Tomcat源碼學(xué)習(xí)第3篇 - Bootstrap的啟動(dòng)過(guò)程
上一篇我們看了Tomcat中各個(gè)組件的init過(guò)程,初始化賦值好了,那么接下來(lái)就該輪到start了,話(huà)不多說(shuō),馬上進(jìn)入主題~
1. Bootstrap.start()
通過(guò)start方法我們可以看到他是通過(guò)反射調(diào)用了 Catalina.start()方法,按F7跳到這個(gè)類(lèi)里面看一下。
public void start() throws Exception {
if (catalinaDaemon == null) {
init();
}
// 通過(guò)反射調(diào)用 Catalina.start() 方法
Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("start", (Class [])null);
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object [])null);
}

2. Catalina.start()
進(jìn)來(lái)一看,又是熟悉的套娃風(fēng)格,還得繼續(xù)往里面跳轉(zhuǎn)

3. LifecycleBase.start()
還是這個(gè)熟悉的組件生命周期類(lèi),看到這里就仿佛看到了結(jié)局,肯定是跟initInternal這個(gè)方法一樣一層層嵌套進(jìn)去,讓我們走起~
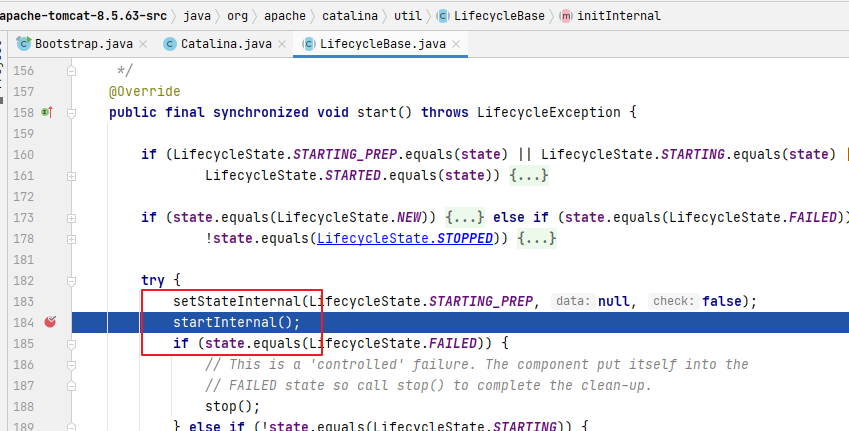
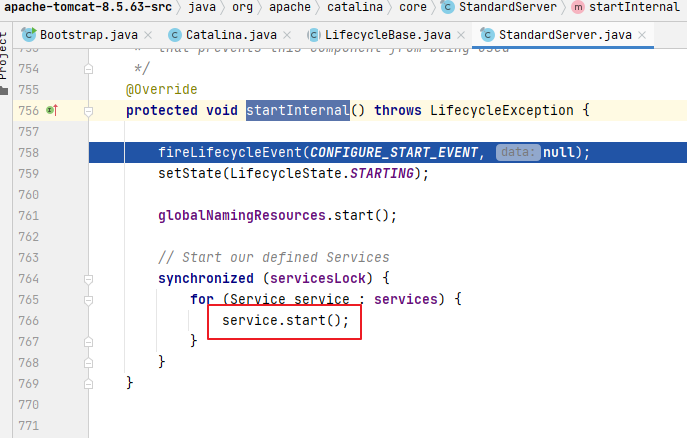
4. StandardServer.startInternal()
之前我們有說(shuō)過(guò)在一個(gè)Tomcat中是可以有多個(gè)service的,所以這里需要遍歷所有的service分別讓各自啟動(dòng)起來(lái)
在server.xml文件中再給他配置一個(gè)<Service>標(biāo)簽即可,如圖所示:
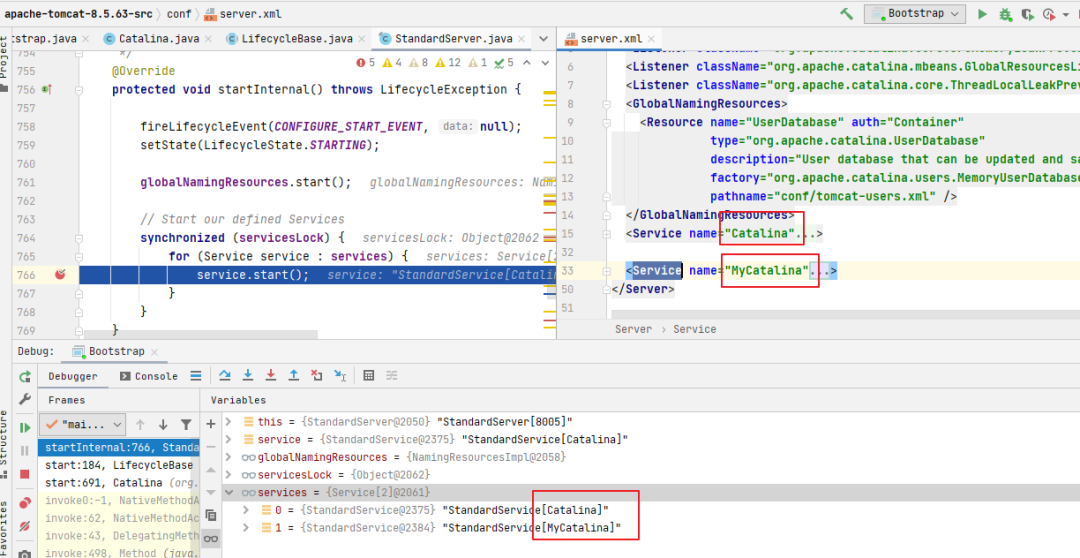
5. StandardService.startInternal()
開(kāi)始進(jìn)入正題了,在這個(gè)方法中我們可以看到它分別做了以下操作:
容器的啟動(dòng): engine.start()連接器的啟動(dòng): connector.start()
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if(log.isInfoEnabled())
log.info(sm.getString("standardService.start.name", this.name));
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// 這里首先啟動(dòng)我們定義的容器 engine
if (engine != null) {
synchronized (engine) {
// 啟動(dòng) engine 子容器
engine.start();
}
}
synchronized (executors) {
for (Executor executor: executors) {
executor.start();
}
}
mapperListener.start();
// Start our defined Connectors second
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector: connectors) {
try {
// If it has already failed, don't try and start it
if (connector.getState() != LifecycleState.FAILED) {
// 啟動(dòng)連接器
connector.start();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"standardService.connector.startFailed",
connector), e);
}
}
}
}
6. StandardEngine.startInternal()
