branch and price求解VRPTW問題代碼詳解
一、前言
記得公眾號很久之前推出過一個branch and price的概念推文,后來小編找到了部分(不完整)的代碼,經(jīng)過研究以后補齊了這部分代碼,能夠運行以后也分享了給大家。詳情可以看:
干貨 | 10分鐘帶你掌握branch and price(分支定價)算法超詳細(xì)原理解析)
干貨 | Branch and Price算法求解VRPTW問題(附JAVA代碼分享)
前陣子一個學(xué)姐問我這個代碼,我看了一下然后發(fā)現(xiàn)自己看不懂了……這幾天剛好要做相關(guān)的課題,又回來惡補了一番。把代碼的邏輯梳理了一遍,今天就寫寫,方便大家學(xué)習(xí)。
二、branch and price
branch and price其實是column generation和branch and bound的結(jié)合。為什么要結(jié)合呢?前面的文章中介紹過,column generation是求解大規(guī)模線性規(guī)劃問題的,注意是線性規(guī)劃問題,不是整數(shù)或者混合整數(shù)規(guī)劃問題。
因此在用column generation求解VRPTW的Set-Partitioning Model的時候,需要先將決策變量由整數(shù)松弛為實數(shù),詳情參見:
干貨 | 10分鐘教你使用Column Generation求解VRPTW的線性松弛模型
那么問題來了,既然column generation只能求解線性松弛模型,求得的解如果恰好是整數(shù)解那還好說。但是大部分情況得到的可能是一個非整數(shù)解,這顯然不是我們VRPTW問題的最終解。
這個時候就需要用到branch and bound去找整數(shù)解了。我記得前面的推文也提到過,branch and bound本身是一個比較通用的算法,只要設(shè)計好問題的branch和bound,即可用來求解該問題。因此branch and bound也可以用來求解整數(shù)規(guī)劃問題,詳情可以參見:
干貨 | 10分鐘帶你全面掌握branch and bound(分支定界)算法-概念篇
干貨 | 10分鐘搞懂branch and bound算法的代碼實現(xiàn)附帶java代碼
branch and bound在求解整數(shù)規(guī)劃模型的時候通過對當(dāng)前模型加約束的方式,來對決策變量進行分支,而支路的lower bound可以通過求解該支路下整數(shù)規(guī)劃模型的線性松弛而獲得。求解一般線性規(guī)劃問題可以用單純形法,但是VRPTW的Set-Partitioning Model線性松弛后是超大規(guī)模的線性規(guī)劃問題,沒法枚舉所有列。因此采用column generation來進行求解。
不知道大家暈了沒有呢!暈的話可以把上面的推文好好看一遍,這些都是經(jīng)過整理的,能節(jié)省你們再去瞎找資料亂學(xué)習(xí)所需要的時間成本。
三、branch and bound
關(guān)于VRPTW的Set-Partitioning Model是這樣的:
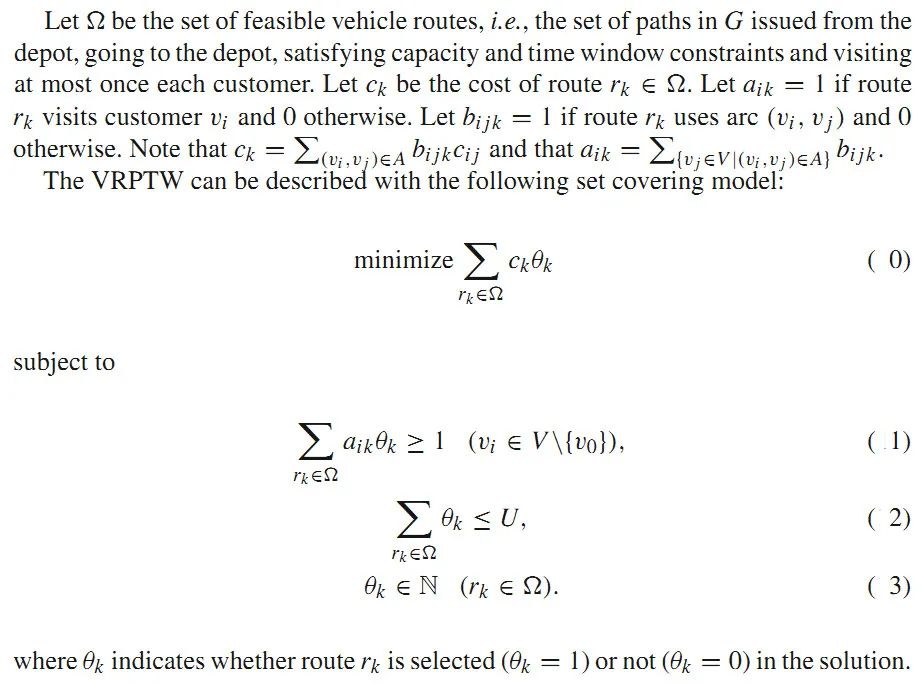
