JUC并發(fā)編程之Semaphore源碼詳解
在前面分享的一篇文章中,我分享到了ReentrantLock源碼,它是基于AQS進行實現(xiàn)的,那么今天本文分享的同樣也是基于AQS實現(xiàn)的Semaphore工具類
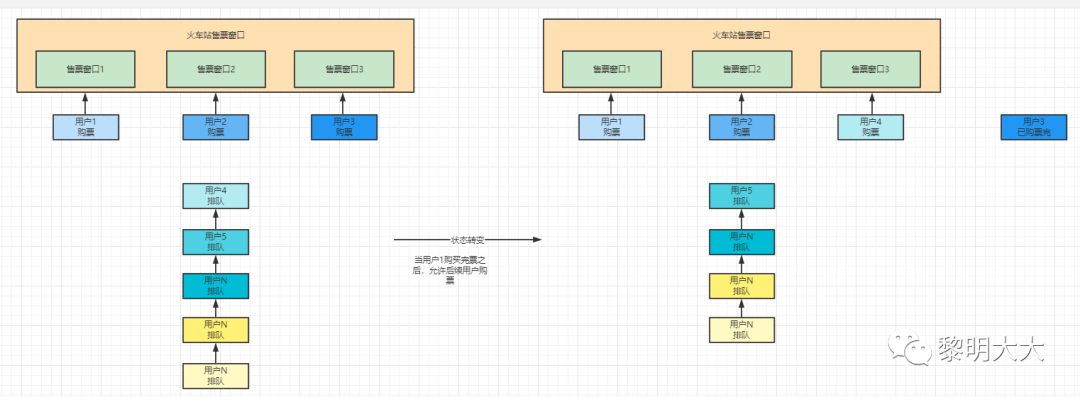
Semaphore字面意思是信號量的意思,這種說法并不能夠很好的描述它的作用,更通俗的來說應(yīng)該是令牌管理器。官方文檔說明Semaphore是一個計數(shù)信號量,從概念來講Semaphore包含了一組許可證。每個用戶都必須拿到許可證才能訪問后續(xù)資源,沒有拿到許可證的用于則需要進行等待獲取許可證。
這么說會稍微有點不好理解,舉個很通俗易懂例子:
這個案例的人就是線程,而正在購票的操作表示線程正在執(zhí)行業(yè)務(wù)邏輯,離開窗口則表示線程執(zhí)行完畢,看到窗口有人正在購票則排隊等待則表示線程即將入隊阻塞。
public class SemaphoreTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 聲明3個窗口Semaphore windows = new Semaphore(3, true);for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {new Thread(() -> {try {//占用窗口windows.acquire();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":開始買票");//模擬買票流程Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":購買成功");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {windows.release();}}).start();}}}
源碼分析
// 默認(rèn)構(gòu)造方法,走非公平鎖流程,permits:支持令牌數(shù)量public Semaphore(int permits) {sync = new NonfairSync(permits);}// 根據(jù)fair屬性決定是否走公平還是非公平鎖流程,permits:支持令牌數(shù)量public Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair) {sync = fair ? new FairSync(permits) : new NonfairSync(permits);}
public void acquire() throws InterruptedException {sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);}
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)throws InterruptedException {if (Thread.interrupted())throw new InterruptedException();if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int arg) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires);}
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) {for (;;) { // 自旋int available = getState(); //獲得當(dāng)前令牌數(shù)量int remaining = available - acquires; // 計算令牌數(shù)量if (remaining < 0 ||compareAndSetState(available, remaining)) // 還有令牌可用的話,則直接進行CAS獲取令牌return remaining;}}
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)throws InterruptedException {if (Thread.interrupted())throw new InterruptedException();if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);}
進入到獲取令牌失敗的邏輯方法,主要的邏輯都在自旋里面,但是外面同樣也有個比較重要的方法,就是addWaiter()方法,該方法傳入的參數(shù)值為 "Node.SHARED" ,而SHARED的值就是new Node() 也就是創(chuàng)建了一個空的節(jié)點,然后我們來看看addWaiter()方法其內(nèi)部邏輯做了些什么事情?
