SpringIOC容器初始化流程12大步源碼解析
點(diǎn)擊上方藍(lán)色字體,選擇“標(biāo)星公眾號(hào)”
優(yōu)質(zhì)文章,第一時(shí)間送達(dá)
1.概要及IOC容器初始化流程圖
下面是IOC初始化的完整流程圖
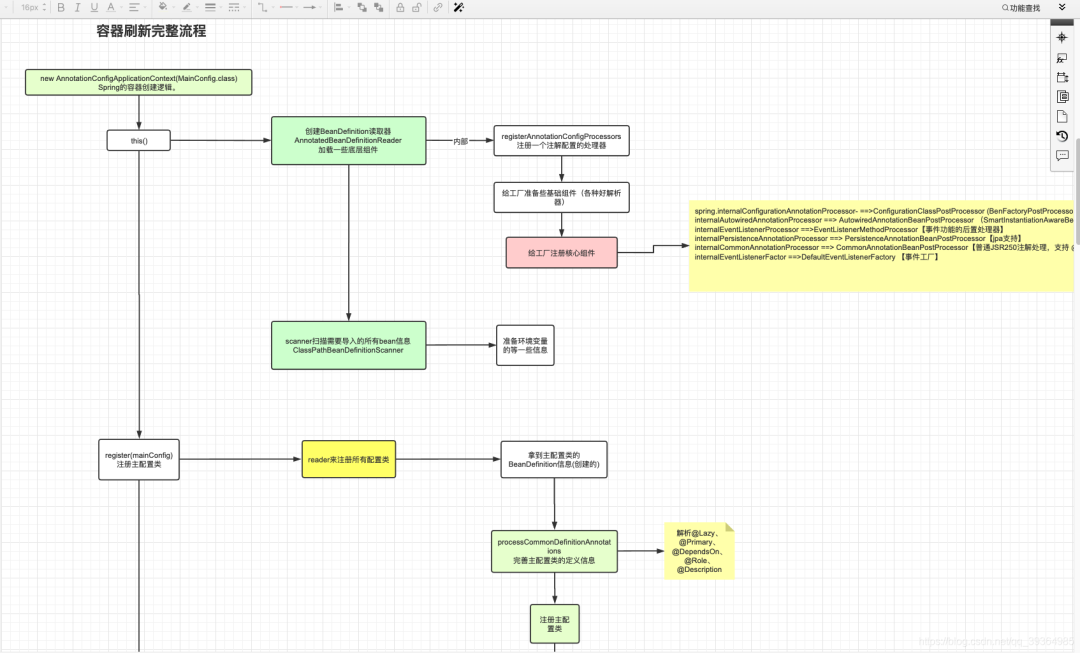

就以我們new了一個(gè)AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 為例,參數(shù)穿傳的是我們的是我們的主配置類(lèi), 配置類(lèi)就簡(jiǎn)單加倆注解@Configuration、@ComponentScan("com.xixi") ,new 一個(gè)AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 就是創(chuàng)建了一個(gè)IOC容器,里面就進(jìn)行了12個(gè)步驟來(lái)初始化容器
//偽代碼 簡(jiǎn)單寫(xiě)下
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
@ComponentScan("com")
@Configuration
public class MainConfig {
}
以下是Spring刷新容器的代碼,Spring中起了個(gè)名叫刷新,其實(shí)就是創(chuàng)建IOC容器,一共就12步 debug逐個(gè)擊破就完了 非常的easy
@Override //容器刷新的十二大步。模板模式
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
//1.準(zhǔn)備上下文環(huán)境 Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 2.工廠創(chuàng)建:BeanFactory第一次開(kāi)始創(chuàng)建的時(shí)候,有xml解析邏輯。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//3.給容器中注冊(cè)了環(huán)境信息作為單實(shí)例Bean方便后續(xù)自動(dòng)裝配;放了一些后置處理器處理(監(jiān)聽(tīng)、xxAware功能) Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//4.留給子類(lèi)的模板方法,允許子類(lèi)繼續(xù)對(duì)工廠執(zhí)行一些處理; Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
//5.【大核心】工廠增強(qiáng):執(zhí)行所有的BeanFactory后置增強(qiáng)器;利用BeanFactory后置增強(qiáng)器對(duì)工廠進(jìn)行修改或者增強(qiáng),配置類(lèi)會(huì)在這里進(jìn)行解析。 Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//6.【核心】注冊(cè)所有的Bean的后置處理器 Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
//7.初始化國(guó)際化功能 Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
//8.初始化事件多播功能(事件派發(fā)) Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//9. Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
//10.注冊(cè)監(jiān)聽(tīng)器,從容器中獲取所有的ApplicationListener; Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//11.【大核心】bean創(chuàng)建;完成 BeanFactory 初始化。(工廠里面所有的組件都好了)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//12.發(fā)布事件 Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
2.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext構(gòu)造器