決策變量為整數(shù),我當(dāng)時想著按照branch and bound求解整數(shù)規(guī)劃模型的思路看代碼,結(jié)果半天沒看出個所以然來。因為我沒找到的相關(guān)分支代碼。然后看著看著就懵逼了。最后我問了下學(xué)長怎么進行分支,他一句話點醒了我:你可以按照Set-Partitioning Model進行分支,也可以按照之前的arc-flow model進行分支。
瞬間醒悟,代碼中的分支方式也是采用arc-flow model進行分支的,那么這兩個是怎樣關(guān)聯(lián)起來的呢?其實是靠"邊",Set-Partitioning Model中的一列其實就代表一條路徑:
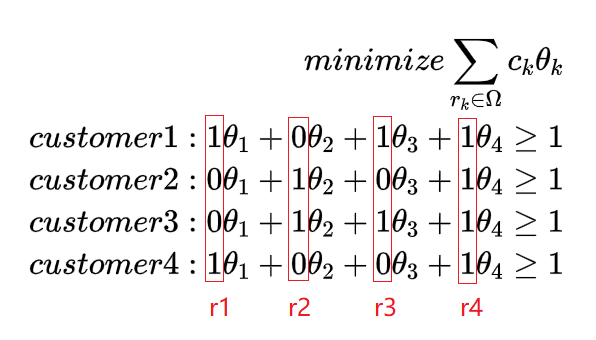
for example,在上面的模型中就包含了4列,每一列就代表一條路徑:
r1 : 1->4
r2 : 2->3
r3 : 1->3
r4 : 1->2->3->4
arc-flow model中的“邊”是不是包含在上面的路徑中了呢,當(dāng)Set-Partitioning Model中的(k=1,2,3,4)不為整數(shù)時,那么這些路徑中相應(yīng)的“邊”在arc-flow model也不是整數(shù)了。這樣兩個模型就可以關(guān)聯(lián)起來了。因此我們在branch and bound的時候也可以按照“邊”來進行分支。
好了,講了這么多,我們來看看代碼是怎么操作的吧!當(dāng)然了我這里也只是講講大概的思路,詳細(xì)的還是自己慢慢去研讀代碼哈。
這里分支樹的搜索采用的是遞歸的方式,遍歷方式是有一個公式進行下一條“邊”的選擇的:
(1) 首先判斷上下界是否達到指定的gap,如果是,則認(rèn)為已經(jīng)完成了搜索,跳出遞歸。
//?check?first?that?we?need?to?solve?this?node.?Not?the?case?if?we?have
//?already?found?a?solution?within?the?gap?precision
if?((upperbound?-?lowerbound)?/?upperbound?????return?true;
(2) 分支節(jié)點為null時,說明為初始狀態(tài),那么分配根節(jié)點,開始進行分支。
//?init
if?(branching?==?null)?{?//?root?node?-?first?call
????//?first?call?-?root?node
????treeBB?newNode?=?new?treeBB();
????newNode.father?=?null;
????newNode.toplevel?=?true;
????newNode.branchFrom?=?-1;
????newNode.branchTo?=?-1;
????newNode.branchValue?=?-1;
????newNode.son0?=?null;
????branching?=?newNode;
}
(3) branchValue<1時,該邊被禁止,否則該邊被選擇(一定要經(jīng)過)。
//?display?some?local?info
if?(branching.branchValue?1)?{
????System.out.println("\nEdge?from?"?+?branching.branchFrom?+?"?to?"
