常見的SQL面試題:經典50例
作者:sh_c_2450957609
blog.csdn.net/u010565545/article/details/100785261
SQL基礎知識整理
select 查詢結果,如: [學號,平均成績:組函數(shù)avg(成績)]from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據,如: [涉及到成績:成績表score]where 查詢條件,如: [b.課程號='0003' and b.成績>80]group by 分組,如: [每個學生的平均:按學號分組](oracle,SQL server中出現(xiàn)在select 子句后的非分組函數(shù),必須出現(xiàn)在group by子句后出現(xiàn)),MySQL中可以不用having 對分組結果指定條件,如: [大于60分]order by 對查詢結果排序,如: [增序: 成績 ASC / 降序: 成績 DESC];limit 使用limt子句返回topN(對應這個問題返回的成績前兩名),如: [ limit 2 ==>從0索引開始讀取2個]limit==>從0索引開始[0,N-1]
select * from table limit 2,1;
-- 含義是跳過2條取出1條數(shù)據,limit后面是從第2條開始讀,讀取1條信息,即讀取第3條數(shù)據
select * from table limit 2 offset 1;
-- 含義是從第1條(不包括)數(shù)據開始取出2條數(shù)據,limit后面跟的是2條數(shù)據,offset后面是從第1條開始讀取,即讀取第2,3條
組函數(shù): 去重 distinct() 統(tǒng)計總數(shù)sum() 計算個數(shù)count() 平均數(shù)avg() 最大值max() 最小數(shù)min()
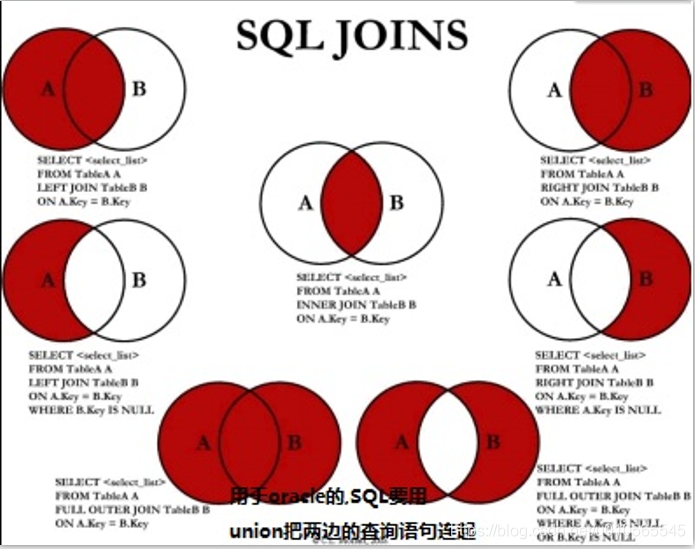
多表連接: 內連接(省略默認inner) join ...on..左連接left join tableName as b on a.key ==b.key右連接right join 連接union(無重復(過濾去重))和union all(有重復[不過濾去重])
union 并集 union all(有重復) oracle(SQL server)數(shù)據庫
intersect 交集 minus(except) 相減(差集)
oracle
一、數(shù)據庫對象:表(table) 視圖(view) 序列(sequence) 索引(index) 同義詞(synonym)
1. 視圖: 存儲起來的 select 語句
create view emp_vw
as
select employee_id, last_name, salary
from employees
where department_id = 90;
select * from emp_vw;
可以對簡單視圖進行 DML 操作
update emp_vw
set last_name = 'HelloKitty'
where employee_id = 100;
select * from employees
where employee_id = 100;
1). 復雜視圖
create view emp_vw2
as
select department_id, avg(salary) avg_sal
from employees
group by department_id;
select * from emp_vw2;
復雜視圖不能進行 DML 操作
update emp_vw2
set avg_sal = 10000
where department_id = 100;
2. 序列:用于生成一組有規(guī)律的數(shù)值。(通常用于為主鍵設置值)
create sequence emp_seq1
start with 1
increment by 1
maxvalue 10000
minvalue 1
cycle
nocache;
select emp_seq1.currval from dual;
select emp_seq1.nextval from dual;
問題:裂縫,原因:
當多個表共用同一個序列時。 rollback 發(fā)生異常
create table emp1(
id number(10),
name varchar2(30)
);
insert into emp1
values(emp_seq1.nextval, '張三');
select * from emp1;
3. 索引:提高查詢效率
自動創(chuàng)建:Oracle 會為具有唯一約束(唯一約束,主鍵約束)的列,自動創(chuàng)建索引
create table emp2(
id number(10) primary key,
name varchar2(30)
)
手動創(chuàng)建
create index emp_idx
on emp2(name);
create index emp_idx2
on emp2(id, name);
4. 同義詞
create synonym d1 for departments;
select * from d1;
5. 表:
DDL :數(shù)據定義語言 create table .../ drop table ... / rename ... to..../ truncate table.../alter table ...
DML : 數(shù)據操縱語言
insert into ... values ...
update ... set ... where ...
delete from ... where ...
