一份簡單夠用的 Nginx Location 配置講解
作者:冴羽
來源:SegmentFault 思否社區(qū)
前言
Location 是 Nginx 中一個非常核心的配置,這篇重點(diǎn)講解一下 Location 的配置問題以及一些注意事項(xiàng)。
語法
關(guān)于 Location,舉個簡單的配置例子:
http {
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.yayujs.com;
location / {
root /home/www/ts/;
index index.html;
}
}
}
大致的意思是,當(dāng)你訪問 www.yayujs.com 的 80 端口的時候,返回 /home/www/ts/index.html 文件。
我們看下 Location 的具體語法:
location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { ... }
重點(diǎn)看方括號中的 [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ],其中 | 分隔的內(nèi)容表示你可能會用到的語法,其中:
= 表示精確匹配,比如:
location = /test {
return 200 "hello";
}
# /test ok
# /test/ not ok
# /test2 not ok
# /test/2 not ok
~ 表示區(qū)分大小寫的正則匹配,比如:
location ~ ^/test$ {
[ configuration ]
}
# /test ok
# /Test not ok
# /test/ not ok
# /test2 not ok
~* 表示不區(qū)分大小寫的正則匹配
location ~* ^/test$ {
[ configuration ]
}
# /test ok
# /Test ok
# /test/ not ok
# /test2 not ok
^~ 表示 uri 以某個字符串開頭
location ^~ /images/ {
[ configuration ]
}
# /images/1.gif ok
而當(dāng)你不使用這些語法的時候,只寫 uri 的時候:
/ 表示通用匹配:
location / {
[ configuration ]
}
# /index.html ok
location /test {
[ configuration ]
}
# /test ok
# /test2 ok
# /test/ ok
匹配順序
當(dāng)存在多個 location 的時候,他們的匹配順序引用 Nginx 官方文檔就是:
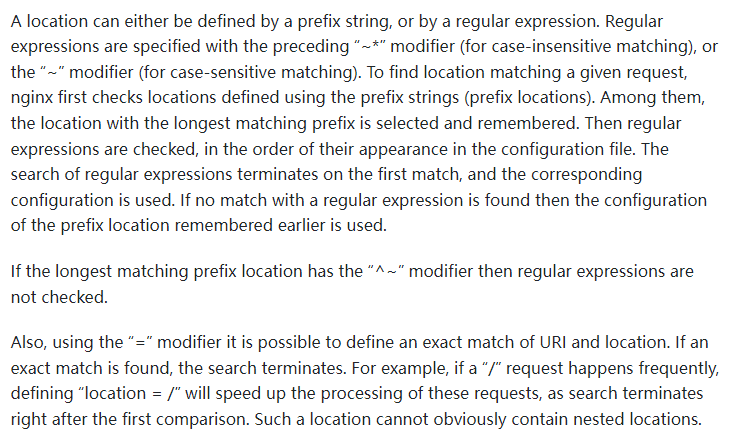
翻譯整理后就是:
location 的定義分為兩種:
前綴字符串(prefix string)
正則表達(dá)式(regular expression),具體為前面帶 ~* 和 ~ 修飾符的
而匹配 location 的順序?yàn)椋?/span>
檢查使用前綴字符串的 locations,在使用前綴字符串的 locations 中選擇最長匹配的,并將結(jié)果進(jìn)行儲存
如果符合帶有 = 修飾符的 URI,則立刻停止匹配
如果符合帶有 ^~ 修飾符的 URI,則也立刻停止匹配。
然后按照定義文件的順序,檢查正則表達(dá)式,匹配到就停止
當(dāng)正則表達(dá)式匹配不到的時候,使用之前儲存的前綴字符串
再總結(jié)一下就是:
在順序上,前綴字符串順序不重要,按照匹配長度來確定,正則表達(dá)式則按照定義順序。
在優(yōu)先級上,= 修飾符最高,^~ 次之,再者是正則,最后是前綴字符串匹配。
我們舉幾個簡單的例子復(fù)習(xí)下:
server {
location /doc {
[ configuration A ]
}
location /docu {
[ configuration B ]
}
}
# 請求 /document 使用 configuration B
# 雖然 /doc 也能匹配到,但在順序上,前綴字符串順序不重要,按照匹配長度來確定
server {
location ~ ^/doc {
[ configuration A ]
}
location ~ ^/docu {
[ configuration B ]
}
}
# 請求 /document 使用 configuration A
# 雖然 ~ ^/docu 也能匹配到,但正則表達(dá)式則按照定義順序
server {
location ^~ /doc {
[ configuration A ]
}
location ~ ^/docu {
[ configuration B ]
}
}
# 請求 /document 使用 configuration A
# 雖然 ~ ^/docu 也能匹配到,但 ^~ 的優(yōu)先級更高
server {
location /document {
[ configuration A ]
}
location ~ ^/docu {
[ configuration B ]
}
}
# 請求 /document 使用 configuration B
# 雖然 /document 也能匹配到,但正則的優(yōu)先級更高
root 與 alias 的區(qū)別
當(dāng)我們這樣設(shè)置 root 的時候:
location /i/ {
root /data/w3;
}
當(dāng)請求 /i/top.gif ,/data/w3/i/top.gif 會被返回。
當(dāng)我們這樣設(shè)置 alias 的時候:
location /i/ {
alias /data/w3/images/;
}
當(dāng)請求 /i/top.gif ,/data/w3/images/top.gif 會被返回。
乍一看兩者很像,但細(xì)一看,就能看出兩者的區(qū)別,root 是直接拼接 root + location 而 alias 是用 alias 替換 location,所以 root 中最后的路徑里有 /i/,而 alias 中最后的路徑里沒有 /i/ 。
所以如果你這樣使用 allias 定義一個路徑:
location /images/ {
alias /data/w3/images/;
}
其實(shí)使用 root 會更好:
location /images/ {
root /data/w3;
}
server 和 location 中的 root
server 和 location 中都可以使用 root,舉個例子:
http {
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.yayujs.com;
root /home/www/website/;
location / {
root /home/www/ts/;
index index.html;
}
}
}
如果兩者都出現(xiàn),是怎樣的優(yōu)先級呢?
簡單的來說,就是就近原則,如果 location 中能匹配到,就是用 location 中的 root 配置,忽略 server 中的 root,當(dāng) location 中匹配不到的時候,則使用 server 中的 root 配置。
系列文章
博客搭建系列是我至今寫的唯一一個偏實(shí)戰(zhàn)的系列教程,講解如何使用 VuePress 搭建博客,并部署到 GitHub、Gitee、個人服務(wù)器等平臺。
一篇帶你用 VuePress + GitHub Pages 搭建博客
https://github.com/mqyqingfeng/Blog/issues/235
一篇教你代碼同步 GitHub 和 Gitee
https://github.com/mqyqingfeng/Blog/issues/236
還不會用 GitHub Actions ?看看這篇
https://github.com/mqyqingfeng/Blog/issues/237
Gitee 如何自動部署 Pages?還是用 GitHub Actions!
https://github.com/mqyqingfeng/Blog/issues/238
一份前端夠用的 Linux 命令
https://github.com/mqyqingfeng/Blog/issues/239
如果有錯誤或者不嚴(yán)謹(jǐn)?shù)牡胤剑垊?wù)必給予指正,十分感謝。如果喜歡或者 有所啟發(fā),歡迎 star,對作者也是一種鼓勵。