你的 import 被 webpack 編譯成了什么?
(給前端大學加星標,提升前端技能.)
作者:李永寧
https://juejin.cn/post/6859569958742196237
面試官,問:
import moduleName from 'xxModule'和import('xxModule')經(jīng)過webpack編譯打包后最終變成了什么?在瀏覽器中是怎么運行的?
求職者,答:
嗯。。。,不好意思,我只知道
import可以用來加載模塊,然后第二個import一般用在需要懶加載的地方,其它的就不知道了
這兩個語句我們應(yīng)該經(jīng)常能看到,第一個import就不用說了,可以說現(xiàn)在的前端項目隨處可見,第二個import可以在需要懶加載的地方看到,比如vue-router的懶加載配置,但是大家好像卻從來都沒太深究過這個東西。
前奏
import是es module提供的一個加載模塊的方法,目前主流的瀏覽器也都支持,像現(xiàn)在比較火的vite就是利用了瀏覽器原生支持import的能力來實現(xiàn)的,當然它還有一個server端使用koa實現(xiàn)的。
我們都知道webpack的打包過程大概流程是這樣的:
合并 webpack.config.js和命令行傳遞的參數(shù),形成最終的配置解析配置,得到 entry入口讀取入口文件內(nèi)容,通過 @babel/parse將入口內(nèi)容(code)轉(zhuǎn)換成ast通過 @babel/traverse遍歷ast得到模塊的各個依賴通過 @babel/core(實際的轉(zhuǎn)換工作是由@babel/preset-env來完成的)將ast轉(zhuǎn)換成es5 code通過循環(huán)偽遞歸的方式拿到所有模塊的所有依賴并都轉(zhuǎn)換成 es5
從以上內(nèi)容可以看出來,最終的代碼中肯定是沒有import語句的,因為es5就沒有import;那么我們從哪去找答案呢?有兩個地方,一是webpack源碼,二是打包后的文件,對于今天的問題而言,后者更簡單直接一些。
項目
現(xiàn)在我們來建一個測試項目
初始化項目
mkdir webpack-bundle-analysis && cd webpack-bundle-analysis && npm init -y && npm i webpack webpack-cli -D