【重要】
select ...組函數(shù)(MIN()/MAX()/SUM()/AVG()/COUNT())from ...join ... on ...左外連接:left join ... on ... 右外連接: right join ... on ...where ...group by ...(oracle,SQL server中出現(xiàn)在select 子句后的非分組函數(shù),必須出現(xiàn)在 group by子句后)having ...用于過濾 組函數(shù)order by ...asc 升序, desc 降序limit (0,4)限制N條數(shù)據 如: topN數(shù)據
union 并集 union all(有重復) intersect 交集 minus 相減
DCL : 數(shù)據控制語言 commit : 提交 / rollback : 回滾 / 授權grant...to... /revoke

索引


何時創(chuàng)建索引:


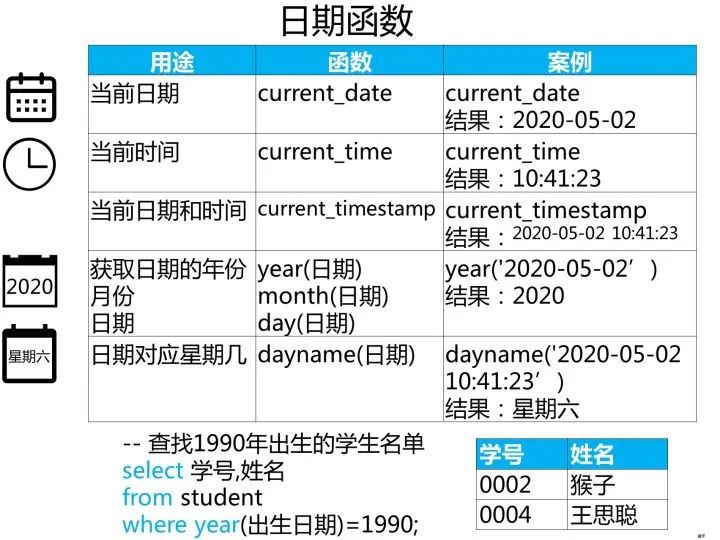
一、
select employee_id, last_name, salary, department_id
from employees
where department_id in (70, 80) --> 70:1 80:34
union 并集 union all(有重復部分) intersect 交集 minus 相減
select employee_id, last_name, salary, department_id
from employees
where department_id in (80, 90) --> 90:4 80:34
問題:查詢工資大于149號員工工資的員工的信息
select *
from employees
where salary > (
select salary
from employees
where employee_id = 149
)
問題:查詢與141號或174號員工的manager_id和department_id相同的其他員工的employee_id, manager_id, department_id
select employee_id, manager_id, department_id
from employees
where manager_id in (
select manager_id
from employees
where employee_id in(141, 174)
) and department_id in (
select department_id
from employees
where employee_id in(141, 174)
) and employee_id not in (141, 174);
select employee_id, manager_id, department_id
from employees
where (manager_id, department_id) in (
select manager_id, department_id
from employees
where employee_id in (141, 174)
) and employee_id not in(141, 174);
from 子句中使用子查詢
select max(avg(salary))
from employees
group by department_id;
select max(avg_sal)
from (
select avg(salary) avg_sal
from employees
group by department_id
) e
問題:返回比本部門平均工資高的員工的last_name, department_id, salary及平均工資
select last_name, department_id, salary, (select avg(salary) from employees where department_id = e1.department_id)
from employees e1
where salary > (
select avg(salary)
from employees e2
where e1.department_id = e2.department_id
)
select last_name, e1.department_id, salary, avg_sal
from employees e1, (
select department_id, avg(salary) avg_sal
from employees
group by department_id
) e2
where e1.department_id = e2.department_id
and e1.salary > e2.avg_sal;
case...when ... then... when ... then ... else ... end
查詢:若部門為10 查看工資的 1.1 倍,部門號為 20 工資的1.2倍,其余 1.3 倍
SELECT
employee_id,
last_name,
salary,
CASE
department_id
WHEN 10 THEN
salary * 1.1
WHEN 20 THEN
salary * 1.2 ELSE salary * 1.3
END "new_salary"
FROM
employees;
SELECT
employee_id,
last_name,
salary,
decode( department_id, 10, salary * 1.1, 20, salary * 1.2, salary * 1.3 ) "new_salary"
FROM
employees;
問題:顯式員工的employee_id,last_name和location。其中,若員工department_id與location_id為1800的department_id相同,則location為’Canada’,其余則為’USA’。