分析12大步之前先看下this()里邊干了啥
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
this();
register(componentClasses);
refresh(); //容器完整刷新(創(chuàng)建出所有組件,組織好所有功能)
}
下面是this中的代碼,可以看到主要就創(chuàng)建了倆基礎(chǔ)組件 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader Bean定義的讀取器,ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner bean定義的掃描器,用來(lái)掃描指定路徑下所有的bean信息
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
StartupStep createAnnotatedBeanDefReader = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.context.annotated-bean-reader.create");
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
createAnnotatedBeanDefReader.end();
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
重點(diǎn)看下創(chuàng)建讀取器過(guò)程,里面調(diào)用了registerAnnotationConfigProcessors方法給工廠創(chuàng)建了很多基礎(chǔ)組件,各種解析器
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
可以看到里面注冊(cè)了ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 配置類(lèi)的后置處理器,我們加了@Configuration注解的類(lèi)就是用這個(gè)處理器來(lái)解析的,還有AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor自動(dòng)化裝配相關(guān)的后置處理器等等
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
//注冊(cè)底層的 配置文件處理器
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//注冊(cè)底層的自動(dòng)裝配處理器
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//注冊(cè)支持JSR-250的處理
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
}
this()里邊就是定義一些Spring容器底層用到的一些基礎(chǔ)組件。
然后看下一步register(componentClasses);方法,componentClasses是我們的主配置類(lèi),是個(gè)可變參數(shù)我們可以傳多個(gè),然后i就全部注冊(cè)到工廠里存著 也是解析成BeanDefinition存到Map里
@Override
public void register(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
Assert.notEmpty(componentClasses, "At least one component class must be specified");
StartupStep registerComponentClass = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.context.component-classes.register")
.tag("classes", () -> Arrays.toString(componentClasses));
this.reader.register(componentClasses);
registerComponentClass.end();
}
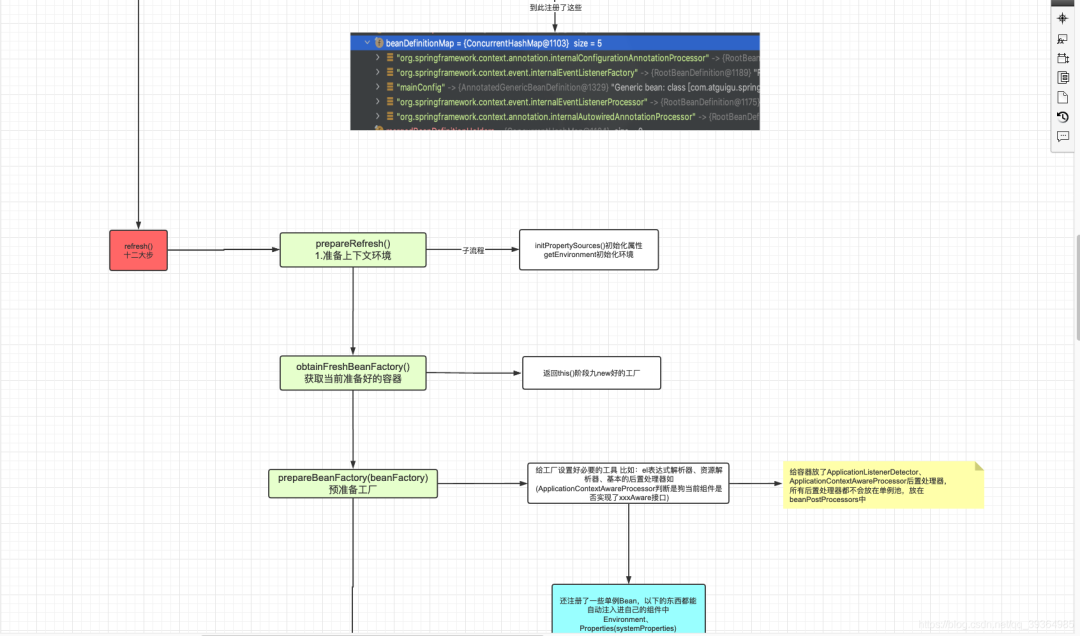
