設(shè)計(jì)模式詳解——組合模式

前言
今天我們分享的這個(gè)設(shè)計(jì)模式,用一句話來(lái)概括的話,就是化零為整,再進(jìn)一步解釋就是,通過(guò)這個(gè)設(shè)計(jì)模式,我們可以像操作一個(gè)對(duì)象一樣操作一個(gè)對(duì)象的集合,不過(guò)這個(gè)對(duì)象在組合模式中被稱作葉節(jié)點(diǎn),而對(duì)象的集合被稱為組合,而這個(gè)結(jié)合本身也是也節(jié)點(diǎn)的樹形結(jié)構(gòu)的集合。是不是感覺越來(lái)越繞了呢?沒關(guān)系,下面我就來(lái)詳細(xì)看下組合模式的基本原理和具體實(shí)現(xiàn)。
組合模式
組合模式允許我們將對(duì)象組合成樹形結(jié)構(gòu)來(lái)表現(xiàn)“整體/部分”層次結(jié)構(gòu)。組合能讓客戶以一致的方式處理個(gè)別對(duì)象以及對(duì)象組合。
它在我們樹型結(jié)構(gòu)的問題中,模糊了簡(jiǎn)單元素和復(fù)雜元素的概念,客戶程序可以像處理簡(jiǎn)單元素一樣來(lái)處理復(fù)雜元素,從而使得客戶程序與復(fù)雜元素的內(nèi)部結(jié)構(gòu)解耦。
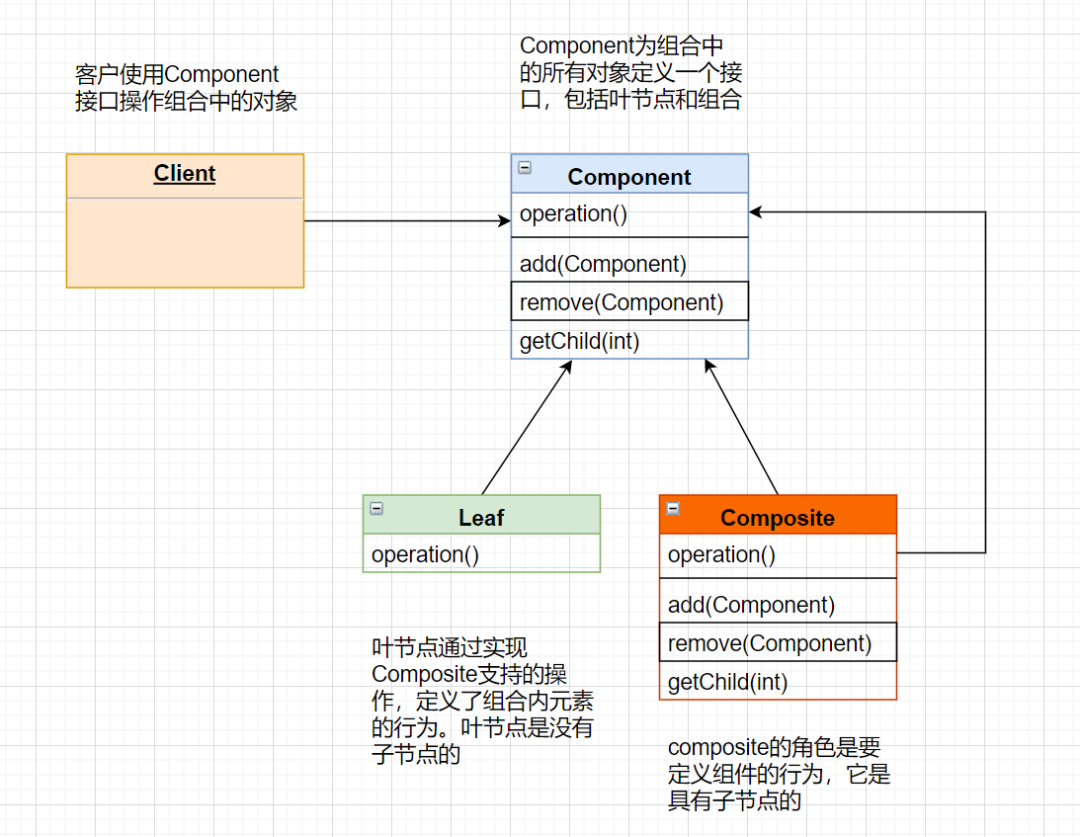
使用場(chǎng)景
想表示對(duì)象的部分-整體層次結(jié)構(gòu)(樹形結(jié)構(gòu))。
希望用戶忽略組合對(duì)象與單個(gè)對(duì)象的不同,用戶將統(tǒng)一地使用組合結(jié)構(gòu)中的所有對(duì)象。
要點(diǎn)
組合模式讓我們能用樹形方式創(chuàng)建對(duì)象的結(jié)構(gòu),樹里面包含了組合以及個(gè)別的對(duì)象 使用組合模式,我們能把相同的操作應(yīng)用到組合和個(gè)別對(duì)象上。換句話說(shuō),在大多數(shù)情況下,我們可以忽略對(duì)象組合和個(gè)別對(duì)象之間的差別。
示例
下面我們通過(guò)一個(gè)具體實(shí)例來(lái)演示下組合模式到底是如何工作的。這里我們直接用了《Head First設(shè)計(jì)模式》上的示例,是對(duì)餐廳菜單的模擬,只不過(guò)我引入了一個(gè)通用接口。
組合接口
首先是組合的接口,這個(gè)接口不論是葉節(jié)點(diǎn)還是葉節(jié)點(diǎn)組合都需要繼承,不過(guò)都不是直接繼承。
public?interface?Component?{
????void?add(Component?component);
????void?remove(Component?component);
????Component?getChild(int?i);
}
組合抽象類
這個(gè)抽象類就是給葉節(jié)點(diǎn)和節(jié)點(diǎn)組合繼承的,其中方法都有了默認(rèn)實(shí)現(xiàn),默認(rèn)都拋出了UnsupportedOperationException
public?abstract?class?MenuComponent?implements?Component?{
????@Override
????public?void?add(Component?component)?{
????????throw?new?UnsupportedOperationException();
????}
????@Override
????public?void?remove(Component?component)?{
????????throw?new?UnsupportedOperationException();
????}
????@Override
????public?Component?getChild(int?i)?{
????????throw?new?UnsupportedOperationException();
????}
????public?String?getName()?{
????????throw?new?UnsupportedOperationException();
????}
????public?String?getDescription()?{
????????throw?new?UnsupportedOperationException();
????}
????public?double?getPrice()?{
????????throw?new?UnsupportedOperationException();
????}
????public?boolean?isVegetarian()?{
????????throw?new?UnsupportedOperationException();
????}
????public?void?print()?{
