自學(xué)鴻蒙應(yīng)用開發(fā)(44)- 秒表應(yīng)用開發(fā)(2)
經(jīng)過幾天的開發(fā),秒表應(yīng)用終于初具規(guī)模了,先看執(zhí)行效果:
指針式秒表組件
下面是自定義指針式模擬秒表組件的實現(xiàn)代碼。具體內(nèi)容參見注釋。
//指針式秒表組件類public class AnalogStopWatch extends Component implements Component.DrawTask {private long start_time = 0; //計時開始時刻,毫秒單位private long millisecond = 0; //計時時間,毫秒單位private boolean running = false;//執(zhí)行狀態(tài)//構(gòu)造函數(shù)public AnalogStopWatch(Context context) {super(context);Initialize(null);}//構(gòu)造函數(shù)public AnalogStopWatch(Context context, AttrSet attrSet) {super(context, attrSet);Initialize(attrSet);}//構(gòu)造函數(shù)public AnalogStopWatch(Context context, AttrSet attrSet, String styleName) {super(context, attrSet, styleName);Initialize(attrSet);}//構(gòu)造函數(shù)public AnalogStopWatch(Context context, AttrSet attrSet, int resId) {super(context, attrSet, resId);Initialize(attrSet);}//獲取運行狀態(tài)public boolean isRunning(){return running;}//獲取當(dāng)前計時時長public long getMiliseconds(){return millisecond;}//根據(jù)目前的運行狀態(tài),開始或停止計時public void start_stop(){if(!running) {start_time = Calendar.getInstance().getTimeInMillis();millisecond = 0;running = true;onRunTimer();}else{running = false;}}//計時Timervoid onRunTimer(){final long delayTime = 100L; //延時時間,毫秒單位millisecond = Calendar.getInstance().getTimeInMillis() - start_time;invalidate(); //更新畫面表示if(running) {//如果處于運行狀態(tài),觸發(fā)下一次延時執(zhí)行TaskDispatcher uiTaskDispatcher = mContext.getUITaskDispatcher();Revocable revocable = uiTaskDispatcher.delayDispatch(new Runnable() {public void run() {onRunTimer();}}, delayTime);}}//歸零public void reset(){if(!running && millisecond > 0) {onResetTimer(); //啟動歸零處理}}//歸零處理void onResetTimer(){final long delayTime = 10L;long second_value = millisecond / 1000 % 60;long minute_value = millisecond / 1000 / 60;if(second_value > 0){millisecond -= 1000; //秒針反轉(zhuǎn)}if(minute_value > 0){millisecond -= 1000 * 60; //分針反轉(zhuǎn)}if(second_value > 0 || minute_value >0) {//如果反轉(zhuǎn)未到位,觸發(fā)下次延時處理TaskDispatcher uiTaskDispatcher = mContext.getUITaskDispatcher();Revocable revocable = uiTaskDispatcher.delayDispatch(new Runnable() {public void run() {onResetTimer();}}, delayTime);}else{millisecond = 0;}invalidate();}public void onDraw(Component component, Canvas canvas){Paint paint = new Paint();RectFloat bound = getBoundRect();Point main_center = bound.getCenter();drawScale(canvas, paint, main_center, getRadius(), 1);drawScaleValue(canvas, paint, main_center, getRadius() * 0.8f,12, 5, (int)(getRadius() * 0.2f));Point center = new Point(main_center.getPointX(),bound.top + getRadius() * 0.6f);float radius = getRadius() / 3;drawScale(canvas, paint, center, radius, 