warn("Session expired {}. Reconnecting...", zookeeper, e);
throw e;
} catch (KeeperException.ConnectionLossException e) {
if (exception == null) {
exception = e;
}
LOG.debug("Attempt {} failed with connection loss. Reconnecting...", i);
retryDelay(i);
}
}
throw exception;
}
public class WriteLock extends ProtocolSupport {
private class LockZooKeeperOperation implements ZooKeeperOperation {
private void findPrefixInChildren(String prefix, ZooKeeper zookeeper, String dir)
throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
List<String> names = zookeeper.getChildren(dir, false);
for (String name : names) {
if (name.startsWith(prefix)) {
id = name;
LOG.debug("Found id created last time: {}", id);
break;
}
}
if (id == null) {
id = zookeeper.create(dir + "/" + prefix, data, getAcl(), EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL);
LOG.debug("Created id: {}", id);
}
}
@SuppressFBWarnings(
value = "NP_NULL_PARAM_DEREF_NONVIRTUAL",
justification = "findPrefixInChildren will assign a value to this.id")
public boolean execute() throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
do {
if (id == null) {
long sessionId = zookeeper.getSessionId();
String prefix = "x-" + sessionId + "-";
//創(chuàng)建臨時(shí)順序節(jié)點(diǎn)
findPrefixInChildren(prefix, zookeeper, dir);
idName = new ZNodeName(id);
}
//獲取所有子節(jié)點(diǎn)
List<String> names = zookeeper.getChildren(dir, false);
if (names.isEmpty()) {
LOG.warn("No children in: {} when we've just created one! Lets recreate it...", dir);
id = null;
} else {
//對(duì)所有子節(jié)點(diǎn)進(jìn)行排序
SortedSet<ZNodeName> sortedNames = new TreeSet<>();
for (String name : names) {
sortedNames.add(new ZNodeName(dir + "/" + name));
}
ownerId = sortedNames.first().getName();
SortedSet<ZNodeName> lessThanMe = sortedNames.headSet(idName);
//是否存在序號(hào)比自己小的節(jié)點(diǎn)
if (!lessThanMe.isEmpty()) {
ZNodeName lastChildName = lessThanMe.last();
lastChildId = lastChildName.getName();
LOG.debug("Watching less than me node: {}", lastChildId);
//有序號(hào)比自己小的節(jié)點(diǎn),則調(diào)用exist()向前一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)注冊(cè)watcher
Stat stat = zookeeper.exists(lastChildId, new LockWatcher());
if (stat != null) {
return Boolean.FALSE;
} else {
LOG.warn("Could not find the stats for less than me: {}", lastChildName.getName());
}
}
//沒(méi)有序號(hào)比自己小的節(jié)點(diǎn),則獲取鎖
else {
if (isOwner()) {
LockListener lockListener = getLockListener();
if (lockListener != null) {
lockListener.lockAcquired();
}
return Boolean.TRUE;
}
}
}
}
while (id == null);
return Boolean.FALSE;
}
2)解鎖過(guò)程
public class WriteLock extends ProtocolSupport {
public synchronized void unlock() throws RuntimeException {
if (!isClosed() && id != null) {
try {
//刪除當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn),此時(shí)會(huì)觸發(fā)后一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)的watcher
ZooKeeperOperation zopdel = () -> {
zookeeper.delete(id, -1);
return Boolean.TRUE;
};
zopdel.execute();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.warn("Unexpected exception", e);
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
} catch (KeeperException.NoNodeException e) {
} catch (KeeperException e) {