3.第一步--prepareRefresh()準(zhǔn)備上下文環(huán)境
容器刷新的12大步是在 AbstractApplicationContext 抽象類(lèi)中進(jìn)行,說(shuō)明AbstractApplicationContext是個(gè)模板類(lèi),定義了容器初始化的基本步驟,不一定每個(gè)方法都是他來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)。
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
}
else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
//其他子容器自行實(shí)現(xiàn)(比如:WebApplicationContext) Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
initPropertySources();
//準(zhǔn)備環(huán)境變量信息 Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// 存儲(chǔ)子容器早期運(yùn)行的一些監(jiān)聽(tīng)器; Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
}
else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
//早期的一些時(shí)間存儲(chǔ)到這里 Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
1.前邊三行代碼記錄下容器啟動(dòng)時(shí)間,關(guān)閉狀態(tài)設(shè)置成false,活躍狀態(tài)設(shè)置為true,很好理解。
2.然后 initPropertySources 這個(gè)方法在AbstractApplicationContext中就沒(méi)有實(shí)現(xiàn),而是交給子類(lèi)實(shí)現(xiàn),這個(gè)方法可以定義一些自己的初始化操作。比如Web環(huán)境下的IOC容器就在這加載一些應(yīng)用上下文信息
3.getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties(); 方法創(chuàng)建了 StandardEnvironment環(huán)境對(duì)象,debug下可以看到首先拿到了一些我們系統(tǒng)的環(huán)境變量,比如JAVA_HOME ,系統(tǒng)時(shí)間等等

4.存儲(chǔ)一些早期的監(jiān)聽(tīng)器,如果是單純的IOC環(huán)境,暫時(shí)沒(méi)有任何監(jiān)聽(tīng)器存在,到此IOC容器刷新第一步準(zhǔn)備環(huán)境上下文就結(jié)束了
4.第二步創(chuàng)建工廠實(shí)例
obtainFreshBeanFactory方法返回了在this()階段就創(chuàng)建好的工廠實(shí)例, 說(shuō)明ApplicationContext其實(shí)并沒(méi)有實(shí)現(xiàn)任何的創(chuàng)建bean的功能,而是組合持有了工廠來(lái)配合實(shí)現(xiàn)整個(gè)流程
// 2.工廠創(chuàng)建:BeanFactory第一次開(kāi)始創(chuàng)建的時(shí)候,有xml解析邏輯。
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
5. 第三步預(yù)準(zhǔn)備工廠
這個(gè)階段繼續(xù)創(chuàng)建了一些Spring底層用到的基礎(chǔ)組件,例如StandardBeanExpressionResolver EL表達(dá)式的解析器 解析 ${}這些玩意的,還有ResourceEditorRegistrar資源解析器,基礎(chǔ)的后置處理器ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(判斷那些實(shí)現(xiàn)Aware接口)等
最后還把一些默認(rèn)組件放到了單例池子
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
if (!shouldIgnoreSpel) { //解釋器模式 ${ }
