Java中操作Excel的3種方法,太好用了!
一、介紹
在平時(shí)的業(yè)務(wù)系統(tǒng)開發(fā)中,少不了需要用到導(dǎo)出、導(dǎo)入excel功能,今天我們就一起來總結(jié)一下,如果你正為此需求感到困惑,那么閱讀完本文,你一定會有所收獲!
二、poi
大概在很久很久以前,微軟的電子表格軟件 Excel 以操作簡單、存儲數(shù)據(jù)直觀方便,還支持打印報(bào)表,在誕生之初,可謂深得辦公室里的白領(lǐng)青睞,極大的提升了工作的效率,不久之后,便成了辦公室里的必備工具。
隨著更多的新語言的崛起,例如我們所熟悉的 java,后來便有一些團(tuán)隊(duì)開始開發(fā)一套能與 Excel 軟件無縫切換的操作工具!
這其中就有我們所熟悉的 apache 的 poi,其前身是 Jakarta 的 POI Project項(xiàng)目,之后將其開源給 apache 基金會!
當(dāng)然,在java生態(tài)體系里面,能與Excel無縫銜接的第三方工具還有很多,因?yàn)?apache poi 在業(yè)界使用的最廣泛,因此其他的工具不做過多介紹!
話不多說,直接開擼!
2.1、首先引入apache poi的依賴
<dependencies>
<!--xls(03)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>4.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--xlsx(07)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>4.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--時(shí)間格式化工具-->
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-time</groupId>
<artifactId>joda-time</artifactId>
<version>2.10.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.2、導(dǎo)出excel
導(dǎo)出操作,即使用 Java 寫出數(shù)據(jù)到 Excel 中,常見場景是將頁面上的數(shù)據(jù)導(dǎo)出,這些數(shù)據(jù)可能是財(cái)務(wù)數(shù)據(jù),也可能是商品數(shù)據(jù),生成 Excel 后返回給用戶下載文件。
在 poi 工具庫中,導(dǎo)出 api 可以分三種方式
HSSF方式:這種方式導(dǎo)出的文件格式為office 2003專用格式,即 .xls,優(yōu)點(diǎn)是導(dǎo)出數(shù)據(jù)速度快,但是最多65536行數(shù)據(jù)XSSF方式:這種方式導(dǎo)出的文件格式為office 2007專用格式,即 .xlsx,優(yōu)點(diǎn)是導(dǎo)出的數(shù)據(jù)不受行數(shù)限制,缺點(diǎn)導(dǎo)出速度慢SXSSF方式:SXSSF 是 XSSF API的兼容流式擴(kuò)展,主要解決當(dāng)使用 XSSF 方式導(dǎo)出大數(shù)據(jù)量時(shí),內(nèi)存溢出的問題,支持導(dǎo)出大批量的excel數(shù)據(jù)
2.2.1、HSSF方式導(dǎo)出
HSSF方式,最多只支持65536條數(shù)據(jù)導(dǎo)出,超過這個(gè)條數(shù)會報(bào)錯(cuò)!
public class ExcelWrite2003Test {
public static String PATH = "/Users/hello/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//時(shí)間
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//創(chuàng)建一個(gè)工作簿
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
//創(chuàng)建表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
//寫入數(shù)據(jù)
for (int rowNumber = 0; rowNumber < 65536; rowNumber++) {
//創(chuàng)建行
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNumber);
for (int cellNumber = 0; cellNumber < 10; cellNumber++) {
//創(chuàng)建列
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNumber);
cell.setCellValue(cellNumber);
}
}
System.out.println("over");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH + "用戶信息表2003BigData.xls");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((double) (end - begin) / 1000);//4.29s
}
}
2.2.2、XSSF方式導(dǎo)出
XSSF方式支持大批量數(shù)據(jù)導(dǎo)出,所有的數(shù)據(jù)先寫入內(nèi)存再導(dǎo)出,容易出現(xiàn)內(nèi)存溢出!