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)throws InterruptedException {final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED); // 構(gòu)建雙向鏈表 或 入隊操作boolean failed = true;try {for (;;) { // 自旋final Node p = node.predecessor(); //獲取當(dāng)前節(jié)點的前驅(qū)節(jié)點if (p == head) {int r = tryAcquireShared(arg); // 嘗試獲取令牌if (r >= 0) { // 獲取令牌成功setHeadAndPropagate(node, r); //傳播鏈表p.next = null; // help GC 將前驅(qū)節(jié)點的引用指向為NULL,待垃圾回收器回收failed = false;return; // 獲取令牌成功,退出自旋}}if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&parkAndCheckInterrupt()) // 阻塞當(dāng)前線程throw new InterruptedException();}} finally {// 如果某個線程被中斷,非正常流程退出則將當(dāng)前線程的節(jié)點設(shè)置為cancel狀態(tài)if (failed)cancelAcquire(node);}}
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode); // 封裝節(jié)點// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failureNode pred = tail; // 獲取末尾節(jié)點if (pred != null) {node.prev = pred; // 當(dāng)前節(jié)點的前驅(qū)引用指向為predif (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { // 將當(dāng)前節(jié)點設(shè)置為鏈表末尾節(jié)點pred.next = node; // 原末尾節(jié)點后驅(qū)引用指向為當(dāng)前節(jié)點return node;}}enq(node);return node;}
基于FIFO入隊流程圖
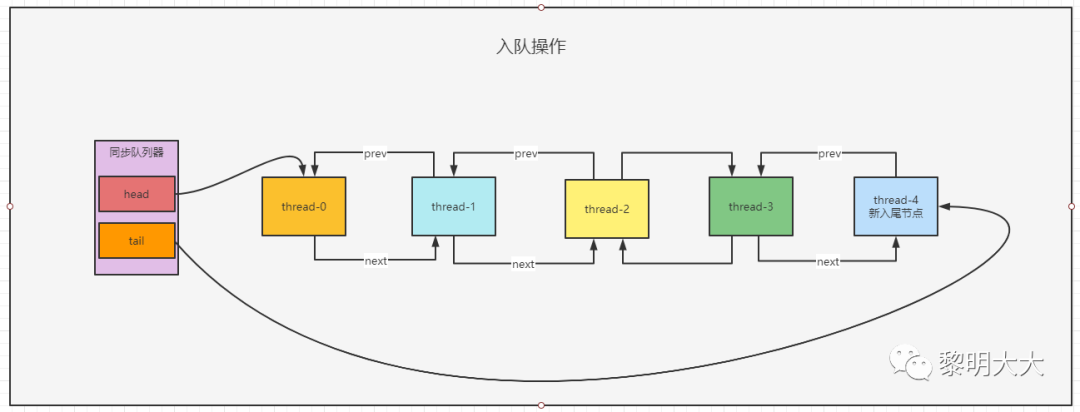
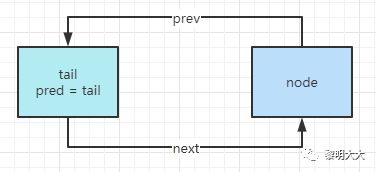
private Node enq(final Node node) {for (;;) {Node t = tail; // 獲取末尾節(jié)點if (t == null) { // Must initialize // 構(gòu)建雙向鏈表if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))tail = head;} else {node.prev = t;if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {t.next = node;return t;}}}}
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)throws InterruptedException {final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED); // 構(gòu)建雙向鏈表 或 入隊操作boolean failed = true;try {for (;;) { // 自旋final Node p = node.predecessor(); //獲取當(dāng)前節(jié)點的前驅(qū)節(jié)點if (p == head) {int r = tryAcquireShared(arg); // 嘗試獲取令牌if (r >= 0) { // 獲取令牌成功setHeadAndPropagate(node, r); //傳播鏈表p.next = null; // help GC 將前驅(qū)節(jié)點的引用指向為NULL,待垃圾回收器回收failed = false;return; // 獲取令牌成功,退出自旋}}if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && //判斷線程是否需要被阻塞parkAndCheckInterrupt()) // 阻塞當(dāng)前線程throw new InterruptedException();}} finally {// 如果某個線程被中斷,非正常流程退出則將當(dāng)前線程的節(jié)點設(shè)置為cancel狀態(tài)if (failed)cancelAcquire(node);}}
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {Node h = head; // Record old head for check belowsetHead(node);/** Try to signal next queued node if:* Propagation was indicated by caller,* or was recorded (as h.waitStatus either before* or after setHead) by a previous operation* (note: this uses sign-check of waitStatus because* PROPAGATE status may transition to SIGNAL.)* and* The next node is waiting in shared mode,* or we don't know, because it appears null** The conservatism in both of these checks may cause* unnecessary wake-ups, but only when there are multiple* racing acquires/releases, so most need signals now or soon* anyway.*/if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 || // 還有令牌可獲取 || 頭節(jié)點狀態(tài)處于等待狀態(tài)(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {Node s = node.next; // 獲取當(dāng)前下一節(jié)點if (s == null || s.isShared()) // 判斷下節(jié)點是否為共享節(jié)點doReleaseShared(); // 傳播~~ 具體傳播什么呢???}}