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this)); //準(zhǔn)備一個(gè)處理Aware接口功能的后置處理器
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class); //告訴Spring先別管這些接口
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationStartupAware.class);
//注冊(cè)可以解析到的依賴(lài) BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
//注冊(cè)默認(rèn)組件: Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_STARTUP_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_STARTUP_BEAN_NAME, getApplicationStartup());
}
}
6.第四步postProcessBeanFactory
postProcessBeanFactory這個(gè)方法工廠沒(méi)有實(shí)現(xiàn) 是留給子類(lèi)的模板方法,允許子類(lèi)繼承對(duì)工廠執(zhí)行一些處理
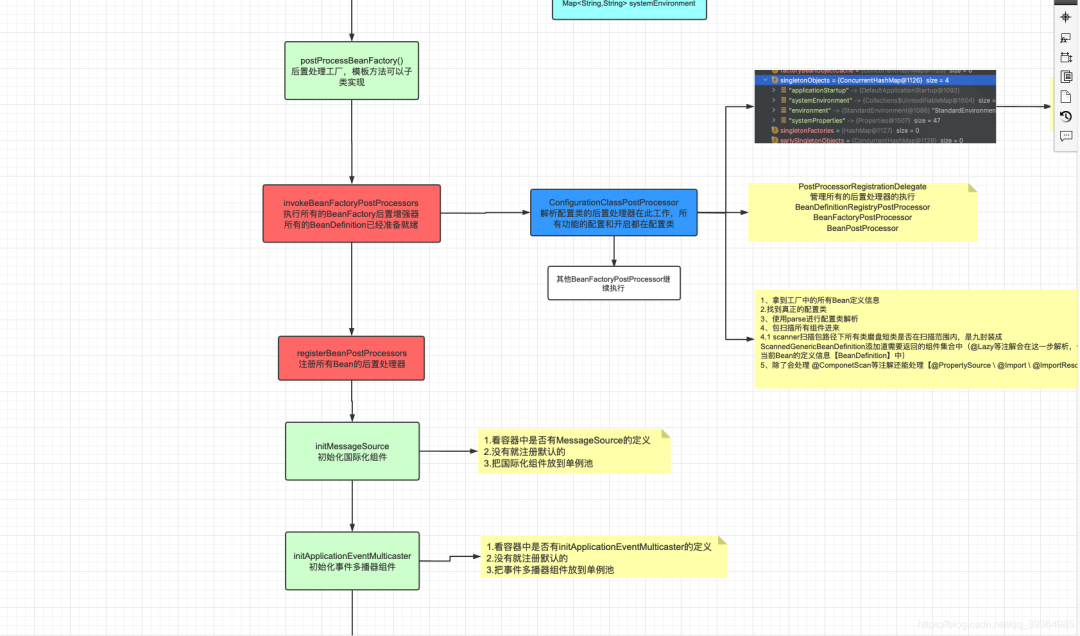
7. 第五步執(zhí)行所有的BeanFactory后置增強(qiáng)器
這里邊調(diào)用了
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());來(lái)執(zhí)行所有的工廠增強(qiáng)器
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate類(lèi)可以說(shuō)是一個(gè)門(mén)面模式或者一個(gè)裝飾者,他用來(lái)處理Spring的所有后置處理器
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()); //執(zhí)行所有的工廠增強(qiáng)器
//上面的類(lèi)叫:后置處理器的注冊(cè)代理(門(mén)面模式-裝飾模式)
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
此方法執(zhí)行了所有的BeanFactory的后置處理器,BeanFactory的后置處理器一共兩種 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 和 BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
先執(zhí)行默認(rèn)的處理器,-> 然后再取出實(shí)現(xiàn)了PriorityOrdered排序接口的處理器進(jìn)行排序,執(zhí)行處理器 ->接下來(lái)取出實(shí)現(xiàn)了Ordered排序接口的的處理器,排序然后執(zhí)行。 兩類(lèi)處理器都是這個(gè)執(zhí)行流程
//執(zhí)行工廠的后置處理器
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// WARNING: Although it may appear that the body of this method can be easily
// refactored to avoid the use of multiple loops and multiple lists, the use
// of multiple lists and multiple passes over the names of processors is
// intentional. We must ensure that we honor the contracts for PriorityOrdered
// and Ordered processors. Specifically, we must NOT cause processors to be
// instantiated (via getBean() invocations) or registered in the ApplicationContext
// in the wrong order.
