Redis 實(shí)現(xiàn)搶紅包,是我想簡單了
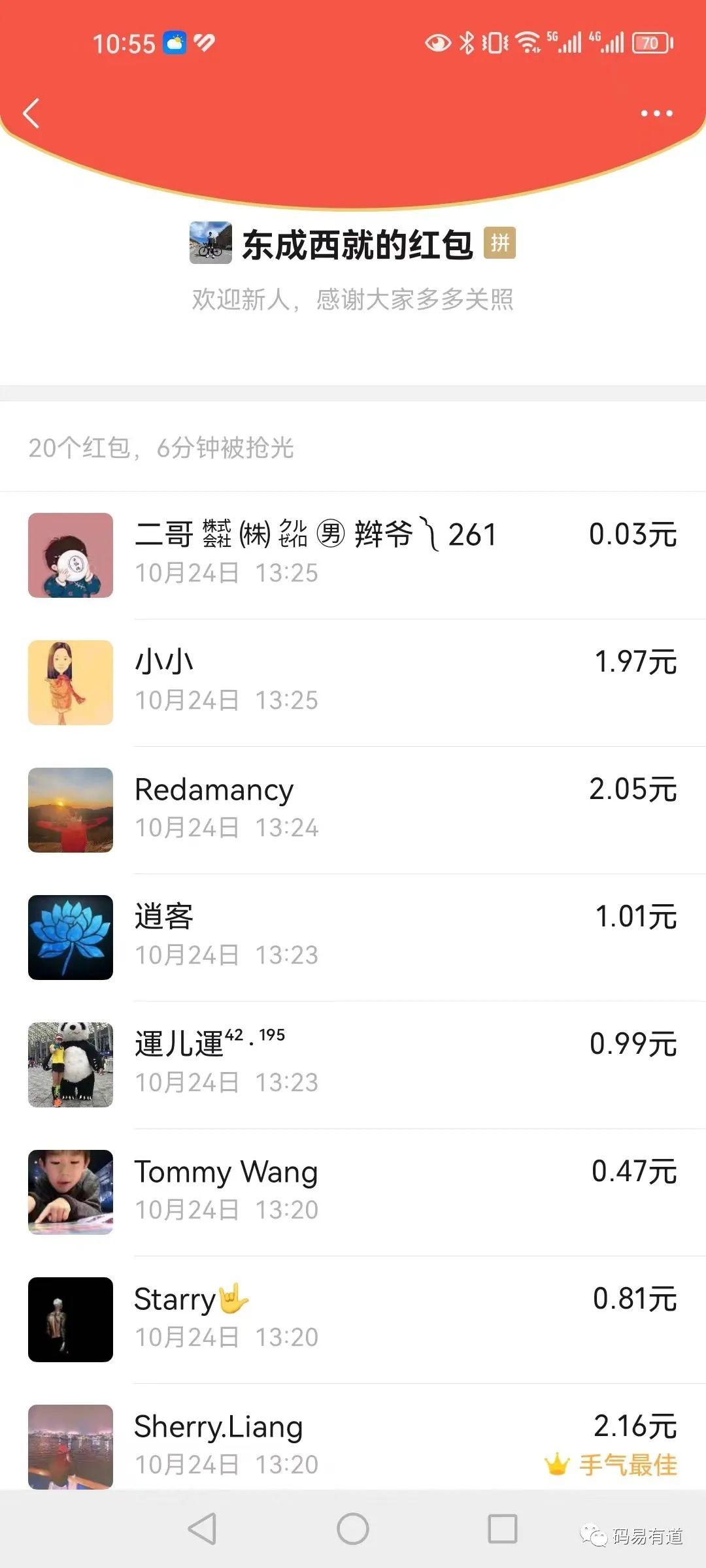 根據(jù)上圖我們思考幾個問題:
根據(jù)上圖我們思考幾個問題:
-
新人入群,發(fā)紅包+搶紅包,屬于高并發(fā)業(yè)務(wù)要求,不能用mysql來做,嘗試用redis實(shí)現(xiàn)
-
一個總的大紅包,會有可能拆分成多個小紅包,總金額= 分金額1+分金額2+分金額3......分金額N
-
每個人只能搶一次,需要有記錄,比如100塊錢,被拆分成10個紅包發(fā)出去,總計(jì)有10個紅包,搶一個少一個,總數(shù)顯示(10/6)直到搶完,需要記錄哪些人搶到了紅包。
-
有可能還需要你計(jì)時,從發(fā)出全部搶完,耗時多少?
