SpringBoot 服務(wù)接口限流,搞定!
胖虎和朋友原創(chuàng)的視頻教程有興趣的可以看看:
(文末附課程大綱)
在開發(fā)高并發(fā)系統(tǒng)時有三把利器用來保護系統(tǒng):緩存、降級和限流。限流可以認為服務(wù)降級的一種,限流通過限制請求的流量以達到保護系統(tǒng)的目的。
一般來說,系統(tǒng)的吞吐量是可以計算出一個閾值的,為了保證系統(tǒng)的穩(wěn)定運行,一旦達到這個閾值,就需要限制流量并采取一些措施以完成限制流量的目的。比如:延遲處理,拒絕處理,或者部分拒絕處理等等。否則,很容易導(dǎo)致服務(wù)器的宕機。
常見限流算
計數(shù)器限流
計數(shù)器限流算法是最為簡單粗暴的解決方案,主要用來限制總并發(fā)數(shù),比如數(shù)據(jù)庫連接池大小、線程池大小、接口訪問并發(fā)數(shù)等都是使用計數(shù)器算法。
如:使用 AomicInteger 來進行統(tǒng)計當(dāng)前正在并發(fā)執(zhí)行的次數(shù),如果超過域值就直接拒絕請求,提示系統(tǒng)繁忙。
漏桶算法

漏桶算法思路很簡單,我們把水比作是 請求,漏桶比作是 系統(tǒng)處理能力極限,水先進入到漏桶里,漏桶里的水按一定速率流出,當(dāng)流出的速率小于流入的速率時,由于漏桶容量有限,后續(xù)進入的水直接溢出(拒絕請求),以此實現(xiàn)限流。
令牌桶算法
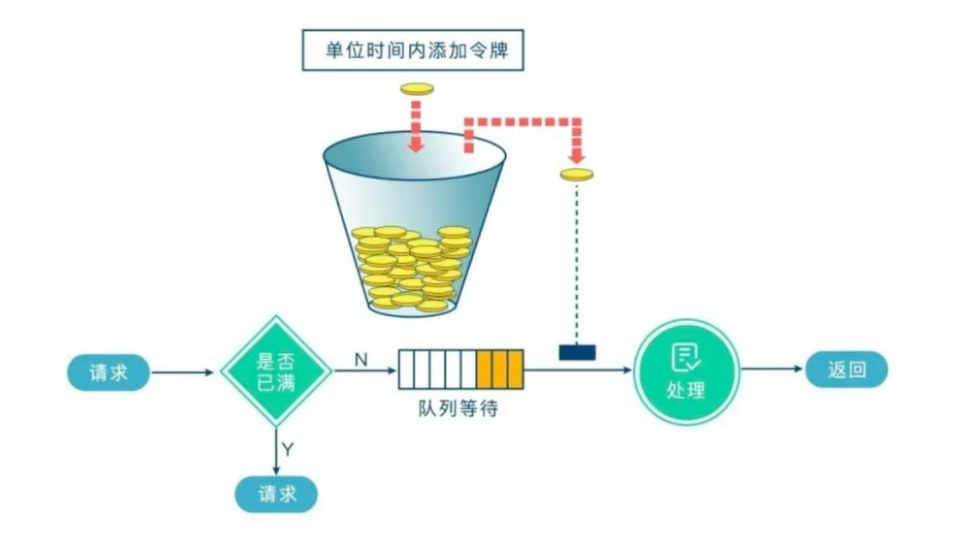
令牌桶算法的原理也比較簡單,我們可以理解成醫(yī)院的掛號看病,只有拿到號以后才可以進行診病。
系統(tǒng)會維護一個令牌(token)桶,以一個恒定的速度往桶里放入令牌(token),這時如果有請求進來想要被處理,則需要先從桶里獲取一個令牌(token),當(dāng)桶里沒有令牌(token)可取時,則該請求將被拒絕服務(wù)。令牌桶算法通過控制桶的容量、發(fā)放令牌的速率,來達到對請求的限制。
單機模式
Google 開源工具包 Guava 提供了限流工具類 RateLimiter,該類基于令牌桶算法實現(xiàn)流量限制,使用十分方便,而且十分高效
引入依賴 pom
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>30.1-jre</version>
</dependency>
創(chuàng)建注解 Limit
package com.example.demo.common.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Documented
public @interface Limit {
// 資源key
String key() default "";
// 最多訪問次數(shù)
double permitsPerSecond();
// 時間
long timeout();
// 時間類型
TimeUnit timeunit() default TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS;
// 提示信息
String msg() default "系統(tǒng)繁忙,請稍后再試";
}
注解 aop 實現(xiàn)
package com.example.demo.common.aspect;
import com.example.demo.common.annotation.Limit;
import com.example.demo.common.dto.R;
import com.example.demo.common.exception.LimitException;
import com.google.common.collect.Maps;
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class LimitAspect {
private final Map<String, RateLimiter> limitMap = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
@Around("@annotation(com.example.demo.common.annotation.Limit)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature)pjp.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
//拿limit的注解
Limit limit = method.getAnnotation(Limit.class);
if (limit != null) {
//key作用:不同的接口,不同的流量控制
String key=limit.key();
RateLimiter rateLimiter;
//驗證緩存是否有命中key
if (!limitMap.containsKey(key)) {
// 創(chuàng)建令牌桶
rateLimiter = RateLimiter.create(limit.permitsPerSecond());
limitMap.put(key, rateLimiter);
log.info("新建了令牌桶={},容量={}",key,limit.permitsPerSecond());
}
rateLimiter = limitMap.get(key);
// 拿令牌
boolean acquire = rateLimiter.tryAcquire(limit.timeout(), limit.timeunit());
// 拿不到命令,直接返回異常提示
if (!acquire) {
log.debug("令牌桶={},獲取令牌失敗",key);
throw new LimitException(limit.msg());
}
}
return pjp.proceed();
}
}
注解使用
-
