Spring Boot中的MVC支持詳解
本來已收錄到我寫的10萬字Springboot經(jīng)典學(xué)習(xí)筆記中,筆記在持續(xù)更新……文末有領(lǐng)取方式
Spring Boot 的 MVC 支持主要來介紹實際項目中最常用的幾個注解,包括 @RestController、 @RequestMapping、@PathVariable、@RequestParam 以及 @RequestBody。主要介紹這幾個注解常用的使用方式和特點。
1. @RestController
@RestController 是 Spring Boot 新增的一個注解,我們看一下該注解都包含了哪些東西。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public?@interface?RestController?{
????String?value()?default?"";
}
可以看出, @RestController 注解包含了原來的 @Controller 和 @ResponseBody 注解,使用過 Spring 的朋友對 @Controller 注解已經(jīng)非常了解了,這里不再贅述, @ResponseBody 注解是將返回的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)轉(zhuǎn)換為 Json 格式。所以 @RestController 可以看作是 @Controller 和 @ResponseBody 的結(jié)合體,相當于偷個懶,我們使用 @RestController 之后就不用再使用 @Controller 了。但是需要注意一個問題:如果是前后端分離,不用模板渲染的話,比如 Thymeleaf,這種情況下是可以直接使用@RestController 將數(shù)據(jù)以 json 格式傳給前端,前端拿到之后解析;但如果不是前后端分離,需要使用模板來渲染的話,一般 Controller 中都會返回到具體的頁面,那么此時就不能使用@RestController了,比如:
public?String?getUser()?{
?return?"user";
}
其實是需要返回到 user.html 頁面的,如果使用 @RestController 的話,會將 user 作為字符串返回的,所以這時候我們需要使用 @Controller 注解。這在下一節(jié) Spring Boot 集成 Thymeleaf 模板引擎中會再說明。
2. @RequestMapping
@RequestMapping 是一個用來處理請求地址映射的注解,它可以用于類上,也可以用于方法上。在類的級別上的注解會將一個特定請求或者請求模式映射到一個控制器之上,表示類中的所有響應(yīng)請求的方法都是以該地址作為父路徑;在方法的級別表示進一步指定到處理方法的映射關(guān)系。
該注解有6個屬性,一般在項目中比較常用的有三個屬性:value、method 和 produces。
value 屬性:指定請求的實際地址,value 可以省略不寫 method 屬性:指定請求的類型,主要有 GET、PUT、POST、DELETE,默認為 GET produces屬性:指定返回內(nèi)容類型,如 produces = "application/json; charset=UTF-8"
@RequestMapping 注解比較簡單,舉個例子:
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value?=?"/test",?produces?=?"application/json;?charset=UTF-8")
public?class?TestController?{
????@RequestMapping(value?=?"/get",?method?=?RequestMethod.GET)
????public?String?testGet()?{
????????return?"success";
????}
}
這個很簡單,啟動項目在瀏覽器中輸入 localhost:8080/test/get 測試一下即可。
針對四種不同的請求方式,是有相應(yīng)注解的,不用每次在 @RequestMapping 注解中加 method 屬性來指定,上面的 GET 方式請求可以直接使用 @GetMapping("/get") 注解,效果一樣。相應(yīng)地,PUT 方式、POST 方式和 DELETE 方式對應(yīng)的注解分別為 @PutMapping、@PostMapping 和 DeleteMapping。
3. @PathVariable
@PathVariable 注解主要是用來獲取 url 參數(shù),Spring Boot 支持 restfull 風(fēng)格的 url,比如一個 GET 請求攜帶一個參數(shù) id 過來,我們將 id 作為參數(shù)接收,可以使用 @PathVariable 注解。如下:
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public?String?testPathVariable(@PathVariable?Integer?id)?{
?System.out.println("獲取到的id為:"?+?id);
?return?"success";
}
這里需要注意一個問題,如果想要 url 中占位符中的 id 值直接賦值到參數(shù) id 中,需要保證 url 中的參數(shù)和方法接收參數(shù)一致,否則就無法接收。如果不一致的話,其實也可以解決,需要用 @PathVariable 中的 value 屬性來指定對應(yīng)關(guān)系。如下:
@RequestMapping("/user/{idd}")
public?String?testPathVariable(@PathVariable(value?=?"idd")?Integer?id)?{
?System.out.println("獲取到的id為:"?+?id);
?return?"success";
}
對于訪問的 url,占位符的位置可以在任何位置,不一定非要在最后,比如這樣也行:/xxx/{id}/user。另外,url 也支持多個占位符,方法參數(shù)使用同樣數(shù)量的參數(shù)來接收,原理和一個參數(shù)是一樣的,例如:
@GetMapping("/user/{idd}/{name}")
????public?String?testPathVariable(@PathVariable(value?=?"idd")?Integer?id,?@PathVariable?String?name)?{
????????System.out.println("獲取到的id為:"?+?id);
????????System.out.println("獲取到的name為:"?+?name);
????????return?"success";
????}
運行項目,在瀏覽器中請求 localhost:8080/test/user/2/zhangsan 可以看到控制臺輸出如下信息:
獲取到的id為:2
獲取到的name為:zhangsan
所以支持多個參數(shù)的接收。同樣地,如果 url 中的參數(shù)和方法中的參數(shù)名稱不同的話,也需要使用 value 屬性來綁定兩個參數(shù)。
4. @RequestParam
@RequestParam 注解顧名思義,也是獲取請求參數(shù)的,上面我們介紹了 @PathValiable 注解也是獲取請求參數(shù)的,那么 @RequestParam 和 @PathVariable 有什么不同呢?主要區(qū)別在于:@PathValiable 是從 url 模板中獲取參數(shù)值, 即這種風(fēng)格的 url:http://localhost:8080/user/{id} ;而 @RequestParam 是從 request 里面獲取參數(shù)值,即這種風(fēng)格的 url:http://localhost:8080/user?id=1 ?。我們使用該 url 帶上參數(shù) id 來測試一下如下代碼:
@GetMapping("/user")
public?String?testRequestParam(@RequestParam?Integer?id)?{
?System.out.println("獲取到的id為:"?+?id);
?return?"success";
}
可以正常從控制臺打印出 id 信息。同樣地,url 上面的參數(shù)和方法的參數(shù)需要一致,如果不一致,也需要使用 value 屬性來說明,比如 url 為:http://localhost:8080/user?idd=1
@RequestMapping("/user")
public?String?testRequestParam(@RequestParam(value?=?"idd",?required?=?false)?Integer?id)?{
?System.out.println("獲取到的id為:"?+?id);
?return?"success";
}
除了 value 屬性外,還有個兩個屬性比較常用:
required 屬性:true 表示該參數(shù)必須要傳,否則就會報 404 錯誤,false 表示可有可無。 defaultValue 屬性:默認值,表示如果請求中沒有同名參數(shù)時的默認值。
從 url 中可以看出,@RequestParam 注解用于 GET 請求上時,接收拼接在 url 中的參數(shù)。除此之外,該注解還可以用于 POST 請求,接收前端表單提交的參數(shù),假如前端通過表單提交 username 和 password 兩個參數(shù),那我們可以使用 @RequestParam 來接收,用法和上面一樣。