//
// Before submitting a pull request (PR) to change this method, please review the
// list of all declined PRs involving changes to PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate
// to ensure that your proposal does not result in a breaking change:
// https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues?q=PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate+is%3Aclosed+label%3A%22status%3A+declined%22
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//先拿到底層默認(rèn)有的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 首先:從工廠中獲取所有的實(shí)現(xiàn)了 PriorityOrdered 接口的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor; First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); //拿到系統(tǒng)中每一個(gè)組件的BD信息,進(jìn)行類(lèi)型對(duì)比,是否匹配指定的類(lèi)型
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));//從工廠中獲取這個(gè)組件【getBean整個(gè)組件創(chuàng)建的流程】并放到這個(gè)集合
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
} //下面利用優(yōu)先級(jí)排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup()); //執(zhí)行這些BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// 接下來(lái),獲取所有實(shí)現(xiàn)了Ordered接口的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName); //即使實(shí)現(xiàn)了 PriorityOrdered 和Ordered,也是以 PriorityOrdered
}
}//排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup()); //執(zhí)行
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// 最后,我們自定義的一般沒(méi)有任何優(yōu)先級(jí)和排序接口 Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);//拿到所有的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}//排序,根據(jù)類(lèi)名大小寫(xiě)進(jìn)行排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); //防止重復(fù)執(zhí)行
}
// 接下來(lái),再來(lái)執(zhí)行postProcessBeanFactory的回調(diào), Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
//以前在執(zhí)行 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor ,以后來(lái)執(zhí)行 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// 首先執(zhí)行所有實(shí)現(xiàn)了 PriorityOrdered 的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor;First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 接下來(lái)執(zhí)行,實(shí)現(xiàn)了 Ordered 接口的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 最后執(zhí)行沒(méi)有任何優(yōu)先級(jí)和排序接口的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); //執(zhí)行所有的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
8. 第六步注冊(cè)所有的bean的后置處理器 BeanPostProcessors
取出所有的BeanPostProcessor后置處理器,該排序的排序,然后全都放到容器的集合中
容器有一個(gè)集合屬性來(lái)保存所有的BeanPostProcessor
/** BeanPostProcessors to apply. 保存了所有的Bean后置增強(qiáng)器 */
private final List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors = new BeanPostProcessorCacheAwareList();
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// WARNING: Although it may appear that the body of this method can be easily
// refactored to avoid the use of multiple loops and multiple lists, the use
// of multiple lists and multiple passes over the names of processors is
// intentional. We must ensure that we honor the contracts for PriorityOrdered
// and Ordered processors. Specifically, we must NOT cause processors to be
// instantiated (via getBean() invocations) or registered in the ApplicationContext
// in the wrong order.
//
// Before submitting a pull request (PR) to change this method, please review the
// list of all declined PRs involving changes to PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate
// to ensure that your proposal does not result in a breaking change:
// https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues?q=PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate+is%3Aclosed+label%3A%22status%3A+declined%22
//獲取到容器中所有的 BeanPostProcessor; Bean的后置處理器
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { //獲取所有實(shí)現(xiàn)了 PriorityOrdered 的 BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
//首先,注冊(cè)所有的實(shí)現(xiàn)了 PriorityOrdered 的 BeanPostProcessor ; First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
//接下來(lái),注冊(cè)所有的實(shí)現(xiàn)了 Ordered 的 BeanPostProcessor Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); //獲取后置處理器對(duì)象
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// 最后,注冊(cè)所有普通的 BeanPostProcessor ;Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); //從容器中獲取這個(gè)組件
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
//最后,重新注冊(cè)所有internal的BeanPostProcessors Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// 重新注冊(cè)一下這個(gè)后置處理器 Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// 把他放到后置處理器的最后一位; moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
9. 第七步初始化國(guó)際化組件
MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME 對(duì)應(yīng)的值是 "messageSource", 先從容器中拿一個(gè)名為 “messageSource” 類(lèi)型為MessageSource的組件,拿到就賦值給工廠,拿不到就創(chuàng)建個(gè)DelegatingMessageSource類(lèi)型的組件
protected void initMessageSource() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.messageSource = beanFactory.getBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, MessageSource.class);
// Make MessageSource aware of parent MessageSource.
if (this.parent != null && this.messageSource instanceof HierarchicalMessageSource) {
HierarchicalMessageSource hms = (HierarchicalMessageSource) this.messageSource;
if (hms.getParentMessageSource() == null) {
// Only set parent context as parent MessageSource if no parent MessageSource
// registered already.
hms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using MessageSource [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
else {
// Use empty MessageSource to be able to accept getMessage calls.
DelegatingMessageSource dms = new DelegatingMessageSource();
dms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
this.messageSource = dms;
beanFactory.registerSingleton(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, this.messageSource);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
}
10. 第八步初始化事件多播器組件
先從容器中拿一個(gè)名為applicationEventMulticaster的組件,拿到設(shè)置給容器。拿不到就創(chuàng)建一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的事件多播器
Spring監(jiān)聽(tīng)器是觀察者模式的應(yīng)用。
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster); //注冊(cè)一個(gè)事件派發(fā)器
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
11. 第九步onRefresh
這一步啥也沒(méi)實(shí)現(xiàn),也是留給子類(lèi)實(shí)現(xiàn)的
12. 第十步注冊(cè)早期的監(jiān)聽(tīng)器
/** 多播器和監(jiān)聽(tīng)器是觀察者模式(里面包含了所有的監(jiān)聽(tīng)器)
* Add beans that implement ApplicationListener as listeners.
