使用關(guān)鍵點進(jìn)行小目標(biāo)檢測
【GiantPandaCV導(dǎo)語】本文是筆者出于興趣搞了一個小的庫,主要是用于定位紅外小目標(biāo)。由于其具有尺度很小的特點,所以可以嘗試用點的方式代表其位置。本文主要采用了回歸和heatmap兩種方式來回歸關(guān)鍵點,是一個很簡單基礎(chǔ)的項目,代碼量很小,可供新手學(xué)習(xí)。
1. 數(shù)據(jù)來源
數(shù)據(jù)集:數(shù)據(jù)來源自小武,經(jīng)過小武的授權(quán)使用,但不會公開。本項目只用了其中很少一部分共108張圖片。
標(biāo)注工具:https://github.com/pprp/landmark_annotation
標(biāo)注工具也可以在GiantPandaCV公眾號后臺回復(fù)“l(fā)andmark”關(guān)鍵字獲取

上圖是數(shù)據(jù)集中的兩張圖片,紅圈代表對應(yīng)的目標(biāo),標(biāo)注的時候只需要在其中心點一下即可得到該點對應(yīng)的橫縱坐標(biāo)。
該數(shù)據(jù)集有一個特點,每張圖只有一個目標(biāo)(不然沒法用簡單的方法回歸),多余一個目標(biāo)的圖片被剔除了。
1
0.42 0.596
以上是一個標(biāo)注文件的例子,1.jpg對應(yīng)1.txt
2. 回歸確定關(guān)鍵點
回歸確定關(guān)鍵點比較簡單,網(wǎng)絡(luò)部分采用手工構(gòu)建的一個兩層的小網(wǎng)絡(luò),訓(xùn)練采用的是MSELoss。
這部分代碼在:https://github.com/pprp/SimpleCVReproduction/tree/master/simple_keypoint/regression
2.1 數(shù)據(jù)加載
數(shù)據(jù)的組織比較簡單,按照以下格式組織:
- data
- images
- 1.jpg
- 2.jpg
- ...
- labels
- 1.txt
- 2.txt
- ...
重寫一下Dataset類,用于加載數(shù)據(jù)集。
class KeyPointDatasets(Dataset):
def __init__(self, root_dir="./data", transforms=None):
super(KeyPointDatasets, self).__init__()
self.img_path = os.path.join(root_dir, "images")
# self.txt_path = os.path.join(root_dir, "labels")
self.img_list = glob.glob(os.path.join(self.img_path, "*.jpg"))
self.txt_list = [item.replace(".jpg", ".txt").replace(
"images", "labels") for item in self.img_list]
if transforms is not None:
self.transforms = transforms
def __getitem__(self, index):
img = self.img_list[index]
txt = self.txt_list[index]
img = cv2.imread(img)
if self.transforms:
img = self.transforms(img)
label = []
with open(txt, "r") as f:
for i, line in enumerate(f):
if i == 0:
# 第一行
num_point = int(line.strip())
else:
x1, y1 = [(t.strip()) for t in line.split()]
# range from 0 to 1
x1, y1 = float(x1), float(y1)
tmp_label = (x1, y1)
label.append(tmp_label)
return img, torch.tensor(label[0])
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_list)
@staticmethod
def collect_fn(batch):
imgs, labels = zip(*batch)
return torch.stack(imgs, 0), torch.stack(labels, 0)
返回的結(jié)果是圖片和對應(yīng)坐標(biāo)位置。
