MySQL必須掌握4種語言!
本篇文章主要給大家介紹的是MySQL中常用的4種語言:
一、DDL
DDL,data defination language,指的是數(shù)據(jù)定義語言,其主要作用是創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)庫,對庫表的結(jié)構(gòu)進行刪除和修改等操作。
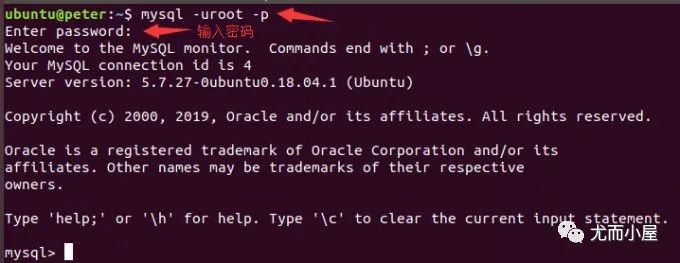
進入數(shù)據(jù)庫
mysql -uroot -p -- 使用這種方式,接下來需要輸入密碼。密碼是暗文
mysql -uroot -p123456 -- 可以直接將密碼123456放在參數(shù)p的后面,不安全參數(shù)解釋:
u:指定用戶
p:指定密碼
全部命令
1. 數(shù)據(jù)庫操作
show databases; // 顯示所有的數(shù)據(jù)庫
use school; // 使用school數(shù)據(jù)庫
create database school; // 創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)庫
drop database school; // 刪除某個數(shù)據(jù)庫
2. 表操作
-- 創(chuàng)建表
create table user(字段1,字段2,...,字段n);
-- 查看創(chuàng)建表的SQL語句
show create table user;
-- 查看表的結(jié)構(gòu)
desc user;
-- 刪除表
drop table user;
-- 修改表名
alter table user rename to users;數(shù)據(jù)庫操作
show databases; // 顯示所有的數(shù)據(jù)庫
use school; // 使用school數(shù)據(jù)庫
create database school; // 創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)庫
drop database school; // 刪除某個數(shù)據(jù)庫
mysql> show databases; // 顯示數(shù)據(jù)庫
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| peter |
| school |
| sys |
+--------------------+
6 rows in set (0.04 sec)
mysql> use school; // 選擇使用數(shù)據(jù)庫
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A表操作
// 1、創(chuàng)建表
create table user(字段1,
字段2,
...,
字段n
); // 最后的分號不能忘記
// 2、查看所有的表
show tables;
// 3、查看表的結(jié)構(gòu)
desc user;
// 4、查看創(chuàng)建表的SQL語句
show create table user;
// 5、刪除表
drop table user;
// 6、修改表名
alter table user rename to users; # 表名改為users;to可省略最后的分號不能忘記??
mysql> use school; // 使用一個數(shù)據(jù)庫
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show tables; // 查看數(shù)據(jù)庫下的所有表
+------------------+
| Tables_in_school |
+------------------+
| course |
| score |
| student |
| teacher |