????????throw?new?UnsupportedOperationException();
????}
}
葉節(jié)點(diǎn)實(shí)現(xiàn)
這里的葉節(jié)點(diǎn)主要覆寫了父類的getName、getDescription、isVegetarian和getPrice等方法,這些方法也主要是針對(duì)具體菜單的
public?class?MenuItem?extends?MenuComponent?{
????private?String?name;
????private?String?description;
????private?boolean?vegetarian;
????private?double?price;
????public?MenuItem(String?name,?String?description,?boolean?vegetarian,?double?price)?{
????????this.name?=?name;
????????this.description?=?description;
????????this.vegetarian?=?vegetarian;
????????this.price?=?price;
????}
????@Override
????public?String?getName()?{
????????return?name;
????}
????@Override
????public?String?getDescription()?{
????????return?description;
????}
????@Override
????public?boolean?isVegetarian()?{
????????return?vegetarian;
????}
????@Override
????public?double?getPrice()?{
????????return?price;
????}
????@Override
????public?void?print()?{
????????System.out.println("==========start=============");
????????System.out.printf("name:?%s??price:?¥%s%n",?this.getName(),?this.getPrice());
????????System.out.printf("description:?%s??isVegetarian:?%s%n",?this.getDescription(),?this.isVegetarian());
????????System.out.println("==========end=============");
????}
}
節(jié)點(diǎn)組合實(shí)現(xiàn)
因?yàn)楣?jié)點(diǎn)組合要管理葉節(jié)點(diǎn),所以這里主要實(shí)現(xiàn)了add、remove、getChild等方法,當(dāng)然也實(shí)現(xiàn)了getName和getDescription等基礎(chǔ)方法:
public?class?Menu?extends?MenuComponent?{
????ArrayList?menuComponents?=?new?ArrayList<>();
????String?name;
????String?description;
????public?Menu(String?name,?String?description)?{
????????this.name?=?name;
????????this.description?=?description;
????}
????@Override
????public?void?add(Component?component)?{
????????menuComponents.add(component);
????}
????@Override
????public?void?remove(Component?component)?{
????????menuComponents.remove(component);
????}
????@Override
????public?Component?getChild(int?i)?{
????????return?menuComponents.get(i);
????}
????@Override
????public?String?getName()?{
????????return?super.getName();
????}
????@Override
????public?String?getDescription()?{
????????return?super.getDescription();
????}
????@Override
