為了甩鍋,我寫了個牛逼的日志切面!
點擊上方藍色字體,選擇“設為星標”

最近項目進入聯(lián)調階段,服務層的接口需要和協(xié)議層進行交互,協(xié)議層需要將入?yún)json字符串]組裝成服務層所需的json字符串,組裝的過程中很容易出錯。入?yún)⒊鲥e導致接口調試失敗問題在聯(lián)調中出現(xiàn)很多次,因此就想寫一個請求日志切面把入?yún)⑿畔⒋蛴∫幌拢瑫r協(xié)議層調用服務層接口名稱對不上也出現(xiàn)了幾次,通過請求日志切面就可以知道上層是否有沒有發(fā)起調用,方便前后端甩鍋還能拿出證據(jù)
寫在前面
本篇文章是實戰(zhàn)性的,對于切面的原理不會講解,只會簡單介紹一下切面的知識點
切面介紹
面向切面編程是一種編程范式,它作為OOP面向對象編程的一種補充,用于處理系統(tǒng)中分布于各個模塊的橫切關注點,比如事務管理、權限控制、緩存控制、日志打印等等。AOP把軟件的功能模塊分為兩個部分:核心關注點和橫切關注點。業(yè)務處理的主要功能為核心關注點,而非核心、需要拓展的功能為橫切關注點。AOP的作用在于分離系統(tǒng)中的各種關注點,將核心關注點和橫切關注點進行分離,使用切面有以下好處:
集中處理某一關注點/橫切邏輯 可以很方便的添加/刪除關注點 侵入性少,增強代碼可讀性及可維護性 因此當想打印請求日志時很容易想到切面,對控制層代碼0侵入
切面的使用【基于注解】
@Aspect => 聲明該類為一個注解類
切點注解:
@Pointcut => 定義一個切點,可以簡化代碼
通知注解:
@Before => 在切點之前執(zhí)行代碼 @After => 在切點之后執(zhí)行代碼 @AfterReturning => 切點返回內容后執(zhí)行代碼,可以對切點的返回值進行封裝 @AfterThrowing => 切點拋出異常后執(zhí)行 @Around => 環(huán)繞,在切點前后執(zhí)行代碼
動手寫一個請求日志切面
使用@Pointcut定義切點
@Pointcut("execution(* you_package.controller..*(..))")
public void requestServer() {
}
@Pointcut定義了一個切點,因為是請求日志切邊,因此切點定義的是Controller包下的所有類下的方法。定義切點以后在通知注解中直接使用requestServer方法名就可以了
使用@Before再切點前執(zhí)行
@Before("requestServer()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes)
RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
LOGGER.info("===============================Start========================");
LOGGER.info("IP : {}", request.getRemoteAddr());
LOGGER.info("URL : {}", request.getRequestURL().toString());
LOGGER.info("HTTP Method : {}", request.getMethod());
LOGGER.info("Class Method : {}.{}", joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(), joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
在進入Controller方法前,打印出調用方IP、請求URL、HTTP請求類型、調用的方法名
使用@Around打印進入控制層的入?yún)?/section>
@Around("requestServer()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
LOGGER.info("Request Params : {}", getRequestParams(proceedingJoinPoint));
LOGGER.info("Result : {}", result);
LOGGER.info("Time Cost : {} ms", System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
return result;
}
打印了入?yún)ⅰ⒔Y果以及耗時
getRquestParams方法
private Map<String, Object> getRequestParams(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
Map<String, Object> requestParams = new HashMap<>();
//參數(shù)名
String[] paramNames = ((MethodSignature)proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature()).getParameterNames();
//參數(shù)值
Object[] paramValues = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
for (int i = 0; i < paramNames.length; i++) {
Object value = paramValues[i];
//如果是文件對象
if (value instanceof MultipartFile) {
MultipartFile file = (MultipartFile) value;
value = file.getOriginalFilename(); //獲取文件名
}
requestParams.put(paramNames[i], value);
}
return requestParams;
}
通過 @PathVariable以及@RequestParam注解傳遞的參數(shù)無法打印出參數(shù)名,因此需要手動拼接一下參數(shù)名,同時對文件對象進行了特殊處理,只需獲取文件名即可 。
@After方法調用后執(zhí)行
@After("requestServer()")
public void doAfter(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
LOGGER.info("===============================End========================");
}
沒有業(yè)務邏輯只是打印了End
完整切面代碼
@Component
@Aspect
public class RequestLogAspect {
private final static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RequestLogAspect.class);
@Pointcut("execution(* you_package.controller..*(..))")
