C語(yǔ)言各數(shù)據(jù)類型的內(nèi)存映像
來源:網(wǎng)路素材
C語(yǔ)言各種數(shù)據(jù)類型的內(nèi)存映像(32位平臺(tái)):
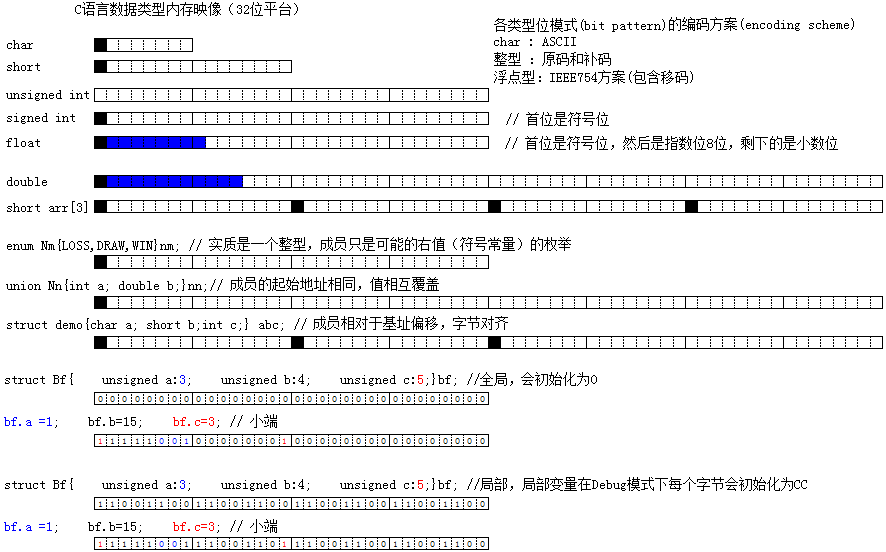
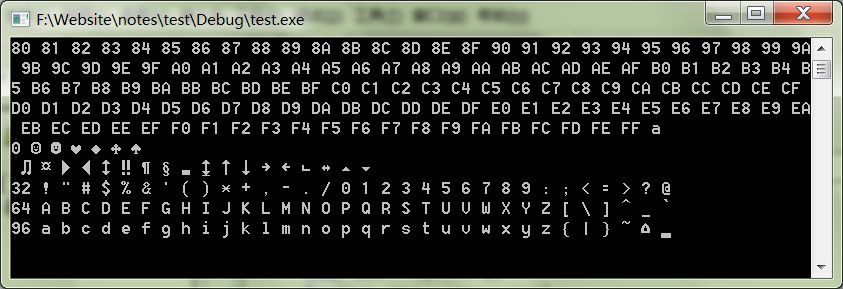
0、signed char
#include <stdio.h>int main(){ char min = 1<<7; char max = (1<<7)-1; for(int i=min;i<=max;i++) if(i<0) printf("%.2X ",(unsigned char)i); else
{ printf("%c ",i); if(i%32==0) printf("\n%d ",i);
}
getchar();
}output:
1、整型的signed和unsigned
#include <stdio.h>int main(){ signed int smin = 1<<31; signed int smax = (1<<31)-1; printf("%d\n",smin); // -2147483648
printf("%d\n",smax); // 2147483647
unsigned int umax = -1; printf("%u\n",umax); // 4294967295
umax = (1<<32)-1; printf("%u\n",umax); // 4294967295}如果一個(gè)表達(dá)式同時(shí)包含signed和unsigned整型,signed會(huì)提升為unsgined,可能會(huì)隱藏一些意想不到的錯(cuò)誤,特別是用在比較運(yùn)算時(shí):
unsigned int a=4294967290; int b=-6;
printf("%d\n",a==b); // 1 , b promotes to unsigned2、double的二進(jìn)制位顯示
#include <stdio.h>void printByte(double d){ int bs = sizeof d; unsigned char *ch = (unsigned char*)&d; for(int i=0;i<bs;i++) printf("%.2X ",*(ch+i));
}int main(){ int n = 0x01020304; if(*(char*)&n == 4) printf("小端:");//小端:
double d = 15.75; // 1111.11, 指數(shù)位值:1023+3
//0 100 0000 0010 1111100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
printByte(d);//00 00 00 00 00 80 2F 40
// 40 2F 80
// 0100 0000 0010 1111 1000 0000
getchar();
}將double分成4部分顯示:
#include <stdio.h>typedef struct packed_double {
unsigned int low32; // 小數(shù)位 低32位
unsigned int low20:20; // 小數(shù)位 低33-52位
unsigned int exp11:11; // 指數(shù)位 低53-63位,移碼1023+二進(jìn)制整數(shù)位-1
unsigned int sign:1; // 符號(hào)位} packed_double;typedef union { double d;
packed_double b;
} packed;int main(){
packed pd;
pd.d = -15.75;
pd.d = 12.3; printf("%u %u %u %u\n",pd.b.sign,pd.b.exp11,pd.b.low20,pd.b.low32);
getchar();
return 0;
}/*
0 1026 1015808 0
*/3、數(shù)組是相同數(shù)據(jù)類型的依次存儲(chǔ)
數(shù)組名是一個(gè)存儲(chǔ)數(shù)據(jù)首元素地址具有常量性質(zhì)的特殊指針,成員是相對(duì)于基址的偏移:
#include <stdio.h>void printArr(short arr[],int len){ for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{ printf("%d ",*(arr+i));
} printf("\n");
}int main(){
short arr[] = {1,3,2}; int len = sizeof arr / sizeof *arr;
printArr(arr,len);
}4、枚舉只是枚舉可以取值的一些符號(hào)常量的一個(gè)特殊整型
#include <stdio.h>int main(){ enum Nm{LOSS,TIE,WIN}nm; // 實(shí)質(zhì)是一個(gè)整型,成員只是可能的右值(符號(hào)常量)的枚舉
nm = LOSS; printf("%d ",nm); // 0
nm = TIE; printf("%d ",nm); // 1
nm = WIN; printf("%d ",nm); // 2
nm = (enum Nm)3;
printf("%d ",nm); // 3
printf("\n%d",sizeof(enum Nm)); // 4
getchar();
}枚舉讓相關(guān)符號(hào)常量?jī)?nèi)聚為一組,相對(duì)于#define,枚舉對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)的描述性更清晰。
5、共用體成員的起始地址相同,共用一塊內(nèi)存空間,值相互覆蓋
#include <stdio.h>int main(){ union Nn{int a; double b;}nn;// 成員的起始地址相同,值相互覆蓋
nn.a = 123; //
printf("起始地址:%X,內(nèi)存空間占用:%d\n",&nn.a,sizeof nn.a);
