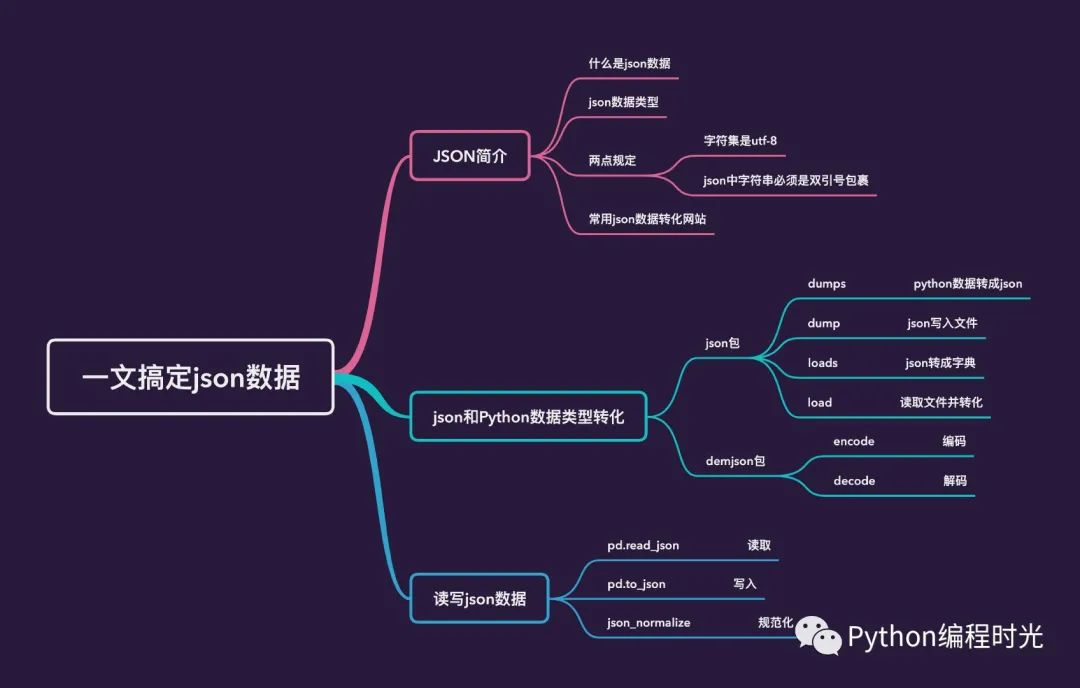
如何用 Python 與 Pandas 高效處理 JSON 數(shù)據(jù)?
作者:Peter
來源:Python編程時光
在實際工作中,尤其是web數(shù)據(jù)的傳輸,我們經(jīng)常會遇到json數(shù)據(jù)。它不像常見的文本數(shù)據(jù)、數(shù)值數(shù)據(jù)那樣友好,而且它和Python中的字典類型數(shù)據(jù)又很相像,給很多人造成了困擾。
本文結(jié)合具體案例詳細介紹了如何利用Python和pandas(Python的第三方庫)來處理json數(shù)據(jù),主要內(nèi)容包含:
json數(shù)據(jù)簡介
常用json數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)化網(wǎng)站
json數(shù)據(jù)和Python數(shù)據(jù)的轉(zhuǎn)化
pandas處理json數(shù)據(jù)
1. JSON 簡單介紹
1.1 什么是json數(shù)據(jù)
首先,我們看一段來自維基百科對json的解釋:
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation,JavaScript對象表示法)是一種由道格拉斯·克羅克福特構(gòu)想和設(shè)計、輕量級的資料交換語言,該語言以易于讓人閱讀的文字為基礎(chǔ),用來傳輸由屬性值或者序列性的值組成的數(shù)據(jù)對象。
JSON 數(shù)據(jù)格式與語言無關(guān)。即便它源自JavaScript,但目前很多編程語言都支持 JSON 格式數(shù)據(jù)的生成和解析。文件擴展名是
.json。
通過上面的官方介紹,我們總結(jié)3點:
JSON是一種文本(資料)語言,超輕量級的數(shù)據(jù)交換格式
JSON數(shù)據(jù)容易閱讀,易讀性強
源自JavaScript,其他語言可解析JSON數(shù)據(jù)
1.2 json數(shù)據(jù)類型
JSON實際上是JavaScript的一個子集,JSON語言中僅有的6種數(shù)據(jù)類型或者它們之間的任意組合:
number:和JavaScript中的number一致
boolean:JavaScript中的true或者false
string:JavaScript中的string
null:JavaScript中的null
array:JavaScript的表示方式:[]
object:JavaScript的
{…}表示方式
1.3 兩點規(guī)定
1、JSON語言中規(guī)定了字符集必須是UTF-8
2、為了統(tǒng)一解析,JSON的字符串規(guī)定必須是雙引號""
2. 常用json數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)化網(wǎng)站
1、json.cn:https://www.json.cn/
2、json菜鳥工具:https://c.runoob.com/front-end/53
3、sojson:https://www.sojson.com/,非常全的json處理網(wǎng)站
4、kjson:https://www.kjson.com/
5、編程獅-json檢驗工具:https://www.w3cschool.cn/tools/index?name=jsoncheck
6、JSONViewer:http://jsonviewer.stack.hu/,用于檢測Json格式是否正確的一個在線應用工具
3. JSON 和 Dict 類型轉(zhuǎn)化
本小節(jié)主要講解的json類型數(shù)據(jù)和Python類型的轉(zhuǎn)化。
json對象和Python字典的轉(zhuǎn)化主要使用的是內(nèi)置json包,下面詳細介紹該包的使用。詳細的學習資料見官網(wǎng):https://docs.python.org/3/library/json.html
首先使用的時候直接導入該包:
import json
json包中存在4中方法用來進行和Python內(nèi)置數(shù)據(jù)類型的轉(zhuǎn)化:
| 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| json.dumps() | 將python對象編碼成Json字符串:字典到json |
| json.loads() | 將Json字符串解碼成python對象:json到字典 |