這里直接調(diào)用的ContainerBase.startInternal方法實(shí)現(xiàn)下屬組件的啟動(dòng)
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Log our server identification information
if(log.isInfoEnabled())
log.info( "Starting Servlet Engine: " + ServerInfo.getServerInfo());
// Standard container startup
super.startInternal();
}
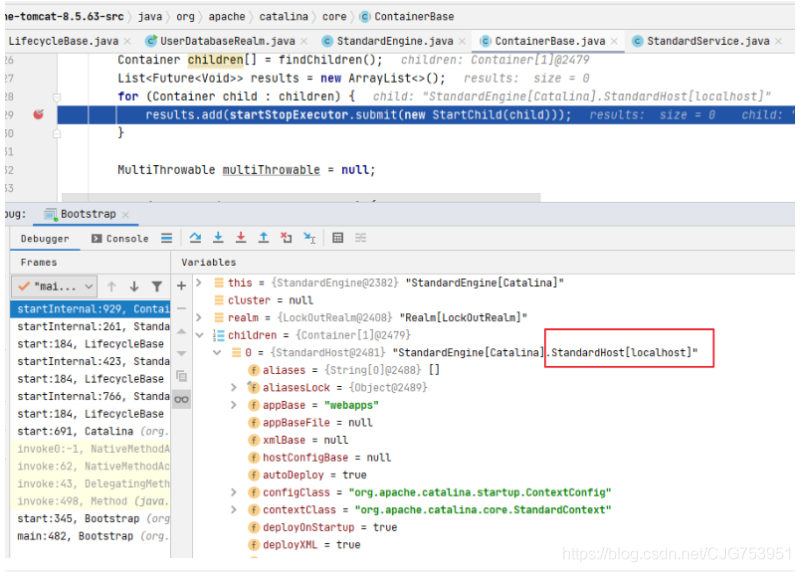
7. ContainerBase.startInternal()
這里使用的是線(xiàn)程池的方式,如果有多個(gè)Host,那么就可以多個(gè)線(xiàn)程并行實(shí)例化Host,加快Tomcat啟動(dòng)速度
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// 啟動(dòng)下屬容器
logger = null;
getLogger();
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if (cluster instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
}
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
}
// 查找并啟動(dòng)子容器,Host 在初始化階段后還是不完整的,需要繼續(xù)封裝,把容器關(guān)系維護(hù)完整
Container children[] = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (Container child : children) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(child)));
}
MultiThrowable multiThrowable = null;
for (Future<Void> result : results) {
try {
result.get();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), e);
if (multiThrowable == null) {
multiThrowable = new MultiThrowable();
}
multiThrowable.add(e);
}
}
if (multiThrowable != null) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"),
multiThrowable.getThrowable());
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
}
// 設(shè)置容器生命周期狀態(tài)
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our thread
threadStart();
}

8. StandardHost.startInternal()
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Set error report valve
String errorValve = getErrorReportValveClass();
if ((errorValve != null) && (!errorValve.equals(""))) {
try {
boolean found = false;
Valve[] valves = getPipeline().getValves();
for (Valve valve : valves) {
if (errorValve.equals(valve.getClass().getName())) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
if(!found) {