public class ExcelWrite2007Test {
public static String PATH = "/Users/hello/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//時(shí)間
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//創(chuàng)建一個(gè)工作簿
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//創(chuàng)建表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
//寫入數(shù)據(jù)
for (int rowNumber = 0; rowNumber < 65537; rowNumber++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNumber);
for (int cellNumber = 0; cellNumber < 10; cellNumber++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNumber);
cell.setCellValue(cellNumber);
}
}
System.out.println("over");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH + "用戶信息表2007BigData.xlsx");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((double) (end - begin) / 1000);//15.87s
}
}
2.2.3、SXSSF方式導(dǎo)出
SXSSF方式是XSSF方式的一種延伸,主要特性是低內(nèi)存,導(dǎo)出的時(shí)候,先將數(shù)據(jù)寫入磁盤再導(dǎo)出,避免報(bào)內(nèi)存不足,導(dǎo)致程序運(yùn)行異常,缺點(diǎn)是運(yùn)行很慢!
public class ExcelWriteSXSSFTest {
public static String PATH = "/Users/hello/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//時(shí)間
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//創(chuàng)建一個(gè)工作簿
Workbook workbook = new SXSSFWorkbook();
//創(chuàng)建表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
//寫入數(shù)據(jù)
for (int rowNumber = 0; rowNumber < 100000; rowNumber++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNumber);
for (int cellNumber = 0; cellNumber < 10; cellNumber++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNumber);
cell.setCellValue(cellNumber);
}
}
System.out.println("over");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH + "用戶信息表2007BigDataS.xlsx");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((double) (end - begin) / 1000);//6.39s
}
}
2.3、導(dǎo)入excel
導(dǎo)入操作,即將 excel 中的數(shù)據(jù)采用java工具庫將其解析出來,進(jìn)而將 excel 數(shù)據(jù)寫入數(shù)據(jù)庫!
同樣,在 poi 工具庫中,導(dǎo)入 api 也分三種方式,與上面的導(dǎo)出一一對應(yīng)!
2.3.1、HSSF方式導(dǎo)入
public class ExcelRead2003Test {
public static String PATH = "/Users/hello/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//獲取文件流
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH + "用戶信息表BigData.xls");
//1.創(chuàng)建工作簿,使用excel能操作的這邊都看看操作
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
//2.得到表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//3.得到行
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
//4.得到列
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
getValue(cell);
inputStream.close();
}
public static void getValue(Cell cell){
//匹配類型數(shù)據(jù)
if (cell != null) {
CellType cellType = cell.getCellType();
String cellValue = "";
switch (cellType) {
case STRING: //字符串
System.out.print("[String類型]");
cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
break;
case BOOLEAN: //布爾類型
System.out.print("[boolean類型]");
cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case BLANK: //空
System.out.print("[BLANK類型]");
break;
case NUMERIC: //數(shù)字(日期、普通數(shù)字)
System.out.print("[NUMERIC類型]");
if (HSSFDateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) { //日期
System.out.print("[日期]");
Date date = cell.getDateCellValue();
cellValue = new DateTime(date).toString("yyyy-MM-dd");
} else {
//不是日期格式,防止數(shù)字過長
System.out.print("[轉(zhuǎn)換為字符串輸出]");
cell.setCellType(CellType.STRING);
cellValue = cell.toString();
}
break;
case ERROR:
System.out.print("[數(shù)據(jù)類型錯(cuò)誤]");
break;
}
System.out.println(cellValue);
}
}
}
2.3.2、XSSF方式導(dǎo)入
public class ExcelRead2007Test {
public static String PATH = "/Users/hello/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//獲取文件流
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH + "用戶信息表2007BigData.xlsx");