????????????+?branching.branchTo?+?":?forbid");
}?else?{
????System.out.println("\nEdge?from?"?+?branching.branchFrom?+?"?to?"
????????????+?branching.branchTo?+?":?set");
}
(4) 利用column generation計算該節(jié)點的lower bound,注意上面有些邊被禁止了,因此這些邊在column generation中是無法被訪問或者強制要經(jīng)過的。
//?Compute?a?solution?for?this?node?using?Column?generation
columngen?CG?=?new?columngen();
CGobj?=?CG.computeColGen(userParam,?routes);
(5) 新的lower bound出來后,看看要不要更新全局的lower bound(其實這里維護一個全局最小的lower bound也沒啥用,就是拿來輸出看看gap的):
//?update?the?global?lowerBound?when?required
????if?((branching.father?!=?null)?&&?(branching.father.son0?!=?null)
????????????&&?branching.father.toplevel)?{
????????//?all?nodes?above?and?on?the?left?have?been?processed=>?we?can?compute
????????//?a?new?lowerBound
????????lowerbound?=?Math.min(branching.lowestValue,?branching.father.son0.lowestValue);
????????branching.toplevel?=?true;
????}?else?if?(branching.father?==?null)?{
????????//?root?node
????????lowerbound?=?CGobj;
????}
(6) 接下來是常規(guī)操作,判斷l(xiāng)ower bound和upper bound的大小,進行剪枝或者再次分支。如果該分支的lower bound > upperbound,那么cut掉:
if?(branching.lowestValue?>?upperbound)?{
????CG?=?null;
????System.out.println("CUT?|?Lower?bound:?"?+?lowerbound
????????????+?"?|?Upper?bound:?"?+?upperbound?+?"?|?Gap:?"
????????????+?((upperbound?-?lowerbound)?/?upperbound)?+?"?|?BB?Depth:?"
????????????+?depth?+?"?|?Local?CG?cost:?"?+?CGobj?+?"?|?"?+?routes.size()
????????????+?"?routes");
????return?true;?//?cut?this?useless?branch
}
(7) 否則,先判斷column generation找到的解是不是整數(shù)解(所有的邊都不能有小數(shù)):
//?///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//?check?the?(integer)?feasibility.?Otherwise?search?for?a?branching
//?variable
feasible?=?true;
bestEdge1?=?-1;
bestEdge2?=?-1;
bestObj?=?-1.0;
bestVal?=?0;
//?transform?the?path?variable?(of?the?CG?model)?into?edges?variables
for?(i?=?0;?i?2;?i++)?{
????java.util.Arrays.fill(userParam.edges[i],?0.0);
}
for?(route?r?:?routes)?{
????if?(r.getQ()?>?1e-6)?{
????????//?we?consider?only?the?routes?in?the?current?local?solution
????????ArrayList?path?=?r.getpath();?//?get?back?the?sequence?of
????????//?cities?(path?for?this?route)
????????prevcity?=?0;
????????for?(i?=?1;?i?????????????city?=?path.get(i);
????????????userParam.edges[prevcity][city]?+=?r.getQ();?//?convert?into?edges
????????????prevcity?=?city;
????????}
????}
}
//?find?a?fractional?edge
for?(i?=?0;?i?2;?i++)?{
????for?(j?=?0;?j?2;?j++)?{
????????coef?=?userParam.edges[i][j];
????????if?((coef?>?1e-6)?&&?((coef?0.9999999999)?||?(coef?>?1.0000000001)))?{
????????????//?this?route?has?a?fractional?coefficient?in?the?solution?=>
????????????//?should?we?branch?on?this?one?
????????????feasible?=?false;
????????????//?what?if?we?impose?this?route?in?the?solution??Q=1
????????????//?keep?the?ref?of?the?edge?which?should?lead?to?the?largest?change
????????????change?=?Math.min(coef,?Math.abs(1.0?-?coef));
????????????change?*=?routes.get(i).getcost();
????????????if?(change?>?bestObj)?{
????????????????bestEdge1?=?i;
????????????????bestEdge2?=?j;
????????????????bestObj?=?change;
????????????????bestVal?=?(Math.abs(1.0?-?coef)?>?coef)???0?:?1;
????????????}
????????}
????}
}
(8) 如果是整數(shù)解,那么就找到了一個新的可行解,判斷是否更新upper bound:
if?(branching.lowestValue?//?new?incumbant?feasible?solution!