| json.dump() | 將python中的對象轉(zhuǎn)化成json儲存到文件中 |
| json.load() | 將文件中的json的格式轉(zhuǎn)化成python對象提取出來 |
筆記:兩個和load相關(guān)的方法只是多了一步和文件相關(guān)的操作。
json.dumps
和dump相關(guān)的兩個函數(shù)是將Python數(shù)據(jù)類型轉(zhuǎn)成json類型,轉(zhuǎn)化對照表如下:
| Python | JSON |
|---|---|
| dict | object |
| list, tuple | array |
| str, unicode | string |
| int, long, float | number |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
json.dumps方法的作用是將Python字典類型的數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)成json格式的數(shù)據(jù),具體的參數(shù)如下:
json.dumps(obj, # 待轉(zhuǎn)化的對象
skipkeys=False, # 默認值是False,若dict的keys內(nèi)的數(shù)據(jù)不是python的基本類型(str,unicode,int,long,float,bool,None),設(shè)置為False時,就會報TypeError的錯誤。此時設(shè)置成True,則會跳過這類key
ensure_ascii=True, # 默認是ASCII碼,若設(shè)置成False,則可以輸出中文
check_circular=True, # 若為False,跳過對容器類型的循環(huán)引用檢查
allow_nan=True, # 若allow_nan為假,則ValueError將序列化超出范圍的浮點值(nan、inf、-inf),嚴格遵守JSON規(guī)范,而不是使用JavaScript等價值(nan、Infinity、-Infinity)
cls=None,
indent=None, # 參數(shù)根據(jù)格式縮進顯示,表示縮進幾個空格
separators=None, # 指定分隔符;包含不同dict項之間的分隔符和key與value之間的分隔符;同時去掉`: `
encoding="utf-8", # 編碼
default=None, # 默認是一個函數(shù),應該返回可序列化的obj版本或者引發(fā)類型錯誤;默認值是只引發(fā)類型錯誤
sort_keys=False, # 若為False,則字典的鍵不排序;設(shè)置成True,按照字典排序(a到z)
**kw)
通過例子來解釋上面幾個常見參數(shù)的作用
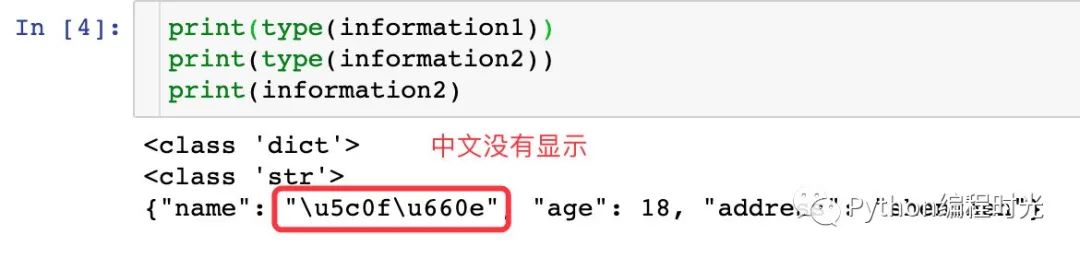
1、當我們的Python類型數(shù)據(jù)中存在中文
information1 = {
'name': '小明',
'age': 18,
'address': 'shenzhen'
}
# 字典轉(zhuǎn)成json數(shù)據(jù)
information2 = json.dumps(information1)
print(type(information1))
print(type(information2))
print(information2)
加上ensure_ascii=False參數(shù)即可顯示中文:
# 字典轉(zhuǎn)成json數(shù)據(jù)
information3 = json.dumps(information1,ensure_ascii=False)
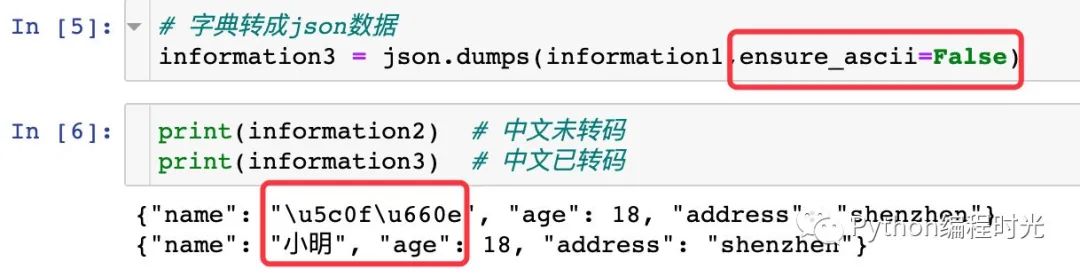
??通過結(jié)果我們發(fā)現(xiàn):json數(shù)據(jù)中全部變成了雙引號,原來的字典類型數(shù)據(jù)中使用的是單引號,再看一個關(guān)于引號變化的例子:
>>> import json
>>> print(json.dumps({'4': 5, '6': 7}, sort_keys=True, indent=4)) # python中的鍵是字符串,用單引號
# 結(jié)果顯示
{
"4": 5, # 變成雙引號
"6": 7
}
2、對json數(shù)據(jù)通過縮進符美觀輸出,使用indent參數(shù)
information4 = {
'name': '小明',
'age': 18,
'skills': 'python',