* Doesn't affect other listeners, which can be added without being beans.
*/
protected void registerListeners() {
//把所有監(jiān)聽(tīng)器保存到多播器的集合中 Register statically specified listeners first.
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them! 獲取ApplicationListener在ioc容器中注冊(cè)的bean的名字
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName); //獲取所有的容器中的監(jiān)聽(tīng)器,并保存他們的名字
}
//派發(fā)之前攢的一些早期事件 Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(earlyEventsToProcess)) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
13. 第十一步大大核心 完成BeanFactory初始化, 創(chuàng)建所有組件
這個(gè)方法最重要一步是preInstantiateSingletons()方法,這里面初始化所有非懶加載的單例bean
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 給工廠設(shè)置好 ConversionService【負(fù)責(zé)類(lèi)型轉(zhuǎn)換的組件服務(wù)】, Initialize conversion service for this context.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// 注冊(cè)一個(gè)默認(rèn)的值解析器("${}") ;Register a default embedded value resolver if no BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// (such as a PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// LoadTimeWeaverAware;aspectj:加載時(shí)織入功能【aop】。 Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName); //從容器中獲取組件,有則直接獲取,沒(méi)則進(jìn)行創(chuàng)建
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//初始化所有的非懶加載的單實(shí)例Bean
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
這個(gè)方法維護(hù)了Bean的整個(gè)生命周期, 其中包含 實(shí)例化Bean ->屬性注入 -> 到初始化Bean,以及在實(shí)例化前后,屬性注入的自動(dòng)裝配,初始化前后執(zhí)行了所有的BeanPostProcessor后置處理器,例如AOP,事務(wù)等就是利用后置處理器在Bean的生命周期的某個(gè)時(shí)期進(jìn)行干預(yù)的。
里面代碼量很大不在此文中詳細(xì)展開(kāi)講了。大致邏輯就是 遍歷所有BeanName 然后通過(guò)BeanName獲取Bean的定義BeanDefinition,接著一些華麗唿哨判斷,例如是否單例,是否抽象,是否是FactoryBean類(lèi)型的,不是的話(huà)走普通創(chuàng)建邏輯, 還有處理循環(huán)依賴(lài)等等很多很多
Spring中所有組件都是通過(guò)getBean方法獲取的,getBean里邊邏輯就是先從單例池獲取,獲取不到再創(chuàng)建。
Spring容器刷新最重要的部分就在這了
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// 創(chuàng)建出所有的單實(shí)例Bean;Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName); //開(kāi)始解析文件的時(shí)候每一個(gè)bean標(biāo)簽被解析封裝成一個(gè)BeanDefinition
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) { //如果是FactoryBean則執(zhí)行下面邏輯
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName); //得到HelloFactory
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else { //不是FactoryBean則執(zhí)行這個(gè),普通的單實(shí)例非懶加載bean的創(chuàng)建
getBean(beanName); //
}
}
}
// 觸發(fā) post-initialization 邏輯; Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
StartupStep smartInitialize = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.beans.smart-initialize")
.tag("beanName", beanName);
SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
smartInitialize.end();
}
}
}
14. 第十二步 收尾工作finishRefresh
最后收尾工作很簡(jiǎn)單了 清理下不用的緩存 ,初始化個(gè)LifecycleProcessor類(lèi)型處理器,干嘛用的我也不知道,發(fā)布下容器刷新完成的事件。完事 至此SpringIOC容器的創(chuàng)建過(guò)程就完全結(jié)束了。
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
clearResourceCaches();
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor();
//告訴LifecycleProcessor容器onRefresh Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
//發(fā)布事件 Publish the final event.
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
//jconsole(暴露MBean端點(diǎn)信息) Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage()) {
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
}
————————————————
版權(quán)聲明:本文為CSDN博主「飛翔的小羊」的原創(chuàng)文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版權(quán)協(xié)議,轉(zhuǎn)載請(qǐng)附上原文出處鏈接及本聲明。
原文鏈接:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39364985/article/details/115308960
鋒哥最新SpringCloud分布式電商秒殺課程發(fā)布
??????
??長(zhǎng)按上方微信二維碼 2 秒
感謝點(diǎn)贊支持下哈 