permitsPerSecond 代表請求總數(shù)量 -
timeout 代表限制時間
即 timeout 時間內(nèi),只允許有 permitsPerSecond 個請求總數(shù)量訪問,超過的將被限制不能訪問
package com.example.demo.module.test;
import com.example.demo.common.annotation.Limit;
import com.example.demo.common.dto.R;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Limit(key = "cachingTest", permitsPerSecond = 1, timeout = 500, msg = "當(dāng)前排隊人數(shù)較多,請稍后再試!")
@GetMapping("cachingTest")
public R cachingTest(){
log.info("------讀取本地------");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("蠟筆小新");
list.add("哆啦A夢");
list.add("四驅(qū)兄弟");
return R.ok(list);
}
}
測試
啟動項目,快讀刷新訪問 /cachingTest 請求
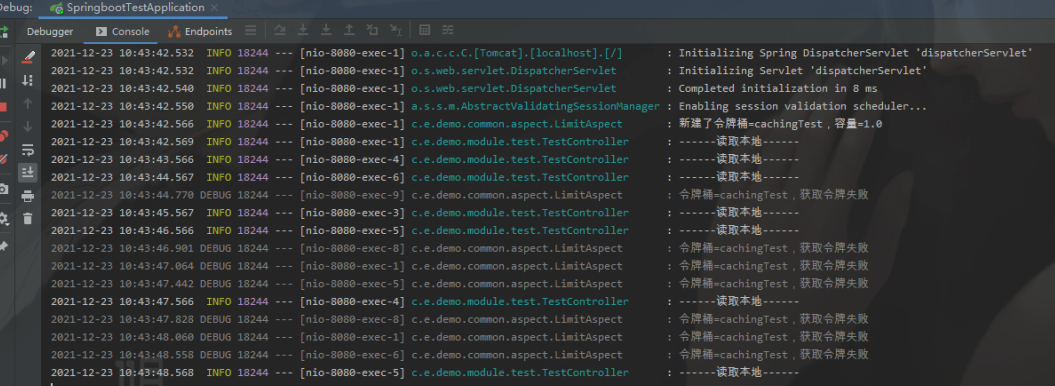
可以看到訪問已有被成功限制
該種方式屬于應(yīng)用級限流,假設(shè)將應(yīng)用部署到多臺機器,應(yīng)用級限流方式只是單應(yīng)用內(nèi)的請求限流,不能進行全局限流。因此我們需要分布式限流和接入層限流來解決這個問題。
分布式模式
基于 redis + lua 腳本的分布式限流
分布式限流最關(guān)鍵的是要將限流服務(wù)做成原子化,而解決方案可以使用 redis+lua 或者 nginx+lua 技術(shù)進行實現(xiàn),通過這兩種技術(shù)可以實現(xiàn)的高并發(fā)和高性能。
首先我們來使用 redis+lua 實現(xiàn)時間窗內(nèi)某個接口的請求數(shù)限流,實現(xiàn)了該功能后可以改造為限流總并發(fā)/請求數(shù)和限制總資源數(shù)。lua 本身就是一種編程語言,也可以使用它實現(xiàn)復(fù)雜的令牌桶或漏桶算法。因操作是在一個 lua 腳本中(相當(dāng)于原子操作),又因 redis 是單線程模型,因此是線程安全的。
相比 redis 事務(wù)來說,lua 腳本有以下優(yōu)點
-
減少網(wǎng)絡(luò)開銷:不使用 lua 的代碼需要向 redis 發(fā)送多次請求,而腳本只需一次即可,減少網(wǎng)絡(luò)傳輸; -
原子操作:redis 將整個腳本作為一個原子執(zhí)行,無需擔(dān)心并發(fā),也就無需事務(wù); -
復(fù)用:腳本會永久保存 redis 中,其他客戶端可繼續(xù)使用。
創(chuàng)建注解 RedisLimit
package com.example.demo.common.annotation;
import com.example.demo.common.enums.LimitType;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface RedisLimit {
// 資源名稱
String name() default "";
// 資源key
String key() default "";
// 前綴
String prefix() default "";
// 時間
int period();
// 最多訪問次數(shù)
int count();
// 類型
LimitType limitType() default LimitType.CUSTOMER;
// 提示信息
String msg() default "系統(tǒng)繁忙,請稍后再試";
}
注解 aop 實現(xiàn)
package com.example.demo.common.aspect;
import com.example.demo.common.annotation.RedisLimit;
import com.example.demo.common.enums.LimitType;
import com.example.demo.common.exception.LimitException;
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Objects;
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Configuration
public class RedisLimitAspect {
private final RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
public RedisLimitAspect(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) {
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
}
@Around("@annotation(com.example.demo.common.annotation.RedisLimit)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature)pjp.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
RedisLimit annotation = method.getAnnotation(RedisLimit.class);
LimitType limitType = annotation.limitType();
String name = annotation.name();
