異常檢測(Anomaly Detection)綜述
點擊上方“小白學視覺”,選擇加"星標"或“置頂”
重磅干貨,第一時間送達
本文轉(zhuǎn)自|計算機視覺life
導讀
異常檢測是一個發(fā)現(xiàn)“少數(shù)派”的過程,本文將目前深度學習的異常檢測的熱門研究方向進行了分類,并列舉了對應(yīng)的文章,并推薦了值得一讀的8篇新穎論文,幫助大家理解學習異常檢測這一領(lǐng)域。
一、簡介
異常檢測一直是機器學習中一個非常重要的子分支,在各種人工智能落地應(yīng)用例如計算機視覺、數(shù)據(jù)挖掘、NLP中,異常檢測算法都是很熱門的研究方向,特別是大數(shù)據(jù)時代,人工處理數(shù)據(jù)的速度已經(jīng)遠遠趕不上機器了,所以更快地檢測數(shù)據(jù)中的異常情況成為了我們當下非常重要的任務(wù)。在深度學習廣泛的推廣之前,傳統(tǒng)的異常檢測算法有很多,例如高斯擬合,半監(jiān)督學習等等,而在深度學習大火之后,人們也開始研究將深度學習應(yīng)用于各種異常任務(wù)中(也就是Deep Anomaly Detection,以下統(tǒng)稱DAD),并取得了很大的成功,本文將把當下該方向熱門的研究方向分類并列舉了對應(yīng)的文章,希望能幫助大家更好地理解此方向的研究。
二、異常檢測的概念
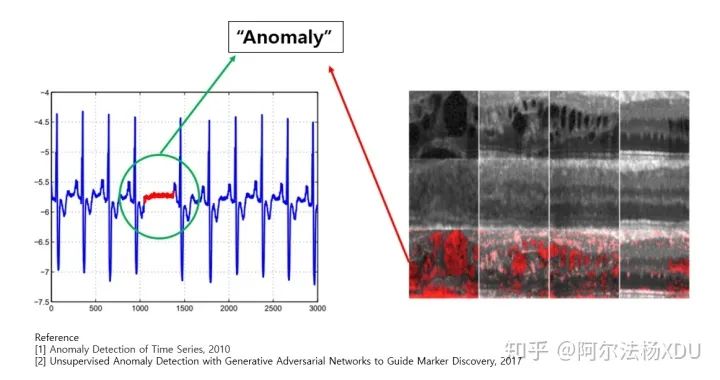
異常檢測,從定義而言就是一種識別不正常情況與挖掘非邏輯數(shù)據(jù)的技術(shù),也叫outliers。例如在計算機視覺的應(yīng)用中,有人在抖音發(fā)表一個視屏,在邊騎車邊打電話,那這就是個不符合規(guī)范的視屏,我們能否采用一些方式來將其檢測出來,再例如在數(shù)據(jù)挖掘領(lǐng)域中,那異常檢測的應(yīng)用就更廣泛了,比如信用卡盜刷,超大金額支出等等。通常情況下,在我們閱讀論文的過程中,異常檢測(Anomaly Detection)也被叫做,Novelty Detection,Outlier Detection,F(xiàn)orgery Detection,Out-of-distribution Detection。在閱讀論文的情況,這些名詞也有輕微的區(qū)別,以計算機視覺為例,如下圖所示。
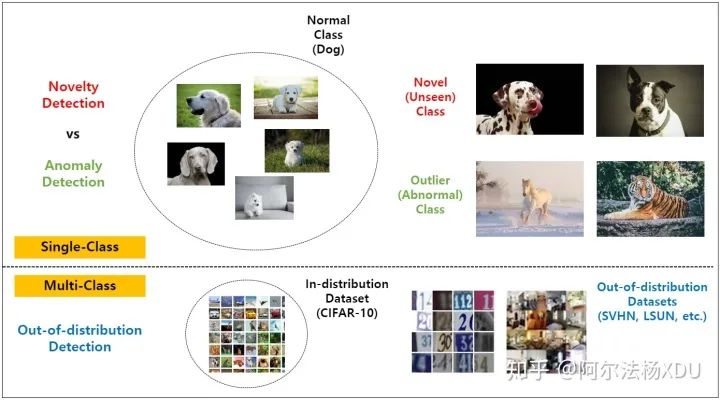
在計算機視覺的基本任務(wù)——圖像分類中,單分類與多分類問題,將幾種概念的細微區(qū)別基本闡述清楚了。Anomaly Detection指在不屬于該分類的數(shù)據(jù)集中,而Novelty是檢測可能屬于該分類但卻沒見過(Unseen)也就是Novel的數(shù)據(jù)集,而OOD(out-of-distribution)則是多分類中不同目標的分布,這些任務(wù)在接下來的論文中,也經(jīng)常有人進行相應(yīng)的研究。
三、異常檢測相關(guān)工作與方向
首先根據(jù)查閱異常檢測方向綜述的文章,我將基于深度學習的異常檢測應(yīng)用方向論文,按照主要的邏輯結(jié)構(gòu)列舉在了下面,我相信這可以更加方便地向你展示異常檢測方向你應(yīng)該怎樣去研究你的論文。
1. DAD研究的主要元素
(1) 異常數(shù)據(jù)集
