Spring SPI 機(jī)制總結(jié)
點(diǎn)擊上方藍(lán)色字體,選擇“標(biāo)星公眾號(hào)”
優(yōu)質(zhì)文章,第一時(shí)間送達(dá)
作者 | ocean.wen
來(lái)源 | urlify.cn/m6niA3
76套java從入門到精通實(shí)戰(zhàn)課程分享
1、概念:
SPI(Service Provider Interface)服務(wù)提供接口,簡(jiǎn)單來(lái)說(shuō)就是用來(lái)解耦,實(shí)現(xiàn)插件的自由插拔,具體實(shí)現(xiàn)方案可參考JDK里的ServiceLoader(加載classpath下所有META-INF/services/目錄下的對(duì)應(yīng)給定接口包路徑的文件,然后通過(guò)反射實(shí)例化配置的所有實(shí)現(xiàn)類,以此將接口定義和邏輯實(shí)現(xiàn)分離)
Spring在3.0.x的時(shí)候就已經(jīng)引入了spring.handlers,很多博客講Spring SPI的時(shí)候并沒(méi)有提到spring.handlers,但是通過(guò)我自己的分析對(duì)比,其實(shí)spring.handlers也是一種SPI的實(shí)現(xiàn),只不過(guò)它是基于xml的,而且在沒(méi)有boot的年代,它幾乎是所有三方框架跟spring整合的必選機(jī)制。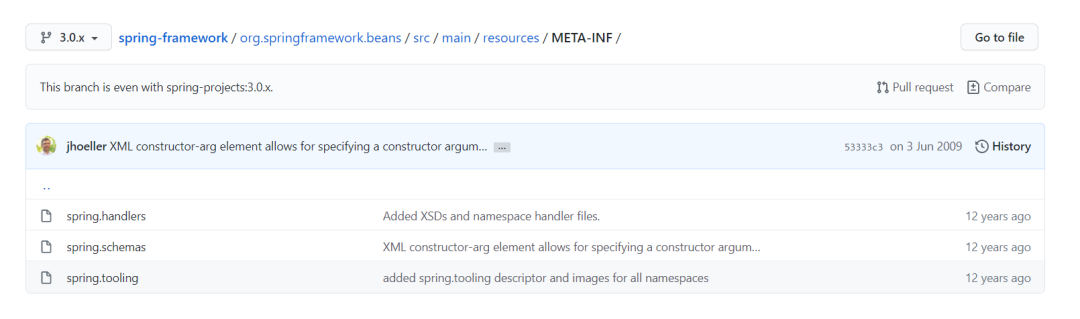
在3.2.x又新引入了spring.factories,它的實(shí)現(xiàn)跟JDK的SPI就基本是相似的了。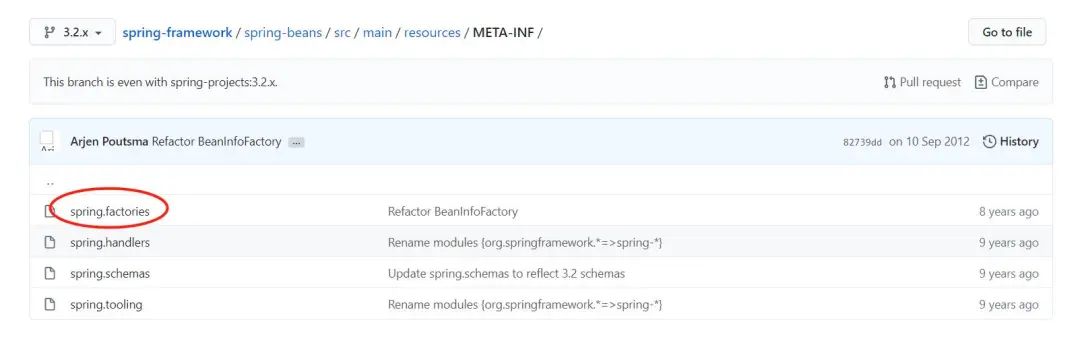
spring.handlers和spring.factories我都把它歸納為Spring為我們提供的SPI機(jī)制,通過(guò)這兩種機(jī)制,我們可以在不修改Spring源碼的前提下,非常輕松的做到對(duì)Spring框架的擴(kuò)展開發(fā)。
2、實(shí)現(xiàn):
2.1 先看看spring.handlers SPI
在Spring里有個(gè)接口NamespaceHandlerResolver,只有一個(gè)默認(rèn)的實(shí)現(xiàn)類DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver,而它的作用就是加載classpath下可能分散在各個(gè)jar包中的META-INF/spring.handlers文件,resolve方法中關(guān)鍵代碼如下:
//加載所有jar包中的META-INF/spring.handlers文件
Properties mappings=
PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties(this.handlerMappingsLocation, this.classLoader);
//把META-INF/spring.handlers中配置的namespaceUri對(duì)應(yīng)實(shí)現(xiàn)類實(shí)例化
NamespaceHandler namespaceHandler =
(NamespaceHandler) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(handlerClass);
DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver.resolve()主要被用在BeanDefinitionParserDelegate的parseCustomElement和decorateIfRequired,所以spring.handlers SPI機(jī)制主要也是被用在bean的掃描和解析過(guò)程中。
2.2 再來(lái)看spring.factories SPI
// 獲取某個(gè)已定義接口的實(shí)現(xiàn)類,跟JDK的ServiceLoader SPI相似度為90%
List<BeanInfoFactory> beanInfoFactories = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(BeanInfoFactory.class, classLoader);
// spring.factories文件的格式為:key=value1,value2,value3
// 從所有jar文件中找到MET-INF/spring.factories文件(注意是:classpath下的所有jar包,所以可插拔、擴(kuò)展性超強(qiáng))
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
String propertyValue = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName);
for (String factoryName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(propertyValue)) {
result.add(factoryName.trim());
}
}
return result;
更多細(xì)節(jié),大家可以參考SpringFactoriesLoader類,Spring自3.2.x引入spring.factories SPI后其實(shí)一直沒(méi)怎么利用起來(lái),只有CachedIntrospectionResults(初始化bean的過(guò)程中)用到了,而且在幾大核心jar包里,也只有bean包里才有用到。
真正把spring.factories發(fā)揚(yáng)光大的,是到了Spring Boot,可以看到boot包里配置了非常多的接口實(shí)現(xiàn)類。大家跟蹤boot的啟動(dòng)類SpringApplication可以發(fā)現(xiàn),有很多地方都調(diào)用了getSpringFactoriesInstances()方法,這些就是spring boot開給我們的擴(kuò)展機(jī)會(huì),就像一座寶藏一樣,大家可以自己去發(fā)掘。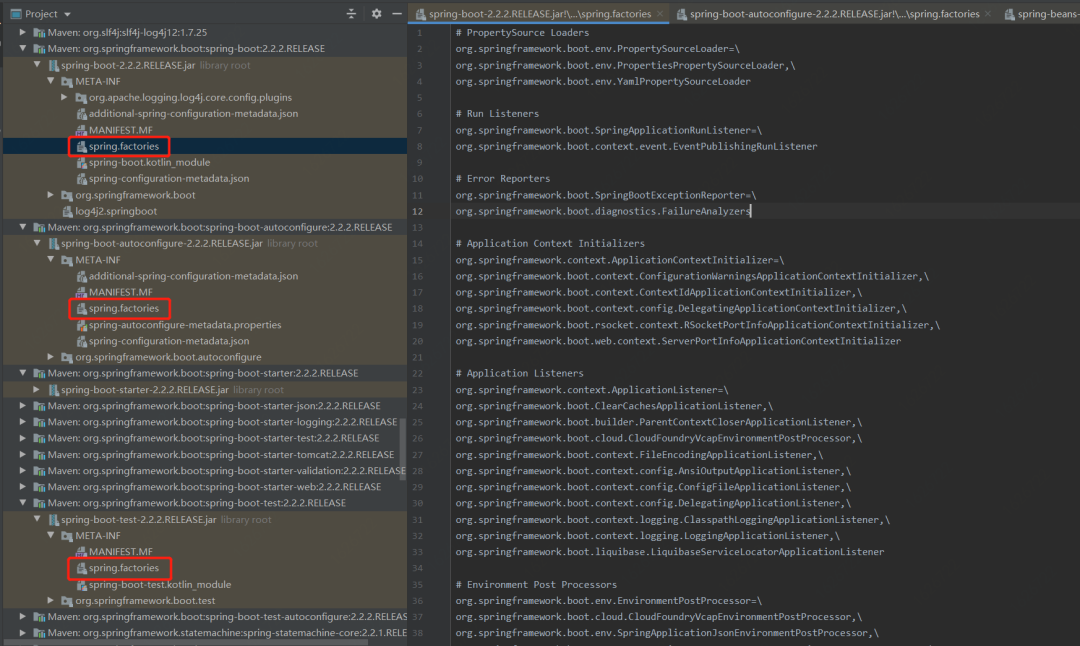
3、應(yīng)用:
先來(lái)看看mybatis和dubbo早期跟Spring整合的實(shí)現(xiàn),他們無(wú)一例外都用到了spring.handlers SPI機(jī)制,以此來(lái)向IOC容器注入自己的Bean。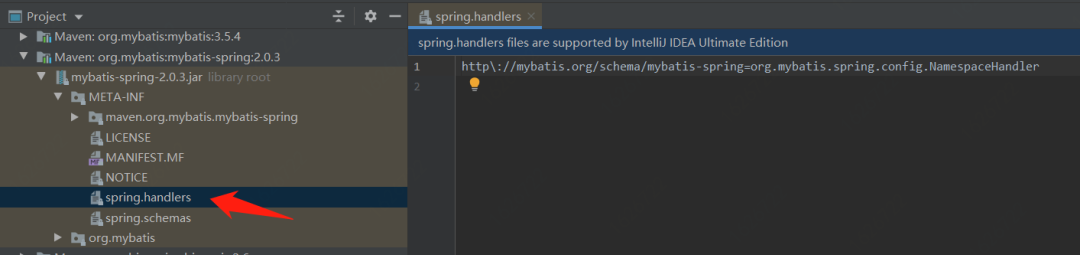
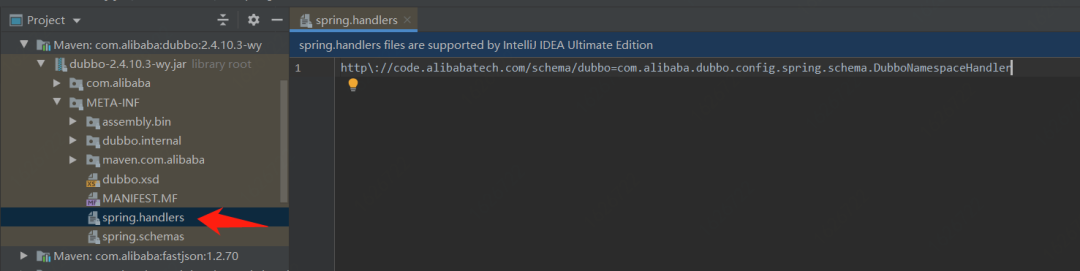
進(jìn)入boot時(shí)代后,spring.factories SPI機(jī)制應(yīng)用得更加廣泛,我們可以在容器啟動(dòng)、環(huán)境準(zhǔn)備、初始化、上下文加載等等環(huán)節(jié)輕輕松松的對(duì)Spring做擴(kuò)展開發(fā)(例如:我們項(xiàng)目中用到spring.factories SPI機(jī)制對(duì)配置文件中的變量實(shí)現(xiàn)動(dòng)態(tài)解密,以及前篇博文中提到的@Replace注解等)。