//1.創(chuàng)建工作簿,使用excel能操作的這邊都看看操作
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
//2.得到表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//3.得到行
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
//4.得到列
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
getValue(cell);
inputStream.close();
}
public static void getValue(Cell cell){
//匹配類型數(shù)據(jù)
if (cell != null) {
CellType cellType = cell.getCellType();
String cellValue = "";
switch (cellType) {
case STRING: //字符串
System.out.print("[String類型]");
cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
break;
case BOOLEAN: //布爾類型
System.out.print("[boolean類型]");
cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case BLANK: //空
System.out.print("[BLANK類型]");
break;
case NUMERIC: //數(shù)字(日期、普通數(shù)字)
System.out.print("[NUMERIC類型]");
if (HSSFDateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) { //日期
System.out.print("[日期]");
Date date = cell.getDateCellValue();
cellValue = new DateTime(date).toString("yyyy-MM-dd");
} else {
//不是日期格式,防止數(shù)字過長
System.out.print("[轉(zhuǎn)換為字符串輸出]");
cell.setCellType(CellType.STRING);
cellValue = cell.toString();
}
break;
case ERROR:
System.out.print("[數(shù)據(jù)類型錯(cuò)誤]");
break;
}
System.out.println(cellValue);
}
}
}
2.3.3、SXSSF方式導(dǎo)入
public class ExcelReadSXSSFTest {
public static String PATH = "/Users/hello/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//獲取文件流
//1.創(chuàng)建工作簿,使用excel能操作的這邊都看看操作
OPCPackage opcPackage = OPCPackage.open(PATH + "用戶信息表2007BigData.xlsx");
XSSFReader xssfReader = new XSSFReader(opcPackage);
StylesTable stylesTable = xssfReader.getStylesTable();
ReadOnlySharedStringsTable sharedStringsTable = new ReadOnlySharedStringsTable(opcPackage);
// 創(chuàng)建XMLReader,設(shè)置ContentHandler
XMLReader xmlReader = SAXHelper.newXMLReader();
xmlReader.setContentHandler(new XSSFSheetXMLHandler(stylesTable, sharedStringsTable, new SimpleSheetContentsHandler(), false));
// 解析每個(gè)Sheet數(shù)據(jù)
Iterator<InputStream> sheetsData = xssfReader.getSheetsData();
while (sheetsData.hasNext()) {
try (InputStream inputStream = sheetsData.next();) {
xmlReader.parse(new InputSource(inputStream));
}
}
}
/**
* 內(nèi)容處理器
*/
public static class SimpleSheetContentsHandler implements XSSFSheetXMLHandler.SheetContentsHandler {
protected List<String> row;
/**
* A row with the (zero based) row number has started
*
* @param rowNum
*/
@Override
public void startRow(int rowNum) {
row = new ArrayList<>();
}
/**
* A row with the (zero based) row number has ended
*
* @param rowNum
*/
@Override
public void endRow(int rowNum) {
if (row.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 處理數(shù)據(jù)
System.out.println(row.stream().collect(Collectors.joining(" ")));
}
/**
* A cell, with the given formatted value (may be null),
* and possibly a comment (may be null), was encountered
*
* @param cellReference
* @param formattedValue
* @param comment
*/
@Override
public void cell(String cellReference, String formattedValue, XSSFComment comment) {
row.add(formattedValue);
}
/**
* A header or footer has been encountered
*
* @param text
* @param isHeader
* @param tagName
*/
@Override
public void headerFooter(String text, boolean isHeader, String tagName) {
}
}
}
三、easypoi
以前的以前,有個(gè)大佬程序員,跳到一家公司之后就和業(yè)務(wù)人員聊上了,這些業(yè)務(wù)員對excel報(bào)表有著許許多多的要求,比如想要一個(gè)報(bào)表,他的表頭是一個(gè)多行表頭,過幾天之后,他想要給這些表頭添加樣式,比如關(guān)鍵的數(shù)據(jù)標(biāo)紅,再過幾天,他想要再末尾添加一條合計(jì)的數(shù)據(jù),等等!
起初還好,都是copy、copy,之后發(fā)現(xiàn)系統(tǒng)中出現(xiàn)大量的重復(fù)代碼,于是有一天真的忍受不了了,采用注解搞定來搞定這些定制化成程度高的邏輯,將公共化抽離出來,于是誕生了 easypoi!
easypoi 的底層也是基于 apache poi 進(jìn)行深度開發(fā)的,它主要的特點(diǎn)就是將更多重復(fù)的工作,全部簡單化,避免編寫重復(fù)的代碼!