'english': 'CET6',
'major': '會計',
'address': '深圳'
}
information5 = json.dumps(information4, ensure_ascii=False) # 不縮進
information6 = json.dumps(information4, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2) # 縮進2個空格
information7 = json.dumps(information4, ensure_ascii=False, indent=5) # 縮進5個空格
print(information5)
print(information6)
print(information7)

3、對Python數(shù)據(jù)類型中鍵進行排序輸出
information4 = {
'name': '小明',
'age': 18,
'skills': 'python',
'english': 'CET6',
'major': '會計',
'address': '深圳'
}
information8 = json.dumps(information4, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2) #
information9 = json.dumps(information4, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2,sort_keys=True) # 鍵的排序設(shè)置成True
print(information8)
print(information9)

通過sort_keys=True的設(shè)置,可以觀察到輸出的結(jié)果進行了首寫字母的排序;當首寫字母相同,按照第二個字母再進行排序。
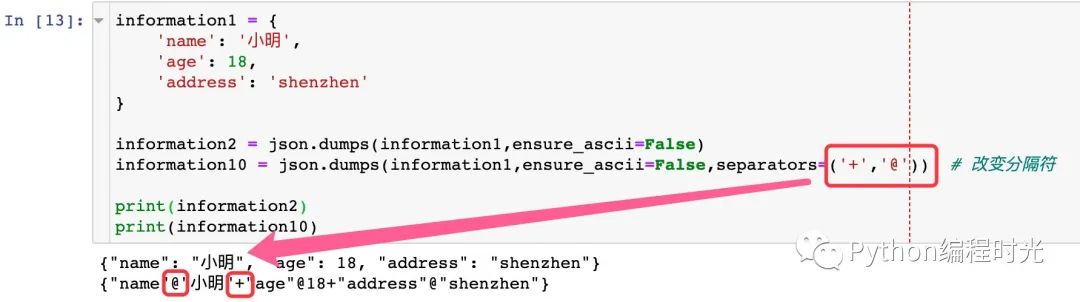
4、輸出分隔符的控制
使用separators參數(shù)來設(shè)置不同的輸出分隔符;不同的dic元素之間默認是,,鍵值對之間默認是:
information1 = {
'name': '小明',
'age': 18,
'address': 'shenzhen'
}
information2 = json.dumps(information1,ensure_ascii=False)
information10 = json.dumps(information1,ensure_ascii=False,separators=('+','@')) # 改變分隔符
print(information2) # 默認連接符
print(information10)
json.dump
json.dump功能和json.dumps類似,只是需要將數(shù)據(jù)存入到文件中,二者參數(shù)相同
我們嘗試將下面的個人信息寫入到文件中
information = {
'name': '小明',
'age': 18,
'skills': 'python',
'english': 'CET6',
'major': '會計',
'address': '深圳'
}
1、如果不使用indent參數(shù),全部信息顯示為一行
# 使用json.dump;json數(shù)據(jù)一定是雙引號
with open("information_1_to_json.json", "w", encoding='utf-8') as f:
# json.dump(dic_, f) # 全部寫入一行數(shù)據(jù),不換行
json.dump(information, # 待寫入數(shù)據(jù)
f, # File對象
sort_keys=True, # 鍵的排序
ensure_ascii=False) # 顯示中文
看看實際的保存效果:
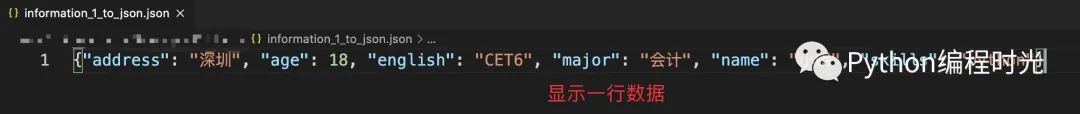
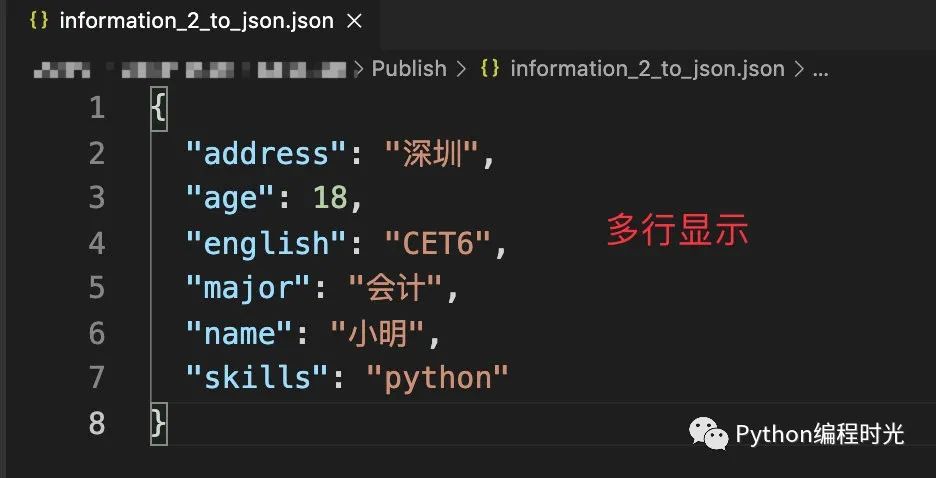
加入indent參數(shù),會顯示成多行數(shù)據(jù):
with open("information_2_to_json.json", "w", encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(information,
f,
indent=2, # 空格縮進符,寫入多行
sort_keys=True,
ensure_ascii=False)
json.loads