webpack.config.js
const path = require('path')
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
// 為了利于分析打包后的代碼,這里選擇開發(fā)模式
mode: 'development',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, './dist'),
filename: 'main.js'
}
}
寫代碼,/src
/src/index.js
/**
* 入口文件,引入 print 方法,并執(zhí)行
* 定義了一個 button 方法,為頁面添加一個按鈕,并為按鈕設(shè)置了一個 onclick 事件,負責動態(tài)引入一個文件
*/
import { print } from './num.js'
print()
function button () {
const button = document.createElement('button')
const text = document.createTextNode('click me')
button.appendChild(text)
button.onclick = e => import('./info.js').then(res => {
console.log(res.log)
})
return button
}
document.body.appendChild(button())
/src/num.js
import { tmpPrint } from './tmp.js'
export function print () {
tmpPrint()
console.log('我是 num.js 的 print 方法')
}
/src/tmp.js
export function tmpPrint () {
console.log('tmp.js print')
}
/src/info.js
export const log = "log info"
打包
項目根目錄執(zhí)行
npx webpack
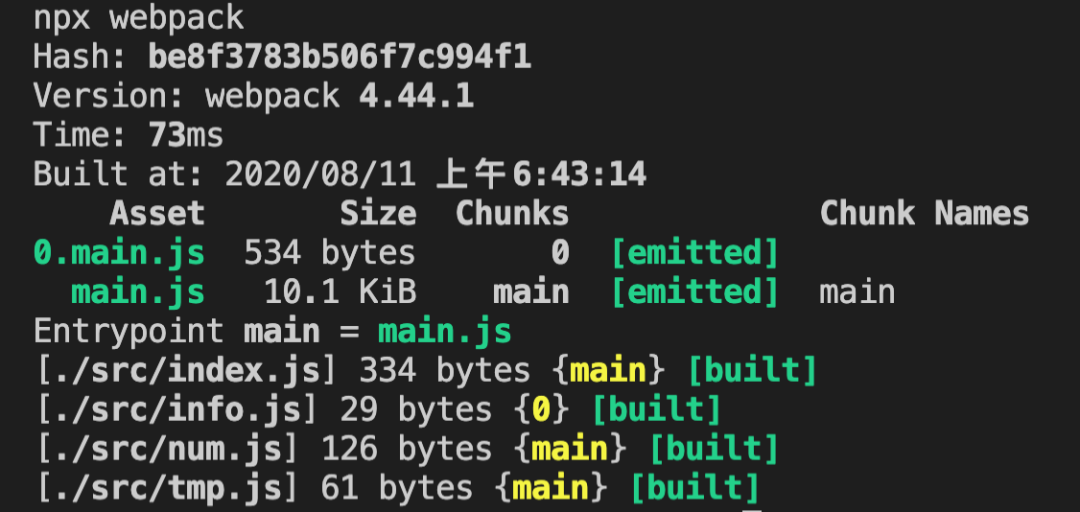
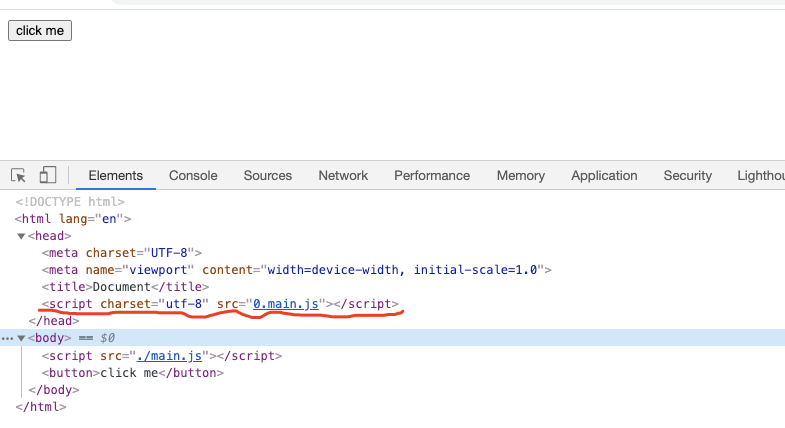
會看到多了一個 dist 目錄,且看輸出結(jié)果,main.js大家肯定都知道是什么,這個是我們在webpack.config.js中配置的輸出的文件名,但是0.main.js呢?這是什么?我們也沒配置,可以先想一下,之后我們從代碼中找答案
模版文件
新建/dist/index.html文件,并引入打包后的main.js
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src = "./main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
在瀏覽器打開 index.html
Network
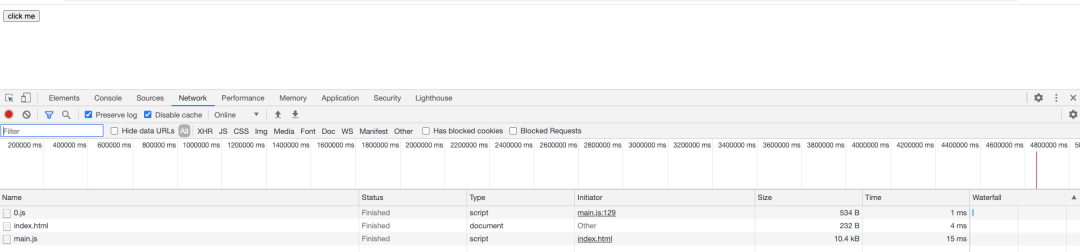
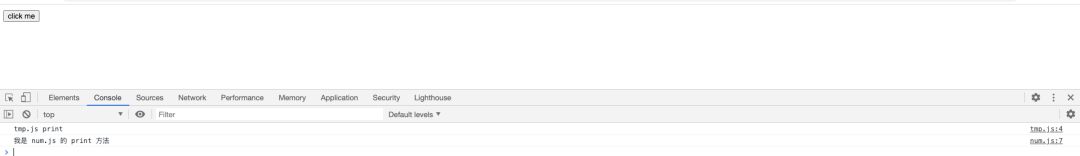
Console
Elements
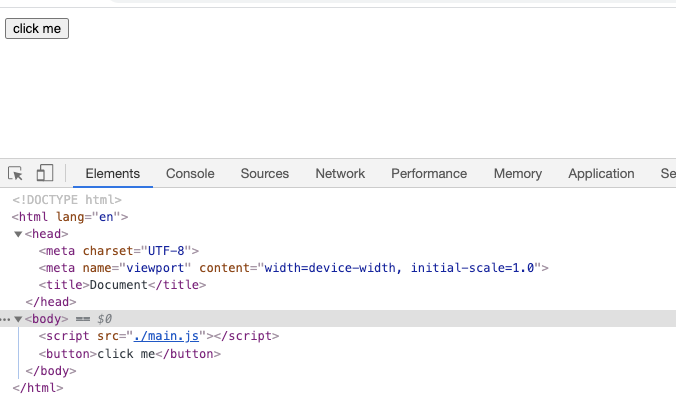
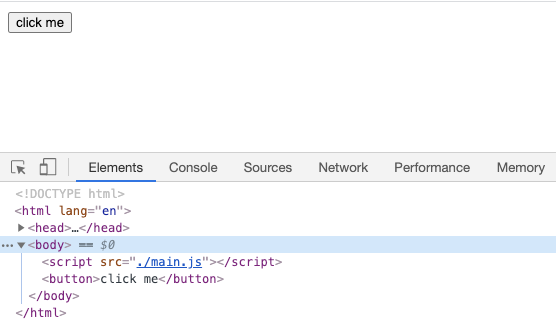
可以看到index.html加載以后資源加載以及代碼的執(zhí)行情況,會發(fā)現(xiàn)我們寫的代碼中的同步邏輯均已執(zhí)行,接下來看看異步邏輯(點擊按鈕),這里為了效果,點擊之前分別清空了Network和Console兩個標簽的內(nèi)容
Network
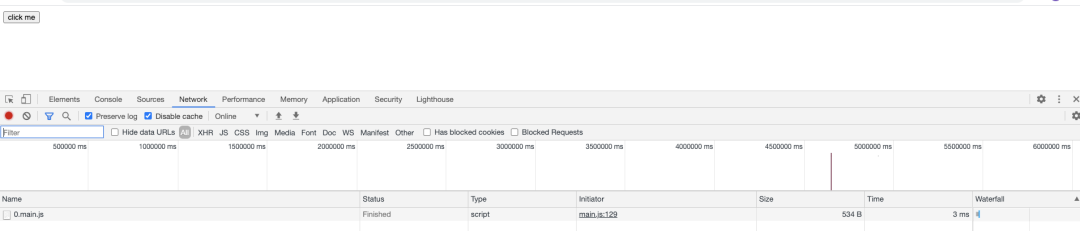
Console
Elements
大家注意看信息,點擊按鈕以后發(fā)生了什么?從表面看似乎是這樣的:
點擊按鈕,在
html中動態(tài)添加了一個script標簽,引入了一個文件(0.main.js),然后發(fā)送兩個一個http請求進行資源加載,加載成功以后在控制臺輸出一段日志。
到這里其實有一部分的答案已經(jīng)出來,
import('xxModule),它提供了一種懶加載的機制,動態(tài)往html中添加script`標簽,然后加載資源并執(zhí)行,那具體是怎么做的呢?
