一名合格前端工程師必備素質:代碼整潔之道
內容出自《代碼整潔之道》、Alex Kondov[1]的博文tao-of-react[2]和《Clean Code of Javascript》
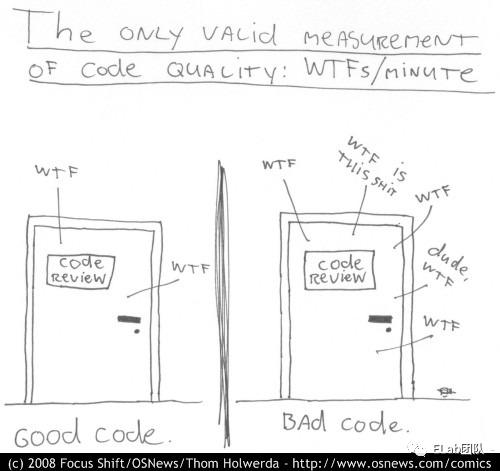
代碼整潔有什么用?

思路清晰,降低bug幾率 更容易維護,利于團隊協(xié)作 看起來舒服,提高效率 ......
軟件質量與代碼整潔度成正比 --Robert.C.Martin
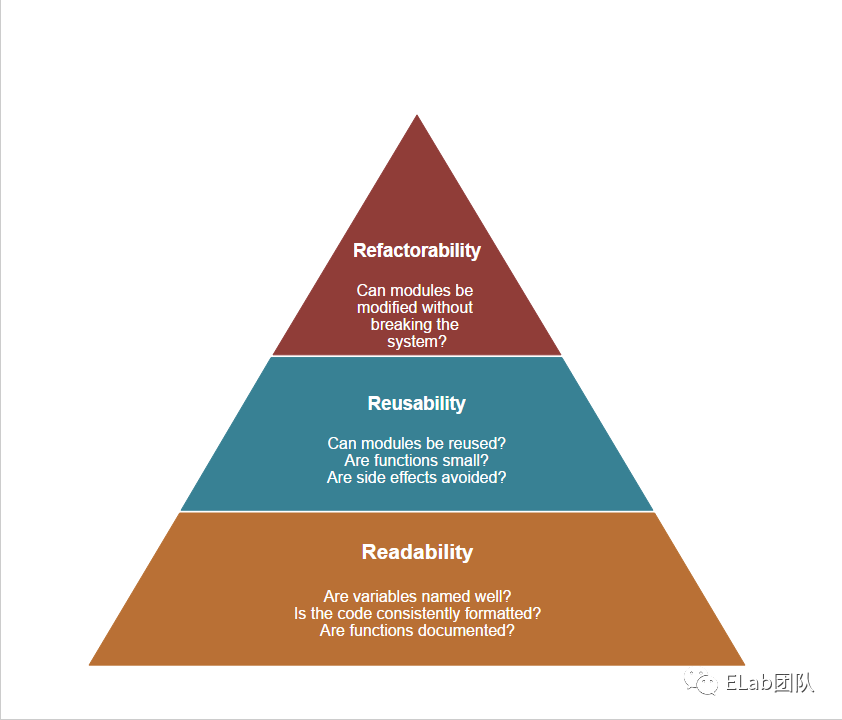
軟件設計3R層次結構:readable, reusable, and refactorable[3] 可讀性、可重用性、可重構性
 下面這些原則是作者提出的一些最佳實踐,但不是強制約束
下面這些原則是作者提出的一些最佳實踐,但不是強制約束
關于命名
1.使用有意義且易讀的變量名
?? const yyyymmdstr = moment().format("YYYY/MM/DD");
?? const currentDate = moment().format("YYYY/MM/DD");
2.使用有意義的變量代替數(shù)組下標
??
const address = "One Infinite Loop, Cupertino 95014";
const cityZipCodeRegex = /^[^,\\]+[,\\\s]+(.+?)\s*(\d{5})?$/;
saveCityZipCode(
address.match(cityZipCodeRegex)[1],
address.match(cityZipCodeRegex)[2]
);
??
const address = "One Infinite Loop, Cupertino 95014";
const cityZipCodeRegex = /^[^,\\]+[,\\\s]+(.+?)\s*(\d{5})?$/;
const [_, city, zipCode] = address.match(cityZipCodeRegex) || [];
saveCityZipCode(city, zipCode);
3.變量名要簡潔,不要附加無用信息
??