????public?void?print()?{
????????System.out.println("==========start=============");
????????System.out.printf("name:?%s",?this.getName());
????????System.out.printf("description:?%s",?this.getDescription());
????????System.out.println("==========child?start=============");
????????Iterator?iterator?=?menuComponents.iterator();
????????while?(iterator.hasNext())?{
????????????MenuComponent?component?=?(MenuComponent)iterator.next();
????????????component.print();
????????}
????????System.out.println("==========child?end=============");
????????System.out.println("============end===========");
????}
}
測(cè)試代碼
下面我們開始編寫測(cè)試代碼。這里我們分別構(gòu)造了多個(gè)葉節(jié)點(diǎn),并將其中一部分組成節(jié)點(diǎn)組合,最后分別執(zhí)行葉節(jié)點(diǎn)和子節(jié)點(diǎn)的print方法(這里的print方法其實(shí)就是我們?cè)O(shè)計(jì)模式原理圖中的operation方法)
????@Test
????public?void?testComponent()?{
????????//?葉節(jié)點(diǎn)
????????MenuItem?slr?=?new?MenuItem("燒鹿茸",?"好吃美味,價(jià)格實(shí)惠",?Boolean.FALSE,?180.0);
????????MenuItem?sxz?=?new?MenuItem("燒熊掌",?"好吃美味,價(jià)格實(shí)惠",?Boolean.FALSE,?190.0);
????????MenuItem?hsr?=?new?MenuItem("紅燒肉",?"好吃美味,價(jià)格實(shí)惠",?Boolean.FALSE,?36.0);
????????MenuItem?hsqz?=?new?MenuItem("紅燒茄子",?"好吃美味,價(jià)格實(shí)惠",?Boolean.TRUE,?14.0);
????????MenuItem?hsjk?=?new?MenuItem("紅燒雞塊",?"好吃美味,價(jià)格實(shí)惠",?Boolean.FALSE,?38.0);
????????MenuItem?yxrs?=?new?MenuItem("魚香肉絲",?"好吃美味,價(jià)格實(shí)惠",?Boolean.FALSE,?22.0);
????????MenuItem?ssbc?=?new?MenuItem("手撕包菜",?"好吃美味,價(jià)格實(shí)惠",?Boolean.TRUE,?12.0);
????????//?組合節(jié)點(diǎn)
????????Menu?menu?=?new?Menu("家常菜",?"美味家常菜");
????????menu.add(hsr);
????????menu.add(hsqz);
????????menu.add(hsjk);
????????menu.add(yxrs);
????????menu.add(ssbc);
????????//?子節(jié)點(diǎn)print方法
????????slr.print();
????????sxz.print();
????????//?組合節(jié)點(diǎn)print方法
????????menu.print();
????}
運(yùn)行結(jié)果

總結(jié)
想必通過(guò)上面的示例,各位小伙伴已經(jīng)對(duì)組合模式有了一定的認(rèn)知,對(duì)這種設(shè)計(jì)模式適用的場(chǎng)景也有了比較明確認(rèn)識(shí):如果在一個(gè)業(yè)務(wù)中,單個(gè)對(duì)象和對(duì)象的集合需要具備同樣的類型和方法,那組合模式就是最佳選擇,比如我們這里的菜單和菜單組合,當(dāng)然,更具體的應(yīng)用場(chǎng)景,還需要各位小伙伴結(jié)合具體應(yīng)用場(chǎng)景分析,但是學(xué)習(xí)的時(shí)候多思考應(yīng)用場(chǎng)景才是學(xué)習(xí)正在的目的。好了,今天就到這里吧!
- END -