和load相關(guān)的兩個函數(shù)是將json轉(zhuǎn)成Python數(shù)據(jù)類型,轉(zhuǎn)化對照表如下:
| JSON | Python |
|---|---|
| object | dict |
| array | list |
| string | unicode |
| number (int) | int, long |
| number (real) | float |
| true | True |
| false | False |
| null | None |
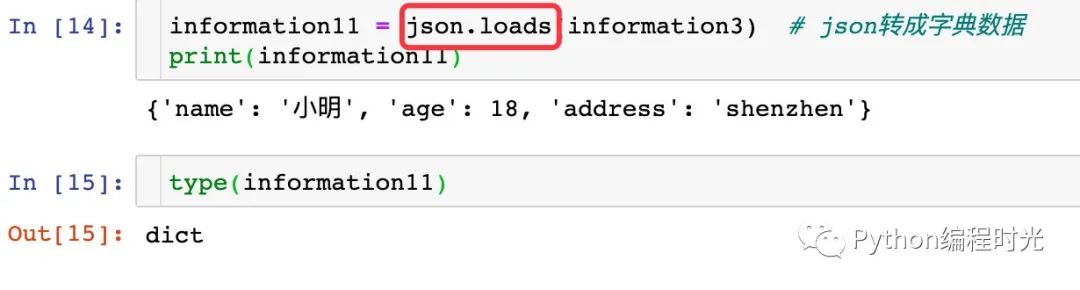
json.loads的作用是將json格式的數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)成Python字典類型的數(shù)據(jù)。
information1 = {
'name': '小明',
'age': 18,
'address': 'shenzhen'
}
# 字典轉(zhuǎn)成json數(shù)據(jù)
information3 = json.dumps(information1,ensure_ascii=False)
information11 = json.loads(information3) # json轉(zhuǎn)成字典數(shù)據(jù)
print(information11)
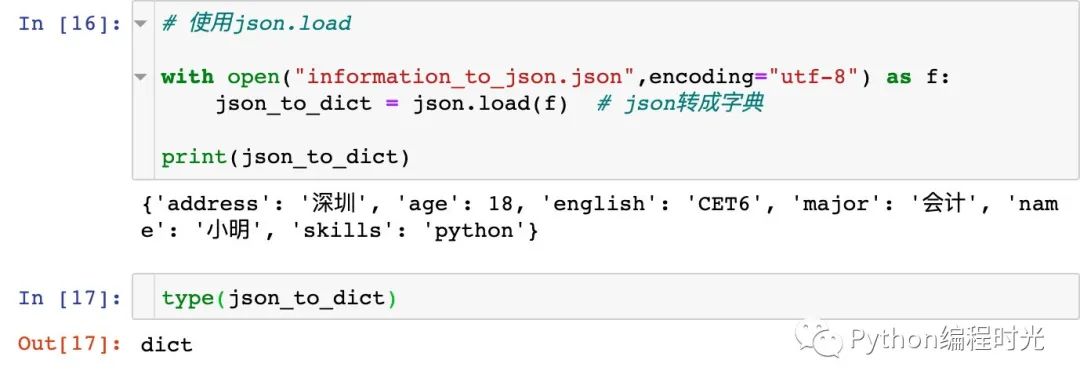
json.load
打開json文件再轉(zhuǎn)成字典形式的數(shù)據(jù)
# 使用json.load
with open("information_to_json.json",encoding="utf-8") as f:
json_to_dict = json.load(f) # json轉(zhuǎn)成字典
print(json_to_dict)
4. JSON 和 非 Dict 類型的轉(zhuǎn)化
上面介紹的主要是json格式數(shù)據(jù)和Python字典之間的轉(zhuǎn)化,下面講解了Python其他數(shù)據(jù)類型通過json.dumps方法轉(zhuǎn)成json個數(shù)據(jù):
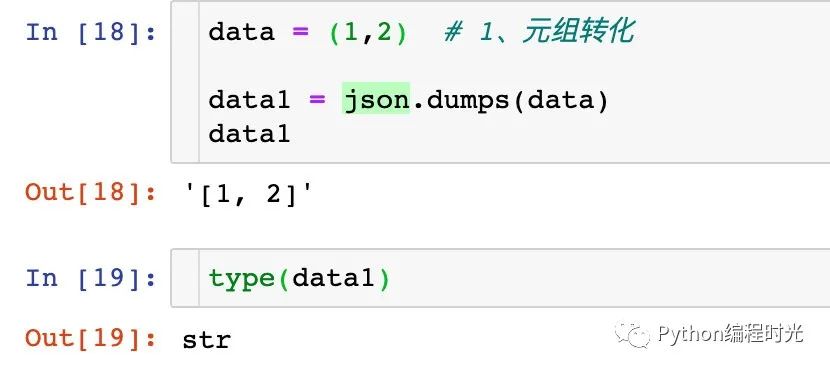
1、元組轉(zhuǎn)化
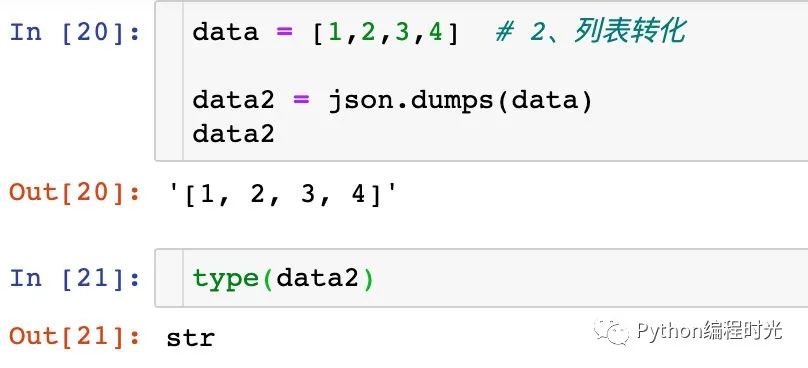
2、列表轉(zhuǎn)化
3、布爾值轉(zhuǎn)化

4、數(shù)值型數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)化

5. 利用 Demjson 來解析
Demjson是Python的第三方庫,能夠用于編碼和解碼json數(shù)據(jù):
encode:將 Python 對象編碼成 JSON 字符串
decode:將已編碼的 JSON 字符串解碼為 Python 對象
安裝demjson
直接使用pip install demjson安裝,kan'dao看到如下界面表示安裝成功。
使用demjson
使用之前先進行導入:
import demjson # 導入包
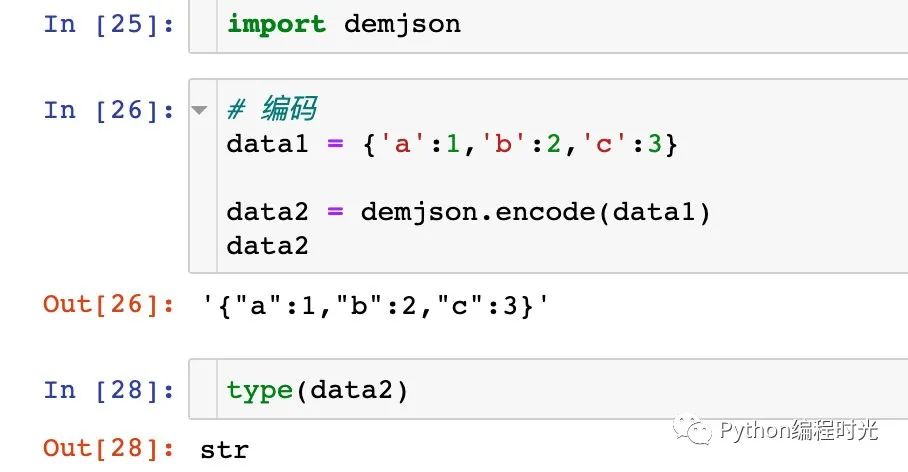
1、編碼功能
2、解碼功能

demjson包一個明顯的缺點就是不能直接解析中文數(shù)據(jù):

如果我們想看到中文數(shù)據(jù),可以使用eval函數(shù):
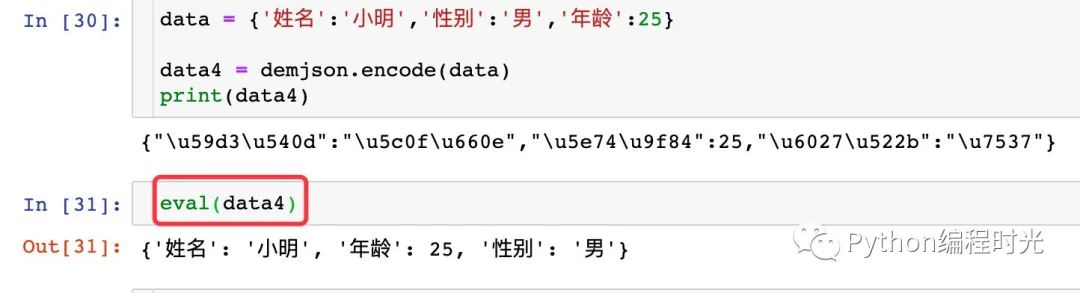
6. Pandas處理 json
下面介紹pandas庫對json數(shù)據(jù)的處理:
read_json:從json文件中讀取數(shù)據(jù)
to_json:將pandas中的數(shù)據(jù)寫入到json文件中
json_normalize:對json數(shù)據(jù)進行規(guī)范化處理
https://geek-docs.com/pandas/pandas-read-write/pandas-reading-and-writing-json.html
6.1 read_json
首先看看官網(wǎng)中read_json的參數(shù):
pandas.read_json(
path_or_buf=None, # json文件路徑
orient=None, # 重點參數(shù),取值為:"split"、"records"、"index"、"columns"、"values"
typ='frame', # 要恢復的對象類型(系列或框架),默認’框架’.
