面試官:你能說說Ribbon的負載均衡策略及原理嘛?
你知道的越多,不知道的就越多,業(yè)余的像一棵小草!
你來,我們一起精進!你不來,我和你的競爭對手一起精進!
編輯:業(yè)余草
blog.csdn.net/wudiyong22
推薦:https://www.xttblog.com/?p=5172
Load Balance負載均衡是用于解決一臺機器(一個進程)無法解決所有請求而產(chǎn)生的一種算法。像nginx可以使用負載均衡分配流量,ribbon為客戶端提供負載均衡,dubbo服務(wù)調(diào)用里的負載均衡等等,很多地方都使用到了負載均衡。
使用負載均衡帶來的好處很明顯:
當集群里的1臺或者多臺服務(wù)器down的時候,剩余的沒有down的服務(wù)器可以保證服務(wù)的繼續(xù)使用 使用了更多的機器保證了機器的良性使用,不會由于某一高峰時刻導致系統(tǒng)cpu急劇上升
負載均衡有好幾種實現(xiàn)策略,常見的有:
隨機 (Random) 輪詢 (RoundRobin) 一致性哈希 (ConsistentHash) 哈希 (Hash) 加權(quán)(Weighted)
ILoadBalance 負載均衡器
ribbon是一個為客戶端提供負載均衡功能的服務(wù),它內(nèi)部提供了一個叫做ILoadBalance的接口代表負載均衡器的操作,比如有添加服務(wù)器操作、選擇服務(wù)器操作、獲取所有的服務(wù)器列表、獲取可用的服務(wù)器列表等等。
ILoadBalance的繼承關(guān)系如下:
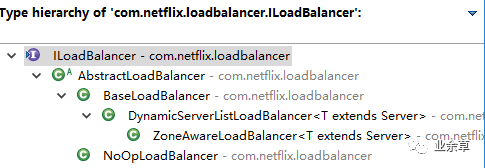
負載均衡器是從EurekaClient(EurekaClient的實現(xiàn)類為DiscoveryClient)獲取服務(wù)信息,根據(jù)IRule去路由,并且根據(jù)IPing判斷服務(wù)的可用性。
負載均衡器多久一次去獲取一次從Eureka Client獲取注冊信息呢?在BaseLoadBalancer類下,BaseLoadBalancer的構(gòu)造函數(shù),該構(gòu)造函數(shù)開啟了一個PingTask任務(wù)setupPingTask();,代碼如下:
public BaseLoadBalancer(String name, IRule rule, LoadBalancerStats stats,
IPing ping, IPingStrategy pingStrategy) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("LoadBalancer: initialized");
}
this.name = name;
this.ping = ping;
this.pingStrategy = pingStrategy;
setRule(rule);
setupPingTask();
lbStats = stats;
init();
}
setupPingTask()的具體代碼邏輯,它開啟了ShutdownEnabledTimer執(zhí)行PingTask任務(wù),在默認情況下pingIntervalSeconds為10,即每10秒鐘,向EurekaClient發(fā)送一次”ping”。
void setupPingTask() {
if (canSkipPing()) {
return;
}
if (lbTimer != null) {
lbTimer.cancel();
}
lbTimer = new ShutdownEnabledTimer("NFLoadBalancer-PingTimer-" + name,
true);
lbTimer.schedule(new PingTask(), 0, pingIntervalSeconds * 1000);
forceQuickPing();
}
PingTask源碼,即new一個Pinger對象,并執(zhí)行runPinger()方法。
查看Pinger的runPinger()方法,最終根據(jù) pingerStrategy.pingServers(ping, allServers)來獲取服務(wù)的可用性,如果該返回結(jié)果,如之前相同,則不去向EurekaClient獲取注冊列表,如果不同則通知ServerStatusChangeListener或者changeListeners發(fā)生了改變,進行更新或者重新拉取。
完整過程是:
LoadBalancerClient(RibbonLoadBalancerClient是實現(xiàn)類)在初始化的時候(execute方法),會通過ILoadBalance(BaseLoadBalancer是實現(xiàn)類)向Eureka注冊中心獲取服務(wù)注冊列表,并且每10s一次向EurekaClient發(fā)送“ping”,來判斷服務(wù)的可用性,如果服務(wù)的可用性發(fā)生了改變或者服務(wù)數(shù)量和之前的不一致,則從注冊中心更新或者重新拉取。LoadBalancerClient有了這些服務(wù)注冊列表,就可以根據(jù)具體的IRule來進行負載均衡。