Valve valve =
(Valve) Class.forName(errorValve).getConstructor().newInstance();
getPipeline().addValve(valve);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString(
"standardHost.invalidErrorReportValveClass",
errorValve), t);
}
}
super.startInternal();
}
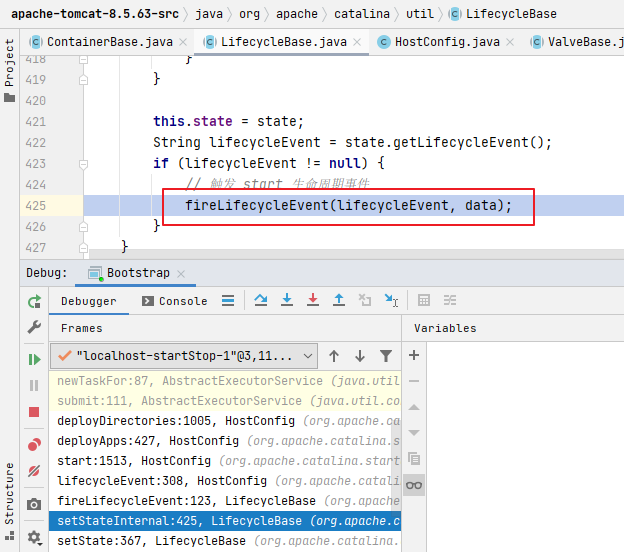
Host的實(shí)例化,是通過(guò)設(shè)置生命周期狀態(tài)來(lái)進(jìn)行促發(fā)生命周期事件fireLifecycleEvent來(lái)執(zhí)行后續(xù)工作的。
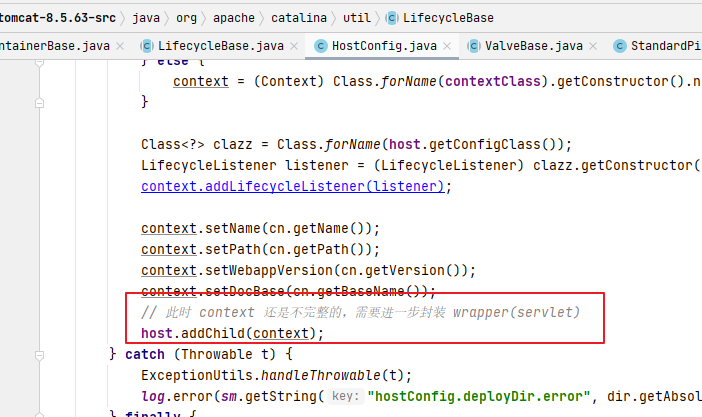
deployApps:處理host下多個(gè)應(yīng)用deployDirectories:處理host下面以目錄方式部署的(results.add(),這里也是以多線(xiàn)程的方式并行執(zhí)行的)host.addChild():這時(shí)才觸發(fā)context實(shí)例核心內(nèi)容context:具體讀取web.xml封裝wrapper過(guò)程使用事件驅(qū)動(dòng)交給ContextConfig(它也是一個(gè)事件監(jiān)聽(tīng)器)



9. MapperListener.startInternal()
public void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// 得到 engine 容器
Engine engine = service.getContainer();
if (engine == null) {
return;
}
// 找到默認(rèn)主機(jī)
findDefaultHost();
// 為當(dāng)前容器以及子容器添加監(jiān)聽(tīng)器
addListeners(engine);
// 注冊(cè)engine下所有的host
Container[] conHosts = engine.findChildren();
for (Container conHost : conHosts) {
Host host = (Host) conHost;
if (!LifecycleState.NEW.equals(host.getState())) {
// 注冊(cè)上下文和包裝器
registerHost(host);
}
}
}
10. Connector.startInternal()
截至到這里,容器的注冊(cè)與啟動(dòng)已經(jīng)完成了,接下來(lái)到連接器的啟動(dòng)了
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Validate settings before starting
if (getPort() < 0) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString(
"coyoteConnector.invalidPort", Integer.valueOf(getPort())));
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
try {
protocolHandler.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStartFailed"), e);
}
}
11. AbstractProtocol.start()
這里對(duì) EndPoint進(jìn)行初始化
public void start() throws Exception {
if (getLog().isInfoEnabled()) {
getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.start", getName()));
}
endpoint.start();
// Start timeout thread
asyncTimeout = new AsyncTimeout();