const Car = {
carMake: "Honda",
carModel: "Accord",
carColor: "Blue"
};
function paintCar(car, color) {
car.carColor = color;
}
??
const Car = {
make: "Honda",
model: "Accord",
color: "Blue"
};
function paintCar(car, color) {
car.color = color;
}
4.消除魔術字符串
?? setTimeout(blastOff, 86400000);
?? const MILLISECONDS_PER_DAY = 60 * 60 * 24 * 1000; //86400000;
setTimeout(blastOff, MILLISECONDS_PER_DAY);
5.使用默認參數(shù)替代短路運算符
??
function createMicrobrewery(name) {
const breweryName = name || "Hipster Brew Co.";
// ...
}
??
function createMicrobrewery(name = "Hipster Brew Co.") {
// ...
}
關于函數(shù)
1.一個函數(shù)只做一件事的好處在于易于理解、易于測試。
??
function emailClients(clients) {
clients.forEach(client => {
const clientRecord = database.lookup(client);
if (clientRecord.isActive()) {
email(client);
}
});
}
??
function emailActiveClients(clients) {
clients.filter(isActiveClient).forEach(email);
}
function isActiveClient(client) {
const clientRecord = database.lookup(client);
return clientRecord.isActive();
}
---------------------分割線-----------------------
??
function createFile(name, temp) {
if (temp) {
fs.create(`./temp/${name}`);
} else {
fs.create(name);
}
}
??
function createFile(name) {
fs.create(name);
}
function createTempFile(name) {
createFile(`./temp/${name}`);
}
2.函數(shù)參數(shù)不多于2個,如果有很多參數(shù)就利用object傳遞,并使用解構。
推薦使用解構的幾個原因:
看到函數(shù)簽名可以立即了解有哪些參數(shù) 解構能克隆傳遞到函數(shù)中的參數(shù)對象的值(淺克隆),有助于防止副作用. linter可以提示有哪些參數(shù)未被使用
??
function createMenu(title, body, buttonText, cancellable) {
// ...
}
createMenu("Foo", "Bar", "Baz", true);
??
function createMenu({ title, body, buttonText, cancellable }) {
// ...
}
createMenu({
title: "Foo",
body: "Bar",
buttonText: "Baz",
cancellable: true
});
3.函數(shù)名應該直接反映函數(shù)的作用
??
function addToDate(date, month) {
// ...
}
const date = new Date();
// It's hard to tell from the function name what is added
addToDate(date, 1);
??
function addMonthToDate(month, date) {
// ...
}
const date = new Date();
addMonthToDate(1, date);
4.一個函數(shù)的抽象層級不要太多,如果你的函數(shù)做了太多事,就需要把它拆分成多個函數(shù)
??
function parseBetterJSAlternative(code) {
const REGEXES = [
// ...
];
const statements = code.split(" ");
const tokens = [];
REGEXES.forEach(REGEX => {
statements.forEach(statement => {
// ...
});
});
const ast = [];
tokens.forEach(token => {
// lex...
});
ast.forEach(node => {
// parse...
});
}
??
function parseBetterJSAlternative(code) {
const tokens = tokenize(code);
const syntaxTree = parse(tokens);
syntaxTree.forEach(node => {
// parse...
});
}
function tokenize(code) {
const REGEXES = [
// ...
];
const statements = code.split(" ");
const tokens = [];
REGEXES.forEach(REGEX => {
statements.forEach(statement => {
tokens.push(/* ... */);
});
});
return tokens;
}
function parse(tokens) {
const syntaxTree = [];
tokens.forEach(token => {
syntaxTree.push(/* ... */);
});
return syntaxTree;
}
5.減少重復代碼
??
function showDeveloperList(developers) {
developers.forEach(developer => {
const expectedSalary = developer.calculateExpectedSalary();
const experience = developer.getExperience();
const githubLink = developer.getGithubLink();
const data = {
expectedSalary,
experience,
githubLink
};
render(data);
});
}
function showManagerList(managers) {
managers.forEach(manager => {
const expectedSalary = manager.calculateExpectedSalary();
const experience = manager.getExperience();
const portfolio = manager.getMBAProjects();
const data = {
expectedSalary,
experience,
portfolio
};
render(data);
});
}
??