select employee_id, last_name, case department_id when (
select department_id
from departments
where location_id = 1800
) then 'Canada' else 'USA' end "location"
from employees;
問題:查詢員工的employee_id,last_name,要求按照員工的department_name排序
select employee_id, last_name
from employees e1
order by (
select department_name
from departments d1
where e1.department_id = d1.department_id
)
SQL 優(yōu)化:能使用 EXISTS 就不要使用 IN
問題:查詢公司管理者的employee_id,last_name,job_id,department_id信息
select employee_id, last_name, job_id, department_id
from employees
where employee_id in (
select manager_id
from employees
)
select employee_id, last_name, job_id, department_id
from employees e1
where exists (
select 'x'
from employees e2
where e1.employee_id = e2.manager_id
)
問題:查詢departments表中,不存在于employees表中的部門的department_id和department_name
select department_id, department_name
from departments d1
where not exists (
select 'x'
from employees e1
where e1.department_id = d1.department_id
)
更改 108 員工的信息: 使其工資變?yōu)樗诓块T中的最高工資, job 變?yōu)楣局衅骄べY最低的 job
update employees e1
set salary = (
select max(salary)
from employees e2
where e1.department_id = e2.department_id
), job_id = (
select job_id
from employees
group by job_id
having avg(salary) = (
select min(avg(salary))
from employees
group by job_id
)
)
where employee_id = 108;
刪除 108 號員工所在部門中工資最低的那個員工.
delete from employees e1
where salary = (
select min(salary)
from employees
where department_id = (
select department_id
from employees
where employee_id = 108
)
)
select * from employees where employee_id = 108;
select * from employees where department_id = 100
order by salary;
rollback;
常見的SQL面試題:經典50題
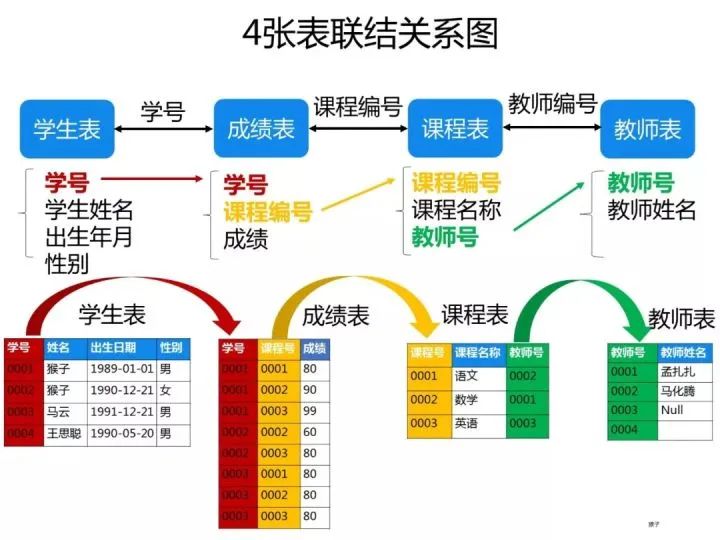
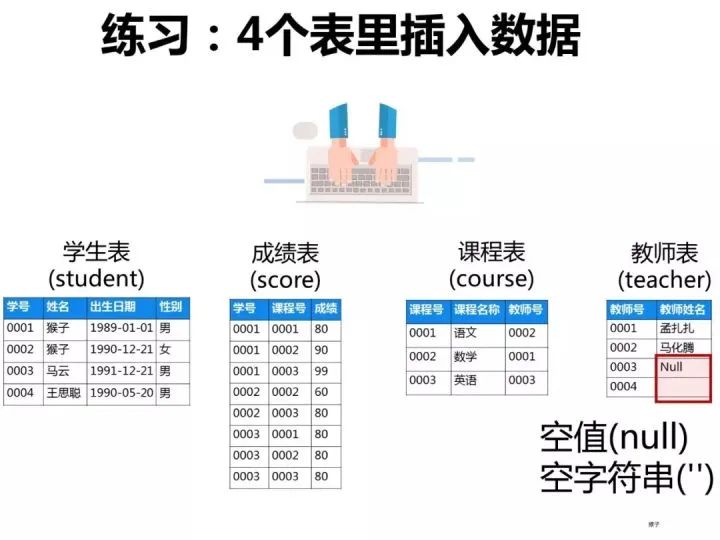
已知有如下4張表:
學生表:student(學號,學生姓名,出生年月,性別) 成績表:score(學號,課程號,成績) 課程表:course(課程號,課程名稱,教師號) 教師表:teacher(教師號,教師姓名)
根據以上信息按照下面要求寫出對應的SQL語句。(搜索公眾號Java知音,回復“2021”,送你一份Java面試題寶典)
ps:這些題考察SQL的編寫能力,對于這類型的題目,需要你先把4張表之間的關聯(lián)關系搞清楚了,最好的辦法是自己在草稿紙上畫出關聯(lián)圖,然后再編寫對應的SQL語句就比較容易了。下圖是我畫的這4張表的關系圖,可以看出它們之間是通過哪些外鍵關聯(lián)起來的:
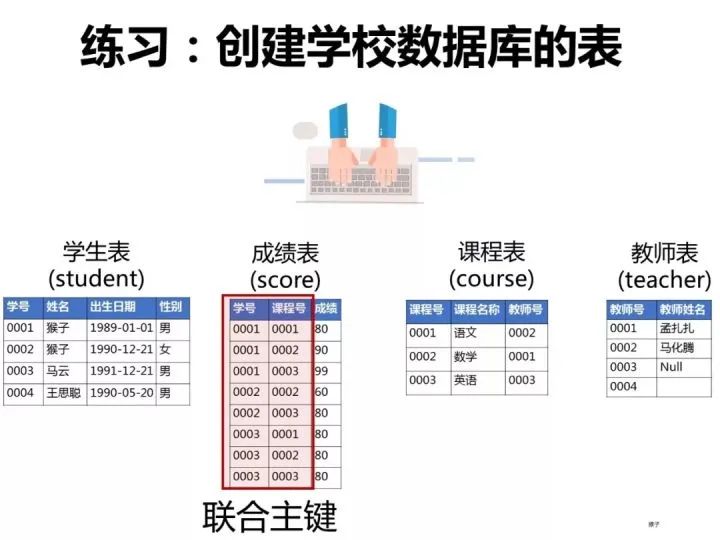
一、創(chuàng)建數(shù)據庫和表
為了演示題目的運行過程,我們先按下面語句在客戶端navicat中創(chuàng)建數(shù)據庫和表。
如何你還不懂什么是數(shù)據庫,什么是客戶端navicat,可以先學習這個:
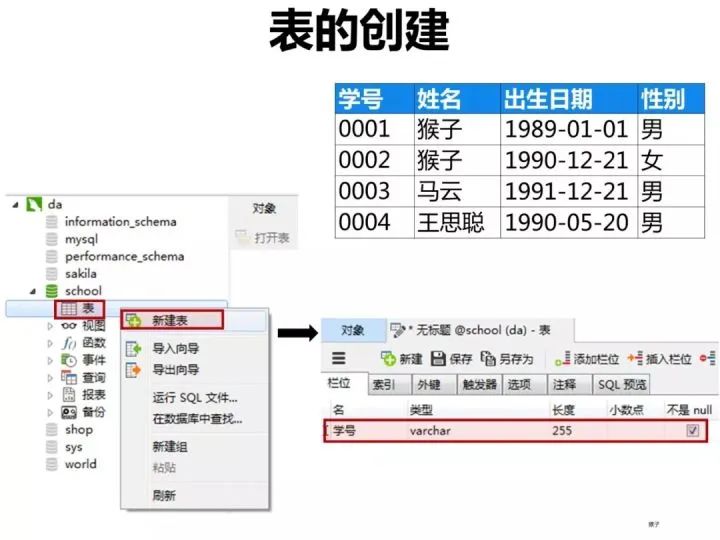
1.創(chuàng)建表
1)創(chuàng)建學生表(student)
按下圖在客戶端navicat里創(chuàng)建學生表。推薦:250期面試題匯總
學生表的“學號”列設置為主鍵約束,下圖是每一列設置的數(shù)據類型和約束
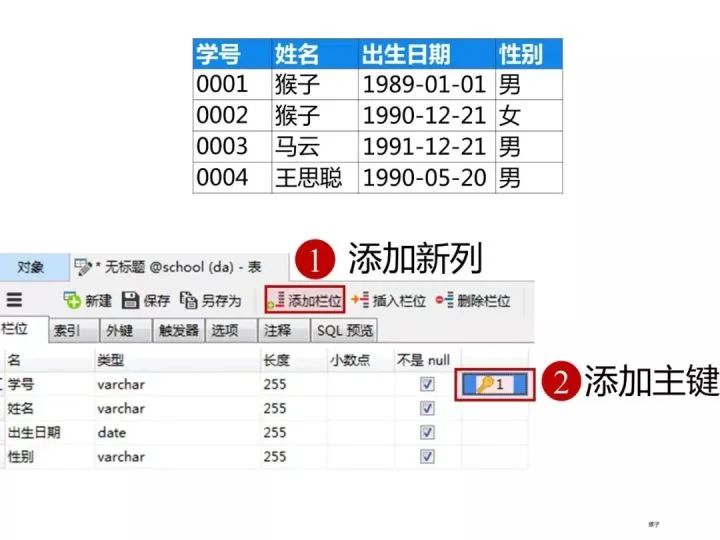
創(chuàng)建完表,點擊“保存”
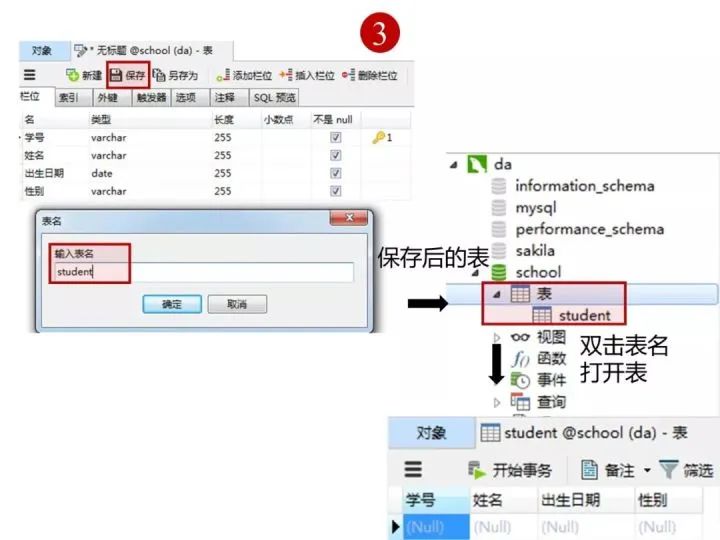
2)創(chuàng)建成績表(score)
同樣的步驟,創(chuàng)建"成績表“。“課程表的“學號”和“課程號”一起設置為主鍵約束(聯(lián)合主鍵),“成績”這一列設置為數(shù)值類型(float,浮點數(shù)值)
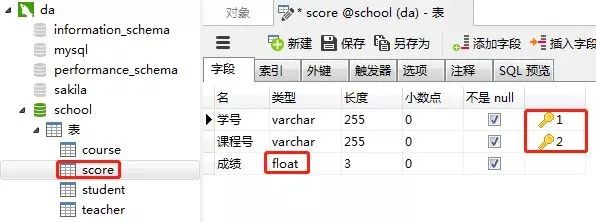
3)創(chuàng)建課程表(course)