Thread timeoutThread = new Thread(asyncTimeout, getNameInternal() + "-AsyncTimeout");
int priority = endpoint.getThreadPriority();
if (priority < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY || priority > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) {
priority = Thread.NORM_PRIORITY;
}
timeoutThread.setPriority(priority);
timeoutThread.setDaemon(true);
timeoutThread.start();
}

12. AbstractEndpoint.start()
public final void start() throws Exception {
if (bindState == BindState.UNBOUND) {
bind();
bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_START;
}
startInternal();
}
13. NioEndpoint.bind()
public void bind() throws Exception {
if (!getUseInheritedChannel()) {
// 獲取 nio 通道 channel
serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open();
socketProperties.setProperties(serverSock.socket());
InetSocketAddress addr = (getAddress()!=null?new InetSocketAddress(getAddress(),getPort()):new InetSocketAddress(getPort()));
// 綁定端口,但尚未使用 accept 獲取客戶(hù)端連接
serverSock.socket().bind(addr,getAcceptCount());
} else {
// Retrieve the channel provided by the OS
Channel ic = System.inheritedChannel();
if (ic instanceof ServerSocketChannel) {
serverSock = (ServerSocketChannel) ic;
}
if (serverSock == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(sm.getString("endpoint.init.bind.inherited"));
}
}
serverSock.configureBlocking(true); //mimic APR behavior
// Initialize thread count defaults for acceptor, poller
if (acceptorThreadCount == 0) {
// FIXME: Doesn't seem to work that well with multiple accept threads
acceptorThreadCount = 1;
}
if (pollerThreadCount <= 0) {
//minimum one poller thread
pollerThreadCount = 1;
}
setStopLatch(new CountDownLatch(pollerThreadCount));
// Initialize SSL if needed
initialiseSsl();
selectorPool.open();
}
14. NioEndpoint.startInternal()
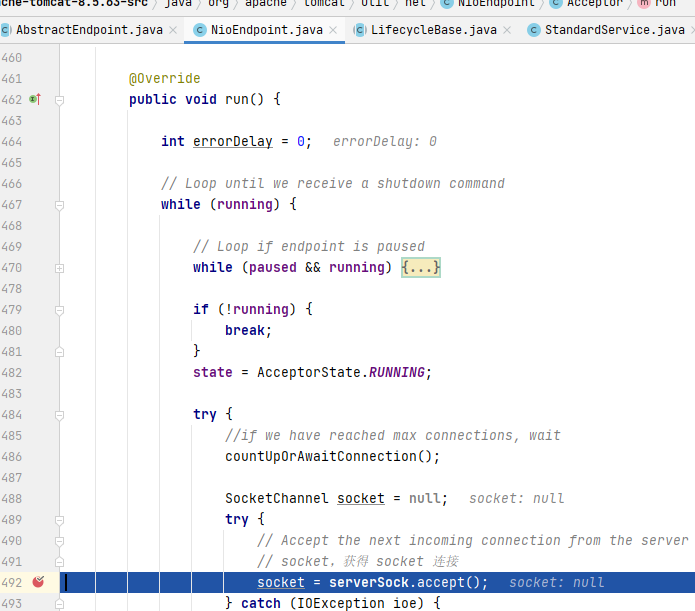
這里通過(guò)startAcceptorThreads啟動(dòng)Accepter線(xiàn)程,該線(xiàn)程用于接收新的Socket連接


總結(jié)

