懶加載 React 長頁面 - 動態(tài)渲染組件
背景
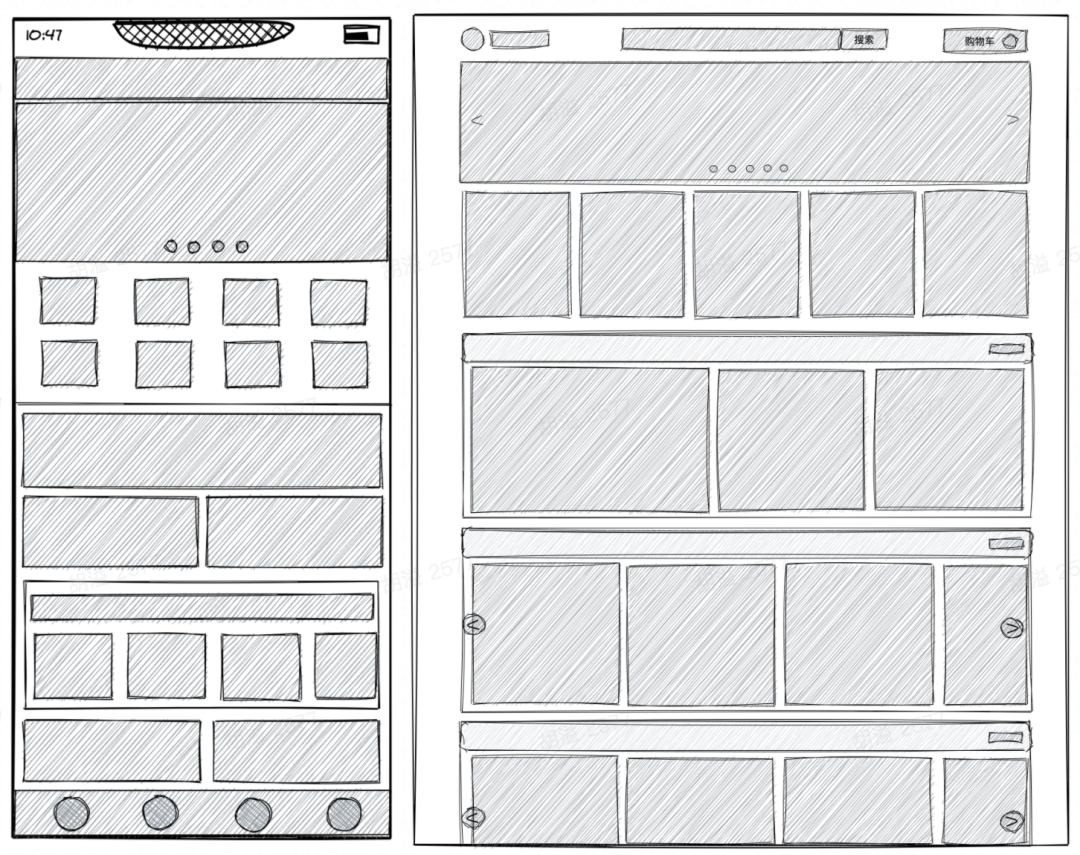
長頁面在前端開發(fā)中是非常常見的。例如下圖中的電商首頁,樓層數(shù)據(jù)來自運營人員在后臺的配置,樓層數(shù)量是不固定的,同時每個樓層可能會依賴更多翻頁數(shù)據(jù)。在這種情況下,如果一次性將頁面全部渲染,可想而知,我們的頁面直出效率(fmp, fid)會受到影響。
為了更好的用戶體驗,我們需要考慮在用戶滾動到下一屏?xí)r,渲染下一屏的組件。
設(shè)計思路
假設(shè)頁面預(yù)期渲染 n 個組件,每個組件均會觸發(fā)請求其他接口。設(shè)計這樣一個長頁面,我們主要會面臨以下兩個問題:
渲染下一屏組件的時機應(yīng)該如何判斷?
在數(shù)據(jù)反復(fù)更新的過程中,如何讓組件不重復(fù)發(fā)起數(shù)據(jù)請求?