dtype=None, # boolean或dict,默認為True
convert_axes=None,
convert_dates=True,
keep_default_dates=True,
numpy=False,
precise_float=False,
date_unit=None,
encoding=None,
lines=False, # 布爾值,默認為False,每行讀取該文件作為json對象
chunksize=None,
compression='infer',
nrows=None,
storage_options=None)
詳細的參數(shù)解析可以參考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41562377/article/details/90203805
假設(shè)我們現(xiàn)在有一份json數(shù)據(jù),如下圖所示:
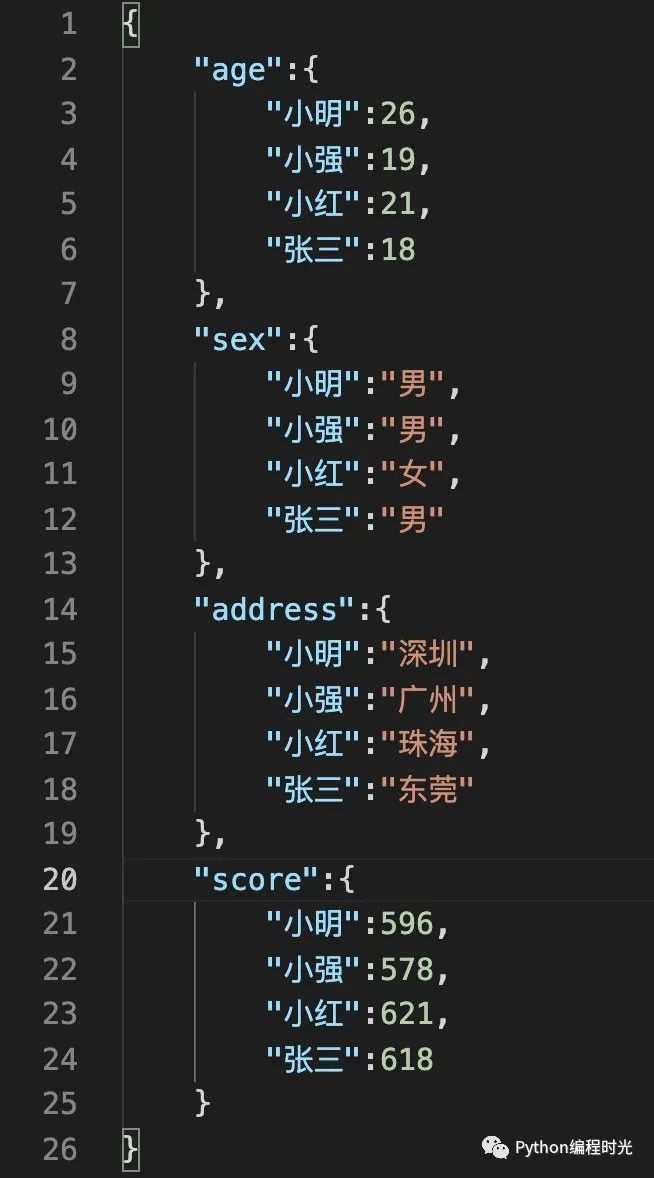
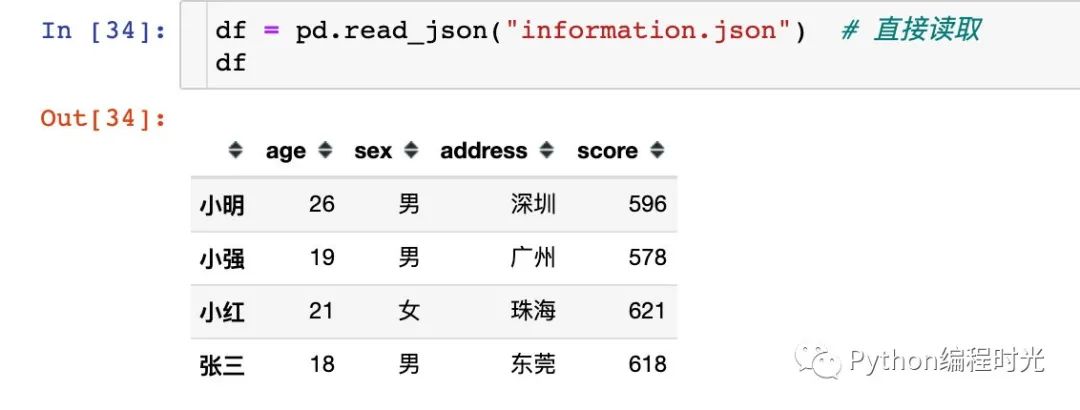
我們將上面的數(shù)據(jù)讀取進來,由于數(shù)據(jù)是比較規(guī)范的,所以直接填寫文件路徑即可讀取:
重點講解下參數(shù)orient:
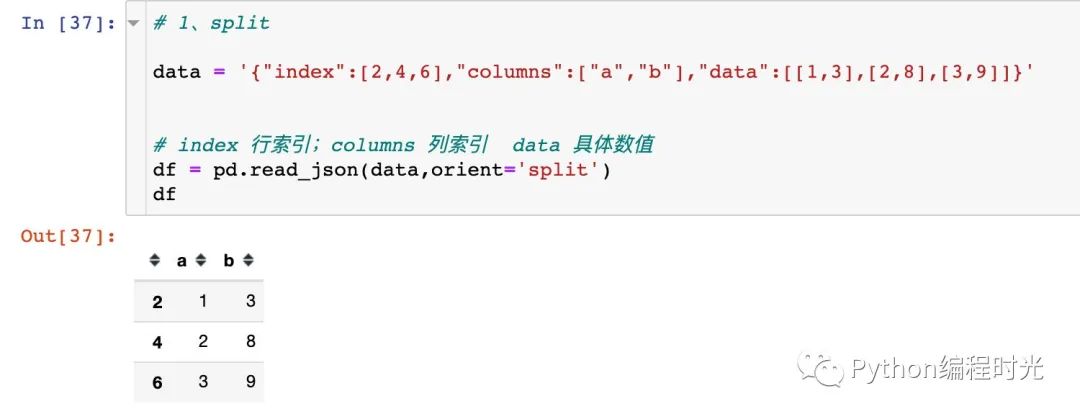