@PostMapping("/form1")
????public?String?testForm(@RequestParam?String?username,?@RequestParam?String?password)?{
????????System.out.println("獲取到的username為:"?+?username);
????????System.out.println("獲取到的password為:"?+?password);
????????return?"success";
????}
我們使用 postman 來模擬一下表單提交,測試一下接口:
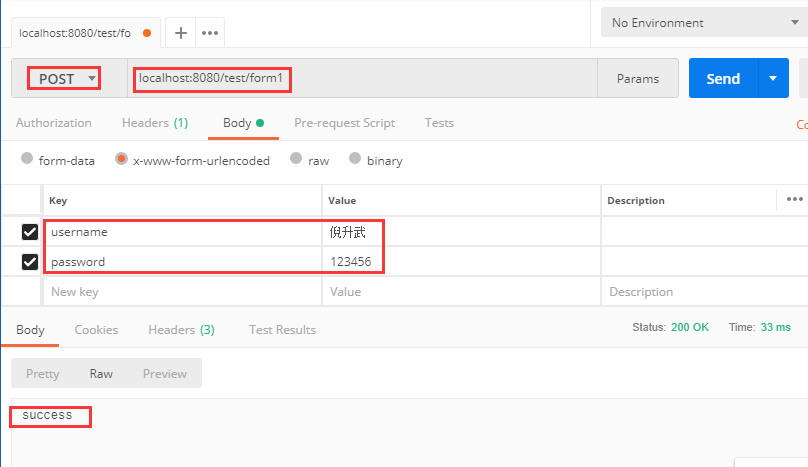
那么問題來了,如果表單數(shù)據(jù)很多,我們不可能在后臺方法中寫上很多參數(shù),每個參數(shù)還要 @RequestParam 注解。針對這種情況,我們需要封裝一個實體類來接收這些參數(shù),實體中的屬性名和表單中的參數(shù)名一致即可。
public?class?User?{
?private?String?username;
?private?String?password;
?//?set?get
}
使用實體接收的話,我們不能在前面加 @RequestParam 注解了,直接使用即可。
@PostMapping("/form2")
????public?String?testForm(User?user)?{
????????System.out.println("獲取到的username為:"?+?user.getUsername());
????????System.out.println("獲取到的password為:"?+?user.getPassword());
????????return?"success";
????}
使用 postman 再次測試一下表單提交,觀察一下返回值和控制臺打印出的日志即可。在實際項目中,一般都是封裝一個實體類來接收表單數(shù)據(jù),因為實際項目中表單數(shù)據(jù)一般都很多。
5. @RequestBody
@RequestBody 注解用于接收前端傳來的實體,接收參數(shù)也是對應(yīng)的實體,比如前端通過 json 提交傳來兩個參數(shù) username 和 password,此時我們需要在后端封裝一個實體來接收。在傳遞的參數(shù)比較多的情況下,使用 @RequestBody 接收會非常方便。例如:
public?class?User?{
?private?String?username;
?private?String?password;
?//?set?get
}
@PostMapping("/user")
public?String?testRequestBody(@RequestBody?User?user)?{
?System.out.println("獲取到的username為:"?+?user.getUsername());
?System.out.println("獲取到的password為:"?+?user.getPassword());
?return?"success";
}
我們使用 postman 工具來測試一下效果,打開 postman,然后輸入請求地址和參數(shù),參數(shù)我們用 json 來模擬,如下圖所有,調(diào)用之后返回 success。
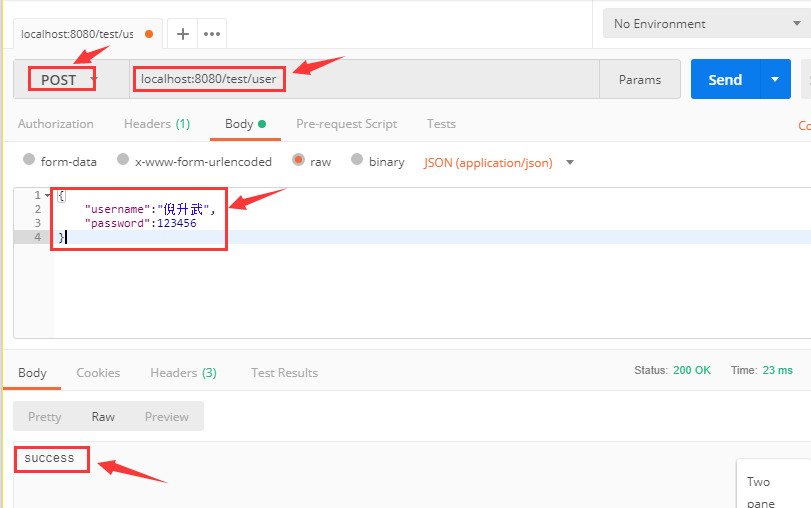
同時看一下后臺控制臺輸出的日志:
獲取到的username為:倪升武
獲取到的password為:123456
可以看出,@RequestBody 注解用于 POST 請求上,接收 json 實體參數(shù)。它和上面我們介紹的表單提交有點類似,只不過參數(shù)的格式不同,一個是 json 實體,一個是表單提交。在實際項目中根據(jù)具體場景和需要使用對應(yīng)的注解即可。
6. 總結(jié)
本節(jié)課主要講解了 Spring Boot 中對 MVC 的支持,分析了 @RestController、 @RequestMapping、@PathVariable、 @RequestParam 和 @RequestBody 四個注解的使用方式,由于 @RestController 中集成了 @ResponseBody 所以對返回 json 的注解不再贅述。以上四個注解是使用頻率很高的注解,在所有的實際項目中基本都會遇到,要熟練掌握。
該文已收錄到我寫的《10萬字Springboot經(jīng)典學(xué)習(xí)筆記》中,歡迎掃描下方二維碼領(lǐng)取全套筆記。
關(guān)注Java開發(fā)寶典
回復(fù):筆記
點贊是最大的支持?


