Serverless 工程實踐 | Serverless 應用開發(fā)觀念的轉變

作者 | 劉宇(江昱)
Serverless 應用開發(fā)觀念的轉變
f = request.files['file']f.save('my_file_path')
一般情況下,一些云平臺的API網關觸發(fā)器會將二進制文件轉換成字符串,不便直接獲取和存儲; 一般情況下,API 網關與 FaaS 平臺之間傳遞的數(shù)據(jù)包有大小限制,很多平臺限制數(shù)據(jù)包大小為 6MB 以內;
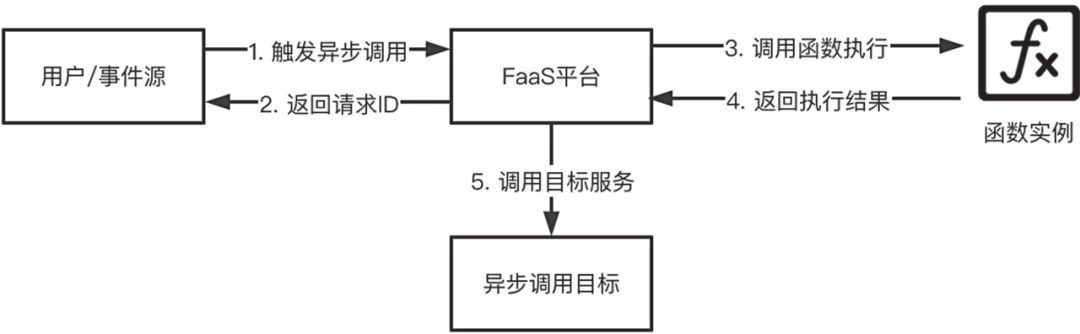
FaaS 平臺大多是無狀態(tài)的,即使存儲到當前實例中,也會隨著實例釋放而使文件丟失。
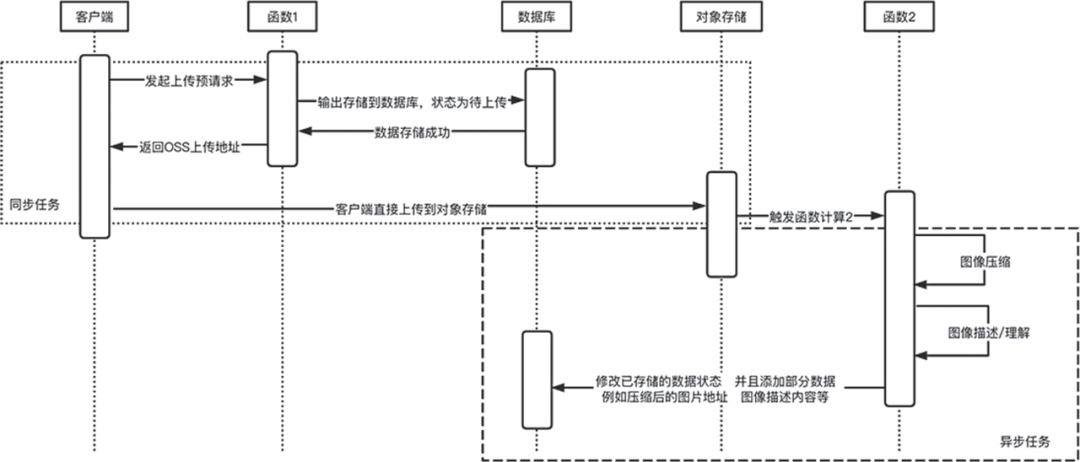
在 Serverless 架構下文件上傳文件示例
AccessKey = {"id": '',"secret": ''}OSSConf = {'endPoint': 'oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com','bucketName': 'bucketName','objectSignUrlTimeOut': 60}#獲取/上傳文件到OSS的臨時地址auth = oss2.Auth(AccessKey['id'], AccessKey['secret'])bucket = oss2.Bucket(auth, OSSConf['endPoint'], OSSConf['bucketName'])#對象存儲操作getUrl = lambda object, method: bucket.sign_url(method, object, OSSConf['objectSignUrlTimeOut'])getSignUrl = lambda object: getUrl(object, "GET")putSignUrl = lambda object: getUrl(object, "PUT")#獲取隨機字符串randomStr = lambda len: "".join(random.sample('abcdefghijklqrstuvwxyz123456789ABCDEFGZSA' * 100, len))
#文件上傳# URI: /file/upload# Method: POST.route('/file/upload', "POST")def postFileUpload():try:pictureBase64 = bottle.request.GET.get('picture', '').split("base64,")[1]object = randomStr(100)with open('/tmp/%s' % object, 'wb') as f:f.write(base64.b64decode(pictureBase64))bucket.put_object_from_file(object, '/tmp/%s' % object)return response({"status": 'ok',})except Exception as e:print("Error: ", e)return response(ERROR['SystemError'], 'SystemError')
@bottle.route('/file/upload/url', "GET")def getFileUploadUrl():try:object = randomStr(100)return response({"upload": putSignUrl(object),"download": 'https://download.xshu.cn/%s' % (object)})except Exception as e:print("Error: ", e)return response(ERROR['SystemError'], 'SystemError')