private void setHead(Node node) {head = node;node.thread = null;node.prev = null;}
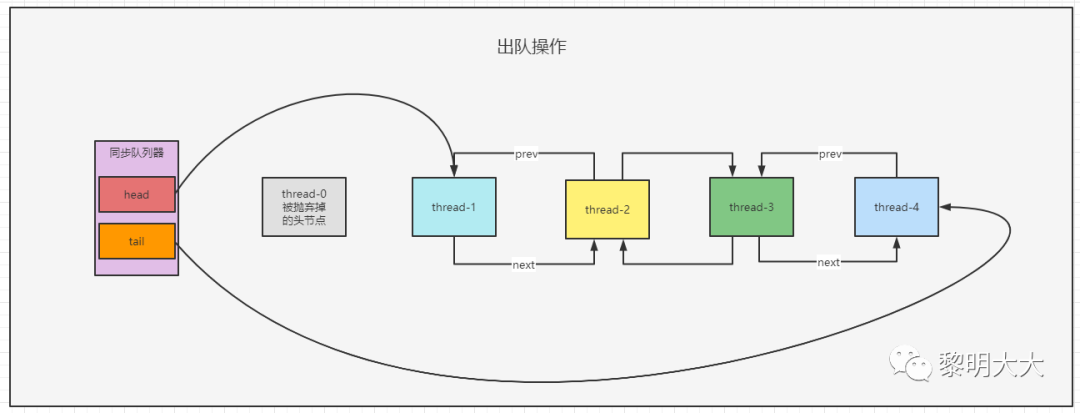
private void doReleaseShared() {/** Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other* in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual* way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs* signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to* ensure that upon release, propagation continues.* Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added* while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of* unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status* fails, if so rechecking.*/for (;;) { // 自旋 可以理解為傳播 【加自旋的原因,可能同時有多個令牌被釋放,那么在這里就可以喚醒后續(xù)所有節(jié)點去獲取令牌,就不用在前面再去判斷是否要去喚醒后驅(qū)節(jié)點了。如果沒有獲取到令牌也沒關(guān)系,后面還是會將沒有搶到的線程進行阻塞住】Node h = head;if (h != null && h != tail) { // 頭節(jié)點不為null 其 頭非等于尾節(jié)點 則證明當(dāng)前鏈表還有多個節(jié)點int ws = h.waitStatus; // 獲取head的節(jié)點狀態(tài)if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) { // 如果當(dāng)前節(jié)點狀態(tài)為SIGNAL,就代表后驅(qū)節(jié)點正在被阻塞著if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0)) // 通過cas將狀態(tài)從等待更換為非等待,然后取反的話,將下一個節(jié)點喚醒continue; // loop to recheck casesunparkSuccessor(h); // 喚醒線程 去獲取令牌}else if (ws == 0 &&!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE)) // 如果節(jié)點狀態(tài)已經(jīng)為0,則會將節(jié)點的狀態(tài)更新為PROPAGATE PROPAGATE:表示下一次共享式同步狀態(tài)獲取將會被無條件地傳播下去continue; // loop on failed CAS}if (h == head) // loop if head changedbreak; // 跳出當(dāng)前循環(huán)}}

sync.releaseShared(1);public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) { //通用釋放令牌doReleaseShared(); //喚醒后驅(qū)節(jié)點return true;}return false;}
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {for (;;) {int current = getState();int next = current + releases;if (next < current) // overflowthrow new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded");if (compareAndSetState(current, next))return true;}}
private void doReleaseShared() {/** Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other* in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual* way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs* signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to* ensure that upon release, propagation continues.* Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added* while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of* unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status* fails, if so rechecking.