下面,我們就一起來了解一下這款高大上的開源工具:easypoi
3.1、首先添加依賴包
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-base</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-web</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-annotation</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3.2、采用注解導(dǎo)出導(dǎo)入
easypoi 最大的亮點(diǎn)就是基于注解實(shí)體類來導(dǎo)出、導(dǎo)入excel,使用起來非常簡單!
首先,我們創(chuàng)建一個(gè)實(shí)體類UserEntity,其中@Excel注解表示導(dǎo)出文件的頭部信息。
public class UserEntity {
@Excel(name = "姓名")
private String name;
@Excel(name = "年齡")
private int age;
@Excel(name = "操作時(shí)間",format="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", width = 20.0)
private Date time;
//set、get省略
}
接著,我們來編寫導(dǎo)出服務(wù)!
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
List<UserEntity> dataList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
UserEntity userEntity = new UserEntity();
userEntity.setName("張三" + i);
userEntity.setAge(20 + i);
userEntity.setTime(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + i));
dataList.add(userEntity);
}
//生成excel文檔
Workbook workbook = ExcelExportUtil.exportExcel(new ExportParams("用戶","用戶信息"),
UserEntity.class, dataList);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/hello/Documents/easypoi-user1.xls");
workbook.write(fos);
fos.close();
}
導(dǎo)出的文件預(yù)覽如下:
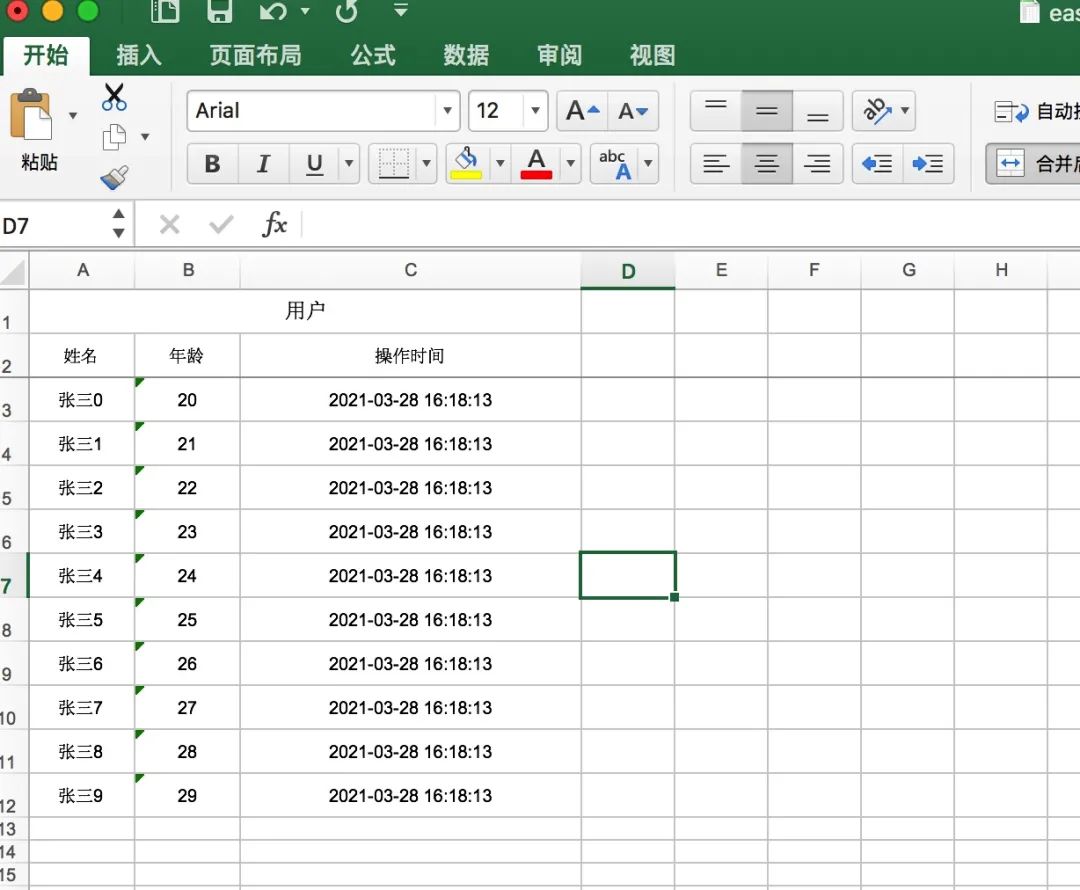
對應(yīng)的導(dǎo)入操作,也很簡單,源碼如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImportParams params = new ImportParams();
params.setTitleRows(1);
params.setHeadRows(1);
long start = new Date().getTime();
List<StudentEntity> list = ExcelImportUtil.importExcel(new File("/Users/hello/Documents/easypoi-user1.xls"),
UserEntity.class, params);
System.out.println(new Date().getTime() - start);
System.out.println(JSONArray.toJSONString(list));
}
運(yùn)行程序,輸出結(jié)果如下:
[{"age":20,"name":"張三0","time":1616919493000},{"age":21,"name":"張三1","time":1616919493000},{"age":22,"name":"張三2","time":1616919493000},{"age":23,"name":"張三3","time":1616919493000},{"age":24,"name":"張三4","time":1616919493000},{"age":25,"name":"張三5","time":1616919493000},{"age":26,"name":"張三6","time":1616919493000},{"age":27,"name":"張三7","time":1616919493000},{"age":28,"name":"張三8","time":1616919493000},{"age":29,"name":"張三9","time":1616919493000}]
