Golang單元測(cè)試
目錄
1、單元測(cè)試概述
1.1 什么是單元&單元測(cè)試
1.2 為什么進(jìn)行單元測(cè)試
1.3 單元測(cè)試用例編寫的原則
1.4 單測(cè)用例規(guī)定
2、golang 常用的單測(cè)框架
2.1 testing
2.2 goconvey
2.3 testify

1、單元測(cè)試概述
1.1 什么是單元&單元測(cè)試
單元是應(yīng)用的最小可測(cè)試部件,如函數(shù)和對(duì)象的方法 單元測(cè)試是軟件開發(fā)中對(duì)最小單位進(jìn)行正確性檢驗(yàn)的測(cè)試工作
1.2 為什么進(jìn)行單元測(cè)試
保證變更/重構(gòu)的正確性,特別是在一些頻繁變動(dòng)和多人合作開發(fā)的項(xiàng)目中 簡化調(diào)試過程:可以輕松的讓我們知道哪一部分代碼出了問題 單測(cè)最好的文檔:在單測(cè)中直接給出具體接口的使用方法,是最好的實(shí)例代碼
1.3 單元測(cè)試用例編寫的原則
單一原則:一個(gè)測(cè)試用例只負(fù)責(zé)一個(gè)場(chǎng)景 原子性:結(jié)果只有兩種情況: Pass、Fail優(yōu)先要核心組件和邏輯的測(cè)試用例 高頻使用庫, util,重點(diǎn)覆蓋
1.4 單測(cè)用例規(guī)定
文件名必須要 xx_test.go命名測(cè)試方法必須是 TestXXX開頭方法中的參數(shù)必須是 t *testing.T測(cè)試文件和被測(cè)試文件必須在一個(gè)包中
2、golang 常用的單測(cè)框架
2.1 testing
https://golang.google.cn/pkg/testing/
2.1.1 單元測(cè)試
Go提供了test工具用于代碼的單元測(cè)試,test工具會(huì)查找包下以_test.go結(jié)尾的文件,調(diào)用測(cè)試文件中以 Test或Benchmark開頭的函數(shù)并給出運(yùn)行結(jié)果
測(cè)試函數(shù)需要導(dǎo)入testing包,并定義以Test開頭的函數(shù),參數(shù)為testing.T指針類型,在測(cè)試函數(shù)中調(diào)用函數(shù)進(jìn)行返回值測(cè)試,當(dāng)測(cè)試失敗可通過testing.T結(jié)構(gòu)體的Error函數(shù)拋出錯(cuò)誤
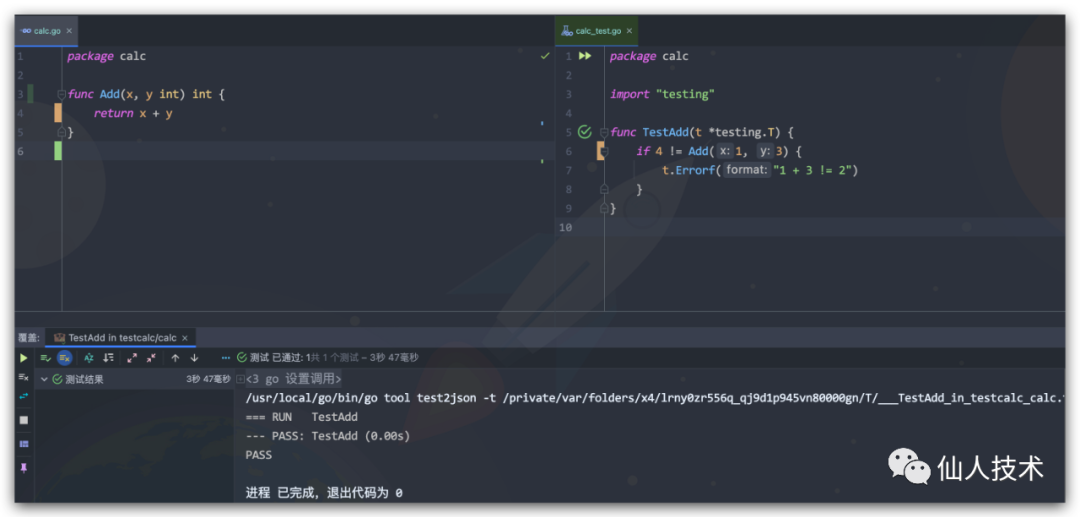
單元測(cè)試是對(duì)某個(gè)功能的測(cè)試 命令行執(zhí)行
go test 包名 # 測(cè)試整個(gè)包
go test -v .