2.2 網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class KeyPointModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(KeyPointModel, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 3, 1, 1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(6)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU(True)
self.maxpool1 = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 2))
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 12, 3, 1, 1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(12)
self.relu2 = nn.ReLU(True)
self.maxpool2 = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 2))
self.gap = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(12, 2),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu1(x)
x = self.maxpool1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.bn2(x)
x = self.relu2(x)
x = self.maxpool2(x)
x = self.gap(x)
x = x.view(x.shape[0], -1)
return self.classifier(x)
其結(jié)構(gòu)就是卷積+pooling+卷積+pooling+global average pooling+Linear,返回長度為2的tensor。
2.3 訓(xùn)練
def train(model, epoch, dataloader, optimizer, criterion):
model.train()
for itr, (image, label) in enumerate(dataloader):
bs = image.shape[0]
output = model(image)
loss = criterion(output, label)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if itr % 4 == 0:
print("epoch:%2d|step:%04d|loss:%.6f" % (epoch, itr, loss.item()/bs))
vis.plot_many_stack({"train_loss": loss.item()*100/bs})
total_epoch = 300
bs = 10
########################################
transforms_all = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToPILImage(),
transforms.Resize((360,480)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.4372, 0.4372, 0.4373],
std=[0.2479, 0.2475, 0.2485])
])
datasets = KeyPointDatasets(root_dir="./data", transforms=transforms_all)
data_loader = DataLoader(datasets, shuffle=True,
batch_size=bs, collate_fn=datasets.collect_fn)
model = KeyPointModel()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=3e-4)
# criterion = torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss()
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss()
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer,
step_size=30,
gamma=0.1)
for epoch in range(total_epoch):