3.3、自定義數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)導(dǎo)出導(dǎo)入
easypoi 同樣也支持自定義數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)導(dǎo)出導(dǎo)入excel。
自定義數(shù)據(jù)導(dǎo)出 excel
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//封裝表頭
List<ExcelExportEntity> entityList = new ArrayList<ExcelExportEntity>();
entityList.add(new ExcelExportEntity("姓名", "name"));
entityList.add(new ExcelExportEntity("年齡", "age"));
ExcelExportEntity entityTime = new ExcelExportEntity("操作時(shí)間", "time");
entityTime.setFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
entityTime.setWidth(20.0);
entityList.add(entityTime);
//封裝數(shù)據(jù)體
List<Map<String, Object>> dataList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Map<String, Object> userEntityMap = new HashMap<>();
userEntityMap.put("name", "張三" + i);
userEntityMap.put("age", 20 + i);
userEntityMap.put("time", new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + i));
dataList.add(userEntityMap);
}
//生成excel文檔
Workbook workbook = ExcelExportUtil.exportExcel(new ExportParams("學(xué)生","用戶信息"), entityList, dataList);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/panzhi/Documents/easypoi-user2.xls");
workbook.write(fos);
fos.close();
}
導(dǎo)入 excel
public static void main(String[] args) {
ImportParams params = new ImportParams();
params.setTitleRows(1);
params.setHeadRows(1);
long start = new Date().getTime();
List<Map<String, Object>> list = ExcelImportUtil.importExcel(new File("/Users/panzhi/Documents/easypoi-user2.xls"),
Map.class, params);
System.out.println(new Date().getTime() - start);
System.out.println(JSONArray.toJSONString(list));
}
更多的 api 操作可以訪問 Easypoi - 接口文檔
四、easyexcel
easyexcel 是阿里巴巴開源的一款 excel 解析工具,底層邏輯也是基于 apache poi 進(jìn)行二次開發(fā)的。不同的是,再讀寫數(shù)據(jù)的時(shí)候,采用 sax 模式一行一行解析,在并發(fā)量很大的情況下,依然能穩(wěn)定運(yùn)行!
下面,我們就一起來了解一下這款新起之秀!
4.1、首先添加依賴包
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--常用工具庫-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>29.0-jre</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
4.2、采用注解導(dǎo)出導(dǎo)入
easyexcel 同樣也支持采用注解方式進(jìn)行導(dǎo)出、導(dǎo)入!