*/for (;;) { // 自旋 可以理解為傳播 【加自旋的原因,可能同時有多個令牌被釋放,那么在這里就可以喚醒后續(xù)所有節(jié)點去獲取令牌,就不用在前面再去判斷是否要去喚醒后驅(qū)節(jié)點了。如果沒有獲取到令牌也沒關(guān)系,后面還是會將沒有搶到的線程進行阻塞住】Node h = head;if (h != null && h != tail) { // 頭節(jié)點不為null 其 頭非等于尾節(jié)點 則證明當(dāng)前鏈表還有多個節(jié)點int ws = h.waitStatus; // 獲取head的節(jié)點狀態(tài)if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) { // 如果當(dāng)前節(jié)點狀態(tài)為SIGNAL,就代表后驅(qū)節(jié)點正在被阻塞著if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0)) // 通過cas將狀態(tài)從等待更換為非等待,然后取反的話,將下一個節(jié)點喚醒continue; // loop to recheck casesunparkSuccessor(h); // 喚醒線程 去獲取令牌}else if (ws == 0 &&!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE)) // 如果節(jié)點狀態(tài)已經(jīng)為0,則會將節(jié)點的狀態(tài)更新為PROPAGATE PROPAGATE:表示下一次共享式同步狀態(tài)獲取將會被無條件地傳播下去continue; // loop on failed CAS}if (h == head) // loop if head changedbreak; // 跳出當(dāng)前循環(huán)}}
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {// 先獲取head節(jié)點的狀態(tài),應(yīng)該是等于-1,原因在shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire方法中有體現(xiàn)int ws = node.waitStatus;// 由于-1會小于0,所以更新改為0if (ws < 0)compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);// 獲取第一個正常排隊的節(jié)點Node s = node.next;//正常解鎖流程不會走該if判斷if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {s = null;for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)if (t.waitStatus <= 0)s = t;}// 正常來說第一個排隊的節(jié)點不應(yīng)該為空,所以直接把第一個排隊的線程喚醒if (s != null)LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);}
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {LockSupport.park(this);return Thread.interrupted();}
public void acquire() throws InterruptedException {sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);}
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)throws InterruptedException {if (Thread.interrupted())throw new InterruptedException();if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int arg) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {for (;;) {if (hasQueuedPredecessors())return -1;int available = getState();int remaining = available - acquires;if (remaining < 0 ||compareAndSetState(available, remaining))return remaining;}}
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {// The correctness of this depends on head being initialized// before tail and on head.next being accurate if the current// thread is first in queue.Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization orderNode h = head;Node s;return h != t &&((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());}
那么到此Semaphore公平與非公平獲取令牌的與釋放令牌的流程,到此就結(jié)束啦
最后方法Semaphore源碼詳解視頻,可結(jié)合博文一起觀看
我是黎明大大,我知道我沒有驚世的才華,也沒有超于凡人的能力,但畢竟我還有一個不屈服,敢于選擇向命運沖鋒的靈魂,和一個就是傷痕累累也要義無反顧走下去的心。
如果您覺得本文對您有幫助,還請關(guān)注點贊一波,后期將不間斷更新更多技術(shù)文章

●JUC并發(fā)編程之ReentrantLock非公平鎖源碼詳解
●JUC并發(fā)編程之Synchronized關(guān)鍵字詳解
●JUC并發(fā)編程之MESI緩存一致協(xié)議詳解