function showEmployeeList(employees) {
employees.forEach(employee => {
const expectedSalary = employee.calculateExpectedSalary();
const experience = employee.getExperience();
const data = {
expectedSalary,
experience
};
switch (employee.type) {
case "manager":
data.portfolio = employee.getMBAProjects();
break;
case "developer":
data.githubLink = employee.getGithubLink();
break;
}
render(data);
});
}
6.盡量使用純函數(shù) (函數(shù)式編程,not命令式編程)
??
const programmerOutput = [
{
name: "Uncle Bobby",
linesOfCode: 500
},
{
name: "Suzie Q",
linesOfCode: 1500
},
{
name: "Jimmy Gosling",
linesOfCode: 150
},
{
name: "Gracie Hopper",
linesOfCode: 1000
}
];
let totalOutput = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < programmerOutput.length; i++) {
totalOutput += programmerOutput[i].linesOfCode;
}
??
const programmerOutput = [
{
name: "Uncle Bobby",
linesOfCode: 500
},
{
name: "Suzie Q",
linesOfCode: 1500
},
{
name: "Jimmy Gosling",
linesOfCode: 150
},
{
name: "Gracie Hopper",
linesOfCode: 1000
}
];
const totalOutput = programmerOutput.reduce(
(totalLines, output) => totalLines + output.linesOfCode,
0
);
7.注意函數(shù)的副作用
??
const addItemToCart = (cart, item) => {
cart.push({ item, date: Date.now() });
};
??
const addItemToCart = (cart, item) => {
return [...cart, { item, date: Date.now() }];
};
8.不要過度優(yōu)化
現(xiàn)代瀏覽器在運行時進行了大量的優(yōu)化。很多時候,如果你再優(yōu)化,那就是在浪費時間。
??
// On old browsers, each iteration with uncached `list.length` would be costly
// because of `list.length` recomputation. In modern browsers, this is optimized.
for (let i = 0, len = list.length; i < len; i++) {
// ...
}
??
for (let i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
// ...
}
關于注釋
1.Comments are an apology, not a requirement. Good code mostly documents itself.
好的代碼是自注釋的
??
function hashIt(data) {
// The hash
let hash = 0;
// Length of string
const length = data.length;
// Loop through every character in data
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
// Get character code.
const char = data.charCodeAt(i);
// Make the hash
hash = (hash << 5) - hash + char;
// Convert to 32-bit integer
hash &= hash;
}
}
??
function hashIt(data) {
let hash = 0;
const length = data.length;
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
const char = data.charCodeAt(i);
hash = (hash << 5) - hash + char;
// Convert to 32-bit integer
hash &= hash;
}
}
2.git能做的事不要寫在注釋里
??
/**
* 2016-12-20: Removed monads, didn't understand them (RM)
* 2016-10-01: Improved using special monads (JP)
* 2016-02-03: Removed type-checking (LI)
* 2015-03-14: Added combine with type-checking (JR)
*/
function combine(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
??
function combine(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
關于組件
1.盡可能使用函數(shù)組件
函數(shù)式組件有更簡單的語法,沒有生命周期函數(shù),構造函數(shù)。同樣的邏輯和可靠性,函數(shù)式組件可以用更少的代碼完成。
??
class Counter extends React.Component {
state = {
counter: 0,
}
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this)
}
handleClick() {
this.setState({ counter: this.state.counter + 1 })
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<p>counter: {this.state.counter}</p>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>Increment</button>
</div>
)
}
}
??
function Counter() {
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0)
handleClick = () => setCounter(counter + 1)
return (
<div>
<p>counter: {counter}</p>
<button onClick={handleClick}>Increment</button>
</div>
)
}
2.函數(shù)組件中剝離邏輯代碼
盡可能的把邏輯從組件中剝離出去,可以把必要的值用參數(shù)的形式傳給工具類函數(shù)。在函數(shù)組件外組織你的邏輯讓你能夠更簡單的去追蹤 bug 和擴展你的功能。
??
export default function Component() {
const [value, setValue] = useState('')
function isValid() {
// ...
}
return (
<>
<input
value={value}
onChange={e => setValue(e.target.value)}
onBlur={validateInput}
/>
<button
onClick={() => {
if (isValid) {
// ...
}
}}
>
Submit
</button>
</>
)
}
??
function isValid(value) {
// ...
}
export default function Component() {
const [value, setValue] = useState('')
return (
<>
<input
value={value}
onChange={e => setValue(e.target.value)}
onBlur={validateInput}
/>
<button
onClick={() => {
if (isValid(value)) {
// ...