| total |
+------------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)創(chuàng)建表
主鍵 primary key和auto_increment必須連在一起使用書寫規(guī)范:每個字段的語句最好分行寫,容易檢查 最后的分號不能忘記
# 創(chuàng)建user表:6種字段+1個主鍵
create table user( id int(10) unsigned not null auto_increment comment "user_id", //將id作為主鍵
name varchar(20) not null comment "user_name",
email varchar(50) not null comment "user_email",
age tinyint unsigned not null comment "user_age",
fee decimal(10,2) not null default 0.00 comment "user_fee",
createTime timestamp not null comment "user_time",
primary key(id)
); // 記得分號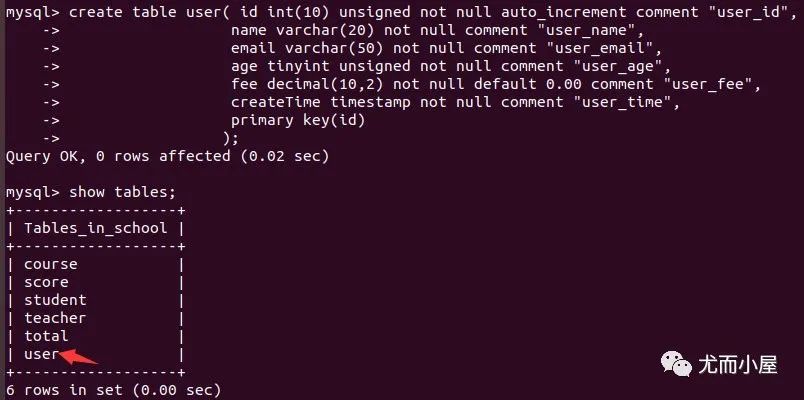
查看表結(jié)構(gòu)
mysql> desc user;
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| email | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | |
| age | tinyint(3) unsigned | NO | | NULL | |
| fee | decimal(10,2) | NO | | 0.00 | |
| createTime | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
6 rows in set (0.02 sec)查看創(chuàng)建表的SQL語句
show create table user;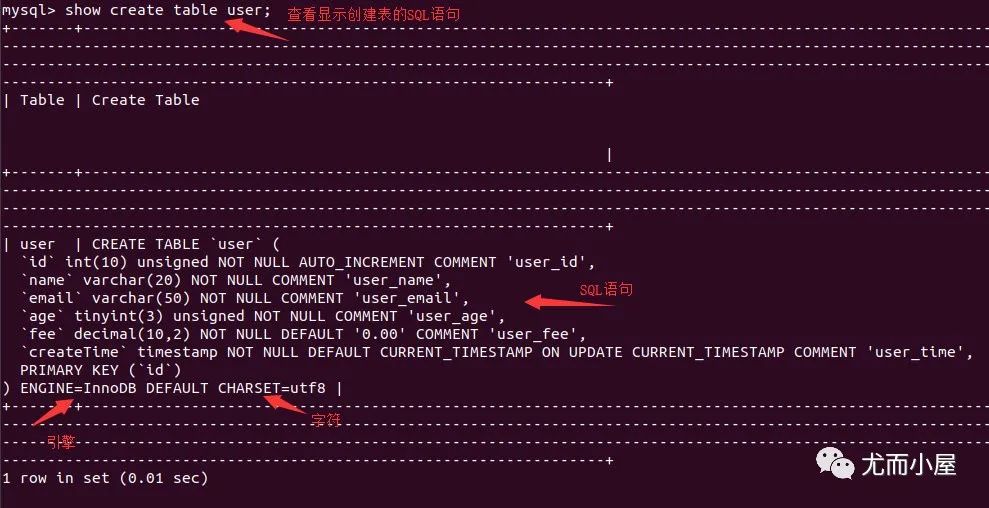
字段操作
關(guān)鍵詞是alter,先選中需要操作的表。
modify:修改change:改變名字add:添加字段 默認(rèn)是末尾 指定位置添加
// 修改字段信息
alter table user modify name varchar(50) not null; # 將字段name 從20改為50個字符
// 修改字段名字
alter table user change email user_email varchar(50) not null; # 將email改成user_email
// 末尾添加字段
alter table user add password char(30) not null comment "user_password"; # 增加password字段
// 指定位置添加字段
alter table user add password1 char(30) not null comment "user_password1" after user_name; # 在name后面增加password1字段
// 刪除字段
alter table user drop password1; #刪除字段password1
// 原來的表格信息
mysql> desc user;
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| email | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | |
| age | tinyint(3) unsigned | NO | | NULL | |
| fee | decimal(10,2) | NO | | 0.00 | |