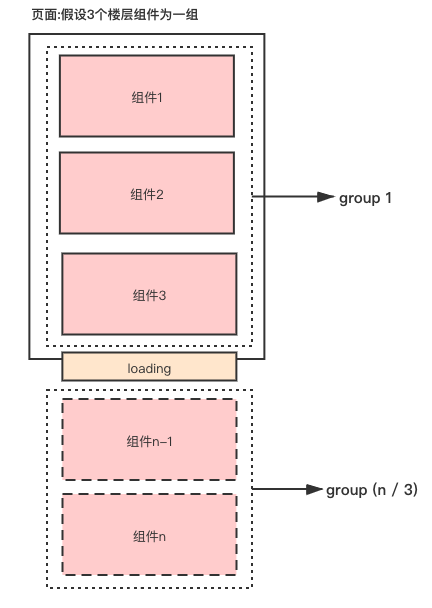 圖 1
圖 1
一、渲染下一屏的時機
1. 初始定義
以首頁為例,我們將樓層數(shù)據(jù)源用 homeInfo 變量保存,而實際渲染的數(shù)據(jù)用 compList 保存。另外,我們需要一個 loading 組件,該組件始終處于樓層組件的最下方。
const homeInfo = [...樓層數(shù)據(jù)];
const [compList, setCompList] = useState([]); // 渲染的組件數(shù)據(jù)
const bottomDomRef = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null);
// 樓層組件
<div>
{compList.map((homeItem, index) => (
<div className="home-floor" key={index}>
// 根據(jù)不同的樓層渲染不同的樓層組件
{renderHomeConfig(homeItem)}
</div>
))}
</div>
// loading DOM
<div ref={bottomDomRef} className='bottom-loading'>
<Icon name="loading" />
</div>
// completed DOM
<div className="bottom-completed">
<p>已經(jīng)到底啦</p>
</div>
2. Loading 組件是否在視圖內(nèi)
如圖 1 所示,當(dāng) loading 組件的位置滾動到視圖中時,并且如果此時還有未渲染的組件,這時便是渲染下一屏的時機。
判斷組件是否在視圖內(nèi)有兩種方式,一種是調(diào)用調(diào)用Element.getBoundingClientRect\(\)[1]方法以獲取 loading 元素的邊界信息,進行判斷,另一種是調(diào)用Intersection Observer API[2]進行判斷。
方法 1:getBoundingClientRect
我們需要知道 窗口高度 以及 Loading 組件的高度。
Element.clientHeight 元素內(nèi)部的高度,包含內(nèi)邊距,但不包括水平滾動條、邊框和外邊距。
Element.scrollHeight 元素內(nèi)容高度的度量,包括由于溢出導(dǎo)致的視圖中不可見內(nèi)容。
Element.getBoundingClientRect() 方法返回元素的大小及其相對于視口的位置。
const scrollRenderHandler = ():void => {
const rect = bottomDomRef.current?.getBoundingClientRect();
// top 是loading組件的位置
const top = rect ? rect.top : 0;
// 視窗高
const clientHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight
|| document.body.clientHeight;
if (top < clientHeight && 組件沒渲染完) {
// 繼續(xù)渲染
}
}
useEffect(() => {
document.addEventListener('scroll', scrollRenderHandler);
return (): void => {
document.removeEventListener('scroll', scrollRenderHandler);
};
}, [scrollRenderHandler]);
方法 2:Intersection Observer
使用 react-intersection-observer 的 api 判斷 loading 元素是否在視圖內(nèi)。
// Use object destructing, so you don't need to remember the exact order