String key;
int period = annotation.period();
int count = annotation.count();
switch (limitType){
case IP:
key = getIpAddress();
break;
case CUSTOMER:
key = annotation.key();
break;
default:
key = StringUtils.upperCase(method.getName());
}
ImmutableList<String> keys = ImmutableList.of(StringUtils.join(annotation.prefix(), key));
try {
String luaScript = buildLuaScript();
DefaultRedisScript<Number> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>(luaScript, Number.class);
Number number = redisTemplate.execute(redisScript, keys, count, period);
log.info("Access try count is {} for name = {} and key = {}", number, name, key);
if(number != null && number.intValue() == 1){
return pjp.proceed();
}
throw new LimitException(annotation.msg());
}catch (Throwable e){
if(e instanceof LimitException){
log.debug("令牌桶={},獲取令牌失敗",key);
throw new LimitException(e.getLocalizedMessage());
}
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("服務(wù)器異常");
}
}
public String buildLuaScript(){
return "redis.replicate_commands(); local listLen,time" +
"\nlistLen = redis.call('LLEN', KEYS[1])" +
// 不超過最大值,則直接寫入時間
"\nif listLen and tonumber(listLen) < tonumber(ARGV[1]) then" +
"\nlocal a = redis.call('TIME');" +
"\nredis.call('LPUSH', KEYS[1], a[1]*1000000+a[2])" +
"\nelse" +
// 取出現(xiàn)存的最早的那個時間,和當(dāng)前時間比較,看是小于時間間隔
"\ntime = redis.call('LINDEX', KEYS[1], -1)" +
"\nlocal a = redis.call('TIME');" +
"\nif a[1]*1000000+a[2] - time < tonumber(ARGV[2])*1000000 then" +
// 訪問頻率超過了限制,返回0表示失敗
"\nreturn 0;" +
"\nelse" +
"\nredis.call('LPUSH', KEYS[1], a[1]*1000000+a[2])" +
"\nredis.call('LTRIM', KEYS[1], 0, tonumber(ARGV[1])-1)" +
"\nend" +
"\nend" +
"\nreturn 1;";
}
public String getIpAddress(){
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) Objects.requireNonNull(RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes())).getRequest();
String ip = request.getHeader("x-forwarded-for");
if(ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)){
ip = request.getHeader("Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if(ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)){
ip = request.getHeader("WL-Client-IP");
}
if(ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ip)){
ip = request.getRemoteAddr();
}
return ip;
}
}
注解使用
-
count 代表請求總數(shù)量 -
period 代表限制時間
即 period 時間內(nèi),只允許有 count 個請求總數(shù)量訪問,超過的將被限制不能訪問
package com.example.demo.module.test;
import com.example.demo.common.annotation.Limit;
import com.example.demo.common.annotation.RedisLimit;
import com.example.demo.common.dto.R;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class TestController {
@RedisLimit(key = "cachingTest", count = 2, period = 2, msg = "當(dāng)前排隊人數(shù)較多,請稍后再試!")