train(model, epoch, data_loader, optimizer, criterion)
loss = test(model, epoch, data_loader, criterion)
if epoch % 10 == 0:
torch.save(model.state_dict(),
"weights/epoch_%d_%.3f.pt" % (epoch, loss*1000))
loss部分使用Smooth L1 loss或者M(jìn)SE loss均可。
MSE Loss:
Smooth L1 Loss:
2.4 測試結(jié)果
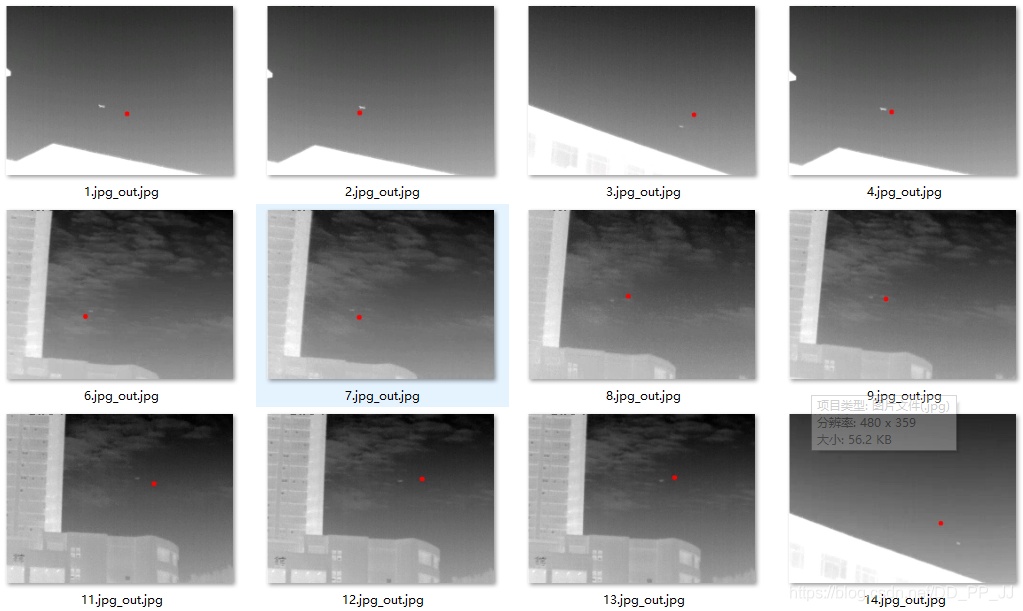
3. heatmap確定關(guān)鍵點
這部分代碼很多參考了CenterNet,不過曾經(jīng)嘗試CenterNet中的loss在這個問題上收斂效果不好,所以參考了kaggle人臉關(guān)鍵點定位的解決方法,發(fā)現(xiàn)使用簡單的MSELoss效果就很好。
3.1 數(shù)據(jù)加載
這部分和CenterNet構(gòu)建heatmap的過程類似,不過半徑的確定是人工的。因為數(shù)據(jù)集中的目標(biāo)都比較小,半徑的范圍最大不超過半徑為30個像素的圓。
class KeyPointDatasets(Dataset):
def __init__(self, root_dir="./data", transforms=None):
super(KeyPointDatasets, self).__init__()
self.down_ratio = 1
self.img_w = 480 // self.down_ratio
self.img_h = 360 // self.down_ratio
self.img_path = os.path.join(root_dir, "images")
self.img_list = glob.glob(os.path.join(self.img_path, "*.jpg"))
self.txt_list = [item.replace(".jpg", ".txt").replace(
"images", "labels") for item in self.img_list]
if transforms is not None:
self.transforms = transforms
def __getitem__(self, index):
img = self.img_list[index]
txt = self.txt_list[index]
img = cv2.imread(img)
if self.transforms:
img = self.transforms(img)
label = []
with open(txt, "r") as f:
for i, line in enumerate(f):
if i == 0:
# 第一行
num_point = int(line.strip())
else:
x1, y1 = [(t.strip()) for t in line.split()]
# range from 0 to 1
x1, y1 = float(x1), float(y1)
cx, cy = x1 * self.img_w, y1 * self.img_h
heatmap = np.zeros((self.img_h, self.img_w))
draw_umich_gaussian(heatmap, (cx, cy), 30)
return img, torch.tensor(heatmap).unsqueeze(0)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_list)
@staticmethod
def collect_fn(batch):
imgs, labels = zip(*batch)
return torch.stack(imgs, 0), torch.stack(labels, 0)
核心函數(shù)是draw_umich_gaussian,具體如下:
def gaussian2D(shape, sigma=1):
m, n = [(ss - 1.) / 2. for ss in shape]
y, x = np.ogrid[-m:m + 1, -n:n + 1]
h = np.exp(-(x * x + y * y) / (2 * sigma * sigma))
h[h < np.finfo(h.dtype).eps * h.max()] = 0
# 限制最小的值
return h
def draw_umich_gaussian(heatmap, center, radius, k=1):
diameter = 2 * radius + 1
