vue3的composition-api實踐總結(jié)
點擊上方 前端Q,關(guān)注公眾號
回復(fù)加群,加入前端Q技術(shù)交流群
因為向往已久vue3的開發(fā)方式,但是組內(nèi)有很多歷史項目,并且我們受制于ie的支持,所以我們決定在vue2中引入composition-api,來使用他的新特性。在使用過程中,我們遇到了很多問題,也積累了一些經(jīng)驗,所以記錄下。
composition-api
首先給大家介紹一下composition-api,他是通過函數(shù)的形式,將vue的功能特性暴露給我們使用

雖然一下子看上去很多,但是只需要先掌握加粗的這一部分,就可以體驗到組合式api的魅力了,其他的可以先做了解等到你真的需要使用它們的時候在做深入。
reactive 用來將對象轉(zhuǎn)變?yōu)轫憫?yīng)式的,與vue2的observable類似,ref用來獲得單獨或者為基礎(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù)類型獲得響應(yīng)性。為什會會有兩個獲得響應(yīng)性的api呢稍后我們將具體說明。computed、watch,provide、inject不用懷疑和vue2中做的是一樣的事情。
你一定注意到下面這些加了on開頭的生命周期鉤子函數(shù),沒錯在組合式api中,這就是他們注冊的方式。但是為什么不見了beforeCreate和created呢?因為setup就是在這個階段執(zhí)行的,而setup就是打開組合式api世界的大門。你可以把setup理解為class的constructor,在vue組件的創(chuàng)建階段,把我們的相關(guān)邏輯執(zhí)行,并且注冊相關(guān)的副作用函數(shù)。
現(xiàn)在我們說回ref和reactive。
reactive在官網(wǎng)中的說明,接受一個對象,返回對象的響應(yīng)式副本。ref在官網(wǎng)中的描述"接受一個內(nèi)部值并返回一個響應(yīng)式且可變的 ref 對象。 ref 對象具有指向內(nèi)部值的單個 property.value"。
聽著很繞口,簡單來講就是reactive可以為對象創(chuàng)建響應(yīng)式而ref除了對象,還可以接收基礎(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù)類型,比如string、boolean等。
那為什么會有這種差異呢?在vue3當(dāng)中響應(yīng)式是基于proxy實現(xiàn)的,而proxy的target必須是復(fù)雜數(shù)據(jù)類型,也就是存放在堆內(nèi)存中,通過指針引用的對象。其實也很好理解,因為基礎(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù)類型,每一次賦值都是全新的對象,所以根本無法代理。那么如果我們想取得簡單類型的響應(yīng)式怎么辦呢?這時候就需要用到ref。
class RefImpl<T> {
private _value: T
public readonly __v_isRef = true
constructor(private _rawValue: T, public readonly _shallow = false) {
this._value = _shallow ? _rawValue : convert(_rawValue)
}
get value() {
track(toRaw(this), TrackOpTypes.GET, 'value')
return this._value
}
set value(newVal) {
if (hasChanged(toRaw(newVal), this._rawValue)) {
this._rawValue = newVal
this._value = this._shallow ? newVal : convert(newVal)
trigger(toRaw(this), TriggerOpTypes.SET, 'value', newVal)
}
}
}
...
const convert = <T extends unknown>(val: T): T =>
isObject(val) ? reactive(val) : val
...
ref通過創(chuàng)建內(nèi)部狀態(tài),將值掛在value上,所以ref生成的對象,要通過value使用。重寫get/set獲得的監(jiān)聽,同時對對象的處理,也依賴了reactive的實現(xiàn)。
由此,ref并不只是具有對基本數(shù)據(jù)類型的響應(yīng)式處理能力,他也是可以處理對象的。所以我認為ref和reactive的區(qū)分并不應(yīng)該只是簡單/復(fù)雜對象的區(qū)分,而是應(yīng)該用編程思想?yún)^(qū)分的。我們應(yīng)該避免,把reactive 當(dāng)作data在頂部將所有變量聲明的想法,而是應(yīng)該結(jié)合具體的邏輯功能,比如一個控制灰度的Flag那他就應(yīng)該是一個ref,而分頁當(dāng)中的頁碼,pageSize,total等就應(yīng)該是一個reactive聲明的對象。也就是說一個setup當(dāng)中可以有多出響應(yīng)變量的聲明,而且他們應(yīng)當(dāng)是與邏輯緊密結(jié)合的.