課程表的“課程號”設置為主鍵約束
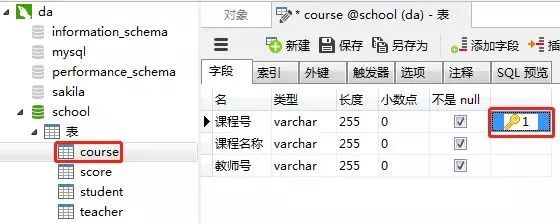
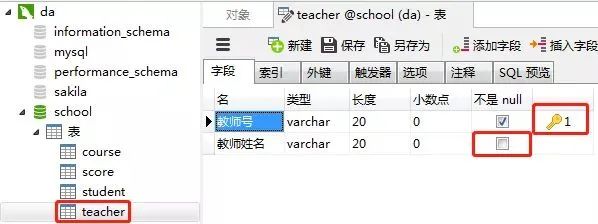
4)教師表(teacher)
教師表的“教師號”列設置為主鍵約束,教師姓名這一列設置約束為“null”(紅框的地方不勾選),表示這一列允許包含空值(null)。推薦:250期面試題匯總
向表中添加數(shù)據
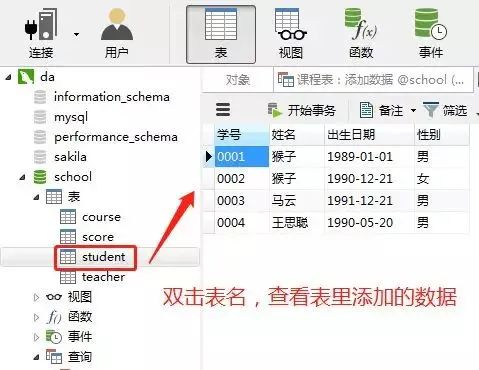
1)向學生表里添加數(shù)據
添加數(shù)據的sql
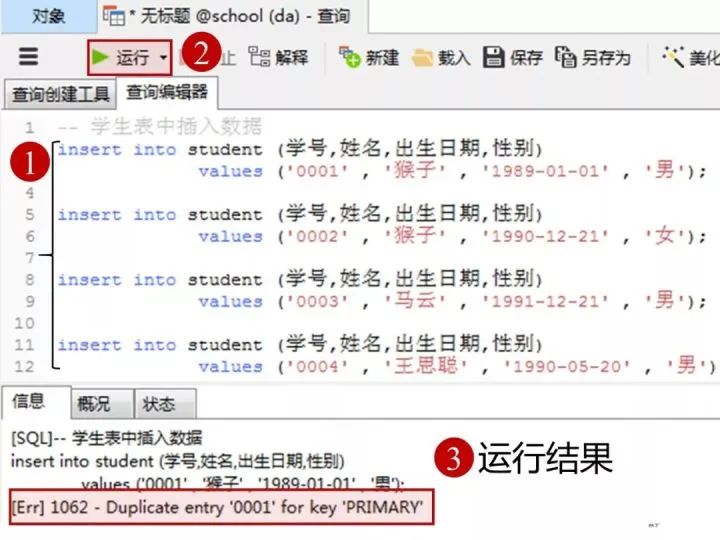
insert into student(學號,姓名,出生日期,性別)
values('0001' , '猴子' , '1989-01-01' , '男');
insert into student(學號,姓名,出生日期,性別)
values('0002' , '猴子' , '1990-12-21' , '女');
insert into student(學號,姓名,出生日期,性別)
values('0003' , '馬云' , '1991-12-21' , '男');
insert into student(學號,姓名,出生日期,性別)
values('0004' , '王思聰' , '1990-05-20' , '男');
在客戶端navicat里的操作
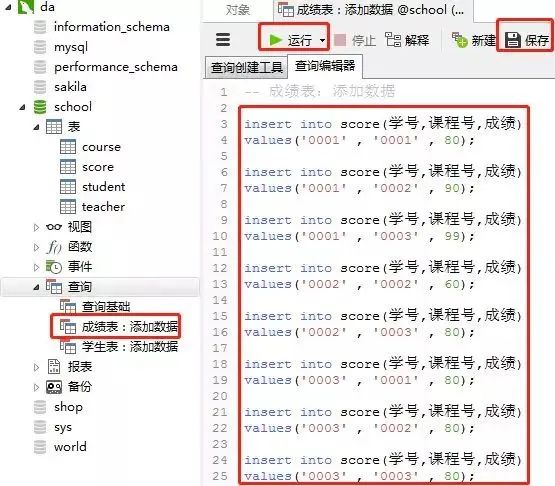
2)成績表(score)
添加數(shù)據的sql
insert into score(學號,課程號,成績)
values('0001' , '0001' , 80);
insert into score(學號,課程號,成績)
values('0001' , '0002' , 90);
insert into score(學號,課程號,成績)
values('0001' , '0003' , 99);
insert into score(學號,課程號,成績)
values('0002' , '0002' , 60);
insert into score(學號,課程號,成績)
values('0002' , '0003' , 80);
insert into score(學號,課程號,成績)
values('0003' , '0001' , 80);
insert into score(學號,課程號,成績)
values('0003' , '0002' , 80);
insert into score(學號,課程號,成績)
values('0003' , '0003' , 80);
客戶端navicat里的操作
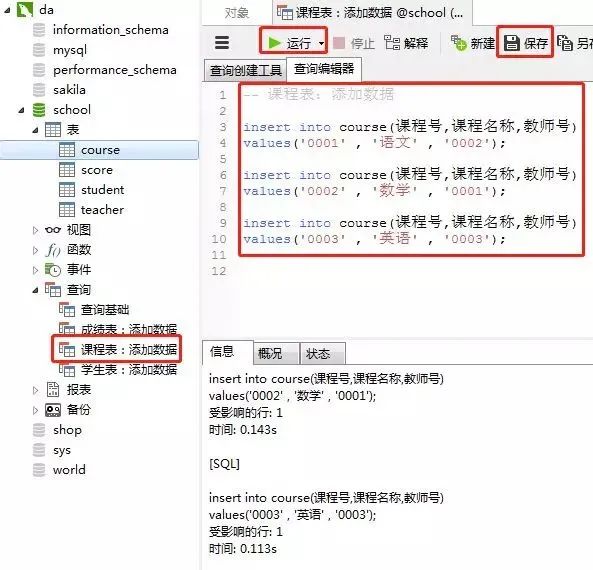
3)課程表
添加數(shù)據的sql
insert into course(課程號,課程名稱,教師號)
values('0001' , '語文' , '0002');
insert into course(課程號,課程名稱,教師號)
values('0002' , '數(shù)學' , '0001');
insert into course(課程號,課程名稱,教師號)
values('0003' , '英語' , '0003');
客戶端navicat里的操作
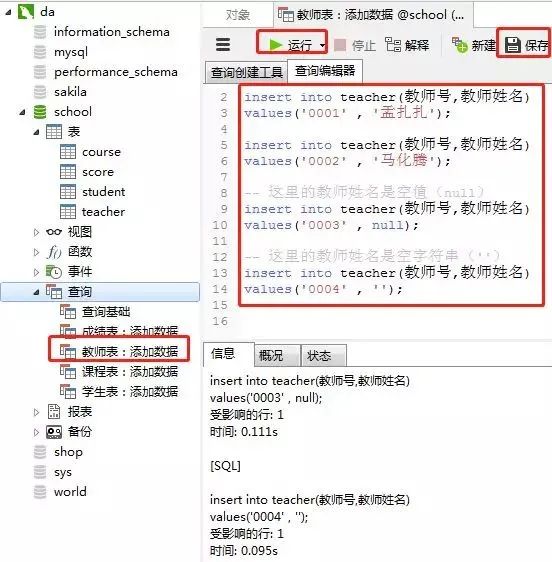
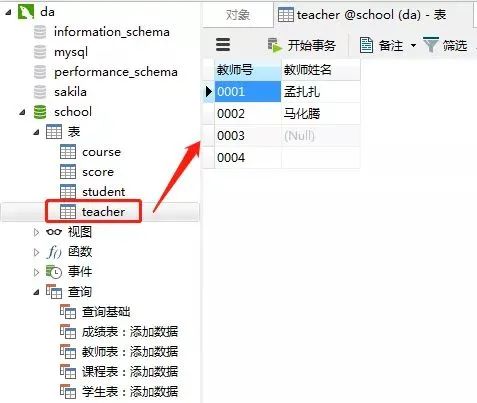
4)教師表里添加數(shù)據
添加數(shù)據的sql
-- 教師表:添加數(shù)據
insert into teacher(教師號,教師姓名)
values('0001' , '孟扎扎');
insert into teacher(教師號,教師姓名)
values('0002' , '馬化騰');
-- 這里的教師姓名是空值(null)
insert into teacher(教師號,教師姓名)
values('0003' , null);
-- 這里的教師姓名是空字符串('')
insert into teacher(教師號,教師姓名)
values('0004' , '');
客戶端navicat里操作
添加結果
三、50道面試題
為了方便學習,我將50道面試題進行了分類
查詢姓“猴”的學生名單

查詢姓“孟”老師的個數(shù)
select count(教師號)
from teacher
where 教師姓名 like '孟%';
2.匯總統(tǒng)計分組分析

面試題:查詢課程編號為“0002”的總成績
--分析思路
--select 查詢結果 [總成績:匯總函數(shù)sum]
--from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據[成績表score]
--where 查詢條件 [課程號是0002]
select sum(成績)
from score
where 課程號 = '0002';
查詢選了課程的學生人數(shù)
--這個題目翻譯成大白話就是:查詢有多少人選了課程
--select 學號,成績表里學號有重復值需要去掉
--from 從課程表查找score;
select count(distinct 學號) as 學生人數(shù)
from score;
查詢各科成績最高和最低的分, 以如下的形式顯示:課程號,最高分,最低分
/*
分析思路
select 查詢結果 [課程ID:是課程號的別名,最高分:max(成績) ,最低分:min(成績)]
from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據 [成績表score]
where 查詢條件 [沒有]
group by 分組 [各科成績:也就是每門課程的成績,需要按課程號分組];
*/
select 課程號,max(成績) as 最高分,min(成績) as 最低分
from score
group by 課程號;