<div style="width: 70%"><div style="text-align: center"><h3>Web端上傳文件</h3></div><hr><div><p>方案1:上傳到函數(shù)計算進行處理再轉存到對象存儲,這種方法比較直觀,問題是 FaaS 平臺與 API 網關處有數(shù)據(jù)包大小上限,而且對二進制文件處理并不好。</p><input type="file" name="file" id="fileFc"/><input type="button" onclick="UpladFileFC()" value="上傳"/></div><hr><div><p>方案2:直接上傳到對象存儲。流程是先從函數(shù)計算獲得臨時地址并進行數(shù)據(jù)存儲(例如將文件信息存到 Redis 等),然后再從客戶端將文件上傳到對象存儲,之后通過對象存儲觸發(fā)器觸發(fā)函數(shù),從存儲系統(tǒng)(例如已經存儲到 Redis)讀取到信息,再對圖像進行處理。</p><input type="file" name="file" id="fileOss"/><input type="button" onclick="UpladFileOSS()" value="上傳"/></div></div>
function UpladFileFC() {const oFReader = new FileReader();oFReader.readAsDataURL(document.getElementById("fileFc").files[0]);oFReader.onload = function (oFREvent) {const xmlhttp = window.XMLHttpRequest ? (new XMLHttpRequest()) : (newActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"))xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function () {if (xmlhttp.readyState == 4 && xmlhttp.status == 200) {alert(xmlhttp.responseText)}}const url = "https://domain.com/file/upload"xmlhttp.open("POST", url, true);xmlhttp.setRequestHeader("Content-type", "application/json");xmlhttp.send(JSON.stringify({picture: oFREvent.target.result}));}}
function doUpload(bodyUrl) {const xmlhttp = window.XMLHttpRequest ? (new XMLHttpRequest()) : (new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"));xmlhttp.open("PUT", bodyUrl, true);xmlhttp.onload = function () {alert(xmlhttp.responseText)};xmlhttp.send(document.getElementById("fileOss").files[0]);}function UpladFileOSS() {const xmlhttp = window.XMLHttpRequest ? (new XMLHttpRequest()) : (new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"))xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function () {if (xmlhttp.readyState == 4 && xmlhttp.status == 200) {const body = JSON.parse(xmlhttp.responseText)if (body['url']) {doUpload(body['url'])}}}const getUploadUrl = 'https://domain.com/file/upload/url'xmlhttp.open("POST", getUploadUrl, true);xmlhttp.setRequestHeader("Content-type", "application/json");xmlhttp.send();}

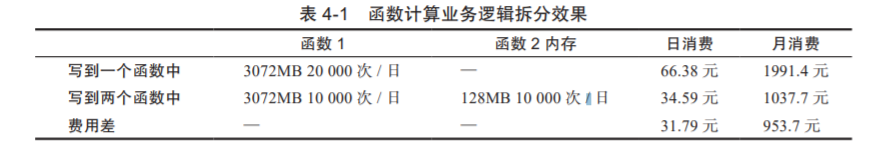
通過上表可以明確看出合理、適當?shù)夭鸱謽I(yè)務會在一定程度上節(jié)約成本。上面例子的成本節(jié)約近 50%。
新書推薦

Serverless 工程實踐系列
評論
圖片
表情