????upperbound?=?branching.lowestValue;
????bestRoutes.clear();
????for?(route?r?:?routes)?{
????????if?(r.getQ()?>?1e-6)?{
????????????route?optim?=?new?route();
????????????optim.setcost(r.getcost());
????????????optim.path?=?r.getpath();
????????????optim.setQ(r.getQ());
????????????bestRoutes.add(optim);
????????}
????}
????System.out.println("OPT?|?Lower?bound:?"?+?lowerbound
????????????+?"?|?Upper?bound:?"?+?upperbound?+?"?|?Gap:?"
????????????+?((upperbound?-?lowerbound)?/?upperbound)?+?"?|?BB?Depth:?"
????????????+?depth?+?"?|?Local?CG?cost:?"?+?CGobj?+?"?|?"?+?routes.size()
????????????+?"?routes");
????System.out.flush();
}?else?{
????System.out.println("FEAS?|?Lower?bound:?"?+?lowerbound
????????????+?"?|?Upper?bound:?"?+?upperbound?+?"?|?Gap:?"
????????????+?((upperbound?-?lowerbound)?/?upperbound)?+?"?|?BB?Depth:?"
????????????+?depth?+?"?|?Local?CG?cost:?"?+?CGobj?+?"?|?"?+?routes.size()
????????????+?"?routes");
}
return?true;
(9) 否則,找一條邊繼續(xù)進行分支(這條邊具體的選擇也會影響分支的速度,選擇看步驟(7)中的 bestEdge1和 bestEdge2),EdgesBasedOnBranching函數(shù)的作用是通過設(shè)置距離矩陣各邊的距離,來禁止或者指定選擇一些邊(比如將一條邊的距離設(shè)置為正無窮,那么該邊就無法訪問了)。這里是先分左支,即該邊被禁止,要移除column generation的RLMP中包含該邊的所有路徑:
//?///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//?branching?(diving?strategy)
//?first?branch?->?set?edges[bestEdge1][bestEdge2]=0
//?record?the?branching?information?in?a?tree?list
treeBB?newNode1?=?new?treeBB();
newNode1.father?=?branching;
newNode1.branchFrom?=?bestEdge1;
newNode1.branchTo?=?bestEdge2;
newNode1.branchValue?=?bestVal;?//?first?version?was?not?with?bestVal
//?but?with?0
newNode1.lowestValue?=?-1E10;
newNode1.son0?=?null;
//?branching?on?edges[bestEdge1][bestEdge2]=0
EdgesBasedOnBranching(userParam,?newNode1,?false);
//?the?initial?lp?for?the?CG?contains?all?the?routes?of?the?previous
//?solution?less(去掉分支的邊)?the?routes?containing?this?arc
ArrayList?nodeRoutes?=?new?ArrayList();
for?(route?r?:?routes)?{
????ArrayList?path?=?r.getpath();
????boolean?accept?=?true;
????if?(path.size()?>?3)?{?//?we?must?keep?trivial?routes
????????//?Depot-City-Depot?in?the?set?to?ensure
????????//?feasibility?of?the?CG
????????prevcity?=?0;
????????for?(j?=?1;?accept?&&?(j?????????????city?=?path.get(j);
????????????if?((prevcity?==?bestEdge1)?&&?(city?==?bestEdge2))
????????????????accept?=?false;
????????????prevcity?=?city;
????????}
????}
????if?(accept)?nodeRoutes.add(r);
}
boolean?ok;
ok?=?BBNode(userParam,?nodeRoutes,?newNode1,?bestRoutes,?depth?+?1);
nodeRoutes?=?null;?//?free?memory
if?(!ok)?{
????return?false;
}
branching.son0?=?newNode1;