好了,現(xiàn)象我們也看完了,接下來我們?nèi)ピ创a中找答案
源碼分析
我們一步一步來拆解打包后的代碼
首先,我們將打包后的代碼進行折疊,如下
(function (modules) {
// xxxx
})({
// xxx
})
這段代碼是不是很熟悉?就是一個自執(zhí)行函數(shù)
函數(shù)參數(shù)
(function (modules) {
// xxxx
})({
// src/index.js 模塊
"./src/index.js":
(function (module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
var _num_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__ = __webpack_require__("./src/num.js");
Object(_num_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__["print"])()
function button() {
const button = document.createElement('button')
const text = document.createTextNode('click me')
button.appendChild(text)
button.onclick = e => __webpack_require__.e(0)
.then(__webpack_require__.bind(null, "./src/info.js"))
.then(res => {
console.log(res.log)
})
return button
}
document.body.appendChild(button())
//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/index.js?");
}),
// ./src/num.js 模塊
"./src/num.js":
(function (module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
__webpack_require__.d(__webpack_exports__, "print", function () { return print; });
var _tmp_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__ = __webpack_require__("./src/tmp.js");
function print() {
Object(_tmp_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__["tmpPrint"])()
console.log('我是 num.js 的 print 方法')
}
//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/num.js?");
}),
// /src/tmp.js 模塊
"./src/tmp.js":
(function (module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
// eval("__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);\n/* harmony export (binding) */ __webpack_require__.d(__webpack_exports__, \"tmpPrint\", function() { return tmpPrint; });\nfunction tmpPrint () {\n console.log('tmp.js print')\n}\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/tmp.js?");
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
__webpack_require__.d(
__webpack_exports__,
"tmpPrint",
function () {
return tmpPrint;
});
function tmpPrint() {
console.log('tmp.js print')
}
//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/tmp.js?");
})
})
看到這里有沒有很熟悉,再回想一下webpack的打包過程,會發(fā)現(xiàn),webpack將所有的import moduleName from 'xxModule'都變成了一個Map對象,key為文件路徑,value為一個可執(zhí)行的函數(shù),而函數(shù)內(nèi)容其實就是模塊中導出的內(nèi)容,當然,模塊自己也被webpack做了一些處理,接著往下進行。
從打包后Map對象中能找到我們代碼中的各個模塊,以及模塊的內(nèi)容,但是也多了很多不屬于我們編寫的代碼,比如以__webpack_require__開頭的代碼,這些又是什么呢?其實是webpack自定義的一些方法,我們接著往下閱讀
函數(shù)體
以下內(nèi)容為打包后的完整代碼,做了一定的格式化,關(guān)鍵地方都寫了詳細的注釋,閱讀時搜索“入口位置”開始一步一步的閱讀,如果有碰到難以理解的地方可配合單步調(diào)試
/**
* modules = {
* './src/index.js': function () {},
* './src/num.js': function () {},
* './src/tmp.js': function () {}
* }
*/
(function (modules) { // webpackBootstrap
/**
* install a JSONP callback for chunk loading
* 模塊加載成功,更改緩存中的模塊狀態(tài),并且執(zhí)行模塊內(nèi)容
* @param {*} data = [
* [chunkId],
* {
* './src/info.js': function () {}
* }
* ]
*/
function webpackJsonpCallback(data) {
var chunkIds = data[0];
var moreModules = data[1];
// add "moreModules" to the modules object,
// then flag all "chunkIds" as loaded and fire callback
var moduleId, chunkId, i = 0, resolves = [];
for (; i < chunkIds.length; i++) {
chunkId = chunkIds[i];
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(installedChunks, chunkId) && installedChunks[chunkId]) {
resolves.push(installedChunks[chunkId][0]);
}
// 這里將模塊的加載狀態(tài)改為了 0,表示加載完成
installedChunks[chunkId] = 0;
}
for (moduleId in moreModules) {
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(moreModules, moduleId)) {
// 執(zhí)行模塊代碼