const { ref, inView, entry } = useInView(options);
// Or array destructing, making it easy to customize the field names
const [ref, inView, entry] = useInView(options);
import { useInView } from 'react-intersection-observer';
const [bottomDomRef, inView] = useInView({
threshold: 0,
});
const scrollRenderHandler = ():void => {
if (inView && 組件沒渲染完) {
// 繼續(xù)渲染
}
}
3. 組件是否渲染完成
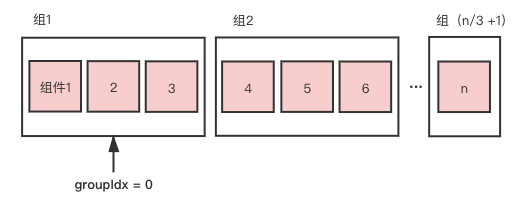
假設(shè)一屏展示 3 個組件,類似常見分頁邏輯中的 pageSize = 3,我們可以將 n 個組件分割成每 3 個 1 組,對每組依次進行渲染,并用 compGroups 保存分割的組,同時使用 groupIdx 指針來指向下一個需要渲染的組序列。
export const splitGroups = (homeList: any[], pageSize: number): any[] => {
const groupsTemp = [];
for (let i = 0; i < homeList.length; i += pageSize) {
groupsTemp.push(homeList.slice(i, i + pageSize));
}
return groupsTemp;
};
const compGroups = useMemo(() => splitGroups(homeInfo, 3), [homeInfo]);
const groupCount = compGroups.length;
const [groupIdx, setGroupIdx] = useState(0);
當(dāng)分割好組后,如何判斷組件沒渲染完的問題便迎刃而解,當(dāng) groupIdx 小于 groupCount,更新 compList 和 groupIdx。
if (top < clientHeight && groupIdx < compGroups.length) {
setCompList(compList.concat(compGroups[groupIdx]));
setGroupIdx(groupIdx + 1);
}
4. 監(jiān)聽滾動優(yōu)化
在滾動時會頻繁觸發(fā) scrollRenderHandler 函數(shù),導(dǎo)致頁面性能低下。此時需要采用節(jié)流,并用 useCallback 緩存 scrollRenderHandler 函數(shù)用來提升性能。
const [scrollRenderHandler] = useDebounce((): void => {
if (inView && groupIdx < groupCount) {
setCompList(compList.concat(compGroups[groupIdx]));
setGroupIdx(groupIdx + 1);
}
},
300,
[compGroups, compList, groupIdx, inView],
);
useEffect(() => {
document.addEventListener('scroll', scrollRenderHandler);
return (): void => {
document.removeEventListener('scroll', scrollRenderHandler);
};
}, [scrollRenderHandler]);
export default function useDebounce<T extends(...args: any[]) => any>(
func: T,
delay: number,
deps: DependencyList = [],
): [T, () => void] {