查詢每門課程被選修的學生數(shù)
/*
分析思路
select 查詢結果 [課程號,選修該課程的學生數(shù):匯總函數(shù)count]
from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據 [成績表score]
where 查詢條件 [沒有]
group by 分組 [每門課程:按課程號分組];
*/
select 課程號, count(學號)
from score
group by 課程號;
查詢男生、女生人數(shù)
/*
分析思路
select 查詢結果 [性別,對應性別的人數(shù):匯總函數(shù)count]
from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據 [性別在學生表中,所以查找的是學生表student]
where 查詢條件 [沒有]
group by 分組 [男生、女生人數(shù):按性別分組]
having 對分組結果指定條件 [沒有]
order by 對查詢結果排序[沒有];
*/
select 性別,count(*)
from student
group by 性別;

查詢平均成績大于60分學生的學號和平均成績
/*
題目翻譯成大白話:
平均成績:展開來說就是計算每個學生的平均成績
這里涉及到“每個”就是要分組了
平均成績大于60分,就是對分組結果指定條件
分析思路
select 查詢結果 [學號,平均成績:匯總函數(shù)avg(成績)]
from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據 [成績在成績表中,所以查找的是成績表score]
where 查詢條件 [沒有]
group by 分組 [平均成績:先按學號分組,再計算平均成績]
having 對分組結果指定條件 [平均成績大于60分]
*/
select 學號, avg(成績)
from score
group by 學號
having avg(成績)>60;
查詢至少選修兩門課程的學生學號
/*
翻譯成大白話:
第1步,需要先計算出每個學生選修的課程數(shù)據,需要按學號分組
第2步,至少選修兩門課程:也就是每個學生選修課程數(shù)目>=2,對分組結果指定條件
分析思路
select 查詢結果 [學號,每個學生選修課程數(shù)目:匯總函數(shù)count]
from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據 [課程的學生學號:課程表score]
where 查詢條件 [至少選修兩門課程:需要先計算出每個學生選修了多少門課,需要用分組,所以這里沒有where子句]
group by 分組 [每個學生選修課程數(shù)目:按課程號分組,然后用匯總函數(shù)count計算出選修了多少門課]
having 對分組結果指定條件 [至少選修兩門課程:每個學生選修課程數(shù)目>=2]
*/
select 學號, count(課程號) as 選修課程數(shù)目
from score
group by 學號
having count(課程號)>=2;
查詢同名同性學生名單并統(tǒng)計同名人數(shù)
/*
翻譯成大白話,問題解析:
1)查找出姓名相同的學生有誰,每個姓名相同學生的人數(shù)
查詢結果:姓名,人數(shù)
條件:怎么算姓名相同?按姓名分組后人數(shù)大于等于2,因為同名的人數(shù)大于等于2
分析思路
select 查詢結果 [姓名,人數(shù):匯總函數(shù)count(*)]
from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據 [學生表student]
where 查詢條件 [沒有]
group by 分組 [姓名相同:按姓名分組]
having 對分組結果指定條件 [姓名相同:count(*)>=2]
order by 對查詢結果排序[沒有];
*/
select 姓名,count(*) as 人數(shù)
from student
group by 姓名
having count(*)>=2;
查詢不及格的課程并按課程號從大到小排列
/*
分析思路
select 查詢結果 [課程號]
from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據 [成績表score]
where 查詢條件 [不及格:成績 <60]
group by 分組 [沒有]
having 對分組結果指定條件 [沒有]
order by 對查詢結果排序[課程號從大到小排列:降序desc];
*/
select 課程號
from score
where 成績<60
order by 課程號 desc;
查詢每門課程的平均成績,結果按平均成績升序排序,平均成績相同時,按課程號降序排列
/*
分析思路
select 查詢結果 [課程號,平均成績:匯總函數(shù)avg(成績)]
from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據 [成績表score]
where 查詢條件 [沒有]
group by 分組 [每門課程:按課程號分組]
having 對分組結果指定條件 [沒有]
order by 對查詢結果排序[按平均成績升序排序:asc,平均成績相同時,按課程號降序排列:desc];
*/
select 課程號, avg(成績) as 平均成績
from score
group by 課程號
order by 平均成績 asc,課程號 desc;
檢索課程編號為“0004”且分數(shù)小于60的學生學號,結果按按分數(shù)降序排列
/*
分析思路
select 查詢結果 []
from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據 [成績表score]
where 查詢條件 [課程編號為“04”且分數(shù)小于60]
group by 分組 [沒有]