modules[moduleId] = moreModules[moduleId];
}
}
if (parentJsonpFunction) parentJsonpFunction(data);
while (resolves.length) {
resolves.shift()();
}
};
// The module cache, 模塊緩存,類似于 commonJS 的 require 緩存機制,只不過這里的 key 是相對路徑
var installedModules = {};
/**
* 定義 chunk 的加載情況,比如 main = 0 是已加載
* object to store loaded and loading chunks
* undefined = chunk not loaded
* null = chunk preloaded/prefetched
* Promise = chunk loading
* 0 = chunk loaded
*/
var installedChunks = {
"main": 0
};
// script path function, 返回需要動態(tài)加載的 chunk 的路徑
function jsonpScriptSrc(chunkId) {
return __webpack_require__.p + "" + chunkId + ".main.js"
}
/**
* The require function
* 接收一個 moduleId,其實就是一個模塊相對路徑,然后查緩存(沒有則添加緩存),
* 然后執(zhí)行模塊代碼,返回模塊運行后的 module.exports
* 一句話總結(jié)就是 加載指定模塊然后執(zhí)行,返回執(zhí)行結(jié)果(module.exports)
*
* __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = "./src/index.js")
*/
function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
// Check if module is in cache
if (installedModules[moduleId]) {
return installedModules[moduleId].exports;
}
/**
* Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
*
* // 示例
* module = installedModules['./src/index.js'] = {
* i: './src/index.js',
* l: false,
* exports: {}
* }
*/
var module = installedModules[moduleId] = {
i: moduleId,
l: false,
exports: {}
};
/**
* Execute the module function
* modules['./src/index.js'] is a function
*/
modules[moduleId].call(module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__);
// Flag the module as loaded
module.l = true;
// Return the exports of the module
return module.exports;
}
// This file contains only the entry chunk.
// The chunk loading function for additional chunks
/**
*
*/
__webpack_require__.e = function requireEnsure(chunkId) {
var promises = [];
// JSONP chunk loading for javascript
// 從緩存中找該模塊
var installedChunkData = installedChunks[chunkId];
// 0 means "already installed".
if (installedChunkData !== 0) {
// 說明模塊沒有安裝
// a Promise means "currently loading".
if (installedChunkData) {
promises.push(installedChunkData[2]);
} else {
// setup Promise in chunk cache
var promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
installedChunkData = installedChunks[chunkId] = [resolve, reject];
});
promises.push(installedChunkData[2] = promise);
// start chunk loading, create script element
var script = document.createElement('script');
var onScriptComplete;
script.charset = 'utf-8';
// 設(shè)置超時時間
script.timeout = 120;
if (__webpack_require__.nc) {
script.setAttribute("nonce", __webpack_require__.nc);
}
// script.src = __webpack_public_path__ + chunkId + main.js, 即模塊路徑
script.src = jsonpScriptSrc(chunkId);
// create error before stack unwound to get useful stacktrace later
var error = new Error();
// 加載結(jié)果處理函數(shù)
onScriptComplete = function (event) {
// avoid mem leaks in IE.
script.onerror = script.onload = null;
clearTimeout(timeout);
var chunk = installedChunks[chunkId];
if (chunk !== 0) {
// chunk 狀態(tài)不為 0 ,說明加載出問題了
if (chunk) {
var errorType = event && (event.type === 'load' ? 'missing' : event.type);
var realSrc = event && event.target && event.target.src;
error.message = 'Loading chunk ' + chunkId + ' failed.\n(' + errorType + ': ' + realSrc + ')';
error.name = 'ChunkLoadError';
error.type = errorType;
error.request = realSrc;
chunk[1](error);
}
installedChunks[chunkId] = undefined;
}
};
// 超時定時器,超時以后執(zhí)行
var timeout = setTimeout(function () {
onScriptComplete({ type: 'timeout', target: script });
}, 120000);
// 加載出錯或者加載成功的處理函數(shù)
script.onerror = script.onload = onScriptComplete;