gaussian = gaussian2D((diameter, diameter), sigma=diameter / 6)
# 一個圓對應(yīng)內(nèi)切正方形的高斯分布
x, y = int(center[0]), int(center[1])
width, height = heatmap.shape
left, right = min(x, radius), min(width - x, radius + 1)
top, bottom = min(y, radius), min(height - y, radius + 1)
masked_heatmap = heatmap[y - top:y + bottom, x - left:x + right]
masked_gaussian = gaussian[radius - top:radius +
bottom, radius - left:radius + right]
if min(masked_gaussian.shape) > 0 and min(masked_heatmap.shape) > 0: # TODO debug
np.maximum(masked_heatmap, masked_gaussian * k, out=masked_heatmap)
# 將高斯分布覆蓋到heatmap上,取最大,而不是疊加
return heatmap
sigma參數(shù)直接沿用了CenterNet中的設(shè)置,沒有調(diào)節(jié)這個超參數(shù)。
3.2 網(wǎng)絡(luò)結(jié)構(gòu)
網(wǎng)絡(luò)結(jié)構(gòu)參考了知乎上一個復(fù)現(xiàn)YOLOv3中提到的模塊,Sematic Embbed Block(SEB)用于上采樣部分,將來自低分辨率的特征圖進(jìn)行上采樣,然后使用3x3卷積和1x1卷積統(tǒng)一通道個數(shù),最后將低分辨率特征圖和高分辨率特征圖相乘得到融合結(jié)果。
class SematicEmbbedBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, high_in_plane, low_in_plane, out_plane):
super(SematicEmbbedBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv3x3 = nn.Conv2d(high_in_plane, out_plane, 3, 1, 1)
self.upsample = nn.UpsamplingBilinear2d(scale_factor=2)
self.conv1x1 = nn.Conv2d(low_in_plane, out_plane, 1)
def forward(self, high_x, low_x):
high_x = self.upsample(self.conv3x3(high_x))
low_x = self.conv1x1(low_x)
return high_x * low_x
class KeyPointModel(nn.Module):
"""
downsample ratio=2
"""
def __init__(self):
super(KeyPointModel, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 3, 1, 1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(6)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU(True)
self.maxpool1 = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 2))
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 12, 3, 1, 1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(12)
self.relu2 = nn.ReLU(True)
self.maxpool2 = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 2))
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(12, 20, 3, 1, 1)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(20)
self.relu3 = nn.ReLU(True)
self.maxpool3 = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 2))