| createTime | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
# 修改字段信息
mysql> alter table user modify name varchar(50);
# 修改字段名字
mysql> alter table user change email user_email varchar(50) not null;
# 添加字段,末尾
mysql> alter table user add password char(30) not null comment "user_password";
# 指定位置添加字段
mysql> alter table user add password1 char(30) not null comment "user_password1" after name;
mysql> desc user;
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(50) | YES | | NULL | |
| password1 | char(30) | NO | | NULL | |
| user_email | varchar(50) | NO | | NULL | |
| age | tinyint(3) unsigned | NO | | NULL | |
| fee | decimal(10,2) | NO | | 0.00 | |
| createTime | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
| password | char(30) | NO | | NULL | |
+------------+---------------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)二、DML
DML,data manipulation language,指的是數(shù)據(jù)操作語言。主要是對數(shù)據(jù)庫中的表記錄進行操作的語言,包含往表中插入數(shù)據(jù)、表中數(shù)據(jù)的更新、表的刪除等
表中插入數(shù)據(jù) 表中數(shù)據(jù)更新 刪除表
表中插入數(shù)據(jù)
-- 將字段名和字段的值一一對應(yīng)起來,可以只插入部分字段
-- 省略了id和createtime字段
mysql> insert into user(
name,
email,
age,
fee,
password)
values("xiaoming",
"[email protected]",
20,
56.56,
Password("xiaoming") // 密碼這里要用函數(shù)Password()
);
-- 包含所有字段信息
insert into user values(10, "nanan", "[email protected]", 38, 89.19, 2019-10-02, Password("nanan"));字符串字段必須用引號括起來 密碼需要使用函數(shù) Password()語句末尾加分號 利用只插入部分字段 可以省去字段名,此時需要加上 id,而且必須填寫所有的字段信息,不能只添加部分?jǐn)?shù)據(jù)
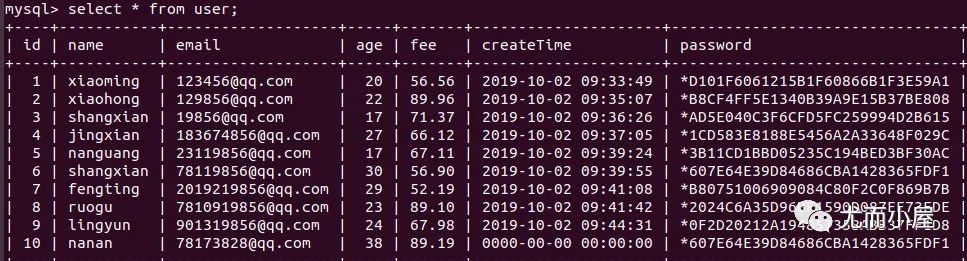
數(shù)據(jù)更新
數(shù)據(jù)更新update使用最多的是where語句,指定某個條件下執(zhí)行;如果不加where,則所有的字段都會被更改(慎重)
指定 id號指定字段的具體值 字段允許有多個,用逗號隔開
mysql> update user set name="nangying" where id=6; // 通過id指定
mysql> update user set fee=88.76 where fee=56.90; // 通過字段名直接指定