點集
連續(xù)集
團隊集
(2) 異常檢測模型
無監(jiān)督學習、AutoEncoder、GAN、矩陣因子分解
半監(jiān)督學習、強化學習
Hybrid(混種)、特征提取+傳統(tǒng)算法
單分類神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)
(3) 異常檢測應(yīng)用
詐騙檢測
網(wǎng)絡(luò)侵入檢測
醫(yī)學異常檢測
傳感器網(wǎng)絡(luò)異常檢測
視屏監(jiān)督
物聯(lián)網(wǎng)大數(shù)據(jù)異常檢測
日志異常檢測
工業(yè)危害檢測
2. 異常檢測論文分類
下面也是我根據(jù)參考文獻,把異常檢測論文分成幾個當前研究方向,相當于列出了一個目錄在這里,可供之后方便查看,關(guān)于論文分類的一些概念,我會在下面的介紹中詳細提及。
(1) 數(shù)據(jù)的連續(xù)性
(2) 數(shù)據(jù)標簽的可用性
監(jiān)督學習Supervised Learning
半監(jiān)督學習Semi-supervised Learning
無監(jiān)督學習Unsupervised Learning
(3) 基于訓練對象的模型
深度混種模型Deep Hybrid Model(DHM)
單分類神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)One-Class Neural Networks(OC-NN)
(4) 數(shù)據(jù)異常類型
點集Point
連續(xù)集Contextual
團隊集Collective or Group
(5) 異常檢測輸出類型
異常分數(shù)Anomaly Score
標簽Lable
(6) 異常檢測應(yīng)用
有將近十種異常檢測相關(guān)的應(yīng)用,由于目前對該部分研究較淺,所以之后會考慮單獨寫篇文章來總結(jié)異常檢測方面的應(yīng)用型論文。
四、原始數(shù)據(jù)的連續(xù)性Nature of Input Data
在DAD問題中選擇怎樣的網(wǎng)絡(luò)結(jié)構(gòu)很大部分取自于原始數(shù)據(jù)(raw/input data)的類型,原始數(shù)據(jù)在廣義上我們可以分為連續(xù)型(Sequential)與非連續(xù)型(Non-sequential),如何選擇相應(yīng)的模型,我列舉在下表中。
原始數(shù)據(jù)類型
舉例
DAD模型選擇
連續(xù)型Sequential | 視屏,DNA序列,自然語言文本 | CNN,RNN,LSTM |
非連續(xù)型Non-sequential | 圖片,傳感器 | CNN,AE及其變種 |
DAD在未降維的高維原始數(shù)據(jù)中表現(xiàn)優(yōu)異,成功提取大規(guī)模數(shù)據(jù)的關(guān)系,通常情況下,網(wǎng)絡(luò)越深,提取效果越好,這個部分感興趣的話可以參考下面這篇文章。
Yann LeCun, Yoshua Bengio, and Geoffrey Hinton. Deep learning. nature, 521(7553):436, 2015.