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(20, 40, 3, 1, 1)
self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(40)
self.relu4 = nn.ReLU(True)
self.seb1 = SematicEmbbedBlock(40, 20, 20)
self.seb2 = SematicEmbbedBlock(20, 12, 12)
self.seb3 = SematicEmbbedBlock(12, 6, 6)
self.heatmap = nn.Conv2d(6, 1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.conv1(x)
x1 = self.bn1(x1)
x1 = self.relu1(x1)
m1 = self.maxpool1(x1)
x2 = self.conv2(m1)
x2 = self.bn2(x2)
x2 = self.relu2(x2)
m2 = self.maxpool2(x2)
x3 = self.conv3(m2)
x3 = self.bn3(x3)
x3 = self.relu3(x3)
m3 = self.maxpool3(x3)
x4 = self.conv4(m3)
x4 = self.bn4(x4)
x4 = self.relu4(x4)
up1 = self.seb1(x4, x3)
up2 = self.seb2(up1, x2)
up3 = self.seb3(up2, x1)
out = self.heatmap(up3)
return out
網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型也是自己寫的小網(wǎng)絡(luò),用了四個卷積層,三個池化層,然后進(jìn)行了三次上采樣。最終輸出分辨率和輸入分辨率相同。
3.3 訓(xùn)練過程
訓(xùn)練過程和基于回歸的方法幾乎一樣,代碼如下:
datasets = KeyPointDatasets(root_dir="./data", transforms=transforms_all)
data_loader = DataLoader(datasets, shuffle=True,
batch_size=bs, collate_fn=datasets.collect_fn)
model = KeyPointModel()
if torch.cuda.is_available():
model = model.cuda()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=3e-3)
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss() # compute_loss
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer,
step_size=30,
gamma=0.1)
for epoch in range(total_epoch):
train(model, epoch, data_loader, optimizer, criterion, scheduler)
loss = test(model, epoch, data_loader, criterion)
if epoch % 5 == 0:
torch.save(model.state_dict(),
"weights/epoch_%d_%.3f.pt" % (epoch, loss*10000))
用的是MSELoss進(jìn)行監(jiān)督,訓(xùn)練曲線如下:
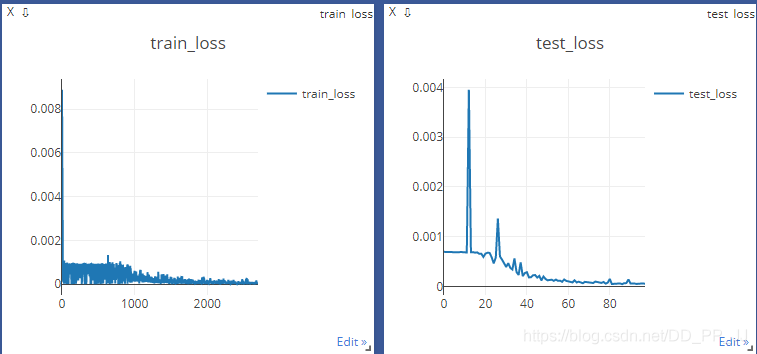
3.4 測試過程
測試過程和CenterNet的推理過程一致,也用到了3x3的maxpooling來篩選極大值點
for iter, (image, label) in enumerate(dataloader):
# print(image.shape)
bs = image.shape[0]
hm = model(image)
hm = _nms(hm)
hm = hm.detach().numpy()
for i in range(bs):
hm = hm[i]
hm = np.maximum(hm, 0)
hm = hm/np.max(hm)
hm = normalization(hm)
hm = np.uint8(255 * hm)
hm = hm[0]