mysql> update user set email="[email protected]", age=54 where id=7; // 同時修改多個值
mysql> update user set fee=88.88 where id in(2,4,6); // in的用法
mysql> update user set fee=66.66 where id between 2 and 6; // between ... and ...刪除
刪除表有兩種情況:
delete:刪除表,插入數(shù)據(jù)從上一次結(jié)束的id號開始繼續(xù)插入;刪除的記錄仍存在truncate:清空表,重新插入數(shù)據(jù)id從1開始;不占內(nèi)存空間
delete table user;
truncate table user;刪除 delete表中的某條記錄
delete from user where id=7; // 刪除記錄
insert into user (name,email,age,fee,password) values("lisi","[email protected]", 36, 81.17, Password("lisi")); // id是從原來的基礎(chǔ)上遞增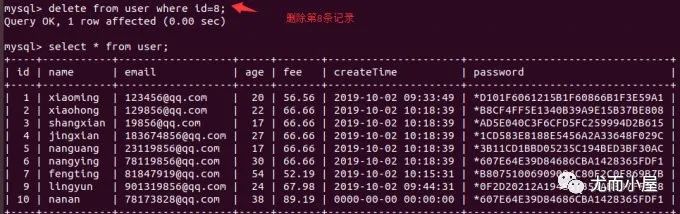
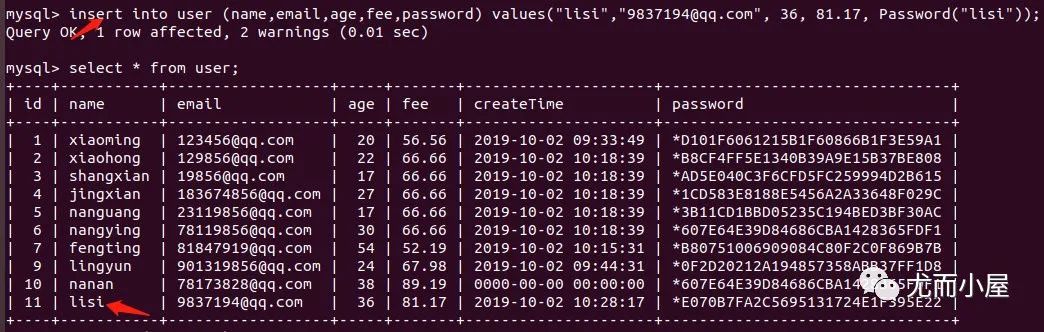
關(guān)于truncate
# 刪除數(shù)據(jù)
mysql> truncate table user;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
mysql> select * from user;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
# 重新插入數(shù)據(jù)
mysql> insert into user (user_name, user_email, user_age, password, fee) values ("peter", "[email protected]", 27, password("101010"), 28.87);
Query OK, 1 row affected, 2 warnings (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from user;
+----+-----------+-----------------+----------+--------------------------------+-------+
| id | user_name | user_email | user_age | password | fee |
+----+-----------+-----------------+----------+--------------------------------+-------+
| 1 | peter | [email protected] | 27 | *C3BC3E91915DCAE22014892F9827D | 28.87 |
+----+-----------+-----------------+----------+--------------------------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)三、DCL
data control language,DCL,指的是數(shù)據(jù)控制語言,主要是對數(shù)據(jù)庫中的登錄和用戶的權(quán)限進行控制的語言,包含
用戶登錄 MySQL數(shù)據(jù)庫修改用戶密碼及忘記密碼如何解決 創(chuàng)建普通用戶及授權(quán) 撤銷權(quán)限 revoke查看權(quán)限及刪除用戶
全部命令
1. 查看數(shù)據(jù)庫中的用戶及信息
mysql -uroot -p
show databases;