-
紅包過期,沒人搶紅包,需在24小時內(nèi)退回發(fā)紅包主賬戶下。
-
雖說是隨機(jī)紅包,但是紅包金額如何設(shè)置才能顯得相對公平?
-
高并發(fā)下如何保證數(shù)據(jù)一致性?
......
【需求分析】
基本業(yè)務(wù)流程如下: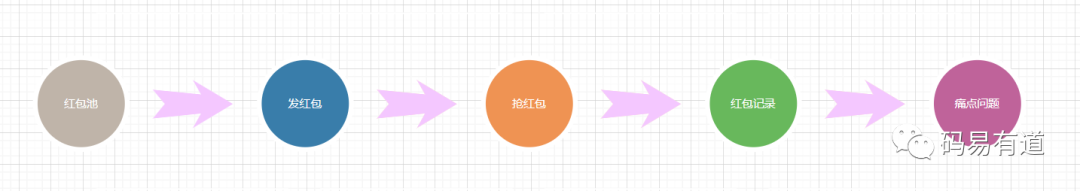 【技術(shù)選型】 搶紅包屬于高并發(fā)場景,為避免頻繁IO導(dǎo)致的性能瓶頸,故選用redis實(shí)現(xiàn)。
【技術(shù)選型】 搶紅包屬于高并發(fā)場景,為避免頻繁IO導(dǎo)致的性能瓶頸,故選用redis實(shí)現(xiàn)。
【落地實(shí)現(xiàn)】
Redis如何支持搶紅包場景的基本操作,不包括完整的業(yè)務(wù)邏輯和異常處理。要在命令行中使用Redis實(shí)現(xiàn)一個簡單的搶紅包場景,可以通過以下步驟使用redis-cli工具來執(zhí)行Redis命令。 以下是生成紅包 池、發(fā)紅包、搶紅包和紅包 記錄的命令示例:
1. 生成紅包池:# 使用RPUSH命令向名為"red_packet_pool"的列表中添加紅包金額,此處示例為10個紅包,總金額100元127.0.0.1:6379> RPUSH red_packet_pool 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
2. 發(fā)紅包:
# 使用LPUSH命令將紅包ID推送到名為"red_packet_ids"的列表中,同時也將紅包金額從"red_packet_pool"中彈出127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH red_packet_ids RP_1127.0.0.1:6379> LPOP red_packet_pool
3. 搶紅包:
# 使用RPOP命令從"red_packet_ids"列表中獲取一個紅包ID127.0.0.1:6379> RPOP red_packet_ids
4. 紅包記錄:
# 使用LPUSH命令將搶到的紅包金額和用戶ID記錄到名為"red_packet_records"的列表中127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH red_packet_records "User1 搶到了 10元"
這只是一個簡單的演示,在真實(shí)應(yīng)用中,這些命令通常會由后端應(yīng)用程序執(zhí)行。以下是代碼實(shí)現(xiàn):首先,確保你的 Spring Boot 項(xiàng)目中已正確配置了 Redis 連接。在application.properties或application.yml中添加Redis連接配置:
?spring.redis.host=localhostspring.redis.port=6379
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.util.List;
public class RedPacketService {private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
public void sendRedPacket(String redPacketId, double totalAmount, int totalPeople) {double remainingAmount = totalAmount;for (int i = 1; i < totalPeople; i++) {double randomAmount = Math.random() * remainingAmount / (totalPeople - i);redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(redPacketId, String.format("%.2f", randomAmount));remainingAmount -= randomAmount;}redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(redPacketId, String.format("%.2f", remainingAmount));}
public String grabRedPacket(String redPacketId) {String amount = redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop(redPacketId);if (amount != null) {double grabbedAmount = Double.parseDouble(amount);String userId = "User" + System.nanoTime();String grabInfo = userId + " 搶到了 " + String.format("%.2f", grabbedAmount) + " 元";redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("grabbed:" + redPacketId, grabInfo);return grabInfo;} else {return "紅包已搶完";}}
public List<String> getRedPacketRecords(String redPacketId) {return redisTemplate.opsForList().range("grabbed:" + redPacketId, 0, -1);}}