# heatmap = torch.sigmoid(heatmap)
# hm = cv2.cvtColor(hm, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
hm = cv2.applyColorMap(hm, cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
cv2.imwrite("./test_output/output_%d_%d.jpg" % (iter, i), hm)
cv2.waitKey(0)
以上的nms和topk代碼都在CenterNet系列最后一篇講過了。這里直接對模型輸出結(jié)果使用nms,然后進(jìn)行可視化,結(jié)果如下:
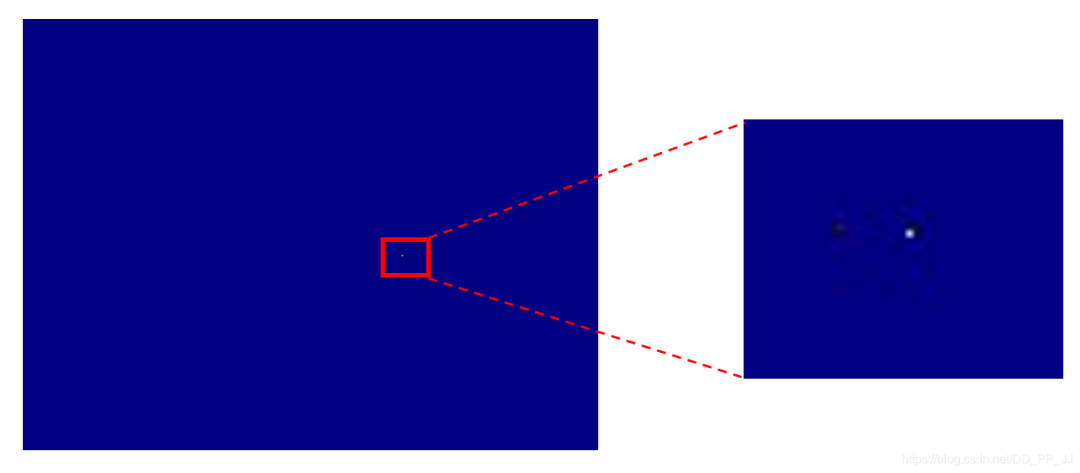
上圖中白色的點就是目標(biāo)位置,為了更形象的查看結(jié)果,detect.py部分負(fù)責(zé)可視化。
3.5 可視化
可視化的問題經(jīng)常遇見,比如CAM、Grad CAM等可視化特征圖的時候就會碰到。以下是可視化的一個簡單的方法(參考了CSDN的一位博主的方案,具體鏈接因太過久遠(yuǎn)找不到了)。
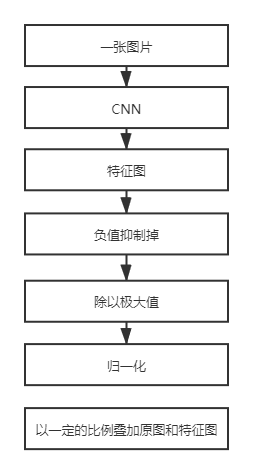
具體實現(xiàn)代碼如下:
def normalization(data):
_range = np.max(data) - np.min(data)
return (data - np.min(data)) / _range
heatmap = model(img_tensor_list)
heatmap = heatmap.squeeze().cpu()
for i in range(bs):
img_path = img_list[i]
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img = cv2.resize(img, (480, 360))
single_map = heatmap[i]
hm = single_map.detach().numpy()
hm = np.maximum(hm, 0)
hm = hm/np.max(hm)
hm = normalization(hm)
hm = np.uint8(255 * hm)
hm = cv2.applyColorMap(hm, cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
hm = cv2.resize(hm, (480, 360))
superimposed_img = hm * 0.2 + img
coord_x, coord_y = landmark_coord[i]
cv2.circle(superimposed_img, (int(coord_x), int(coord_y)), 2, (0, 0, 0), thickness=-1)
cv2.imwrite("./output2/%s_out.jpg" % (img_name_list[i]), superimposed_img)
注意通過處理以后的hm和原圖疊加的時候0.2只是一個參考值,這個值既不會影響原圖顯示又能將heatmap中重點關(guān)注的位置可視化出來。
結(jié)果如下:
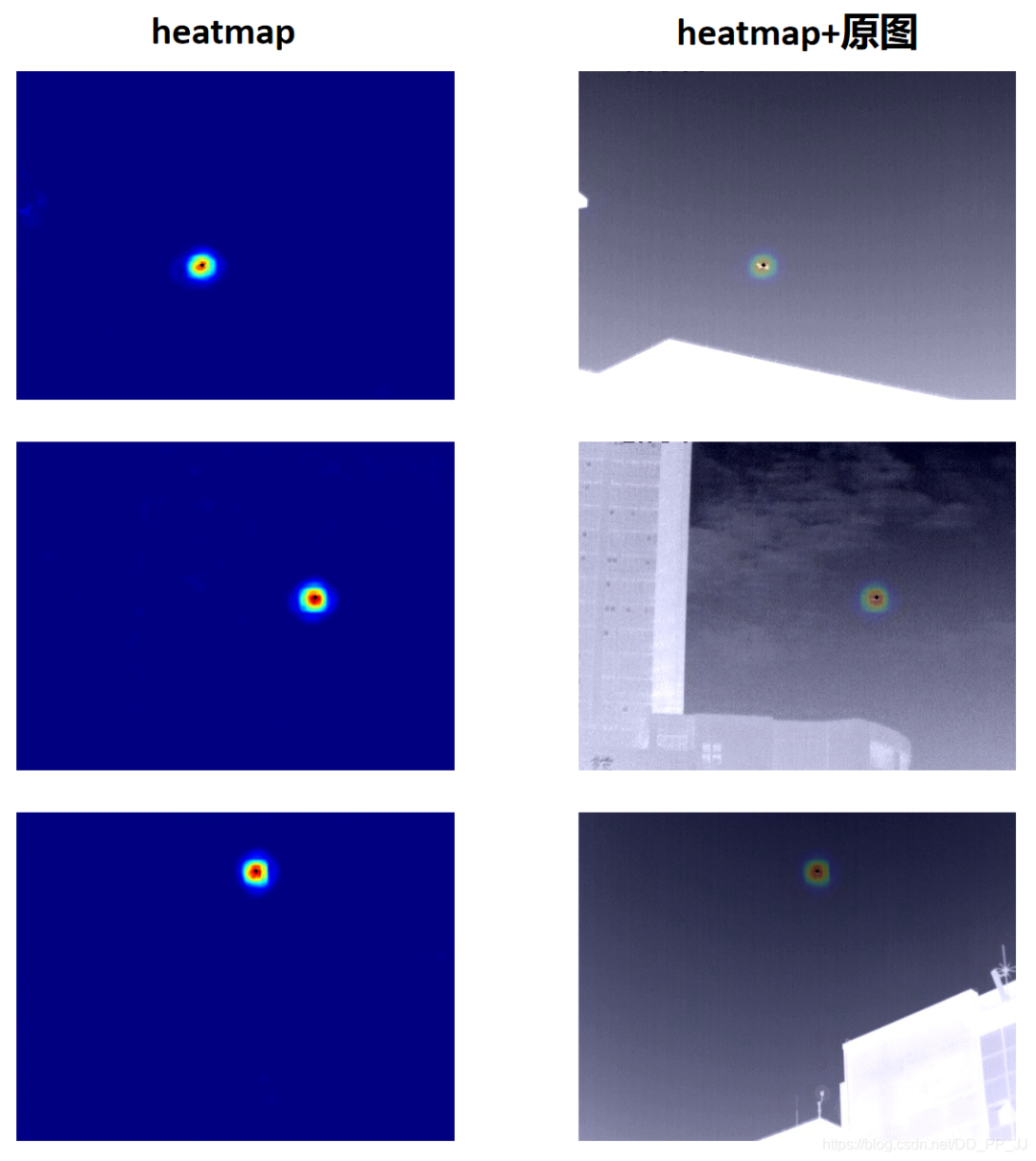
可以看到,定位結(jié)果要比回歸更準(zhǔn)一些,圖中黑色點是獲取到最終坐標(biāo)的位置,幾乎和目標(biāo)是重疊的狀態(tài),效果比較理想。
4. 總結(jié)
筆者做這個小項目初心是想搞清楚如何用關(guān)鍵點進(jìn)行定位的,關(guān)鍵點被用在很多領(lǐng)域比如人臉關(guān)鍵點定位、車牌定位、人體姿態(tài)檢測、目標(biāo)檢測等等領(lǐng)域。當(dāng)時用小武的數(shù)據(jù)的時候,發(fā)現(xiàn)這個數(shù)據(jù)集的特點就是目標(biāo)很小,比較適合用關(guān)鍵點來做。之后又開始陸陸續(xù)續(xù)看CenterNet源碼,借鑒了其中很多代碼,這才完成了這個小項目。
由于本人水平有限,可能使用heatmap進(jìn)行關(guān)鍵點定位的方式有些地方并不合理,是東拼西湊而成的,如果有建議可以在下方添加筆者微信。
為了感謝讀者朋友們的長期支持,我們今天將送出3本由中國工信出版社和人民郵電出版社提供的《深度學(xué)習(xí)訓(xùn)練營》書籍,對本書感興趣的可以在留言版留言,我們將抽取其中三位讀者送出一本正版書籍。

沒中獎的讀者如果有對此書感興趣的,可以考慮點擊下方的當(dāng)當(dāng)網(wǎng)鏈接自行購買。
對文章有疑問或者想加入交流群,歡迎添加筆者微信
為了方便各位獲取公眾號獲取資料,可以加入QQ群獲取資源,更歡迎分享資源