// 將 script 標簽添加到 head 標簽尾部
document.head.appendChild(script);
}
}
return Promise.all(promises);
};
// expose the modules object (__webpack_modules__)
__webpack_require__.m = modules;
// expose the module cache
__webpack_require__.c = installedModules;
/**
* define getter function for harmony exports
* @param {*} exports = {}
* @param {*} name = 模塊名
* @param {*} getter => 模塊函數(shù)
*
* 在 exports 對象上定義一個 key value,key 為模塊名稱,value 為模塊的可執(zhí)行函數(shù)
* exports = {
* moduleName: module function
* }
*/
__webpack_require__.d = function (exports, name, getter) {
if (!__webpack_require__.o(exports, name)) {
Object.defineProperty(exports, name, { enumerable: true, get: getter });
}
};
/**
* define __esModule on exports
* @param {*} exports = {}
*
* exports = {
* __esModule: true
* }
*/
__webpack_require__.r = function (exports) {
if (typeof Symbol !== 'undefined' && Symbol.toStringTag) {
Object.defineProperty(exports, Symbol.toStringTag, { value: 'Module' });
}
Object.defineProperty(exports, '__esModule', { value: true });
};
// create a fake namespace object
// mode & 1: value is a module id, require it
// mode & 2: merge all properties of value into the ns
// mode & 4: return value when already ns object
// mode & 8|1: behave like require
__webpack_require__.t = function (value, mode) {
if (mode & 1) value = __webpack_require__(value);
if (mode & 8) return value;
if ((mode & 4) && typeof value === 'object' && value && value.__esModule) return value;
var ns = Object.create(null);
__webpack_require__.r(ns);
Object.defineProperty(ns, 'default', { enumerable: true, value: value });
if (mode & 2 && typeof value != 'string') for (var key in value) __webpack_require__.d(ns, key, function (key) { return value[key]; }.bind(null, key));
return ns;
};
// getDefaultExport function for compatibility with non-harmony modules
__webpack_require__.n = function (module) {
var getter = module && module.__esModule ?
function getDefault() { return module['default']; } :
function getModuleExports() { return module; };
__webpack_require__.d(getter, 'a', getter);
return getter;
};
// Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call
__webpack_require__.o = function (object, property) { return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(object, property); };
// __webpack_public_path__
__webpack_require__.p = "";
// on error function for async loading
__webpack_require__.oe = function (err) { console.error(err); throw err; };
/**
* 通過全局屬性存儲異步加載的資源項,打包文件首次加載時如果屬性值不為空,則說明已經(jīng)有資源被加載了,
* 將這些資源同步到installedChunks對象中,避免資源重復(fù)加載,當然也是這句導致微應(yīng)用框架single-spa中的所有子應(yīng)用導出的
* 包名需要唯一,否則一旦異步的重名模塊存在,重名的后續(xù)模塊不會被加載,且顯示的資源是第一個加載的重名模塊,
* 也就是所謂的JS全局作用域的污染
*
* 其實上面說的這個問題,webpack官網(wǎng)已經(jīng)提到了
* https://webpack.docschina.org/configuration/output/#outputjsonpfunction
*/
var jsonpArray = window["webpackJsonp"] = window["webpackJsonp"] || [];
var oldJsonpFunction = jsonpArray.push.bind(jsonpArray);
jsonpArray.push = webpackJsonpCallback;
jsonpArray = jsonpArray.slice();
for (var i = 0; i < jsonpArray.length; i++) webpackJsonpCallback(jsonpArray[i]);
var parentJsonpFunction = oldJsonpFunction;
/**
* 入口位置
* Load entry module and return exports
*/
return __webpack_require__(__webpack_require__.s = "./src/index.js");
})
({
// 代碼中所有的 import moduleName from 'xxModule' 變成了以下的 Map 對象
// /src/index.js 模塊
"./src/index.js":
/**
* @param module = {
* i: './src/index.js',
* l: false,
* exports: {}
*
* @param __webpack_exports__ = module.exports = {}
*