接下來我先用一個分頁的功能,用選項式和組合式api給大家對比一下。
一些例子
<template>
<div>
<ul class="article-list">
<li v-for="item in articleList" :key="item.id">
<div>
<div class="title">{{ item.title }}</div>
<div class="content">{{ item.content }}</div>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
<el-pagination
@size-change="handleSizeChange"
@current-change="handleCurrentChange"
:current-page="currentPage"
:page-sizes="pageSizes"
:page-size="pageSize"
layout="total, sizes, prev, pager, next, jumper"
:total="total"
>
</el-pagination>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { getArticleList } from '@/mock/index';
export default {
data() {
return {
articleList: [],
currentPage: 1,
pageSizes: [5, 10, 20],
pageSize: 5,
total: 0,
};
},
created() {
this.getList();
},
methods: {
getList() {
const param = {
currentPage: this.currentPage,
pageSizes: this.pageSizes,
pageSize: this.pageSize,
};
getArticleList(param).then((res) => {
this.articleList = res.data;
this.total = res.total;
});
},
handleSizeChange(val) {
this.pageSize = val;
this.getList();
},
handleCurrentChange(val) {
this.currentPage = val;
this.getList();
},
},
};
</script>
這還是我們熟悉到不能在熟悉的分頁流程,在data中聲明數(shù)據(jù),在method中提供修分頁的方法。當(dāng)我們用composition-api實現(xiàn)的時候他就成了下面的樣子。
<script>
import { defineComponent, reactive, ref, toRefs } from "@vue/composition-api";
import { getArticleList } from "@/mock/index";
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const page = reactive({
currentPage: 1,
pageSizes: [5, 10, 20],
pageSize: 5,
total: 0,
});
function handleSizeChange(val) {
page.pageSize = val;
getList();
}
function handleCurrentChange(val) {
page.currentPage = val;
getList();
}
const articleList = ref([]);
function getList() {
getArticleList(page).then((res) => {
articleList.value = res.data;
page.total = res.total;
});
}
getList();
return {
...toRefs(page),
articleList,
getList,
handleSizeChange,
handleCurrentChange,
};
},
});
</script>
這是以composition-api的方式實現(xiàn)的分頁,你會發(fā)現(xiàn)原本的data,method,還有聲明周期等選項都不見了,所有的邏輯都放到了setup當(dāng)中。通過這一個簡單的例子,我們可以發(fā)現(xiàn)原本分散在各個選項中的邏輯,在這里得到了聚合。這種變化在復(fù)雜場景下更為明顯。在復(fù)雜組件中,這種情況更加明顯。而且當(dāng)邏輯完全聚集在一起,這時候,將他們抽離出來,而且抽離邏輯的可以在別處復(fù)用,至此hook就形成了。
hook形態(tài)的分頁組件
// hooks/useArticleList.js
import { ref } from "@vue/composition-api";
import { getArticleList } from "@/mock/index"; // mock ajax請求
function useArticleList() {
const articleList = ref([]);
function getList(page) {
getArticleList(page).then((res) => {
articleList.value = res.data;
page.total = res.total;
});
}
return {
articleList,
getList,
};
}
export default useArticleList;
// hooks/usePage.js
import { reactive } from "@vue/composition-api";
function usePage(changeFn) {
const page = reactive({
currentPage: 1,
pageSizes: [5, 10, 20],
pageSize: 5,
total: 0,
});
function handleSizeChange(val) {
page.pageSize = val;
changeFn(page);
}
function handleCurrentChange(val) {
page.currentPage = val;
changeFn(page);
}
return {
page,
handleSizeChange,
handleCurrentChange,
};
}
export default usePage;
// views/List.vue
import { defineComponent, toRefs } from "@vue/composition-api";
import usePage from "@/hooks/usePage";
import useArticleList from "@/hooks/useArticleList";
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
const { articleList, getList } = useArticleList();
const { page, handleSizeChange, handleCurrentChange } = usePage(getList);
getList(page);
return {
...toRefs(page),
articleList,
getList,
handleSizeChange,
handleCurrentChange,
};
},
});
在hook使用過程中我們也踩過很多坑
hook中的異步問題
因為hook本質(zhì)上就是函數(shù),所以靈活度非常高,尤其是在涉及異步的邏輯中,考慮不全面就很有可能造成很多問題。hook是可以覆蓋異步情況的,但是必須在setup當(dāng)中執(zhí)行時返回有效對象不能被阻塞。
我們總結(jié)了兩種異步的風(fēng)格,通過一個簡單的hook為例
外部沒有其他依賴,只是交付渲染的響應(yīng)變量 對于這種情況,可以通過聲明、對外暴露響應(yīng)變量,在hook中異步修改的方式
// hooks/useWarehouse.js
import { reactive,toRefs } from '@vue/composition-api';
import { queryWarehouse } from '@/mock/index'; // 查詢倉庫的請求
import getParam from '@/utils/getParam'; // 獲得一些參數(shù)的方法
function useWarehouse(admin) {
const warehouse = reactive({ warehouseList: [] });
const param = { id: admin.id, ...getParam() };
const queryList = async () => {
const { list } = await queryWarehouse(param);
list.forEach(goods=>{
// 一些邏輯...