1、oriden='split'
split’ : dict like {index -> [index], columns -> [columns], data -> [values]}
json文件的key的名字只能為index,cloumns,data這三個,另外多一個key都不行,少一個也不行。舉例說明:
2、orient='records'
‘records’ : list like [{column -> value}, … , {column -> value}]
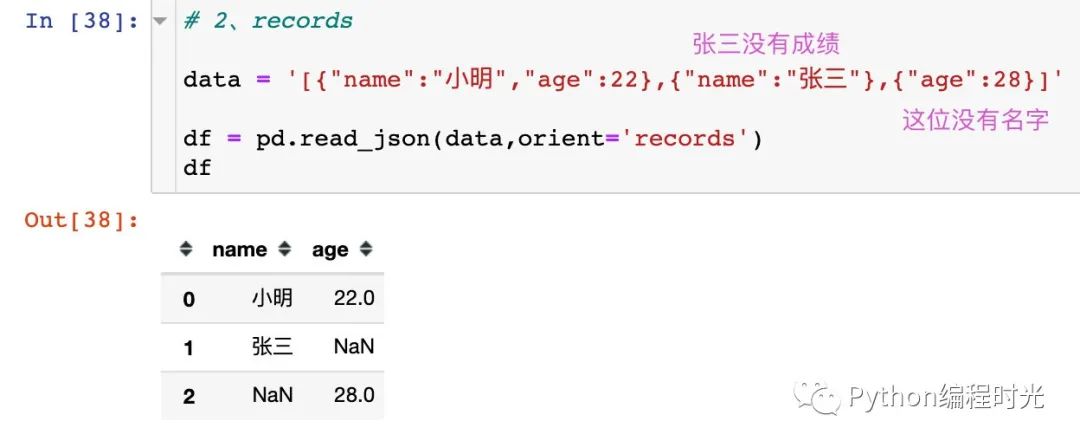
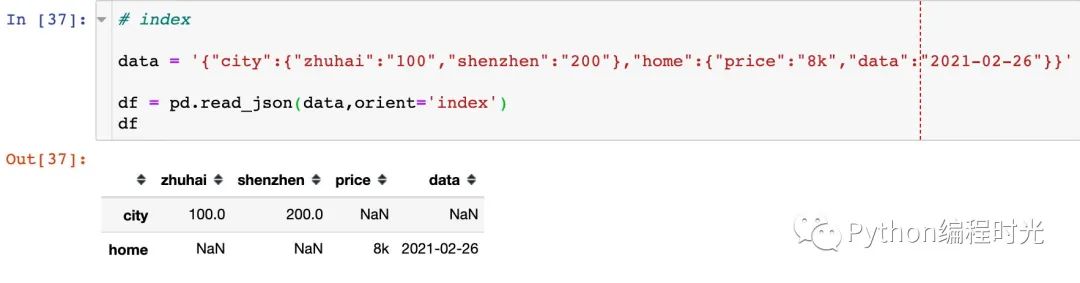
3、orient='index'
dict like {index -> {column -> value}}
4、orient='columns'
dict like {column -> {index -> value}}
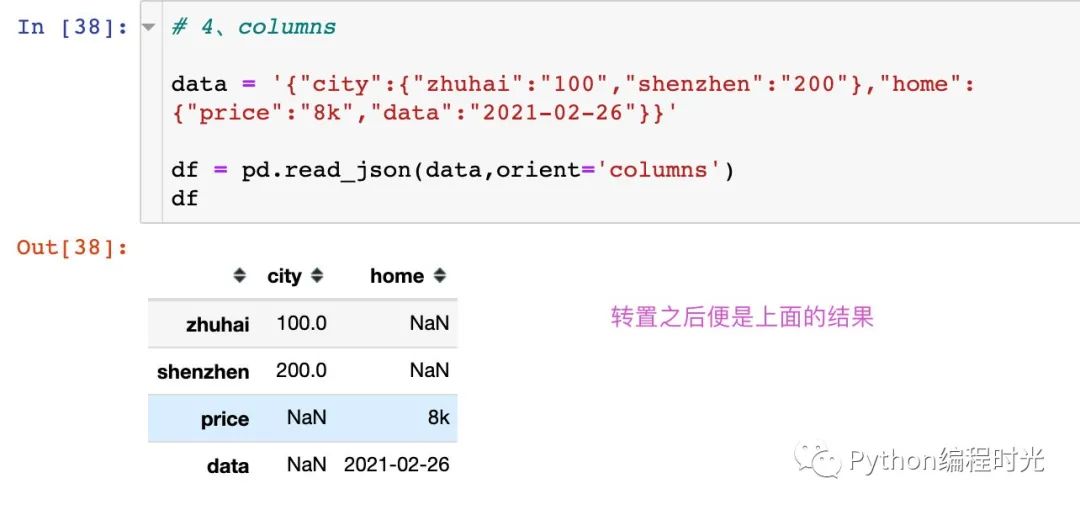
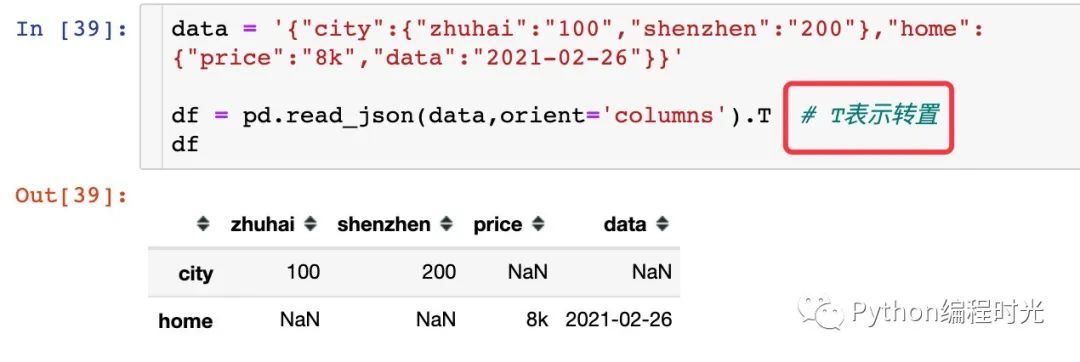
轉(zhuǎn)置之后就是上面orient='index'的結(jié)果
5、orient='values'
‘values’ : just the values array
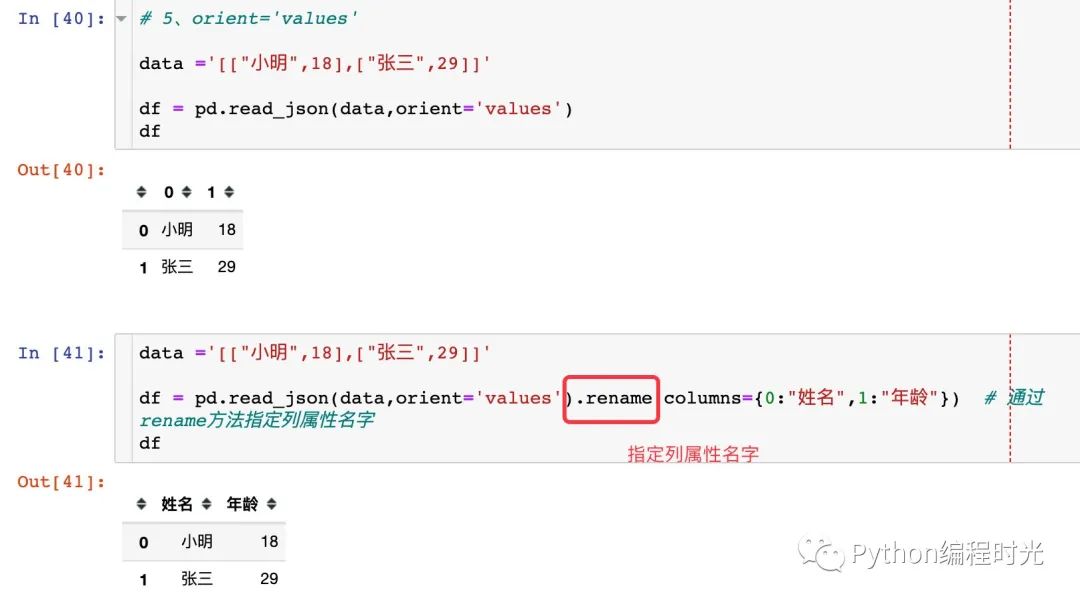