having 對分組結果指定條件 []
order by 對查詢結果排序[查詢結果按按分數(shù)降序排列];
*/
select 學號
from score
where 課程號='04' and 成績 <60
order by 成績 desc;
統(tǒng)計每門課程的學生選修人數(shù)(超過2人的課程才統(tǒng)計)
要求輸出課程號和選修人數(shù),查詢結果按人數(shù)降序排序,若人數(shù)相同,按課程號升序排序
/*
分析思路
select 查詢結果 [要求輸出課程號和選修人數(shù)]
from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據 []
where 查詢條件 []
group by 分組 [每門課程:按課程號分組]
having 對分組結果指定條件 [學生選修人數(shù)(超過2人的課程才統(tǒng)計):每門課程學生人數(shù)>2]
order by 對查詢結果排序[查詢結果按人數(shù)降序排序,若人數(shù)相同,按課程號升序排序];
*/
select 課程號, count(學號) as '選修人數(shù)'
from score
group by 課程號
having count(學號)>2
order by count(學號) desc,課程號 asc;
查詢兩門以上不及格課程的同學的學號及其平均成績
/*
分析思路
先分解題目:
1)[兩門以上][不及格課程]限制條件
2)[同學的學號及其平均成績],也就是每個學生的平均成績,顯示學號,平均成績
分析過程:
第1步:得到每個學生的平均成績,顯示學號,平均成績
第2步:再加上限制條件:
1)不及格課程
2)兩門以上[不及格課程]:課程數(shù)目>2
/*
第1步:得到每個學生的平均成績,顯示學號,平均成績
select 查詢結果 [學號,平均成績:匯總函數(shù)avg(成績)]
from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據 [涉及到成績:成績表score]
where 查詢條件 [沒有]
group by 分組 [每個學生的平均:按學號分組]
having 對分組結果指定條件 [沒有]
order by 對查詢結果排序[沒有];
*/
select 學號, avg(成績) as 平均成績
from score
group by 學號;
/*
第2步:再加上限制條件:
1)不及格課程
2)兩門以上[不及格課程]
select 查詢結果 [學號,平均成績:匯總函數(shù)avg(成績)]
from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據 [涉及到成績:成績表score]
where 查詢條件 [限制條件:不及格課程,平均成績<60]
group by 分組 [每個學生的平均:按學號分組]
having 對分組結果指定條件 [限制條件:課程數(shù)目>2,匯總函數(shù)count(課程號)>2]
order by 對查詢結果排序[沒有];
*/
select 學號, avg(成績) as 平均成績
from score
where 成績 <60
group by 學號
having count(課程號)>=2;
如果上面題目不會做,可以復習這部分涉及到的sql知識:
3.復雜查詢
查詢所有課程成績小于60分學生的學號、姓名
【知識點】子查詢
1.翻譯成大白話
1)查詢結果:學生學號,姓名 2)查詢條件:所有課程成績 < 60 的學生,需要從成績表里查找,用到子查詢
第1步,寫子查詢(所有課程成績 < 60 的學生)
select 查詢結果[學號] from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據[成績表:score] where 查詢條件[成績 < 60] group by 分組[沒有] having 對分組結果指定條件[沒有] order by 對查詢結果排序[沒有] limit 從查詢結果中取出指定行[沒有];
select 學號
from score
where 成績 < 60;
第2步,查詢結果:學生學號,姓名,條件是前面1步查到的學號
select 查詢結果[學號,姓名] from 從哪張表中查找數(shù)據[學生表:student] where 查詢條件[用到運算符in] group by 分組[沒有] having 對分組結果指定條件[沒有] order by 對查詢結果排序[沒有] limit 從查詢結果中取出指定行[沒有];
select 學號,姓名
from student
where 學號 in (
select 學號
from score
where 成績 < 60
);
查詢沒有學全所有課的學生的學號、姓名
/*
查找出學號,條件:沒有學全所有課,也就是該學生選修的課程數(shù) < 總的課程數(shù)
【考察知識點】in,子查詢
*/
select 學號,姓名
from student
where 學號 in(
select 學號
from score
group by 學號
having count(課程號) < (select count(課程號) from course)
);
查詢出只選修了兩門課程的全部學生的學號和姓名
select 學號,姓名
from student
where 學號 in(
select 學號
from score
group by 學號
having count(課程號)=2
);
1990年出生的學生名單

/*
查找1990年出生的學生名單
學生表中出生日期列的類型是datetime
*/
select 學號,姓名
from student
where year(出生日期)=1990;
查詢各科成績前兩名的記錄
這類問題其實就是常見的:分組取每組最大值、最小值,每組最大的N條(top N)記錄。
sql面試題:topN問題
工作中會經常遇到這樣的業(yè)務問題:
如何找到每個類別下用戶最喜歡的產品是哪個? 如果找到每個類別下用戶點擊最多的5個商品是什么?