* @param __webpack_require__ => 自定義的 require 函數(shù),加載指定模塊,并執(zhí)行模塊代碼,返回執(zhí)行結(jié)果
*
*/
(function (module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
/**
*
* define __esModule on exports
* __webpack_exports = module.exports = {
* __esModule: true
* }
*/
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
// 加載 ./src/num.js 模塊
var _num_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__ = __webpack_require__("./src/num.js");
Object(_num_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__["print"])()
function button() {
const button = document.createElement('button')
const text = document.createTextNode('click me')
button.appendChild(text)
/**
* 異步執(zhí)行部分
*/
button.onclick = e => __webpack_require__.e(0)
// 模塊異步加載完成后,開始執(zhí)行模塊內(nèi)容 => window["webpackJsonp"].push = window["webpackJsonp"].push = function (data) {}
.then(__webpack_require__.bind(null, "./src/info.js"))
.then(res => {
console.log(res.log)
})
return button
}
document.body.appendChild(button())
//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/index.js?");
}),
// /src/num.js 模塊
"./src/num.js":
/**
* @param module = {
* i: './src/num.js',
* l: false,
* exports: {}
*
* @param __webpack_exports__ = module.exports = {}
*
* @param __webpack_require__ => 自定義的 require 函數(shù),加載指定模塊,并執(zhí)行模塊代碼,返回執(zhí)行結(jié)果
*
*/
(function (module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
/**
*
* define __esModule on exports
* __webpack_exports = module.exports = {
* __esModule: true
* }
*/
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
/**
* module.exports = {
* __esModule: true,
* print
* }
*/
__webpack_require__.d(__webpack_exports__, "print", function () { return print; });
// 加載 ./src/tmp.js 模塊
var _tmp_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__ = __webpack_require__("./src/tmp.js");
function print() {
Object(_tmp_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__["tmpPrint"])()
console.log('我是 num.js 的 print 方法')
}
//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/num.js?");
}),
// /src/tmp.js 模塊
"./src/tmp.js":
/**
* @param module = {
* i: './src/num.js',
* l: false,
* exports: {}
*
* @param __webpack_exports__ = module.exports = {}
*
* @param __webpack_require__ => 自定義的 require 函數(shù),加載指定模塊,并執(zhí)行模塊代碼,返回執(zhí)行結(jié)果
*
*/
(function (module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) {
"use strict";
/**
*
* define __esModule on exports
* __webpack_exports = module.exports = {
* __esModule: true
* }
*/
__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);
/**
* module.exports = {
* __esModule: true,
* tmpPrint
* }
*/
__webpack_require__.d(__webpack_exports__, "tmpPrint", function () { return tmpPrint; });
function tmpPrint() {
console.log('tmp.js print')
}
//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/tmp.js?");
})
});總結(jié)
經(jīng)過以上內(nèi)容的學習,相比對于一開始的問題,答案呼之欲出了吧。
面試官,問:
import moduleName from 'xxModule'和import('xxModule')經(jīng)過webpack編譯打包后最終變成了什么?在瀏覽器中是怎么運行的?
求職者,答:
import經(jīng)過webpack打包以后變成一些Map對象,key為模塊路徑,value為模塊的可執(zhí)行函數(shù);
代碼加載到瀏覽器以后從入口模塊開始執(zhí)行,其中執(zhí)行的過程中,最重要的就是
webpack定義的__webpack_require__函數(shù),負責實際的模塊加載并執(zhí)行這些模塊內(nèi)容,返回執(zhí)行結(jié)果,其實就是讀取Map對象,然后執(zhí)行相應(yīng)的函數(shù);
當然其中的異步方法(import('xxModule'))比較特殊一些,它會單獨打成一個包,采用動態(tài)加載的方式,具體過程:當用戶觸發(fā)其加載的動作時,會動態(tài)的在
head標簽中創(chuàng)建一個script標簽,然后發(fā)送一個http請求,加載模塊,模塊加載完成以后自動執(zhí)行其中的代碼,主要的工作有兩個,更改緩存中模塊的狀態(tài),另一個就是執(zhí)行模塊代碼。
以上內(nèi)容就是這個面試題的一個完整答案。
github: https://github.com/liyongning/webpack-bundle-analysis
點贊和在看就是最大的支持??