return goods
})
warehouse.warehouseList = list;
};
return { ...toRefs(warehouse), queryList };
}
export default useWarehouse;// components/Warehouse.vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="queryList">queryList</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="goods in warehouseList" :key="goods.id">
{{goods}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { defineComponent } from '@vue/composition-api';
import useWarehouse from '@/hooks/useWarehouse';
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
// 倉庫保管員
const admin = {
id: '1234',
name: '張三',
age: 28,
sex: 'men',
};
const { warehouseList, queryList } = useWarehouse(admin);
return { warehouseList, queryList };
},
});
</script>
外部具有依賴,需要在使用側(cè)進行加工的 可以通過對外暴露Promise的方式,使外部獲得同步操作的能力 在原有例子上拓展,增加一個需要處理的更新時間屬性
// hooks/useWarehouse.js
function useWarehouse(admin) {
const warehouse = reactive({ warehouseList: [] });
const param = { id: admin.id, ...getParam() };
const queryList = async () => {
const { list, updateTime } = await queryWarehouse(param);
list.forEach(goods=>{
// 一些邏輯...
return goods
})
warehouse.warehouseList = list;
return updateTime;
};
return { ...toRefs(warehouse), queryList };
}
export default useWarehouse;// components/Warehouse.vue
<template>
<div>
...
<span>nextUpdateTime:{{nextUpdateTime}}</span>
</div>
</template>
<script>
...
import dayjs from 'dayjs';
export default defineComponent({
setup() {
...
// 倉庫保管員
const admin = {
id: '1234',
name: '張三',
age: 28,
sex: 'men',
};
const { warehouseList, queryList } = useWarehouse(admin);
const nextUpdateTime = ref('');
const interval = 7; // 假設(shè)更新倉庫的時間間隔是7天
const queryHandler = async () => {
const updateTime = await queryList();
nextUpdateTime.value = dayjs(updateTime).add(interval, 'day');
};
return { warehouseList, nextUpdateTime, queryHandler };
},
});
</script>
this的問題
因為setup是beforecreate階段,不能獲取到this,雖然通過setup的第二個參數(shù)context可以獲得一部分的能力。是我們想要操作諸如路由,vuex這樣的能力就收到了限制,最新的router@4、vuex@4都提供了組合式的api。
但是由于vue2的底層限制我們沒有辦法使用這些hook,但是我們可以通過引用實例的方式獲得一定的操縱能力,也可以通過getCurrentInstance獲得組件實例,上面掛載的對象。
由于composition-api中的響應(yīng)式雖然底層原理與vue相同都是通過object.defineproperty改寫屬性實現(xiàn)的,但是具體實現(xiàn)方式存在差異,所以在setup當(dāng)中與vue原生的響應(yīng)式并不互通。這也導(dǎo)致即使我們拿到了相應(yīng)的實例,也沒有辦法監(jiān)聽它們的響應(yīng)式。如果有這方面的需求,只能在選項配置中使用。
總結(jié)
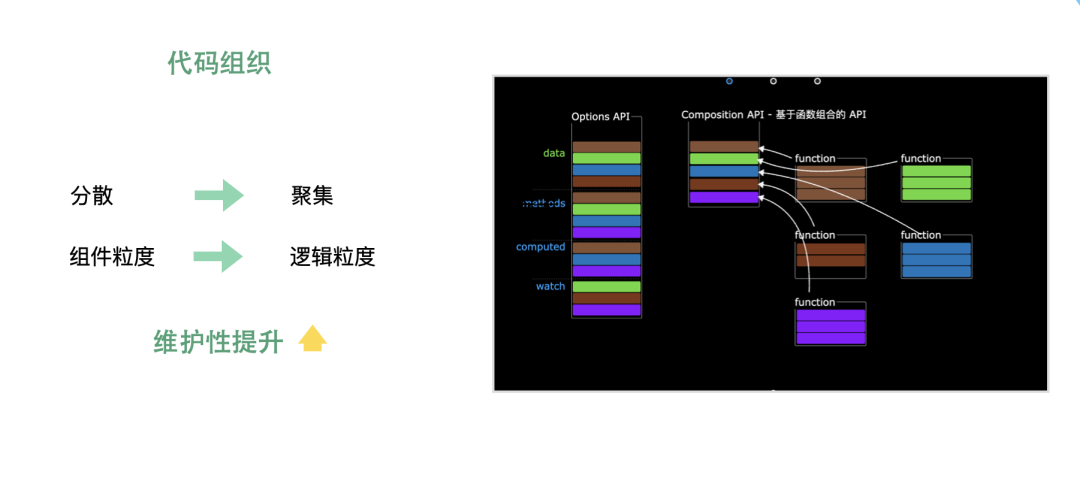
通過vue3組合式、與hook的能力。我們的代碼風(fēng)格有了很大的轉(zhuǎn)變,邏輯更加聚合、純粹。復(fù)用性能力得到了提升。項目整體的維護性有了顯著的提高。這也是我們即便在vue2的項目中,也要使用composition-api引入vue3新特性的原因。若有收獲,就點個贊吧
內(nèi)推社群
我組建了一個氛圍特別好的騰訊內(nèi)推社群,如果你對加入騰訊感興趣的話(后續(xù)有計劃也可以),我們可以一起進行面試相關(guān)的答疑、聊聊面試的故事、并且在你準備好的時候隨時幫你內(nèi)推。下方加 winty 好友回復(fù)「面試」即可。