這類問題其實就是常見的:分組取每組最大值、最小值,每組最大的N條(top N)記錄。
面對該類問題,如何解決呢?
下面我們通過成績表的例子來給出答案。
成績表是學生的成績,里面有學號(學生的學號),課程號(學生選修課程的課程號),成績(學生選修該課程取得的成績)
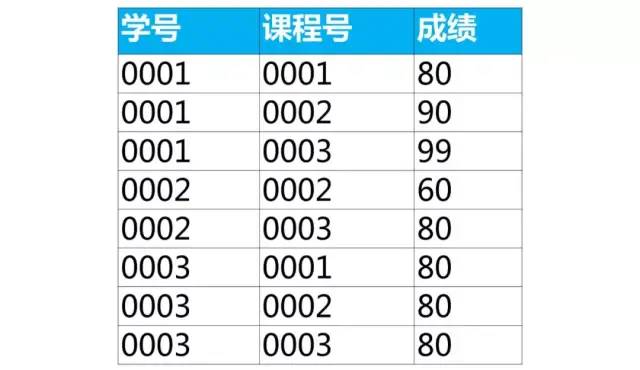
分組取每組最大值
案例:按課程號分組取成績最大值所在行的數(shù)據
我們可以使用分組(group by)和匯總函數(shù)得到每個組里的一個值(最大值,最小值,平均值等)。但是無法得到成績最大值所在行的數(shù)據。
select 課程號,max(成績) as 最大成績
from score
group by 課程號;
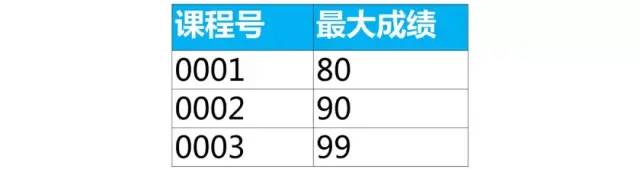
我們可以使用關聯(lián)子查詢來實現(xiàn):
select *
from score as a
where 成績 = (
select max(成績)
from score as b
where b.課程號 = a.課程號);
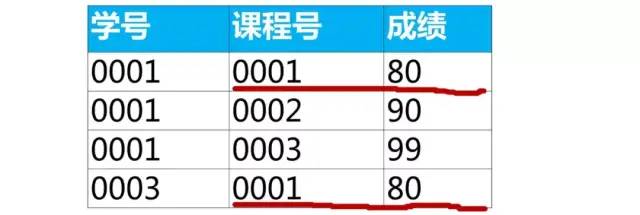
上面查詢結果課程號“0001”有2行數(shù)據,是因為最大成績80有2個
分組取每組最小值
案例:按課程號分組取成績最小值所在行的數(shù)據
同樣的使用關聯(lián)子查詢來實現(xiàn)
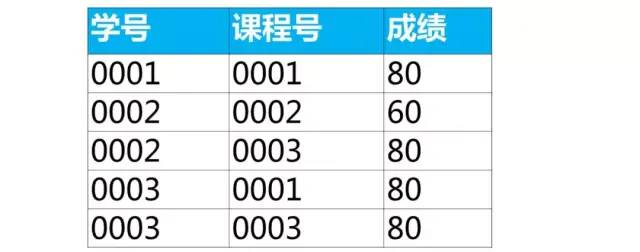
select *
from score as a
where 成績 = (
select min(成績)
from score as b
where b.課程號 = a.課程號);
每組最大的N條記錄
案例:查詢各科成績前兩名的記錄
第1步,查出有哪些組
我們可以按課程號分組,查詢出有哪些組,對應這個問題里就是有哪些課程號
select 課程號,max(成績) as 最大成績
from score
group by 課程號;

第2步:先使用order by子句按成績降序排序(desc),然后使用limt子句返回topN(對應這個問題返回的成績前兩名)
-- 課程號'0001' 這一組里成績前2名
select *
from score
where 課程號 = '0001'
order by 成績 desc
limit 2;
同樣的,可以寫出其他組的(其他課程號)取出成績前2名的sql
第3步,使用union all 將每組選出的數(shù)據合并到一起
-- 左右滑動可以可拿到全部sql
(select * from score where 課程號 = '0001' order by 成績 desc limit 2)
union all
(select * from score where 課程號 = '0002' order by 成績 desc limit 2)
union all
(select * from score where 課程號 = '0003' order by 成績 desc limit 2);
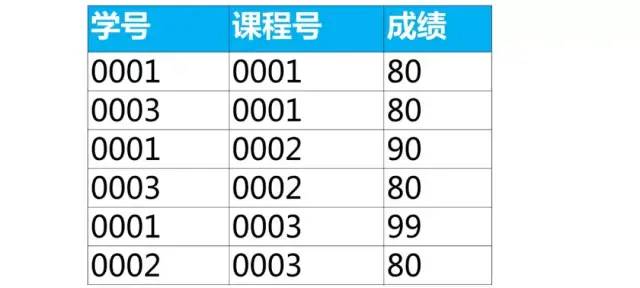
前面我們使用order by子句按某個列降序排序(desc)得到的是每組最大的N個記錄。如果想要達到每組最小的N個記錄,將order by子句按某個列升序排序(asc)即可。
求topN的問題還可以使用自定義變量來實現(xiàn),這個在后續(xù)再介紹。
如果對多表合并還不了解的,可以看下我講過的《從零學會SQL》的“多表查詢”。
總結
常見面試題:分組取每組最大值、最小值,每組最大的N條(top N)記錄。
4.多表查詢
查詢所有學生的學號、姓名、選課數(shù)、總成績
select a.學號,a.姓名,count(b.課程號) as 選課數(shù),sum(b.成績) as 總成績
from student as a left join score as b
on a.學號 = b.學號
group by a.學號;
查詢平均成績大于85的所有學生的學號、姓名和平均成績
select a.學號,a.姓名, avg(b.成績) as 平均成績
from student as a left join score as b
on a.學號 = b.學號
group by a.學號
having avg(b.成績)>85;
查詢學生的選課情況:學號,姓名,課程號,課程名稱
select a.學號, a.姓名, c.課程號,c.課程名稱