IRule 路由
IRule接口代表負載均衡策略:
public interface IRule{
public Server choose(Object key);
public void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb);
public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer();
}
IRule接口的實現(xiàn)類有以下幾種:
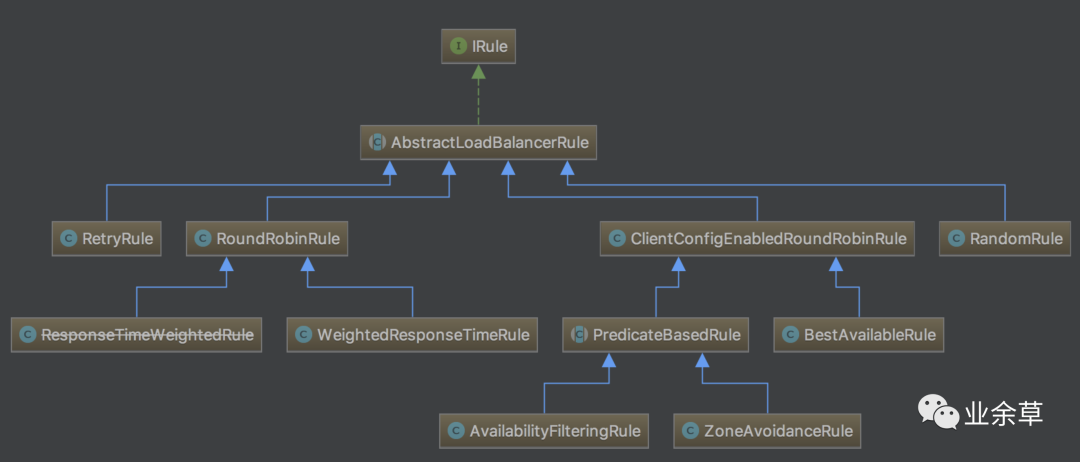
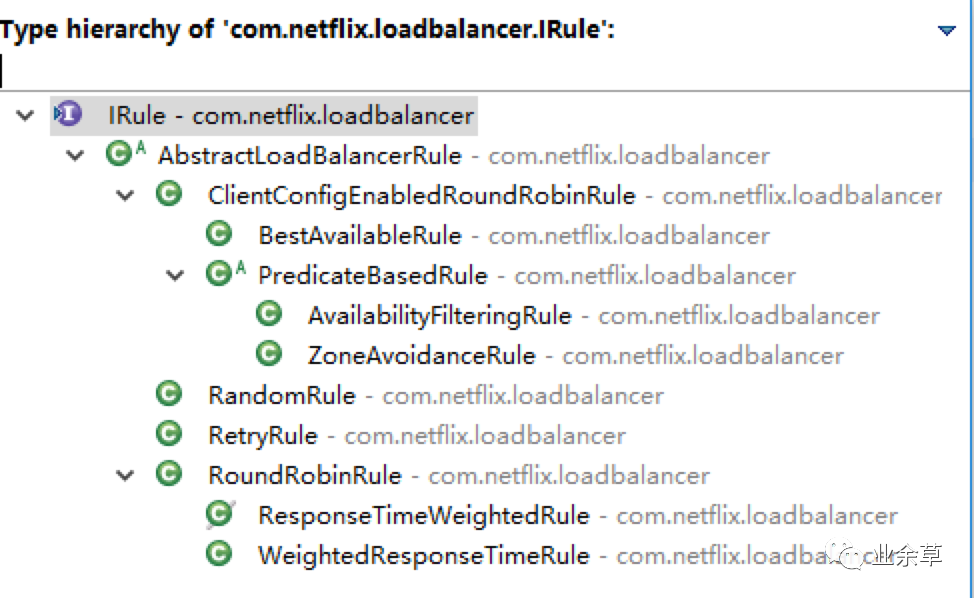
其中RandomRule表示隨機策略、RoundRobinRule表示輪詢策略、WeightedResponseTimeRule表示加權(quán)策略、BestAvailableRule表示請求數(shù)最少策略等等。
隨機策略很簡單,就是從服務(wù)器中隨機選擇一個服務(wù)器,RandomRule的實現(xiàn)代碼如下:
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
return null;
}
Server server = null;
while (server == null) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
return null;
}
List<Server> upList = lb.getReachableServers();
List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers();
int serverCount = allList.size();
if (serverCount == 0) {
return null;
}
int index = rand.nextInt(serverCount); // 使用jdk內(nèi)部的Random類隨機獲取索引值index
server = upList.get(index); // 得到服務(wù)器實例
if (server == null) {
Thread.yield();
continue;
}
if (server.isAlive()) {
return (server);
}
server = null;
Thread.yield();
}
return server;
}
RoundRobinRule輪詢策略表示每次都取下一個服務(wù)器,比如一共有5臺服務(wù)器,第1次取第1臺,第2次取第2臺,第3次取第3臺,以此類推:
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
log.warn("no load balancer");
return null;
}
Server server = null;
int count = 0;
while (server == null && count++ < 10) {
List<Server> reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers();
List<Server> allServers = lb.getAllServers();
int upCount = reachableServers.size();
int serverCount = allServers.size();
if ((upCount == 0) || (serverCount == 0)) {
log.warn("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb);
return null;
}
int nextServerIndex = incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount);
server = allServers.get(nextServerIndex);
if (server == null) {
/* Transient. */
Thread.yield();
continue;
}
if (server.isAlive() && (server.isReadyToServe())) {
return (server);
}
// Next.