五、數(shù)據(jù)標簽的可用性Availability of Labels
數(shù)據(jù)標簽是非常重要的事情,標簽代表著正常(normal)數(shù)據(jù)或是未見過(unseen/novel)的數(shù)據(jù),對于標簽內(nèi)容的使用同樣是現(xiàn)在異常檢測方向論文重點考慮的事情。異常檢測的模型也可以根據(jù)數(shù)據(jù)標簽的內(nèi)容廣義的分為三類,監(jiān)督,半監(jiān)督和無監(jiān)督。
1. 監(jiān)督Supervised DAD
基于監(jiān)督學習的DAD文章,整理了兩篇醫(yī)學方向的,由于監(jiān)督學習對于標簽內(nèi)容的依賴度過重,所以他對于異常檢測的問題并不是那么合適,所以它并不如半監(jiān)督和無監(jiān)督應(yīng)用地那么廣泛。
Raghavendra Chalapathy, Ehsan Zare Borzeshi, and Massimo Piccardi. An investigation of recurrent neural architectures for drug name recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.07585, 2016a.
Raghavendra Chalapathy, Ehsan Zare Borzeshi, and Massimo Piccardi. Bidirectional lstm-crf for clinical concept extraction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.08373, 2016b.
2. 半監(jiān)督Semi-supervised DAD
由于正常數(shù)據(jù)集比異常數(shù)據(jù)集更好獲得,所以半監(jiān)督學習DAD方法被非常廣泛的使用,擁有了足夠的數(shù)據(jù)集,我們能更好地標出正常數(shù)據(jù),異常數(shù)據(jù),新數(shù)據(jù)的界限,半監(jiān)督學習模型列舉三篇論文。
Drausin Wulsin, Justin Blanco, Ram Mani, and Brian Litt. Semi-supervised anomaly detection for eeg waveforms using deep belief nets. In Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), 2010 Ninth International Conference on, pages 436–441. IEEE, 2010.
Mutahir Nadeem, Ochaun Marshall, Sarbjit Singh, Xing Fang, and Xiaohong Yuan. Semi-supervised deep neural network for network intrusion detection. 2016.
Hongchao Song, Zhuqing Jiang, Aidong Men, and Bo Yang. A hybrid semi-supervised anomaly detection model for high-dimensional data. Computational intelligence and neuroscience, 2017.
3. 無監(jiān)督Unsupervised DAD
傳統(tǒng)機器學習算法其實我感覺更傾向于直接從數(shù)據(jù)集中讓機器去學習一些東西,然后直接用參數(shù)的方式表示出來,異常檢測問題同樣我們也用自動標簽的方式去檢測是否異常,因為有時候可能數(shù)據(jù)難以獲取。自動解碼器是無監(jiān)督DAD的核心,所以這里深度學習的一些神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)大有可為,例如RNN,LSTM等等。我們這里只列舉了一種采用變種半監(jiān)督學習方法的論文,應(yīng)用于異常數(shù)據(jù)降維,表現(xiàn)效果超越很多傳統(tǒng)降維算法,如PCA,Isolation等等。
Aaron Tuor, Samuel Kaplan, Brian Hutchinson, Nicole Nichols, and Sean Robinson. Deep learning for unsupervised insider threat detection in structured cybersecurity data streams. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.00811, 2017.
六、基于訓練對象的模型
按照訓練對象的區(qū)別,我們把訓練模型單獨劃分為兩類,變種模型與單分類神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)。
1. 深度變種模型Deep Hybrid Models(DHM)
Jerone TA Andrews, Edward J Morton, and Lewis D Griffin. Detecting anomalous data using auto-encoders. International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing, 6(1):21, 2016a.
Tolga Ergen, Ali Hassan Mirza, and Suleyman Serdar Kozat. Unsupervised and semi-supervised anomaly detection with lstm neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.09207, 2017.