from student a inner join score b on a.學號=b.學號
inner join course c on b.課程號=c.課程號;
查詢出每門課程的及格人數(shù)和不及格人數(shù)
-- 考察case表達式
select 課程號,
sum(case when 成績>=60 then 1
else 0
end) as 及格人數(shù),
sum(case when 成績 < 60 then 1
else 0
end) as 不及格人數(shù)
from score
group by 課程號;
使用分段[100-85],[85-70],[70-60],[<60]來統(tǒng)計各科成績,分別統(tǒng)計:各分數(shù)段人數(shù),課程號和課程名稱
-- 考察case表達式
select a.課程號,b.課程名稱,
sum(case when 成績 between 85 and 100
then 1 else 0 end) as '[100-85]',
sum(case when 成績 >=70 and 成績<85
then 1 else 0 end) as '[85-70]',
sum(case when 成績>=60 and 成績<70
then 1 else 0 end) as '[70-60]',
sum(case when 成績<60 then 1 else 0 end) as '[<60]'
from score as a right join course as b
on a.課程號=b.課程號
group by a.課程號,b.課程名稱;
查詢課程編號為0003且課程成績在80分以上的學生的學號和姓名|
select a.學號,a.姓名
from student as a inner join score as b on a.學號=b.學號
where b.課程號='0003' and b.成績>80;
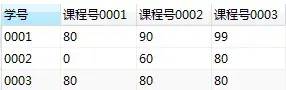
下面是學生的成績表(表名score,列名:學號、課程號、成績)
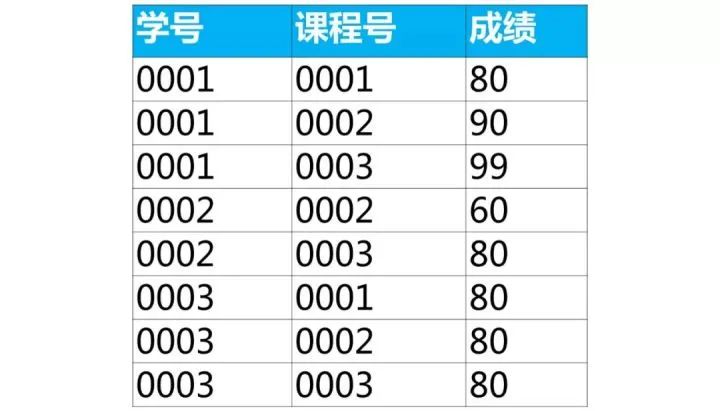
使用sql實現(xiàn)將該表行轉列為下面的表結構
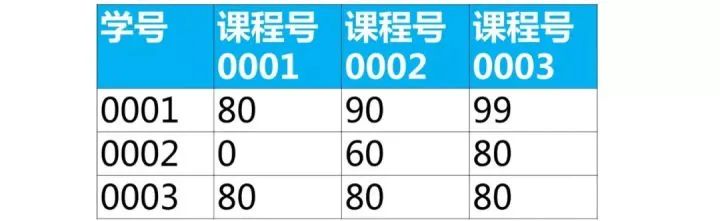
【面試題類型總結】這類題目屬于行列如何互換,解題思路如下:
【面試題】下面是學生的成績表(表名score,列名:學號、課程號、成績)
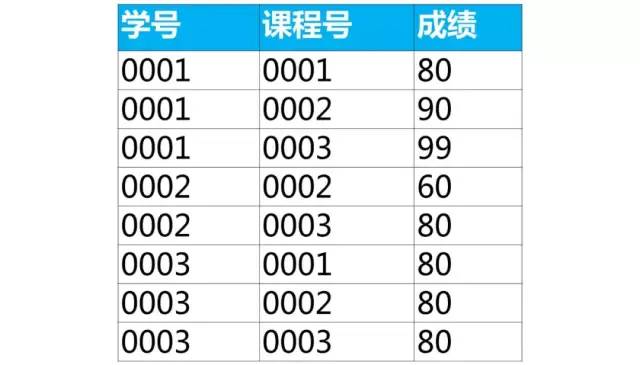
使用sql實現(xiàn)將該表行轉列為下面的表結構
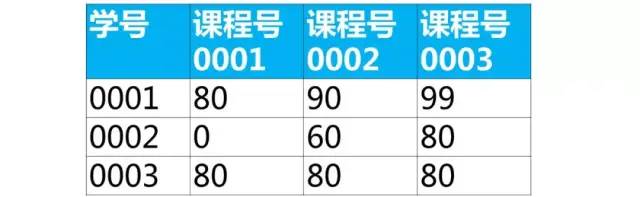
【解答】
第1步,使用常量列輸出目標表的結構
可以看到查詢結果已經和目標表非常接近了
select 學號,'課程號0001','課程號0002','課程號0003'
from score;
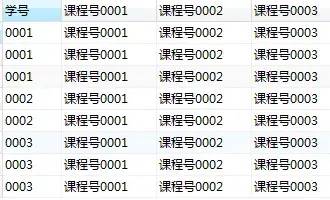
第2步,使用case表達式,替換常量列為對應的成績
select 學號,
(case 課程號 when '0001' then 成績 else 0 end) as '課程號0001',
(case 課程號 when '0002' then 成績 else 0 end) as '課程號0002',
(case 課程號 when '0003' then 成績 else 0 end) as '課程號0003'
from score;
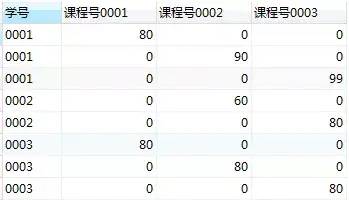
在這個查詢結果中,每一行表示了某個學生某一門課程的成績。比如第一行是'學號0001'選修'課程號00001'的成績,而其他兩列的'課程號0002'和'課程號0003'成績?yōu)?。
每個學生選修某門課程的成績在下圖的每個方塊內。我們可以通過分組,取出每門課程的成績。

第3關,分組
分組,并使用最大值函數(shù)max取出上圖每個方塊里的最大值
select 學號,
max(case 課程號 when '0001' then 成績 else 0 end) as '課程號0001',
max(case 課程號 when '0002' then 成績 else 0 end) as '課程號0002',
max(case 課程號 when '0003' then 成績 else 0 end) as '課程號0003'
from score
group by 學號;
這樣我們就得到了目標表(行列互換)