const timer = useRef<number>();
const cancel = useCallback(() => {
if (timer.current) {
clearTimeout(timer.current);
}
}, []);
const run = useCallback((...args) => {
cancel();
timer.current = window.setTimeout(() => {
func(...args);
}, delay);
}, deps);
return [run as T, cancel];
}
二、不重復(fù)發(fā)起數(shù)據(jù)請求
1. 癥結(jié)分析
至此,隨著屏幕滾動,我們基本完成了組件動態(tài)渲染的要求。但還有另外一個問題:隨著滾動,相同的數(shù)據(jù)接口請求了多次。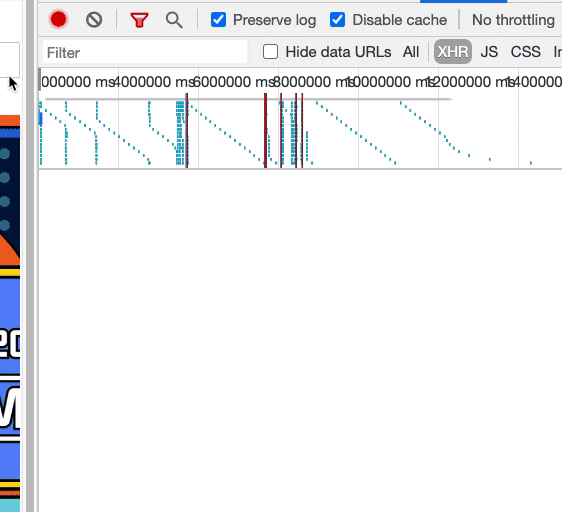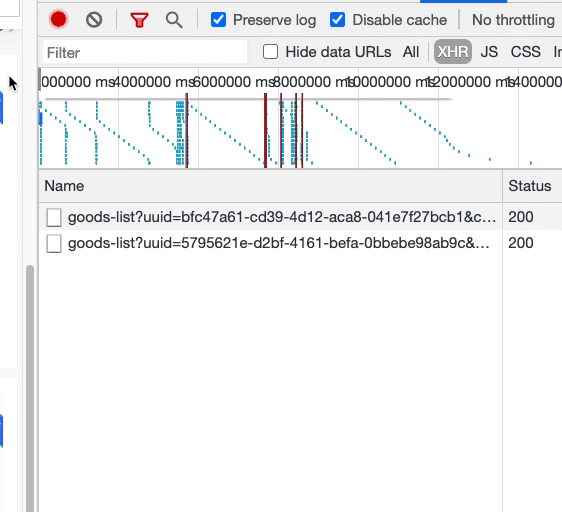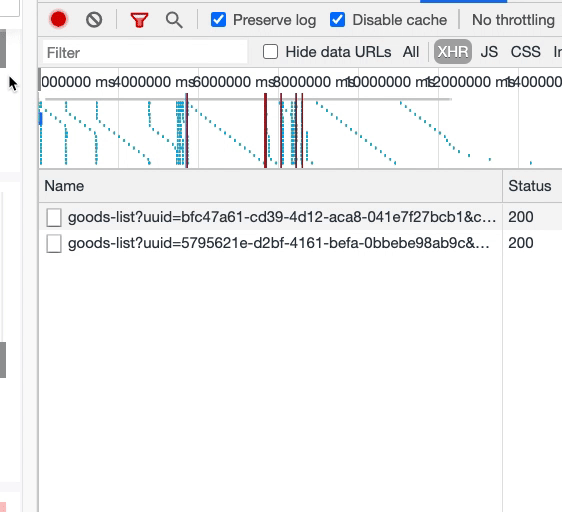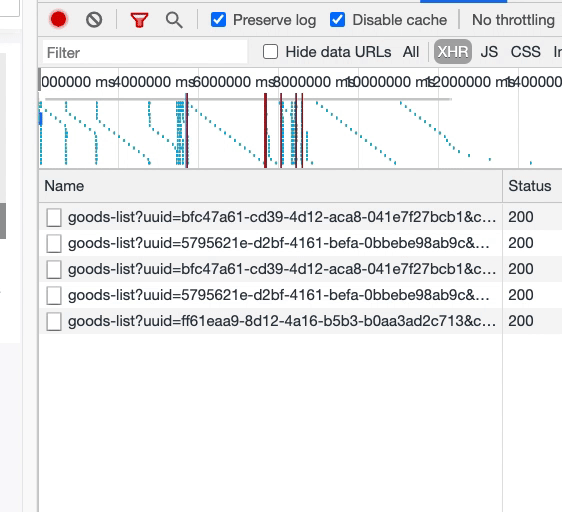
 如上圖,同一樓層的接口被請求了兩遍。這意味著,在窗口滾動的過程中,我們反復(fù)更新了 compList 數(shù)據(jù),從而導(dǎo)致了樓層組件重新渲染,而每個樓層組件的數(shù)據(jù)請求,是放在組件內(nèi)部的,這與該樓層的唯一標(biāo)識 uuid 相關(guān),因此導(dǎo)致數(shù)據(jù)接口的重復(fù)請求。
如上圖,同一樓層的接口被請求了兩遍。這意味著,在窗口滾動的過程中,我們反復(fù)更新了 compList 數(shù)據(jù),從而導(dǎo)致了樓層組件重新渲染,而每個樓層組件的數(shù)據(jù)請求,是放在組件內(nèi)部的,這與該樓層的唯一標(biāo)識 uuid 相關(guān),因此導(dǎo)致數(shù)據(jù)接口的重復(fù)請求。
2. React.memo
React Top-Level API – React[3]
通過上述癥結(jié)我們得知,只要組件不重復(fù)渲染,便可規(guī)避掉重復(fù)請求的問題。
在沒有引入 React.memo 之前,使用 PureComponent 可以達到對 props 淺比較的效果,另外,我們也可以采用 shouldComponentUpdate 來進行具體的比較,從而減少組件的渲染次數(shù)。
具體如:shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)而在函數(shù)組件中,我們可以使用 React.memo ,它的使用方法非常簡單,如下所示。如果不傳 areEqual 則對 props 進行淺比較。若傳入,則需要返回具體的比較結(jié)果 true, false 。
function MyComponent(props) {
/* render using props */
}
function areEqual(prevProps, nextProps) {
/*
return true if passing nextProps to render would return
the same result as passing prevProps to render,
otherwise return false
*/
}
export default React.memo(MyComponent, areEqual);
因此,我們只需要在對應(yīng)的樓層組件中,將組件用 memo 進行包裹,并對比它們的唯一標(biāo)識 uuid 。
代碼如下:
import React, { memo } from 'react';
type GoodsRecommedProps = {
...其他 props,
goodsQuery:{
uuid: '...'
}
}
const GoodsRecommed: React.FC<GoodsRecommedProps> = (props) => {
...