5);drawScaleValue(canvas, paint, center, radius * 0.7f,12, 5, (int)(radius * 0.25f));drawDigitalTime(canvas, paint, main_center.getPointX(),main_center.getPointY() + getRadius() * 0.4f);drawMinute(canvas, center, radius);drawSecond(canvas, bound);}//描畫刻度線private void drawScale(Canvas canvas, Paint paint, Point center, float radius, int scale_interval){paint.setColor(Color.WHITE);float len5sec = radius / 8;float len1sec = radius / 12;float len02sec = radius / 20;paint.setColor(Color.BLACK);for(int i = 0; i < 300; i+= scale_interval){float insideRaduis = radius;if ((i % 25)==0){insideRaduis -= len5sec;paint.setStrokeWidth(radius / 60);}else if((i % 5)==0){insideRaduis -= len1sec;paint.setStrokeWidth(radius / 80);}else{insideRaduis -= len02sec;paint.setStrokeWidth(radius / 120);}drawRadius(canvas, paint, center, insideRaduis, radius, i * Math.PI / 150);}}//描畫全部刻度值private void drawScaleValue(Canvas canvas, Paint paint, Point center, float radius, int count, int offset, int font_size){for(int i = 1; i <= count; i++){drawScaleText(canvas, paint, center, radius, Math.PI * 2 / count * i, offset * i, font_size);}}//描畫秒針private void drawMinute(Canvas canvas, Point center, float radius){Paint paint = new Paint();paint.setColor(Color.RED);paint.setStrokeWidth(radius / 20);paint.setStrokeCap(Paint.StrokeCap.ROUND_CAP);drawRadius(canvas, paint, center, 0, radius * 0.9f, millisecond / 60 * Math.PI * 2 / 60000);float oval_radius = radius / 10;canvas.drawOval(new RectFloat(center.getPointX() - oval_radius, center.getPointY() - oval_radius,center.getPointX() + oval_radius, center.getPointY() + oval_radius),paint);}//描畫分針private void drawSecond(Canvas canvas, RectFloat bound){float radius = getRadius();Paint paint = new Paint();paint.setColor(Color.RED);paint.setStrokeWidth(radius / 40);paint.setStrokeCap(Paint.StrokeCap.ROUND_CAP);drawRadius(canvas, paint, bound.getCenter(), 0, radius * 0.9f, millisecond * Math.PI * 2 / 60000);float oval_radius = radius / 20;Point center = bound.getCenter();canvas.drawOval(new RectFloat(center.getPointX() - oval_radius, center.getPointY() - oval_radius,center.getPointX() + oval_radius, center.getPointY() + oval_radius),paint);}//描畫徑向直線private void drawRadius(Canvas canvas, Paint paint, Point center, float from, float to, double angle){double sin = Math.sin(angle);double cos = Math.cos(angle);canvas.drawLine(new Point(center.getPointX() + (float)(from * sin),center.getPointY() - (float)(from * cos)),new Point(center.getPointX() + (float)(to * sin),center.getPointY() - (float)(to * cos)),paint);}//描畫單一刻度值private void drawScaleText(Canvas canvas, Paint paint, Point center, float radius, double