6.2 to_json
to_json方法就是將DataFrame文件保存成json文件:
df.to_json("個人信息.json") # 直接保存成json文件
如果按照上面的代碼保存,中文是沒有顯示的:
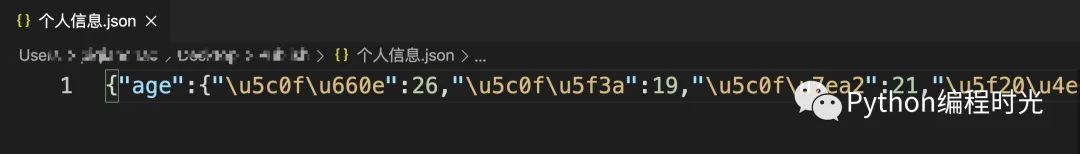
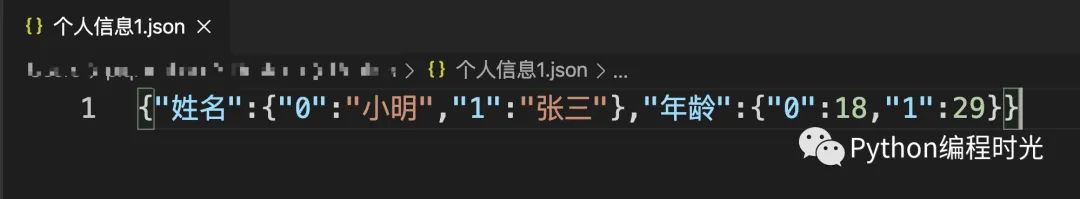
當然我們可以通過json.load將json文件再次讀取進行,顯示中文,我們也可以直接在保存的時候顯示中文:
df.to_json("個人信息1.json",force_ascii=False) # 顯示中文
6.3 json_normalize
https://www.jianshu.com/p/a84772b994a0
上面介紹的json數(shù)據(jù)的保存和讀取中json數(shù)據(jù)都是列表形式的;但是json文件中的數(shù)據(jù)通常不一定全部是列表形式,那么我們需要將字典結(jié)構(gòu)的文件轉(zhuǎn)成列表形式,這個過程就叫做規(guī)范化。
pandas中的json_normalize()函數(shù)能夠?qū)⒆值浠蛄斜磙D(zhuǎn)成表格,使用之前先進行導入:
from pandas.io.json import json_normalize