首先,我們創(chuàng)建一個(gè)實(shí)體類UserEntity,其中@ExcelProperty注解表示導(dǎo)出文件的頭部信息。
public class UserEntity {
@ExcelProperty(value = "姓名")
private String name;
@ExcelProperty(value = "年齡")
private int age;
@DateTimeFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
@ExcelProperty(value = "操作時(shí)間")
private Date time;
//set、get省略
}
接著,我們來編寫導(dǎo)出服務(wù)!
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<UserEntity> dataList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
UserEntity userEntity = new UserEntity();
userEntity.setName("張三" + i);
userEntity.setAge(20 + i);
userEntity.setTime(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + i));
dataList.add(userEntity);
}
EasyExcel.write("/Users/hello/Documents/easyexcel-user1.xls", UserEntity.class).sheet("用戶信息").doWrite(dataList);
}
導(dǎo)出的文件預(yù)覽如下:
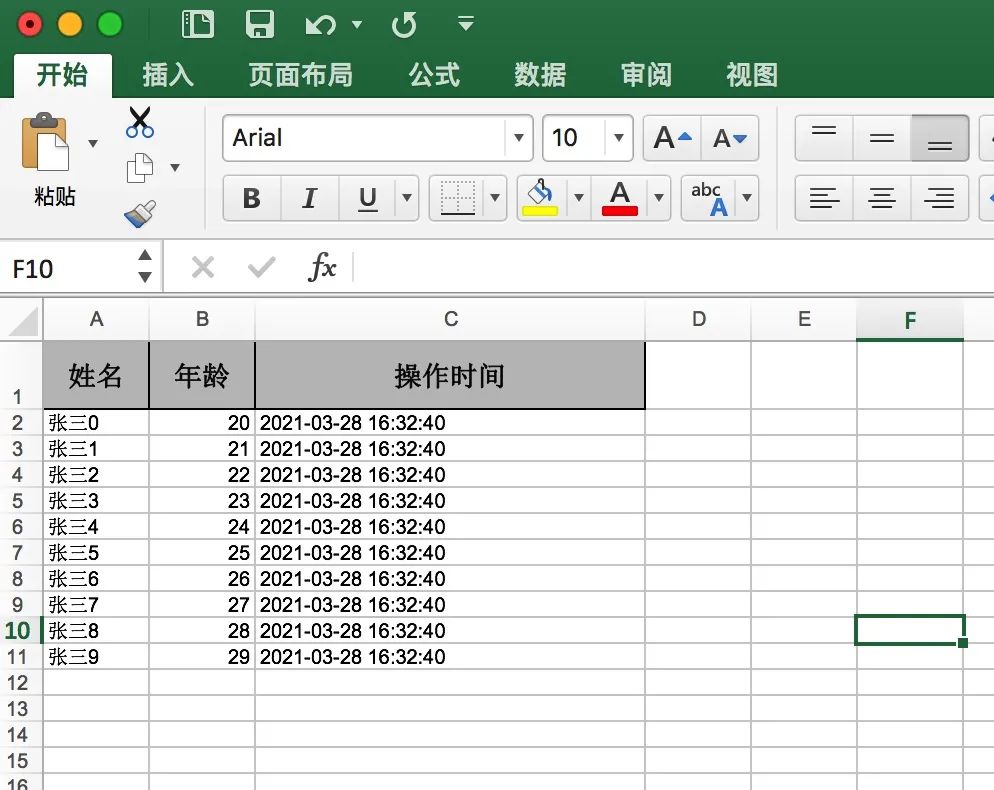
對應(yīng)的導(dǎo)入操作,也很簡單,源碼如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "/Users/hello/Documents/easyexcel-user1.xls";
List<DemoData> list = EasyExcel.read(filePath).head(UserEntity.class).sheet().doReadSync();
System.out.println(JSONArray.toJSONString(list));
}
運(yùn)行程序,輸出結(jié)果如下:
[{"age":20,"name":"張三0","time":1616920360000},{"age":21,"name":"張三1","time":1616920360000},{"age":22,"name":"張三2","time":1616920360000},{"age":23,"name":"張三3","time":1616920360000},{"age":24,"name":"張三4","time":1616920360000},{"age":25,"name":"張三5","time":1616920360000},{"age":26,"name":"張三6","time":1616920360000},{"age":27,"name":"張三7","time":1616920360000},{"age":28,"name":"張三8","time":1616920360000},{"age":29,"name":"張三9","time":1616920360000}]
4.3、自定義數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)導(dǎo)出導(dǎo)入
easyexcel 同樣也支持自定義數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)導(dǎo)出導(dǎo)入excel。
自定義數(shù)據(jù)導(dǎo)出 excel
public static void main(String[] args) {
//表頭
List<List<String>> headList = new ArrayList<>();
headList.add(Lists.newArrayList("姓名"));
headList.add(Lists.newArrayList("年齡"));