go test 包名/文件名 # 測(cè)試某個(gè)文件
簡單使用
準(zhǔn)備待測(cè)代碼compute.go
package pkg03
func Add(a, b int) int {
return a + b
}
func Mul(a, b int) int {
return a * b
}
func Div(a, b int) int {
return a / b
}
準(zhǔn)備測(cè)試用例compute_test.go
package pkg03
import "testing"
func TestAdd(t *testing.T) {
a := 10
b := 20
want := 30
actual := Add(a, b)
if want != actual {
t.Errorf("Add函數(shù)參數(shù):%d %d, 期望: %d, 實(shí)際: %d", a, b, want, actual)
}
}
func TestMul(t *testing.T) {
a := 10
b := 20
want := 300
actual := Mul(a, b)
if want != actual {
t.Errorf("Mul函數(shù)參數(shù):%d %d, 期望: %d, 實(shí)際: %d", a, b, want, actual)
}
}
func TestDiv(t *testing.T) {
a := 10
b := 20
want := 2
actual := Div(a, b)
if want != actual {
t.Errorf("Div函數(shù)參數(shù):%d %d, 期望: %d, 實(shí)際: %d", a, b, want, actual)
}
}
執(zhí)行測(cè)試
? pwd
golang-learning/chapter06/pkg03
? go test -v .
=== RUN TestAdd
--- PASS: TestAdd (0.00s)
=== RUN TestMul
compute_test.go:21: Mul函數(shù)參數(shù):10 20, 期望: 300, 實(shí)際: 200
--- FAIL: TestMul (0.00s)
=== RUN TestDiv
compute_test.go:31: Div函數(shù)參數(shù):10 20, 期望: 2, 實(shí)際: 0
--- FAIL: TestDiv (0.00s)
FAIL
FAIL pkg03 0.198s
FAIL
只執(zhí)行某個(gè)函數(shù)
go test -run=TestAdd -v .
=== RUN TestAdd
--- PASS: TestAdd (0.00s)
PASS
ok pkg03 0.706s
正則過濾函數(shù)名
go test -run=TestM.* -v .
2.1.2 測(cè)試覆蓋率
用于統(tǒng)計(jì)目標(biāo)包有百分之多少的代碼參與了單測(cè)
使用go test工具進(jìn)行單元測(cè)試并將測(cè)試覆蓋率覆蓋分析結(jié)果輸出到cover.out文件
例如上面的例子
go test -v -cover
=== RUN TestAdd
--- PASS: TestAdd (0.00s)
=== RUN TestMul
compute_test.go:21: Mul函數(shù)參數(shù):10 20, 期望: 300, 實(shí)際: 200
--- FAIL: TestMul (0.00s)
=== RUN TestDiv
compute_test.go:31: Div函數(shù)參數(shù):10 20, 期望: 2, 實(shí)際: 0
--- FAIL: TestDiv (0.00s)
FAIL
coverage: 100.0% of statements
exit status 1
FAIL pkg03 0.185s
生成測(cè)試覆蓋率文件
go test -v -coverprofile=cover.out
=== RUN TestAdd
--- PASS: TestAdd (0.00s)
=== RUN TestAddFlag
--- PASS: TestAddFlag (0.00s)
PASS
coverage: 75.0% of statements
ok testcalc/calc 0.960s
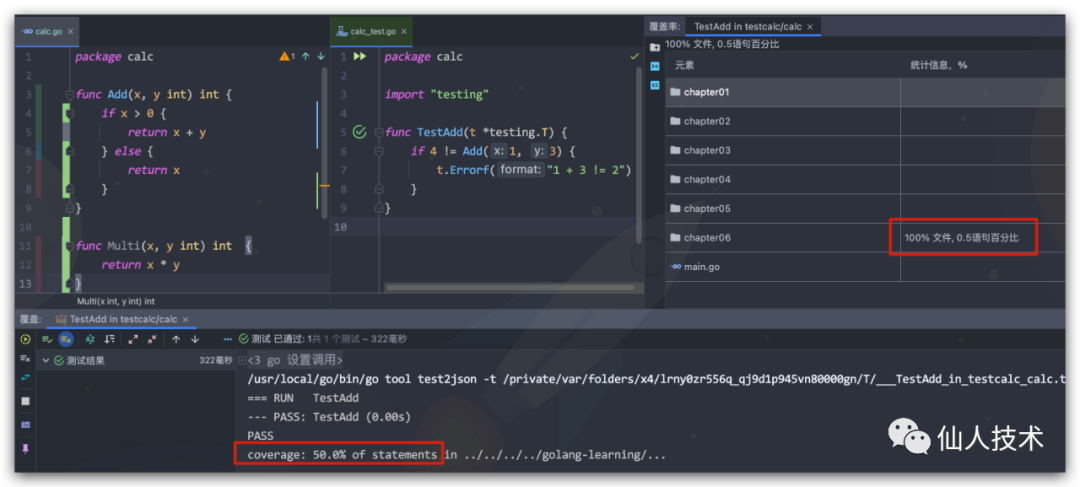
分析測(cè)試結(jié)果,打開測(cè)試覆蓋率結(jié)果文件,查看測(cè)試覆蓋率
go tool cover -html cover.out
2.1.3 子測(cè)試 t.run
func TestMul2(t *testing.T) {
t.Run("正數(shù)", func(t *testing.T) {
if Mul(4, 5) != 20 {
t.Fatal("muli.zhengshu.error")
}
})
t.Run("負(fù)數(shù)", func(t *testing.T) {
if Mul(2, -3) != -6 {
t.Fatal("muli.fushu.error")
}
})
}
執(zhí)行測(cè)試
? go test -v .