use mysql;
show tables;
select user, host, passord from user; # 所有的用戶都在user表中
2. 創(chuàng)建新用戶、授權(quán)、撤銷權(quán)限和刪除
-- 創(chuàng)建
create user "test"@"192.168.2.10" identified by"password"; # 指定用戶test、ip和密碼password
flush privileges; # 刷新權(quán)限
mysql -utest -h192.168.2.10 -p # 用test用戶登錄
-- 授權(quán)
grant select, insert, delete on shop.* to "test"@"192.168.2.10"; # shop 是數(shù)據(jù)庫,test是數(shù)據(jù)庫中的表
flush privileges; # 刷新權(quán)限
systemctl restart mysql; # 重啟mysql
-- 創(chuàng)建用戶的同時進行授權(quán)
grant select, insert, delete on shop.* to "test"@"192.168.2.10" identified by"password";
-- 查看權(quán)限
show grants for "test"@"192.168.2.10"\G # \G參數(shù)是為了輸出好看
-- 撤銷權(quán)限
revoke delete on shop.* to "test"@"192.168.2.10"; # 撤銷shop數(shù)據(jù)庫中test用戶的delete權(quán)限
flush privileges; # 刷新權(quán)限
systemctl restart mysql; # 重啟mysql
-- 刪除用戶
drop user "test"@"192.168.2.10";
-- 謹(jǐn)慎操作
grant all privileges on *.* to "test"@"192.168.2.10" # 將所有的權(quán)限給所有數(shù)據(jù)庫
3. 修改用戶密碼
-- 已知用戶原密碼,能夠進行登錄
mysql -uroot -p
show databases;
use mysql;
show tables;
select user, host, password from user; # 所有的用戶都在user表中
update user set password=PASSWORD("123456admin") where user="test"; # 將test用戶的密碼改成123456admin
flush privileges;
-- 忘記原來的密碼:借助跳躍權(quán)限表,重啟守護進程
mysql skip-grant-tables # 跳躍權(quán)限表
mysql # 重新進入mysql
show databases;use mysql;show tables;
select user, host, password from user; # 所有的用戶都在user表中
update user set password=PASSWORD("123456admin") where user="test"; # 將test用戶的密碼改成123456admin
flush privileges;
4. 查看mysql服務(wù)
-- window
直接去任務(wù)管理器
-- linux
netstat -an # 找到3306端口關(guān)于root賬戶
默認(rèn)情況下,MySQL數(shù)據(jù)庫是指允許root賬戶登錄并且在本機上登錄的。
-uroot表示root賬戶-p表示需要密碼沒有 -h表示默認(rèn)是本機localhost或者127.0.0.1登錄
登錄查看賬戶
MySQL數(shù)據(jù)庫的服務(wù)端口號是3306,通過在mysql數(shù)據(jù)庫的user表中查看登錄數(shù)據(jù)庫用戶信息:
mysql> show databases; # 查看所有的數(shù)據(jù)庫
mysql> use mysql; # 選擇mysql數(shù)據(jù)庫
mysql> show tables; # 查表數(shù)據(jù)庫中的所有表
mysql> select user, host from user; # 查看這個表中的user和host信息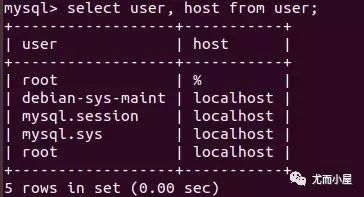
刪除用戶
需要注意的是刪除了某個用戶之后必須進行權(quán)限的刷新:
mysql> delete from user where host="%"; # 刪除host為%的用戶
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> flush privileges; # 刷新權(quán)限
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)注意:當(dāng)在實際的開發(fā)項目中,項目和數(shù)據(jù)庫服務(wù)器不在同一個地方,可以指定ip連接進行訪問
mysql> update user set host="192.168.1.10" where user="root";
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select user,host from user;
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)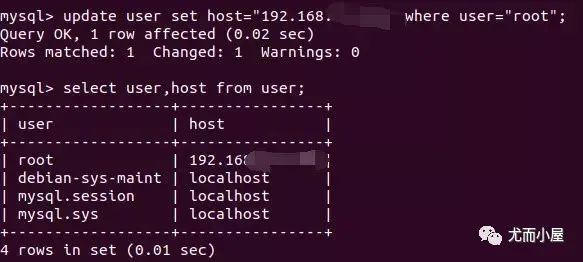
當(dāng)退出mysql重新進入,需要指定IP地址,就是上面設(shè)置的IP:
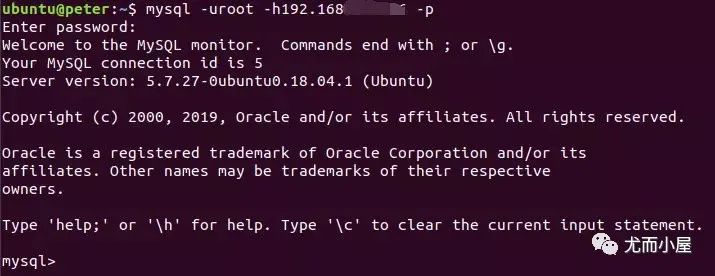
密碼問題
1、修改密碼
同樣需要進入mysql數(shù)據(jù)庫的user表中
mysql>update user set password=PASSWORD("admin") where user="root"; # 將root賬戶的密碼改為admin
mysql> flush privileges; # 更新操作
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)2、忘記密碼
如果忘記了密碼,需要進入配置文件中
ubuntu@peter:~$ vim /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf找到下圖中的
skip-grant-tables,將前面的#去掉,就是取消注釋:取消權(quán)限認(rèn)證,后臺開啟新的進程免密進入MySQL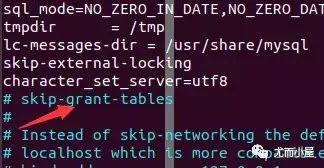
重啟
MySQL服務(wù):systemctl restart mysql通過
MySQL直接進入:
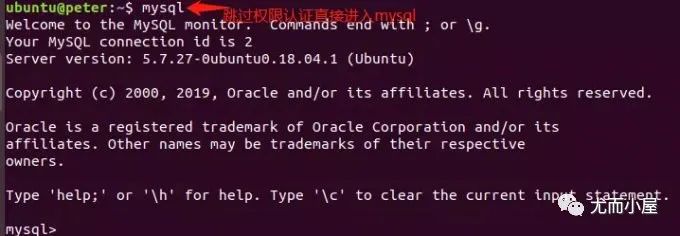
然后按照上面的步驟重新設(shè)置密碼即可
mysql> show databases;
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> select user, password from user;
# 接下來重新設(shè)置密碼即可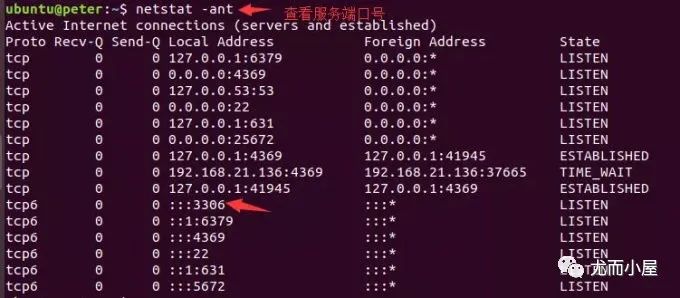
四、DQL
DQL(data query language),指的是數(shù)據(jù)查詢語言,主要的作用是對數(shù)據(jù)庫中的數(shù)據(jù)進行查詢的操作,也是最常見和最重要的功能。
查詢的方法也是多種多樣:聯(lián)合查詢、分組查詢、內(nèi)連查詢、子查詢等,還可以限制查詢的條數(shù)等,下面介紹幾種常見的查詢
格式:
select
column1,