(10) 然后是分右支,該支限定該邊一定要經(jīng)過,因此要要移除column generation的RLMP中不包含該邊的所有路徑:
//?second?branch?->?set?edges[bestEdge1][bestEdge2]=1
//?record?the?branching?information?in?a?tree?list
treeBB?newNode2?=?new?treeBB();
newNode2.father?=?branching;
newNode2.branchFrom?=?bestEdge1;
newNode2.branchTo?=?bestEdge2;
newNode2.branchValue?=?1?-?bestVal;?//?first?version:?always?1
newNode2.lowestValue?=?-1E10;
newNode2.son0?=?null;
//?branching?on?edges[bestEdge1][bestEdge2]=1
//?second?branching=>need?to?reinitialize?the?dist?matrix
for?(i?=?0;?i?2;?i++)?{
????System.arraycopy(userParam.distBase[i],?0,?userParam.dist[i],?0,
????????????userParam.nbclients?+?2);
}
//reinitialize了因此需要recur遞歸一下
EdgesBasedOnBranching(userParam,?newNode2,?true);
//?the?initial?lp?for?the?CG?contains?all?the?routes?of?the?previous
//?solution?less?the?routes?incompatible?with?this?arc
ArrayList?nodeRoutes2?=?new?ArrayList();
for?(route?r?:?routes)?{
????ArrayList?path?=?r.getpath();
????boolean?accept?=?true;
????if?(path.size()?>?3)?{?//?we?must?keep?trivial?routes
????????//?Depot-City-Depot?in?the?set?to?ensure
????????//?feasibility?of?the?CG
????????prevcity?=?0;
????????for?(i?=?1;?accept?&&?(i?????????????city?=?path.get(i);
????????????if?(userParam.dist[prevcity][city]?>=?userParam.verybig?-?1E-6)?accept?=?false;
????????????prevcity?=?city;
????????}
????}
????if?(accept)?nodeRoutes2.add(r);
}
ok?=?BBNode(userParam,?nodeRoutes2,?newNode2,?bestRoutes,?depth?+?1);
nodeRoutes2?=?null;
//?update?lowest?feasible?value?of?this?node
branching.lowestValue?=?Math.min(newNode1.lowestValue,?newNode2.lowestValue);
return?ok;
branch and bound的代碼就到這了,是不是非常簡單呢!細(xì)節(jié)上礙于篇幅我就不多講了。大家可以慢慢看代碼,不懂在留言區(qū)提出來就好了。
四、column generation
這部分分為Master problem和pricing problem,這兩部分的內(nèi)容公眾號已經(jīng)介紹過了。Master problem的代碼基本上是固定的框架,直接拿過來用就好了。而pricing problem的代碼用的是labeling的算法。
注意pricing problem找路徑時,是要結(jié)合之前branch and bound禁止or已經(jīng)選擇的邊進行最短路的尋找,關(guān)于這部分的內(nèi)容可以參照:
干貨 | VRPTW子問題ESPPRC的介紹及其求解算法的C++代碼
最短路問題與標(biāo)號算法(label correcting algorithm)研究(1) - 開篇介紹
最短路問題與標(biāo)號算法(label correcting algorithm)研究(2) - 最短路徑問題簡介
最短路問題與標(biāo)號算法(label correcting algorithm)研究(3)
最短路問題與標(biāo)號算法(label correcting algorithm)研究(4)
五、代碼下載
參見這篇推文:
干貨 | Branch and Price算法求解VRPTW問題(附JAVA代碼分享)
這篇推文包含的內(nèi)容不多,但是如果你剛好在學(xué)習(xí)branch and price算法,不妨看看這個,看看代碼,相信對你會有所幫助的哦。國內(nèi)這塊的資料和代碼都太少了,大佬們的代碼又長又臭,壓根看不下去。

看在我寫了這么多的份上,能不能幫我點個在看呀~
推薦閱讀:
干貨 | 想學(xué)習(xí)優(yōu)化算法,不知從何學(xué)起?
干貨 | 運籌學(xué)從何學(xué)起?如何快速入門運籌學(xué)算法?
干貨 | 學(xué)習(xí)算法,你需要掌握這些編程基礎(chǔ)(包含JAVA和C++)
干貨 | 算法學(xué)習(xí)必備訣竅:算法可視化解密