public void requestServer() {
}
@Before("requestServer()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes)
RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
LOGGER.info("===============================Start========================");
LOGGER.info("IP : {}", request.getRemoteAddr());
LOGGER.info("URL : {}", request.getRequestURL().toString());
LOGGER.info("HTTP Method : {}", request.getMethod());
LOGGER.info("Class Method : {}.{}", joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(),
joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
@Around("requestServer()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
LOGGER.info("Request Params : {}", getRequestParams(proceedingJoinPoint));
LOGGER.info("Result : {}", result);
LOGGER.info("Time Cost : {} ms", System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
return result;
}
@After("requestServer()")
public void doAfter(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
LOGGER.info("===============================End========================");
}
/**
* 獲取入?yún)?br> * @param proceedingJoinPoint
*
* @return
* */
private Map<String, Object> getRequestParams(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
Map<String, Object> requestParams = new HashMap<>();
//參數(shù)名
String[] paramNames =
((MethodSignature)proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature()).getParameterNames();
//參數(shù)值
Object[] paramValues = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
for (int i = 0; i < paramNames.length; i++) {
Object value = paramValues[i];
//如果是文件對象
if (value instanceof MultipartFile) {
MultipartFile file = (MultipartFile) value;
value = file.getOriginalFilename(); //獲取文件名
}
requestParams.put(paramNames[i], value);
}
return requestParams;
}
}
高并發(fā)下請求日志切面
寫完以后對自己的代碼很滿意,但是想著可能還有完善的地方就和朋友交流了一下。emmmm
果然還有繼續(xù)優(yōu)化的地方 每個信息都打印一行,在高并發(fā)請求下確實會出現(xiàn)請求之間打印日志串行的問題,因為測試階段請求數(shù)量較少沒有出現(xiàn)串行的情況,果然生產(chǎn)環(huán)境才是第一發(fā)展力,能夠遇到更多bug,寫更健壯的代碼 解決日志串行的問題只要將多行打印信息合并為一行就可以了,因此構造一個對象
RequestInfo.java
@Data
public class RequestInfo {
private String ip;
private String url;
private String httpMethod;
private String classMethod;
private Object requestParams;
private Object result;
private Long timeCost;
}
環(huán)繞通知方法體
@Around("requestServer()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
RequestInfo requestInfo = new RequestInfo();
requestInfo.setIp(request.getRemoteAddr());
requestInfo.setUrl(request.getRequestURL().toString());
requestInfo.setHttpMethod(request.getMethod());
requestInfo.setClassMethod(String.format("%s.%s", proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(),
proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName()));
requestInfo.setRequestParams(getRequestParamsByProceedingJoinPoint(proceedingJoinPoint));
requestInfo.setResult(result);
requestInfo.setTimeCost(System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
LOGGER.info("Request Info : {}", JSON.toJSONString(requestInfo));
return result;
}
將url、http request這些信息組裝成RequestInfo對象,再序列化打印對象 打印序列化對象結果而不是直接打印對象是因為序列化有更直觀、更清晰,同時可以借助在線解析工具對結果進行解析.
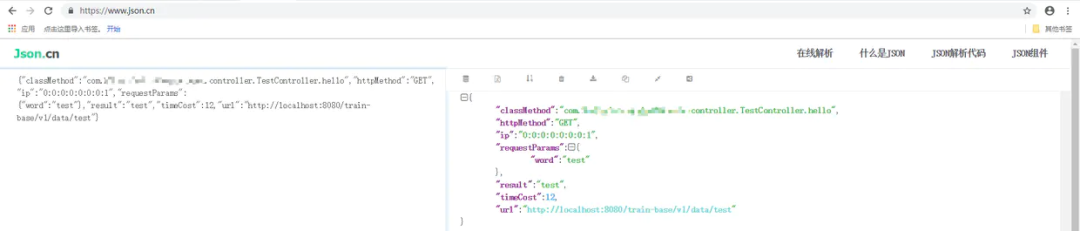
是不是還不錯 在解決高并發(fā)下請求串行問題的同時添加了對異常請求信息的打印,通過使用 @AfterThrowing注解對拋出異常的方法進行處理
RequestErrorInfo.java
@Data
public class RequestErrorInfo {
private String ip;
private String url;
private String httpMethod;
private String classMethod;
private Object requestParams;
private RuntimeException exception;
}
異常通知環(huán)繞體
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "requestServer()", throwing = "e")
public void doAfterThrow(JoinPoint joinPoint, RuntimeException e) {
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
RequestErrorInfo requestErrorInfo = new RequestErrorInfo();
requestErrorInfo.setIp(request.getRemoteAddr());
requestErrorInfo.setUrl(request.getRequestURL().toString());
requestErrorInfo.setHttpMethod(request.getMethod());
requestErrorInfo.setClassMethod(String.format("%s.%s", joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(),
joinPoint.getSignature().getName()));
requestErrorInfo.setRequestParams(getRequestParamsByJoinPoint(joinPoint));
requestErrorInfo.setException(e);
LOGGER.info("Error Request Info : {}", JSON.toJSONString(requestErrorInfo));
}
對于異常,耗時是沒有意義的,因此不統(tǒng)計耗時,而是添加了異常的打印
最后放一下完整日志請求切面代碼:
@Component
@Aspect
public class RequestLogAspect {
private final static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RequestLogAspect.class);
@Pointcut("execution(* you_package.controller..*(..))")