4、實(shí)踐(加載application.xyz配置文件):
Spring里有兩種常見(jiàn)的配置文件類型:application.properties 和 application.yml,其中yml是近年興起的,但說(shuō)實(shí)話同事也包括我自己是被它坑過(guò),沒(méi)有合適的編輯器時(shí)很容易把格式寫錯(cuò),導(dǎo)致上線出問(wèn)題。所以我就在想有沒(méi)有辦法讓Spring支持一種新的配置文件格式,既保留yml的簡(jiǎn)潔優(yōu)雅,有能夠有強(qiáng)制的格式校驗(yàn),暫時(shí)我想到了json格式。
# 這是spring.factories中的配置
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=top.hiccup.json.MyJsonPropertySourceLoader
public class MyJsonPropertySourceLoader implements PropertySourceLoader {
@Override
public String[] getFileExtensions() {
return new String[]{"xyz"};
}
@Override
public List<PropertySource<?>> load(String name, Resource resource) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(resource.getInputStream()));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(line);
}
// 這里只是做了簡(jiǎn)單解析,沒(méi)有做嵌套配置的解析
JSONObject json = JSONObject.parseObject(sb.toString());
List<PropertySource<?>> propertySources = new ArrayList<>();
MapPropertySource mapPropertySource = new MapPropertySource(resource.getFilename(), json);
propertySources.add(mapPropertySource);
return propertySources;
}
}
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(BootTest.class, args);
Custom custom = ctx.getBean(Custom.class);
System.out.println(custom.name);
System.out.println(custom.age);
具體代碼可以參考(https://github.com/hiccup234/web-advanced/tree/master/configFile) ,運(yùn)行得到結(jié)果如下: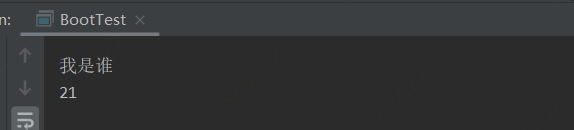
可見(jiàn)我們?cè)诓恍薷腟pring源碼的前提下,輕松通過(guò)Spring開放給我們的擴(kuò)展性實(shí)現(xiàn)了對(duì)新的配置文件類型的加載和解析。
這就是Spring SPI的魅力吧。
粉絲福利:Java從入門到入土學(xué)習(xí)路線圖
??????

??長(zhǎng)按上方微信二維碼 2 秒
感謝點(diǎn)贊支持下哈 