}
const isEqual = (prevProps: GoodsRecommedProps, nextProps: GoodsRecommedProps): boolean => {
if (prevProps.goodsQuery.uuid !== nextProps.goodsQuery.uuid) {
return false;
}
return true;
};
export default memo(GoodsRecommed, isEqual);
最后看一下效果,確實沒有重復(fù)的數(shù)據(jù)請求了。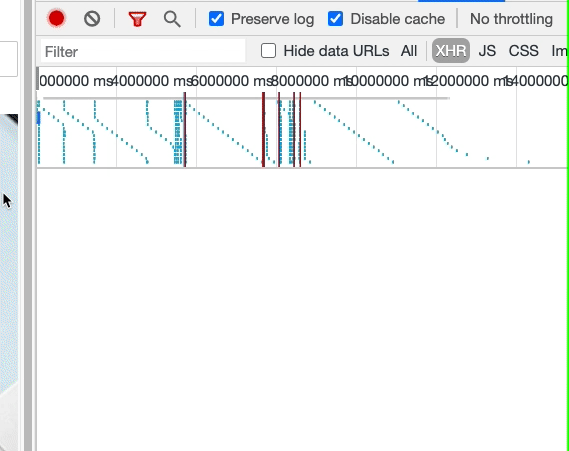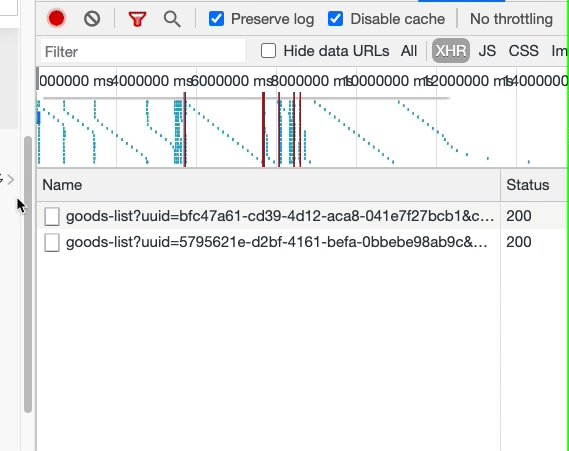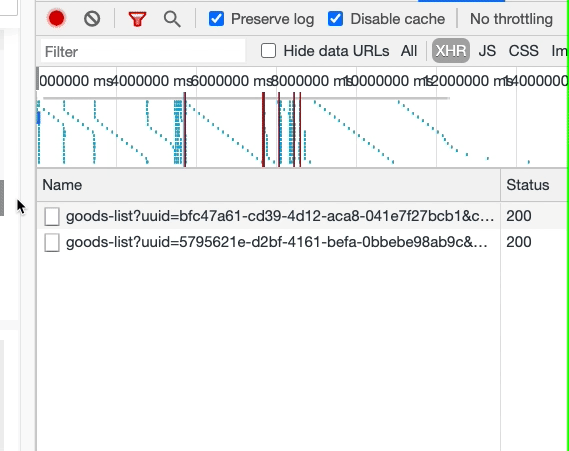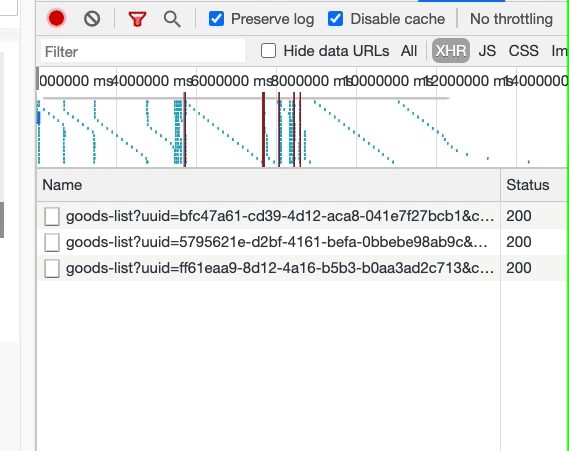

總結(jié)
React.memo 用于組件單位的性能優(yōu)化。
useCallback 根據(jù)依賴緩存第一個參數(shù)的 callback ,多用于緩存函數(shù)。
useMemo 根據(jù)依賴緩存的第一個參數(shù)的返回值,多用于組件內(nèi)更細粒度的某一部分性能優(yōu)化。
在寫一個普通的長頁面的過程中,如果只追求完成,那么將會非常簡單,但如果想要進一步優(yōu)化,那可做的事情就有很多了。
參考資料
Element.getBoundingClientRect(): https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Element/getBoundingClientRect
[2]Intersection Observer API: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Intersection_Observer_API
[3]React Top-Level API – React: https://reactjs.org/docs/react-api.html#reactmemo
[4]React Top-Level API – React: https://reactjs.org/docs/react-api.html#reactmemo
[5]Element.getBoundingClientRect() - Web API 接口參考 | MDN: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Element/getBoundingClientRect
[6]IntersectionObserver API 使用教程 - 阮一峰的網(wǎng)絡(luò)日志: http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/11/intersectionobserver_api.html
[7]精讀《react-intersection-observer 源碼》: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/149926289
[8]useCallback、useMemo 分析 & 差別: https://juejin.cn/post/6844904001998176263#heading-7
[9]thebuilder/react-intersection-observer: https://github.com/thebuilder/react-intersection-observer
[10]React 如何渲染大數(shù)據(jù)量的列表?: https://juejin.cn/post/6844903634036064270
喜歡的話別忘了 分享、點贊、在看 三連哦~。
點擊下方名片,關(guān)注 前端Sharing ,持續(xù)分享技術(shù)文章。