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
public class RedPacketController {private RedPacketService redPacketService;
public void sendRedPacket( String redPacketId, double totalAmount, int totalPeople) {redPacketService.sendRedPacket(redPacketId, totalAmount, totalPeople);}
public String grabRedPacket( String redPacketId) {return redPacketService.grabRedPacket(redPacketId);}
public List<String> getRedPacketRecords( String redPacketId) {return redPacketService.getRedPacketRecords(redPacketId);}}
最后,假設(shè)你的Spring Boot應(yīng)用程序已經(jīng)在主機(jī)
127.0.0.1 的端口 8080 上運(yùn)行。
1、發(fā)紅包操作:
-
URL:
http://114.116.85.56:8080/redpacket/send -
參數(shù):
-
redPacketId:紅包的唯一標(biāo)識符。 -
totalAmount:紅包的總金額。 -
totalPeople:紅包的總領(lǐng)取人數(shù)。
-
示例請求:
http://114.116.85.56:8080/redpacket/send?redPacketId=1&totalAmount=100.0&totalPeople=10
2、搶紅包操作:
-
URL:
http://114.116.85.56:8080/redpacket/grab -
參數(shù):
-
redPacketId:要搶的紅包的唯一標(biāo)識符。
-
URL: http://114.116.85.56:8080/redpacket/grab?redPacketId=1
3、 獲取紅包記錄操作:
-
URL:
http://114.116.85.56:8080/redpacket/records -
參數(shù):
-
redPacketId:要獲取記錄的紅包的唯一標(biāo)識符。
-
http://114.116.85.56:8080/redpacket/records?redPacketId=1redPacketId:要獲取記錄的紅包的唯一標(biāo)識符。br
【痛點(diǎn)問題】
在搶紅包過程中,可能存在一些痛點(diǎn)問題,這些問題需要在系統(tǒng)設(shè)計(jì)和實(shí)現(xiàn)中仔細(xì)考慮和解決。以下是一些可能存在的痛點(diǎn)問題:
- 高并發(fā)問題:搶紅包場景通常伴隨著高并發(fā)操作,多個用戶同時嘗試搶奪同一個紅包。這可能導(dǎo)致競態(tài)條件和數(shù)據(jù)一致性問題。
- 數(shù)據(jù)一致性問題:在高并發(fā)情況下,多個用戶同時修改Redis中的數(shù)據(jù),可能導(dǎo)致數(shù)據(jù)一致性問題。例如,多個用戶同時寫入搶紅包記錄,可能導(dǎo)致數(shù)據(jù)的混亂或丟失。
- 性能問題:處理高并發(fā)搶紅包請求可能對系統(tǒng)的性能產(chǎn)生挑戰(zhàn)。需要考慮系統(tǒng)的擴(kuò)展性和負(fù)載均衡。
- 作弊問題:用戶可能嘗試通過不正當(dāng)手段多次搶奪同一個紅包。需要考慮如何檢測和防止作弊行為。
- 紅包池管理:紅包池的管理和維護(hù)也是一個問題,包括紅包的生成、過期處理和數(shù)據(jù)清理。
- 數(shù)據(jù)安全性:紅包金額的安全性也是一個關(guān)鍵問題。需要確保用戶不能通過惡意請求或攻擊來竊取或篡改紅包金額。
- 用戶體驗(yàn):最終用戶的體驗(yàn)也是關(guān)鍵因素。搶紅包的過程應(yīng)該是流暢的,用戶不應(yīng)該感到等待時間過長或遇到錯誤。
解決這些痛點(diǎn)問題需要綜合考慮多個因素,包括并發(fā)控制、事務(wù)處理、分布式鎖、數(shù)據(jù)模型設(shè)計(jì)、性能優(yōu)化、安全性等。在設(shè)計(jì)搶紅包系統(tǒng)時,需要仔細(xì)權(quán)衡這些因素,以確保系統(tǒng)的可伸縮性、穩(wěn)定性和用戶體驗(yàn)。
我們就高并發(fā)問題可能導(dǎo)致競態(tài)條件和數(shù)據(jù)一致性問題給出解決方案。
方案一:分布式鎖
使用分布式鎖來解決高并發(fā)問題的代碼示例:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class RedPacketService {
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public String grabRedPacket(String redPacketId, String userId) {String redPacketKey = "red_packet:" + redPacketId;String userKey = "user:" + userId;
try {// 使用分布式鎖boolean isLocked = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(userKey, "1", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (isLocked) {// 獲取到鎖,可以繼續(xù)搶紅包