angle, int value, int font_size){double sin = Math.sin(angle);double cos = Math.cos(angle);Font.Builder builder = new Font.Builder("Arial");builder.setWeight(Font.REGULAR);paint.setFont(builder.build());paint.setTextSize(font_size);String text = String.format("%d", value);float width = paint.measureText(text); //計算字符串顯示寬度canvas.drawText(paint, text,center.getPointX() + (float)(radius * sin) - width / 2,center.getPointY() - (float)(radius * cos) + font_size / 3);}//描畫數(shù)字時間private void drawDigitalTime(Canvas canvas, Paint paint, float x, float y){Font.Builder builder = new Font.Builder("Arial");builder.setWeight(Font.REGULAR);paint.setFont(builder.build());int font_size = (int)(getRadius() / 4);paint.setColor(Color.BLUE);paint.setTextSize(font_size);String now = String.format("%02d:%02d:%02d",millisecond/1000/3600, //hourmillisecond/1000/60%60, //minutemillisecond/1000%60); //secondfloat width = paint.measureText(now); //計算字符串顯示寬度canvas.drawText(paint, now, x - width / 2 , y);}//獲取秒表顯示區(qū)域private RectFloat getBoundRect(){float width = getWidth();float height = getHeight();float size = Math.min(width, height);float x_padding = (width - size) / 2;float y_padding = (height - size) / 2;return new RectFloat(x_padding, y_padding, width - x_padding, height - y_padding);}//獲取顯示半徑private float getRadius(){return getBoundRect().getWidth() / 2;}//獲取圓心位置private Point getCenter(){return getBoundRect().getCenter();}//初始化private void Initialize(AttrSet attrSet){addDrawTask(this);}}
在布局中布置指針式秒表組件
在本應(yīng)用的布局中,我們使用了指針式秒表組件、兩個操作按鈕和一個表示計時結(jié)果的Text組件:
<DirectionalLayoutxmlns:ohos="http://schemas.huawei.com/res/ohos"ohos:height="match_parent"ohos:width="match_parent"ohos:orientation="vertical"ohos:alignment="top"><xwg.harmony.stopwatch.AnalogStopWatchohos:id="$+id:analog_stop_watch"ohos:height="300vp"ohos:width="match_parent"/><DirectionalLayoutohos:height="match_content"ohos:width="match_parent"ohos:orientation="horizontal"ohos:alignment="center"ohos:top_margin="5vp"><Componentohos:height="match_parent"ohos:width="0"ohos:weight="1"/><Buttonohos:id="$+id:reset_lap"ohos:height="match_content"ohos:width="0"ohos:weight="5"ohos:text_size="27fp"ohos:text="$string:Reset"ohos:background_element="$graphic:background_button"/><Componentohos:height="match_parent"ohos:width="0"ohos:weight="1"/><Buttonohos:id="$+id:start_stop"ohos:height="match_content"ohos:width="0"ohos:weight="5"ohos:text_size="27fp"ohos:text="$string:Start"ohos:background_element="$graphic:background_button"/><Componentohos:height="match_parent"ohos:width="0"ohos:weight="1"/></DirectionalLayout><Textohos:id="$+id:lap_times"ohos:width="match_parent"ohos:height="match_parent"ohos:text_alignment="horizontal_center"ohos:text_size="30fp"ohos:multiple_lines="true"ohos:scrollable="true"ohos:top_margin="5vp"ohos:left_margin="5vp"ohos:right_margin="5vp"/></DirectionalLayout>