通過官網(wǎng)和一個實際的例子來同時進行學習,首先看看官網(wǎng)的例子:
1、層級字典通過屬性的形式顯示數(shù)據(jù):
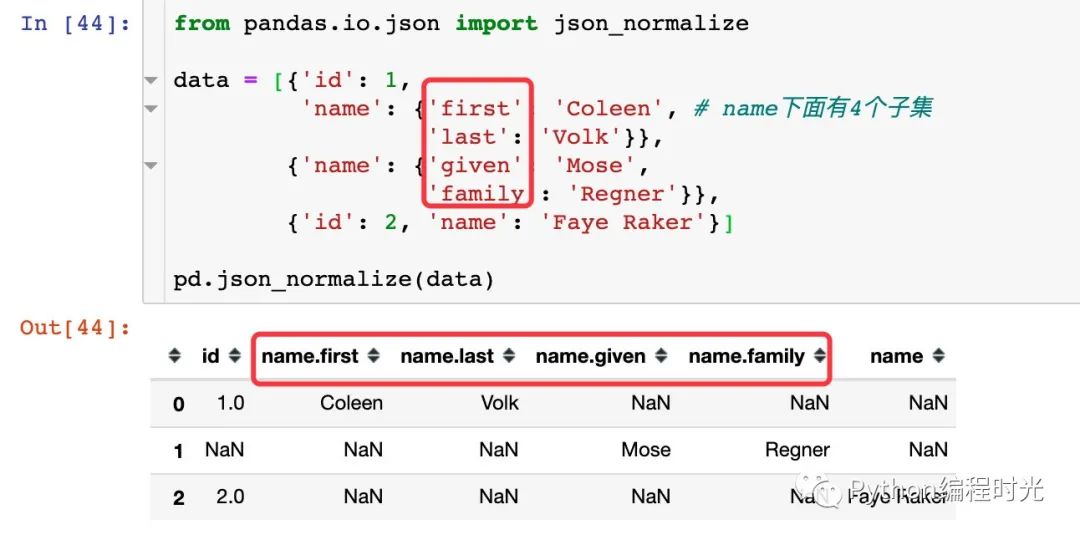
2、如果加入max_level參數(shù)則會顯示不同的效果:
若max_level=0,則嵌套的字典會當做整體,顯示在數(shù)據(jù)框中

若max_level=1,則嵌套的字典會被拆解,里面的鍵會被單獨出來:

3、讀取層級嵌套中的部分內(nèi)容:
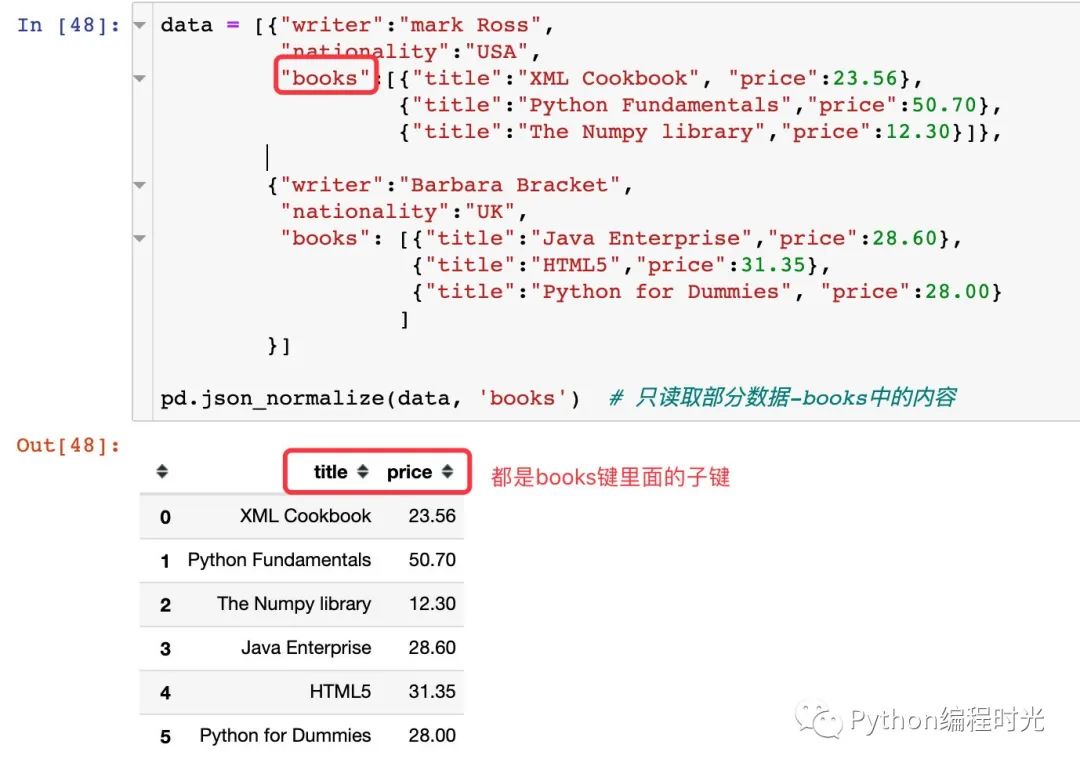
4、讀取全部內(nèi)容
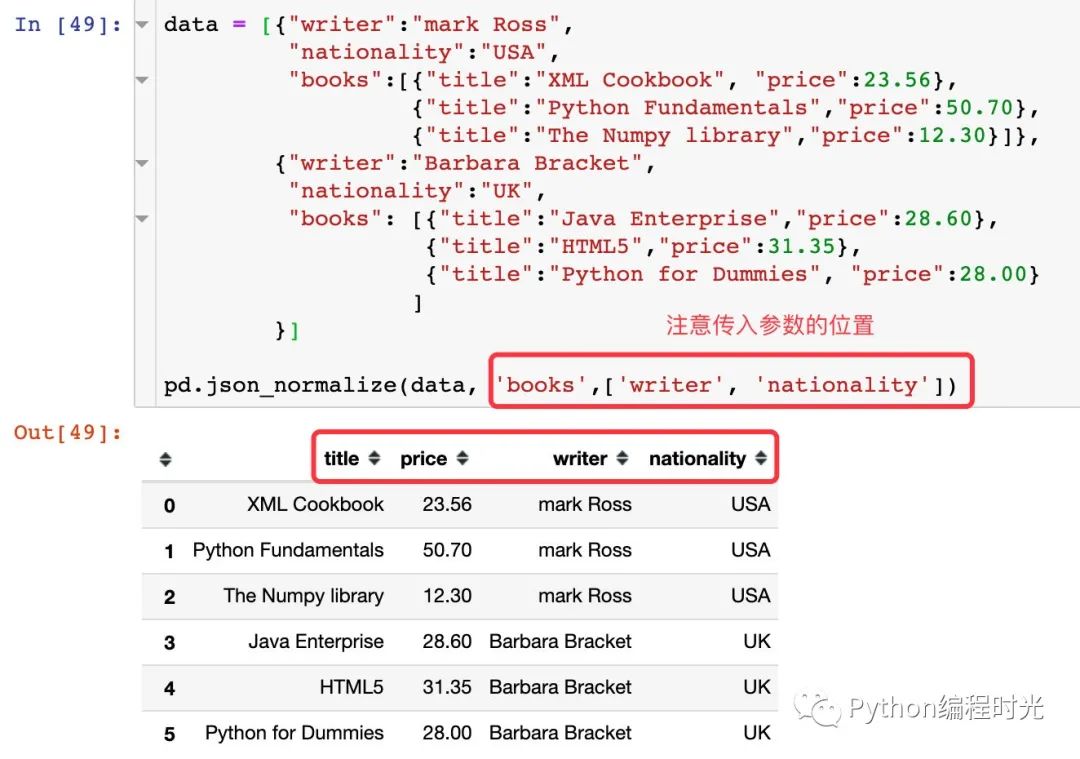
7. 總結(jié)一下
json數(shù)據(jù)是工作中經(jīng)常會遇到的一種數(shù)據(jù)格式,也是很重要的一種數(shù)據(jù)。
本文首先對json數(shù)據(jù)及格式進行了簡介,重新認識json數(shù)據(jù);其次,結(jié)合各種實際案例,將json和Python的各種數(shù)據(jù)類型,尤其是字典類型進行了轉(zhuǎn)化;最后,重要講解了json數(shù)據(jù)的讀取、寫入和規(guī)范化的操作。
希望這篇文章的詳細講解,能夠幫助到各位搞定json數(shù)據(jù)~

近期熱門文章推薦:
分享與在看是對我最大的支持!