column2,... # 需要查詢的字段
from table_name # 表名
where 條件簡單查詢
select
name,
age
from user
where id=4;
where id in(1,3,5,7);
where name = "xiaoming";過濾查詢
過濾查詢的關(guān)鍵字是distinct,去掉字段中的重復(fù)值
-- 過濾重復(fù)字段
select distinct(password) from user; # password是重復(fù)項
select distinct password from user; # 括號可以不用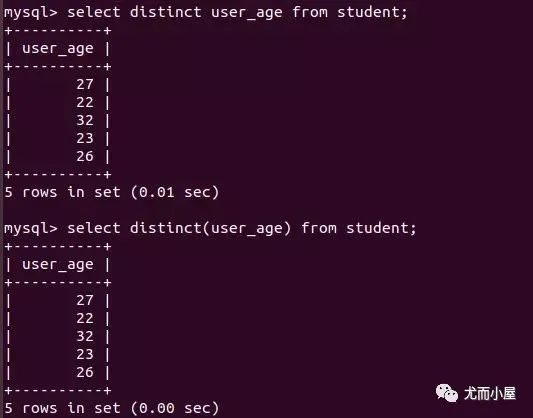
連接查詢
連接查詢的關(guān)鍵字是concat
直接使用系統(tǒng)默認(rèn)的連接方式,將原來的字段通過下劃線進行連接 使用 concat...as...,as后面自己指定連接的新字段名帶上連接符號的查詢 concat_ws("+", 列名1,列名2);其中"+"就是指定連接符
select concat(name, email) from user; # 結(jié)果中顯示concat(name_email)
select concat(name, email) as nameEmail from user; # 將新的字段名用nameEmail來表示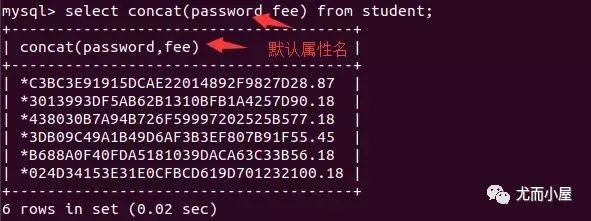
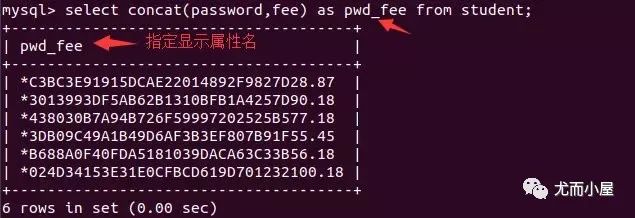
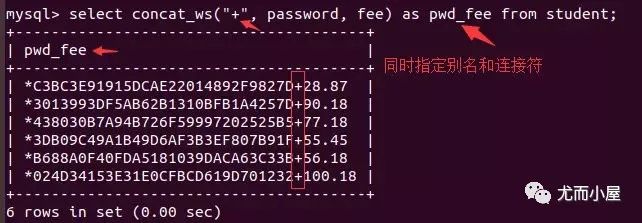
模糊查詢
模糊查詢的關(guān)鍵字是like,中文翻譯成像:
mysql> select user_name from student where user_name like "peter"; # 像peter
mysql> select user_name from student where user_name like "%e"; # %表示任意,表示名字以e結(jié)尾
mysql> select user_name from student where user_name like "%e%"; # 表示名字中含有e排序查詢
對表中的記錄進行升序asc或者降序desc的排列,默認(rèn)的是升序asc,同時需要使用order by關(guān)鍵字:
升序: asc,默認(rèn)情況降序: desc
select * from student order by user_age asc; # 年齡的升序
select * from student order by user_age desc; # 年齡的降序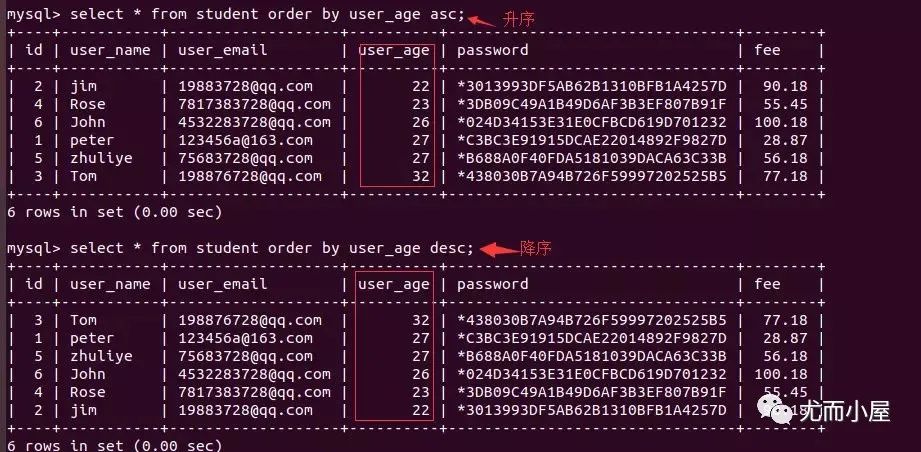
聚合函數(shù)
select count(*) from student; # 總記錄
select sum(列名) from student; # 總和
select avg(列名) from student; # 平均值
select max/min(列名) from student; # 最大/小值限制查詢結(jié)果
限制查詢的條數(shù)使用的是limit關(guān)鍵字
直接使用 limit使用 limit ... offset ...:指定從哪里開始顯示,顯示多少行簡寫: limit 5, 4:表示從第5行開始,顯示4行數(shù)據(jù)
select name, age from user limit 5; -- 只顯示5行數(shù)據(jù)
select name, age from user limit 5 offset 4; -- 從第4(offset)行開始顯示5(limit)行數(shù)據(jù)
select name, age from user limit 4, 5 ; -- 效果同上:逗號之前是offset的內(nèi)容,逗號之后是limit內(nèi)容- END -