headList.add(Lists.newArrayList("操作時(shí)間"));
//數(shù)據(jù)體
List<List<Object>> dataList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
List<Object> data = new ArrayList<>();
data.add("張三" + i);
data.add(20 + i);
data.add(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + i));
dataList.add(data);
}
EasyExcel.write("/Users/hello/Documents/easyexcel-user2.xls").head(headList).sheet("用戶信息").doWrite(dataList);
}
導(dǎo)入 excel
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "/Users/panzhi/Documents/easyexcel-user2.xls";
UserDataListener userDataListener = new UserDataListener();
EasyExcel.read(filePath, userDataListener).sheet().doRead();
System.out.println("表頭:" + JSONArray.toJSONString(userDataListener.getHeadList()));
System.out.println("數(shù)據(jù)體:" + JSONArray.toJSONString(userDataListener.getDataList()));
}
運(yùn)行程序,輸出結(jié)果如下:
表頭:[{0:"姓名",1:"年齡",2:"操作時(shí)間"}]
數(shù)據(jù)體:[{0:"張三0",1:"20",2:"2021-03-28 16:31:39"},{0:"張三1",1:"21",2:"2021-03-28 16:31:39"},{0:"張三2",1:"22",2:"2021-03-28 16:31:39"},{0:"張三3",1:"23",2:"2021-03-28 16:31:39"},{0:"張三4",1:"24",2:"2021-03-28 16:31:39"},{0:"張三5",1:"25",2:"2021-03-28 16:31:39"},{0:"張三6",1:"26",2:"2021-03-28 16:31:39"},{0:"張三7",1:"27",2:"2021-03-28 16:31:39"},{0:"張三8",1:"28",2:"2021-03-28 16:31:39"},{0:"張三9",1:"29",2:"2021-03-28 16:31:39"}]
更多的 api 操作可以訪問 easyexcel - 接口文檔
五、小結(jié)
總體來說,easypoi和easyexcel都是基于apache poi進(jìn)行二次開發(fā)的。
不同點(diǎn)在于:
1、easypoi 在讀寫數(shù)據(jù)的時(shí)候,優(yōu)先是先將數(shù)據(jù)寫入內(nèi)存,優(yōu)點(diǎn)是讀寫性能非常高,但是當(dāng)數(shù)據(jù)量很大的時(shí)候,會出現(xiàn)oom,當(dāng)然它也提供了 sax 模式的讀寫方式,需要調(diào)用特定的方法實(shí)現(xiàn)。
2、easyexcel 基于sax模式進(jìn)行讀寫數(shù)據(jù),不會出現(xiàn)oom情況,程序有過高并發(fā)場景的驗(yàn)證,因此程序運(yùn)行比較穩(wěn)定,相對于 easypoi 來說,讀寫性能稍慢!
easypoi 與 easyexcel 還有一點(diǎn)區(qū)別在于,easypoi 對定制化的導(dǎo)出支持非常的豐富,如果當(dāng)前的項(xiàng)目需求,并發(fā)量不大、數(shù)據(jù)量也不大,但是需要導(dǎo)出 excel 的文件樣式千差萬別,那么我推薦你用 easypoi;反之,使用 easyexcel !
六、參考
1、apache poi - 接口文檔
2、easypoi - 接口文檔
3、easyexcel - 接口文檔