LOG.warn("Unexpected exception", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
LockListener lockListener = getLockListener();
if (lockListener != null) {
lockListener.lockReleased();
}
id = null;
}
}
}
3、選舉
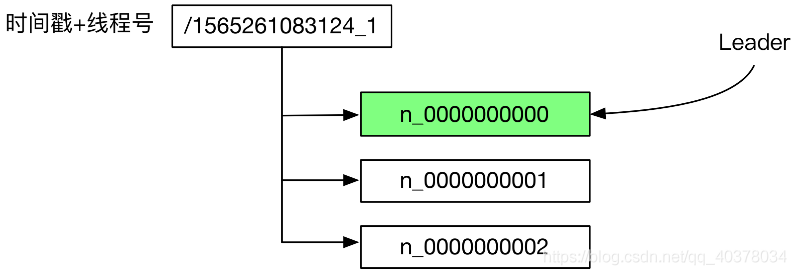
使用臨時(shí)順序znode來(lái)表示選舉請(qǐng)求,創(chuàng)建最小后綴數(shù)字znode的選舉請(qǐng)求成功。在協(xié)同設(shè)計(jì)上和分布式鎖是一樣的,不同之處在于具體實(shí)現(xiàn)。不同于分布式鎖,選舉的具體實(shí)現(xiàn)對(duì)選舉的各個(gè)階段做了細(xì)致的監(jiān)控
public class LeaderElectionSupport implements Watcher {
public synchronized void start() {
state = State.START;
dispatchEvent(EventType.START);
LOG.info("Starting leader election support");
if (zooKeeper == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No instance of zookeeper provided. Hint: use setZooKeeper()");
}
if (hostName == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No hostname provided. Hint: use setHostName()");
}
try {
//發(fā)起選舉請(qǐng)求 創(chuàng)建臨時(shí)順序節(jié)點(diǎn)
makeOffer();
//選舉請(qǐng)求是否被滿足
determineElectionStatus();
} catch (KeeperException | InterruptedException e) {
becomeFailed(e);
}
}
private void makeOffer() throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
state = State.OFFER;
dispatchEvent(EventType.OFFER_START);
LeaderOffer newLeaderOffer = new LeaderOffer();
byte[] hostnameBytes;
synchronized (this) {
newLeaderOffer.setHostName(hostName);
hostnameBytes = hostName.getBytes();
newLeaderOffer.setNodePath(zooKeeper.create(rootNodeName + "/" + "n_",
hostnameBytes, ZooDefs.Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE,
CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL));
leaderOffer = newLeaderOffer;
}
LOG.debug("Created leader offer {}", leaderOffer);
dispatchEvent(EventType.OFFER_COMPLETE);
}
private void determineElectionStatus() throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
state = State.DETERMINE;
dispatchEvent(EventType.DETERMINE_START);
LeaderOffer currentLeaderOffer = getLeaderOffer();
String[] components = currentLeaderOffer.getNodePath().split("/");
currentLeaderOffer.setId(Integer.valueOf(components[components.length - 1].substring("n_".length())));
//獲取所有子節(jié)點(diǎn)并排序
List<LeaderOffer> leaderOffers = toLeaderOffers(zooKeeper.getChildren(rootNodeName, false));
for (int i = 0; i < leaderOffers.size(); i++) {
LeaderOffer leaderOffer = leaderOffers.get(i);
if (leaderOffer.getId().equals(currentLeaderOffer.getId())) {
LOG.debug("There are {} leader offers. I am {} in line.", leaderOffers.size(), i);
dispatchEvent(EventType.DETERMINE_COMPLETE);
//如果當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn)是第一個(gè),則成為L(zhǎng)eader
if (i == 0) {
becomeLeader();
}
//如果有選舉請(qǐng)求在當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn)前面,則進(jìn)行等待,調(diào)用exist()向前一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)注冊(cè)watcher
else {
becomeReady(leaderOffers.get(i - 1));
}
break;
}
}
}
1. 4 款 MySQL 調(diào)優(yōu)工具,公司大神都在用!
最近面試BAT,整理一份面試資料《Java面試BATJ通關(guān)手冊(cè)》,覆蓋了Java核心技術(shù)、JVM、Java并發(fā)、SSM、微服務(wù)、數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)、數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)等等。
獲取方式:點(diǎn)“在看”,關(guān)注公眾號(hào)并回復(fù) Java 領(lǐng)取,更多內(nèi)容陸續(xù)奉上。
文章有幫助的話,在看,轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)吧。
謝謝支持喲 (*^__^*)