if (stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().size(redPacketKey) > 0) {// 紅包池還有紅包,可以繼續(xù)搶String redPacket = stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(redPacketKey);// 記錄搶紅包信息String record = userId + " 搶到了 " + redPacket + " 元";stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("red_packet_records:" + redPacketId, record);
// 釋放用戶鎖stringRedisTemplate.delete(userKey);
return record;} else {// 紅包池已空stringRedisTemplate.delete(userKey);return "紅包已搶光";}} else {// 用戶未成功獲取鎖,表示用戶已經(jīng)搶過紅包return "你已經(jīng)搶過紅包了";}} catch (InterruptedException e) {// 處理異常e.printStackTrace();return "搶紅包出現(xiàn)異常";}}}
方案二:Redis事務(wù)
使用Redis的事務(wù)機(jī)制來確保操作的原子性。Redis的事務(wù)允許一組操作(一系列命令)在一個單一的、原子的事務(wù)中執(zhí)行,這意味著它們要么全部成功,要么全部失敗。在搶紅包的情況下,你可以使用 Redis 的MULTI、EXEC和WATCH命令來創(chuàng)建一個事務(wù)塊。
# 開始一個事務(wù)127.0.0.1:6379> MULTI
# 監(jiān)視紅包池的變化127.0.0.1:6379> WATCH red_packet_pool
# 檢查紅包池中是否還有紅包127.0.0.1:6379> LLEN red_packet_pool(integer) 3
# 如果紅包池中還有紅包,則繼續(xù)操作127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH red_packet_ids RP_1127.0.0.1:6379> LPOP red_packet_pool
# 提交事務(wù)127.0.0.1:6379> EXEC
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId></dependency>
然后,在Spring Boot應(yīng)用中創(chuàng)建一個RedPacketService類,該類包含了處理搶紅包操作的方法:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.SessionCallback;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
public class RedPacketService {
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
public String grabRedPacket(String redPacketId, String userId) {String redPacketKey = "red_packet:" + redPacketId;String userKey = "user:" + userId;
SessionCallback<String> sessionCallback = operations -> {operations.watch(redPacketKey);String redPacket = operations.opsForList().leftPop(redPacketKey);if (redPacket != null) {operations.multi();operations.opsForList().leftPush("red_packet_records:" + redPacketId, userId + " 搶到了 " + redPacket + " 元");operations.exec();}operations.unwatch();return redPacket;};
String result = redisTemplate.execute(sessionCallback);
if (result == null) {return "紅包已搶光";} else if (result.equals("")) {return "你已經(jīng)搶過紅包了";} else {return result;}}}
在這個示例中,我們使用SessionCallback接口來執(zhí)行事務(wù)。 在sessionCallback中,我們首先調(diào)用watch方法來監(jiān)視紅包池的變化。 然后,我們執(zhí)行一系列操作,包括彈出紅包、記錄搶紅包信息,并使用multi和exec方法來提交事務(wù)。 最后,我們使用unwatch來取消監(jiān)視。
【結(jié)尾】
感謝大家認(rèn)真審閱,也歡迎大佬們批評指正。 如果您覺得對日常工作或?qū)W習(xí)有幫助,歡迎點(diǎn)贊,在看,轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)和評論。
???? 點(diǎn)擊下方閱讀原文,獲取魚皮往期編程干貨。
往期推薦