server = null;
}
if (count >= 10) {
log.warn("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: "
+ lb);
}
return server;
}
/**
* Inspired by the implementation of {@link AtomicInteger#incrementAndGet()}.
*
* @param modulo The modulo to bound the value of the counter.
* @return The next value.
*/
private int incrementAndGetModulo(int modulo) {
for (;;) {
int current = nextServerCyclicCounter.get();
int next = (current + 1) % modulo;
if (nextServerCyclicCounter.compareAndSet(current, next))
return next;
}
}
WeightedResponseTimeRule繼承了RoundRobinRule,開始的時候還沒有權(quán)重列表,采用父類的輪詢方式,有一個默認每30秒更新一次權(quán)重列表的定時任務(wù),該定時任務(wù)會根據(jù)實例的響應(yīng)時間來更新權(quán)重列表,choose方法做的事情就是,用一個(0,1)的隨機double數(shù)乘以最大的權(quán)重得到randomWeight,然后遍歷權(quán)重列表,找出第一個比randomWeight大的實例下標,然后返回該實例,代碼略。
BestAvailableRule策略用來選取最少并發(fā)量請求的服務(wù)器:
public Server choose(Object key) {
if (loadBalancerStats == null) {
return super.choose(key);
}
List<Server> serverList = getLoadBalancer().getAllServers(); // 獲取所有的服務(wù)器列表
int minimalConcurrentConnections = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Server chosen = null;
for (Server server: serverList) { // 遍歷每個服務(wù)器
ServerStats serverStats = loadBalancerStats.getSingleServerStat(server); // 獲取各個服務(wù)器的狀態(tài)
if (!serverStats.isCircuitBreakerTripped(currentTime)) { // 沒有觸發(fā)斷路器的話繼續(xù)執(zhí)行
int concurrentConnections = serverStats.getActiveRequestsCount(currentTime); // 獲取當前服務(wù)器的請求個數(shù)
if (concurrentConnections < minimalConcurrentConnections) { // 比較各個服務(wù)器之間的請求數(shù),然后選取請求數(shù)最少的服務(wù)器并放到chosen變量中
minimalConcurrentConnections = concurrentConnections;
chosen = server;
}
}
}
if (chosen == null) { // 如果沒有選上,調(diào)用父類ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule的choose方法,也就是使用RoundRobinRule輪詢的方式進行負載均衡
return super.choose(key);
} else {
return chosen;
}
}
使用Ribbon提供的負載均衡策略很簡單,只需以下幾部:
1、創(chuàng)建具有負載均衡功能的RestTemplate實例
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
使用RestTemplate進行rest操作的時候,會自動使用負載均衡策略,它內(nèi)部會在RestTemplate中加入LoadBalancerInterceptor這個攔截器,這個攔截器的作用就是使用負載均衡。
默認情況下會采用輪詢策略,如果希望采用其它策略,則指定IRule實現(xiàn),如:
@Bean
public IRule ribbonRule() {
return new BestAvailableRule();
}
這種方式對Feign也有效。
我們也可以參考ribbon,自己寫一個負載均衡實現(xiàn)類。
可以通過下面方法獲取負載均衡策略最終選擇了哪個服務(wù)實例:
@Autowired
LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient;
//測試負載均衡最終選中哪個實例
public String getChoosedService() {
ServiceInstance serviceInstance = loadBalancerClient.choose("USERINFO-SERVICE");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("host: ").append(serviceInstance.getHost()).append(", ");
sb.append("port: ").append(serviceInstance.getPort()).append(", ");
sb.append("uri: ").append(serviceInstance.getUri());
return sb.toString();
}