// @Limit(key = "cachingTest", permitsPerSecond = 1, timeout = 500, msg = "當(dāng)前排隊人數(shù)較多,請稍后再試!")
@GetMapping("cachingTest")
public R cachingTest(){
log.info("------讀取本地------");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("蠟筆小新");
list.add("哆啦A夢");
list.add("四驅(qū)兄弟");
return R.ok(list);
}
}
測試
啟動項目,快讀刷新訪問 /cachingTest 請求
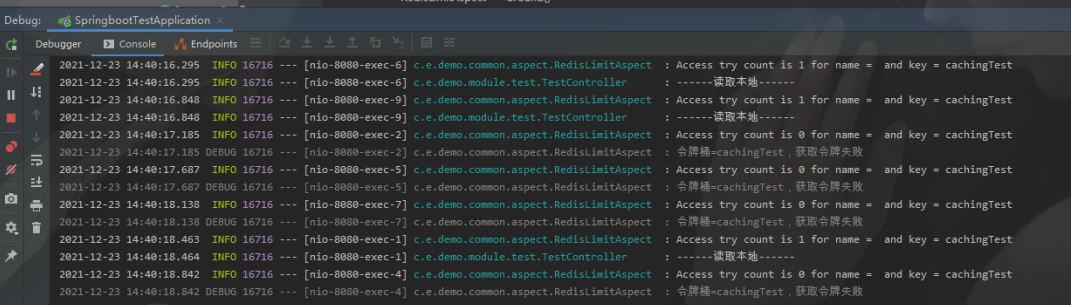
可以看到訪問已經(jīng)有被成功限制
這只是其中一種實現(xiàn)方式,尚有許多實現(xiàn)方案,經(jīng)供參考
來源:blog.csdn.net/qq_34217386/article/details/122100904

胖虎聯(lián)合兩位大佬朋友,一位是知名培訓(xùn)機構(gòu)講師和科大訊飛架構(gòu),聯(lián)合打造了《Java架構(gòu)師成長之路》的視頻教程。完全對標外面2萬左右的培訓(xùn)課程。
除了基本的視頻教程之外,還提供了超詳細的課堂筆記,以及源碼等資料包..
課程階段:
Java核心 提升閱讀源碼的內(nèi)功心法 深入講解企業(yè)開發(fā)必備技術(shù)棧,夯實基礎(chǔ),為跳槽加薪增加籌碼
分布式架構(gòu)設(shè)計方法論。為學(xué)習(xí)分布式微服務(wù)做鋪墊 學(xué)習(xí)NetFilx公司產(chǎn)品,如Eureka、Hystrix、Zuul、Feign、Ribbon等,以及學(xué)習(xí)Spring Cloud Alibabba體系 微服務(wù)架構(gòu)下的性能優(yōu)化 中間件源碼剖析 元原生以及虛擬化技術(shù) 從0開始,項目實戰(zhàn) SpringCloud Alibaba電商項目
點擊下方超鏈接查看詳情
(或者點擊文末閱讀原文):
(點擊查看) 2023年,最新Java架構(gòu)師成長之路 視頻教程!
以下是課程大綱,大家可以雙擊打開原圖查看