使用指針式秒表組件
以下是在AbilitySlice中使用指針式秒表組件的示例代碼:
public class MainAbilitySlice extends AbilitySlice {AnalogStopWatch stopwatch = null;Text lap_time = null;int record_count = 0;public void onStart(Intent intent) {super.onStart(intent);super.setUIContent(ResourceTable.Layout_ability_main);//秒表組件stopwatch = (AnalogStopWatch)findComponentById(ResourceTable.Id_analog_stop_watch);//計時結(jié)果Text組件lap_time = (Text)findComponentById(ResourceTable.Id_lap_times);//開始或停止按鈕Button start_stop = (Button)findComponentById(ResourceTable.Id_start_stop);//清零或保存結(jié)果按鈕Button reset_lap = (Button)findComponentById(ResourceTable.Id_reset_lap);start_stop.setClickedListener(new Component.ClickedListener() {public void onClick(Component component) {stopwatch.start_stop();if(stopwatch.isRunning()){start_stop.setText(ResourceTable.String_Stop);reset_lap.setText(ResourceTable.String_Lap);clearTime();}else{start_stop.setText(ResourceTable.String_Start);reset_lap.setText(ResourceTable.String_Reset);recordTime();}}});reset_lap.setClickedListener(new Component.ClickedListener() {public void onClick(Component component) {if (stopwatch.isRunning()){recordTime();}else{stopwatch.reset();clearTime();}}});}//清除計時結(jié)果private void clearTime(){lap_time.setText("");record_count = 0;}//記錄當(dāng)前時間private void recordTime(){String lap_string = lap_time.getText();long milliseconds = stopwatch.getMiliseconds();String current_time = String.format("Lap%02d %02d:%02d:%02d.%03d",record_count,milliseconds / 1000 / 60 / 60 % 60, //hourmilliseconds / 1000 / 60 % 60, //minutemilliseconds / 1000 % 60, //secondmilliseconds % 1000); //milisecondlap_time.setText(lap_string + "\n" + current_time);record_count++;}}
我們沒有在指針式秒鐘組件中處理按鈕動作,其目的是為了給使用者提供更大的靈活性。
執(zhí)行結(jié)果如下:
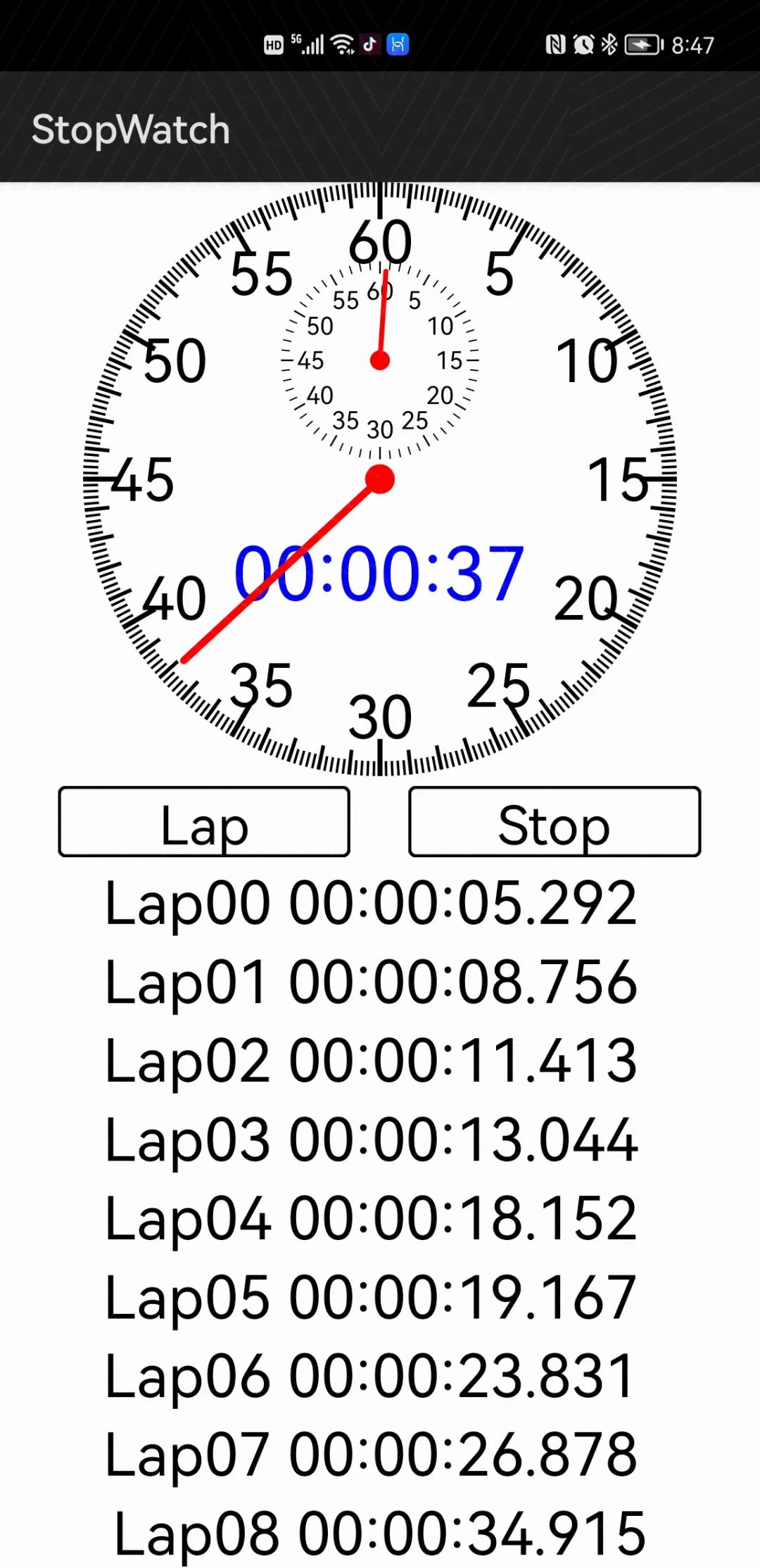
參考代碼
完整代碼可以從以下鏈接下載:
https://github.com/xueweiguo/Harmony/tree/master/StopWatch作者著作介紹
《實戰(zhàn)Python設(shè)計模式》是作者去年3月份出版的技術(shù)書籍,該書利用Python 的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)GUI 工具包tkinter,通過可執(zhí)行的示例對23 個設(shè)計模式逐個進(jìn)行說明。這樣一方面可以使讀者了解真實的軟件開發(fā)工作中每個設(shè)計模式的運用場景和想要解決的問題;另一方面通過對這些問題的解決過程進(jìn)行說明,讓讀者明白在編寫代碼時如何判斷使用設(shè)計模式的利弊,并合理運用設(shè)計模式。

對設(shè)計模式感興趣而且希望隨學(xué)隨用的讀者通過本書可以快速跨越從理解到運用的門檻;希望學(xué)習(xí)Python GUI 編程的讀者可以將本書中的示例作為設(shè)計和開發(fā)的參考;使用Python 語言進(jìn)行圖像分析、數(shù)據(jù)處理工作的讀者可以直接以本書中的示例為基礎(chǔ),迅速構(gòu)建自己的系統(tǒng)架構(gòu)。
覺得本文有幫助?請分享給更多人。
關(guān)注微信公眾號【面向?qū)ο笏伎肌枯p松學(xué)習(xí)每一天!
面向?qū)ο箝_發(fā),面向?qū)ο笏伎迹?/span>