nn.b = 12.3; printf("起始地址:%X,內(nèi)存空間占用:%d\n",&nn.a,sizeof nn.b);
nn.a = 12; printf("起始地址:%X,內(nèi)存空間占用:%d\n",&nn.a,sizeof nn.a);
getchar();
}/*
起始地址:12FF40,內(nèi)存空間占用:4
起始地址:12FF40,內(nèi)存空間占用:8
起始地址:12FF40,內(nèi)存空間占用:4
*/當(dāng)一些事物具有更多共性,但有少量差異時(shí),可以只用一個(gè)內(nèi)嵌一個(gè)共用體的結(jié)構(gòu)體來描述:
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#define MAXPARTS 12struct Parts{ // 零件
int cost; char supplier[12]; char unit[12] ;
};struct Assembly{ // 裝配件
int n_parts; struct {
char partno[12];
short quan;
}parts[MAXPARTS];
};struct Inventory{ // 存貨類型,或是零件,或是裝配件
char partno[10]; int quan; enum{PART,ASSEMBLY}type; // 存貨類型
union { struct Parts parts;
struct Assembly assembly;
}info;
};int main(){ struct Inventory screen;
strcpy(screen.partno,"p001");
screen.quan = 12;
screen.type = Inventory::PART;
screen.info.parts.cost = 122; strcpy(screen.info.parts.supplier,"hw"); strcpy(screen.info.parts.unit,"pcs");
struct Inventory shell;
strcpy(shell.partno,"a001");
shell.quan = 4;
shell.type = Inventory::ASSEMBLY;
shell.info.assembly.n_parts=22; strcpy(shell.info.assembly.parts[0].partno,"d001");
shell.info.assembly.parts[1].quan = 5; int costs; if(shell.type == Inventory::ASSEMBLY)
costs = shell.info.assembly.n_parts;
printf("%d\n",costs); //22
getchar(); return 0;
}6、結(jié)構(gòu)體是不同數(shù)據(jù)類型的數(shù)據(jù)依次存儲(chǔ)在一起
結(jié)構(gòu)體各數(shù)據(jù)成員的引用可以通過其內(nèi)存大小和字節(jié)對(duì)齊來相對(duì)于基址偏移來計(jì)算。結(jié)構(gòu)體通常用于描述某一事物,用其成員來描述該事物的某些關(guān)鍵屬性。讓該事物既可以用結(jié)構(gòu)體變量整體表示,也可以對(duì)其成員分別引用來處理該事物的各個(gè)屬性。
#include <stdio.h>int main()
{ struct demo{char a; short b;int c;} abc; // 成員相對(duì)于基址偏移,字節(jié)對(duì)齊
abc.b=12; short *p = (short*)((int)&abc+sizeof(short)); // 模擬編譯器計(jì)算第2個(gè)成員的偏移地址
printf("%d %d\n",abc.b,*p); // 12 12
printf("%d\n",sizeof(struct demo));// 8
getchar();
}7、位域是對(duì)整型數(shù)據(jù)的按位處理
(一次可以處理n個(gè)位,1<=n<=整形長(zhǎng)度)
位域(全局)二進(jìn)制位顯示:
#include <stdio.h>void printBinM(unsigned int n){ for(int i=31;i>=0;i--) printf("%d",(n & 1<<i)>>i); printf("\n");
}struct Bf{
unsigned a:3;
unsigned b:4;
unsigned c:5;
}bf;int main(){
bf.a =1;
bf.b=15;
bf.c=3; int *p = (int*)&bf; // 505
printf("%d\n",*p);
printBinM(*p);//00000000000000000000000111111001
getchar();
}位域(局部)二進(jìn)制位顯示:
#include <stdio.h>void printBinM(unsigned int n){ for(int i=31;i>=0;i--) printf("%d",(n & 1<<i)>>i); printf("\n");
}int main(){ struct Bf{
unsigned a:3;
unsigned b:4;
unsigned c:5;
}bf;
bf.a =1;
bf.b=15;
bf.c=3; int *p = (int*)&bf; // -858996231
printf("%d\n",*p);
printBinM(*p);//11001100110011001100000111111001
getchar();
}版權(quán)聲明:本文來源網(wǎng)絡(luò),免費(fèi)傳達(dá)知識(shí),版權(quán)歸原作者所有。如涉及作品版權(quán)問題,請(qǐng)聯(lián)系我進(jìn)行刪除。
???????????????? END ???????????????
關(guān)注我的微信公眾號(hào),回復(fù)“加群”按規(guī)則加入技術(shù)交流群。
點(diǎn)擊“閱讀原文”查看更多分享,歡迎點(diǎn)分享、收藏、點(diǎn)贊、在看。