2. 單分類神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)One-Class Neural Networks(OC-NN)
Raghavendra Chalapathy, Aditya Krishna Menon, and Sanjay Chawla. Anomaly detection using one-class neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.06360, 2018a.
七、數(shù)據(jù)異常類型
1. 點集Point
舉信用卡盜刷的例子,點集異常就是指單筆交易大金額支出,比如你都花1塊2塊的錢,突然有一天消費了1k,那可能就出現(xiàn)了異常情況,但這個方向好像沒有人單獨發(fā)過文章。
2. 連續(xù)集Contextual or Conditional
連續(xù)集就是指上下文相關(guān)的連續(xù)數(shù)據(jù),某一個中間數(shù)據(jù)出現(xiàn)了異常情況,可能引起了梯度消失爆炸等等問題。
Xiuyao Song, Mingxi Wu, Christopher Jermaine, and Sanjay Ranka. Conditional anomaly detection. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 19(5):631–645, 2007.
3. 團隊集Collective or Group
還是信用卡盜刷的例子,如果某天你的信用卡突然短時間內(nèi)不停地消費50元,那機器可能會發(fā)現(xiàn),這些團隊數(shù)據(jù)集的消費出現(xiàn)了異常,這種情況我們也在其他場合經(jīng)常遇到。
Raghavendra Chalapathy, Edward Toth, and Sanjay Chawla. Group anomaly detection using deep generative models. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.04876, 2018b.
Lo¨?c Bontemps, James McDermott, Nhien-An Le-Khac, et al. Collective anomaly detection based on long short-term memory recurrent neural networks. In International Conference on Future Data and Security Engineering, pages 141–152. Springer, 2016.
Daniel B Araya, Katarina Grolinger, Hany F ElYamany, Miriam AM Capretz, and G Bitsuamlak. Collective contextual anomaly detection framework for smart buildings. In Neural Networks (IJCNN), 2016 International Joint Conference on, pages 511–518. IEEE, 2016.
Naifan Zhuang, Tuoerhongjiang Yusufu, Jun Ye, and Kien A Hua. Group activity recognition with differential recurrent convolutional neural networks. In Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on, pages 526–531. IEEE, 2017.
八、idea新穎的論文
[1] Liu W, Luo W, Lian D, et al. Future frame prediction for anomaly detection–a new baseline[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2018: 6536-6545.
[2] Gong D, Liu L, Le V, et al. Memorizing normality to detect anomaly: Memory-augmented deep autoencoder for unsupervised anomaly detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2019: 1705-1714.
[3] Park H, Noh J, Ham B. Learning Memory-guided Normality for Anomaly Detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2020: 14372-14381.
[4] Zhao Y, Deng B, Shen C, et al. Spatio-temporal autoencoder for video anomaly detection[C]//Proceedings of the 25th ACM international conference on Multimedia. 2017: 1933-1941.
[5] Ionescu R T, Khan F S, Georgescu M I, et al. Object-centric auto-encoders and dummy anomalies for abnormal event detection in video[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019: 7842-7851.
[6] Liu W, Luo W, Li Z, et al. Margin Learning Embedded Prediction for Video Anomaly Detection with A Few Anomalies[C]//IJCAI. 2019: 3023-3030.
[7] Sultani W, Chen C, Shah M. Real-world anomaly detection in surveillance videos[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2018: 6479-6488.
[8] Luo W, Liu W, Gao S. A revisit of sparse coding based anomaly detection in stacked rnn framework[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2017: 341-349.
—完—
交流群
歡迎加入公眾號讀者群一起和同行交流,目前有SLAM、三維視覺、傳感器、自動駕駛、計算攝影、檢測、分割、識別、醫(yī)學影像、GAN、算法競賽等微信群(以后會逐漸細分),請掃描下面微信號加群,備注:”昵稱+學校/公司+研究方向“,例如:”張三 + 上海交大 + 視覺SLAM“。請按照格式備注,否則不予通過。添加成功后會根據(jù)研究方向邀請進入相關(guān)微信群。請勿在群內(nèi)發(fā)送廣告,否則會請出群,謝謝理解~