}
}}
>
Submit
</button>
</>
)
}
3.控制組件長度,減少UI耦合
函數(shù)組件也是函數(shù),同樣要控制長度,如果組件太長,就要拆成多個組件
??
function Filters({ onFilterClick }) {
return (
<>
<p>Book Genres</p>
<ul>
<li>
<div onClick={() => onFilterClick('fiction')}>Fiction</div>
</li>
<li>
<div onClick={() => onFilterClick('classics')}>
Classics
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div onClick={() => onFilterClick('fantasy')}>Fantasy</div>
</li>
<li>
<div onClick={() => onFilterClick('romance')}>Romance</div>
</li>
</ul>
</>
)
}
// ?? Use loops and configuration objects
const GENRES = [
{
identifier: 'fiction',
name: Fiction,
},
{
identifier: 'classics',
name: Classics,
},
{
identifier: 'fantasy',
name: Fantasy,
},
{
identifier: 'romance',
name: Romance,
},
]
function Filters({ onFilterClick }) {
return (
<>
<p>Book Genres</p>
<ul>
{GENRES.map(genre => (
<li>
<div onClick={() => onFilterClick(genre.identifier)}>
{genre.name}
</div>
</li>
))}
</ul>
</>
)
}
4.盡量避免函數(shù)組件內再定義函數(shù)組件
不要在一個函數(shù)組件中再去書寫一個函數(shù)組件。一個函數(shù)組件應該僅僅是一個函數(shù)。函數(shù)組件內部再定義函數(shù)組件,意味著內部的函數(shù)組件能夠通過作用域訪問到外層組件所有的 state 和 props,這樣會使內部定義組件不可靠。把內部的組件移到外部,避免閉包和作用域的影響。
// ?? Don't write nested render functions
function Component() {
function renderHeader() {
return <header>...</header>
}
return <div>{renderHeader()}</div>
}
// ?? Extract it in its own component
import Header from '@modules/common/components/Header'
function Component() {
return (
<div>
<Header />
</div>
)
}
5.優(yōu)化props
控制props數(shù)量、聚合props、完善渲染條件
如何把控 props 的量是一個值得商榷的問題。但是一個組件傳遞越多的 props 意味著它做的事情越多這是共識。當 props 達到一定數(shù)量的時候,意味著這個組件做的事情太多了。當props的數(shù)量達到5個以上的時候,這個組件就需要被拆分了。在某些極端諸如輸入類型組件的情況下,可能擁有過多的props,但在通常情況下5個props能夠滿足大部分組件的需求。
提示:一個組件擁有越多的 props,越容易被 rerender。
一些場景下使用短路語法來進行條件渲染可能導致期望之外的問題,有可能會渲染一個 0 在界面上。避免這種情況發(fā)生,盡量使用三元操作符。盡管短路操作符能使代碼變得簡潔,但是三元操作符能夠保證渲染的正確性。
// ?? Try to avoid short-circuit operators
function Component() {
const count = 0
return <div>{count && <h1>Messages: {count}</h1>}</div>
}
// ?? Use a ternary instead
function Component() {
const count = 0
return <div>{count ? <h1>Messages: {count}</h1> : null}</div>
}
關于其他
1.把組件放入單獨的文件夾中
// ?? Don't keep all component files together
├── components
├── Header.jsx
├── Header.scss
├── Header.test.jsx
├── Footer.jsx
├── Footer.scss
├── Footer.test.jsx
// ?? Move them in their own folder
├── components
├── Header
├── index.js
├── Header.jsx
├── Header.scss
├── Header.test.jsx
├── Footer
├── index.js
├── Footer.jsx
├── Footer.scss
├── Footer.test.jsx
2.盡量使用絕對路徑
使用絕對路徑可以在移動一個文件的時候能夠盡量少的更改其它文件。絕對路徑也能讓你對所有依賴文件的出處一目了然。
(完)
參考文獻:《代碼整潔之道》
https://github.com/ryanmcdermott/clean-code-javascript
https://github.com/ryanmcdermott/3rs-of-software-architecture
https://alexkondov.com/tao-of-react/
參考資料
Alex Kondov: https://twitter.com/alexanderkondov
[2]tao-of-react: https://alexkondov.com/tao-of-react/
[3]readable, reusable, and refactorable: https://github.com/ryanmcdermott/3rs-of-software-architecture