public void requestServer() {
}
@Around("requestServer()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
RequestInfo requestInfo = new RequestInfo();
requestInfo.setIp(request.getRemoteAddr());
requestInfo.setUrl(request.getRequestURL().toString());
requestInfo.setHttpMethod(request.getMethod());
requestInfo.setClassMethod(String.format("%s.%s", proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(),
proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName()));
requestInfo.setRequestParams(getRequestParamsByProceedingJoinPoint(proceedingJoinPoint));
requestInfo.setResult(result);
requestInfo.setTimeCost(System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
LOGGER.info("Request Info : {}", JSON.toJSONString(requestInfo));
return result;
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "requestServer()", throwing = "e")
public void doAfterThrow(JoinPoint joinPoint, RuntimeException e) {
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
RequestErrorInfo requestErrorInfo = new RequestErrorInfo();
requestErrorInfo.setIp(request.getRemoteAddr());
requestErrorInfo.setUrl(request.getRequestURL().toString());
requestErrorInfo.setHttpMethod(request.getMethod());
requestErrorInfo.setClassMethod(String.format("%s.%s", joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(),
joinPoint.getSignature().getName()));
requestErrorInfo.setRequestParams(getRequestParamsByJoinPoint(joinPoint));
requestErrorInfo.setException(e);
LOGGER.info("Error Request Info : {}", JSON.toJSONString(requestErrorInfo));
}
/**
* 獲取入?yún)?br> * @param proceedingJoinPoint
*
* @return
* */
private Map<String, Object> getRequestParamsByProceedingJoinPoint(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
//參數(shù)名
String[] paramNames = ((MethodSignature)proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature()).getParameterNames();
//參數(shù)值
Object[] paramValues = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
return buildRequestParam(paramNames, paramValues);
}
private Map<String, Object> getRequestParamsByJoinPoint(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//參數(shù)名
String[] paramNames = ((MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature()).getParameterNames();
//參數(shù)值
Object[] paramValues = joinPoint.getArgs();
return buildRequestParam(paramNames, paramValues);
}
private Map<String, Object> buildRequestParam(String[] paramNames, Object[] paramValues) {
Map<String, Object> requestParams = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < paramNames.length; i++) {
Object value = paramValues[i];
//如果是文件對象
if (value instanceof MultipartFile) {
MultipartFile file = (MultipartFile) value;
value = file.getOriginalFilename(); //獲取文件名
}
requestParams.put(paramNames[i], value);
}
return requestParams;
}
@Data
public class RequestInfo {
private String ip;
private String url;
private String httpMethod;
private String classMethod;
private Object requestParams;
private Object result;
private Long timeCost;
}
@Data
public class RequestErrorInfo {
private String ip;
private String url;
private String httpMethod;
private String classMethod;
private Object requestParams;
private RuntimeException exception;
}
}
趕緊給你們的應用加上吧【如果沒加的話】,沒有日志的話,總懷疑上層出錯,但是卻拿不出證據(jù)

關于traceId 跟蹤定位,可以根據(jù)traceId跟蹤整條調用鏈,以log4j2為例介紹如何加入traceId
添加攔截器
public class LogInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
private final static String TRACE_ID = "traceId";
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String traceId = java.util.UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", "").toUpperCase();
ThreadContext.put("traceId", traceId);
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView)
throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
ThreadContext. remove(TRACE_ID);
}
}
在調用前通過ThreadContext加入traceId,調用完成后移除
修改日志配置文件 在原來的日志格式中 添加traceId的占位符
<property name="pattern">[TRACEID:%X{traceId}] %d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} %-5level %class{-1}.%M()/%L - %msg%xEx%n</property>
執(zhí)行效果
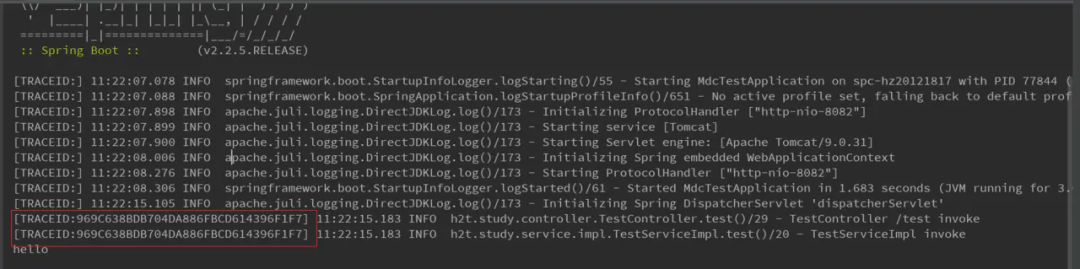
日志跟蹤更方便 DMC是配置logback和log4j使用的,使用方式和ThreadContext差不多,將ThreadContext.put替換為MDC.put即可,同時修改日志配置文件。

MDC是slf4j包下的,其具體使用哪個日志框架與我們的依賴有關.
| 文章僅供參考
入骨相思知不知
玲瓏骰子安紅豆


入我相思門,知我相思苦,長相思兮長相憶,短相思兮無窮極。