=== RUN TestMul2
=== RUN TestMul2/正數(shù)
=== RUN TestMul2/負(fù)數(shù)
--- PASS: TestMul2 (0.00s)
--- PASS: TestMul2/正數(shù) (0.00s)
--- PASS: TestMul2/負(fù)數(shù) (0.00s)
指定func/sub運(yùn)行子測(cè)試
? go test -run=TestMul2/正數(shù) -v
=== RUN TestMul2
=== RUN TestMul2/正數(shù)
--- PASS: TestMul2 (0.00s)
--- PASS: TestMul2/正數(shù) (0.00s)
PASS
ok pkg03 0.675s
子測(cè)試的作用:table-driven tests
所有用例的數(shù)據(jù)組織在切片
cases中,看起來就像一張表,借助循環(huán)創(chuàng)建子測(cè)試。這樣寫的好處有新增用例非常簡單,只需給 cases新增一條測(cè)試數(shù)據(jù)即可測(cè)試代碼可讀性好,直觀地能夠看到每個(gè)子測(cè)試的參數(shù)和期待的返回值 用例失敗時(shí),報(bào)錯(cuò)信息的格式比較統(tǒng)一,測(cè)試報(bào)告易于閱讀 如果數(shù)據(jù)量較大,或是一些二進(jìn)制數(shù)據(jù),推薦使用相對(duì)路徑從文件中讀取 舉例:prometheus 源碼[1]
2.2 goconvey
goconvey是一個(gè)第三方測(cè)試框架,其最大好處就是對(duì)常規(guī)的if else進(jìn)行了高度封裝
2.2.1 基本使用
準(zhǔn)備待測(cè)代碼student.go
package pkg04
import "fmt"
type Student struct {
Name string
ChiScore int
EngScore int
MathScore int
}
func NewStudent(name string) (*Student, error) {
if name == "" {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("name為空")
}
return &Student{
Name: name,
}, nil
}
func (s *Student) GetAvgScore() (int, error) {
score := s.ChiScore + s.EngScore + s.MathScore
if score == 0 {
return 0, fmt.Errorf("全都是0分")
}
return score / 3, nil
}
參考官方示例,準(zhǔn)備測(cè)試用例student_test.go直觀來講,使用goconvey的好處是不用再寫多個(gè)if判斷
package pkg04
import (
. "github.com/smartystreets/goconvey/convey"
"testing"
)
func TestNewStudent(t *testing.T) {
Convey("start test new", t, func() {
stu, err := NewStudent("")
Convey("空的name初始化錯(cuò)誤", func() {
So(err, ShouldBeError)
})
Convey("stu對(duì)象為nil", func() {
So(stu, ShouldBeNil)
})
})
}
func TestScore(t *testing.T) {
stu, _ := NewStudent("hh")
Convey("不設(shè)置分?jǐn)?shù)可能出錯(cuò)", t, func() {
sc, err := stu.GetAvgScore()
Convey("獲取分?jǐn)?shù)出錯(cuò)了", func() {
So(err, ShouldBeError)
})
Convey("分?jǐn)?shù)為0", func() {
So(sc, ShouldEqual, 0)
})
})
Convey("正常情況", t, func() {
stu.ChiScore = 60
stu.EngScore = 70
stu.MathScore = 80
score, err := stu.GetAvgScore()
Convey("獲取分?jǐn)?shù)出錯(cuò)了", func() {
So(err, ShouldBeNil)
})
Convey("平均分大于60", func() {
So(score, ShouldBeGreaterThan, 60)
})
})
}
執(zhí)行go test -v .
? go test -v .
=== RUN TestNewStudent
start test new
空的name初始化錯(cuò)誤 ?
stu對(duì)象為nil ?
2 total assertions
--- PASS: TestNewStudent (0.00s)
=== RUN TestScore
不設(shè)置分?jǐn)?shù)可能出錯(cuò)
獲取分?jǐn)?shù)出錯(cuò)了 ?
分?jǐn)?shù)為0 ?
4 total assertions
正常情況
獲取分?jǐn)?shù)出錯(cuò)了 ?
平均分大于60 ?
6 total assertions
--- PASS: TestScore (0.00s)
PASS
ok pkg04 0.126s
2.2.2 圖形化使用
確保本地有 goconvey的二進(jìn)制
go get github.com/smartystreets/goconvey
# 會(huì)將對(duì)應(yīng)的二進(jìn)制文件放到 $GOPATH/bin 下面
編輯環(huán)境變量把 GOPATH/bin加入PATH里面 或者寫全路徑到測(cè)試的目錄下,執(zhí)行 goconvey,啟動(dòng)http 8000,自動(dòng)運(yùn)行測(cè)試用例瀏覽器訪問 http://127.0.0.1:8000
最終效果如下
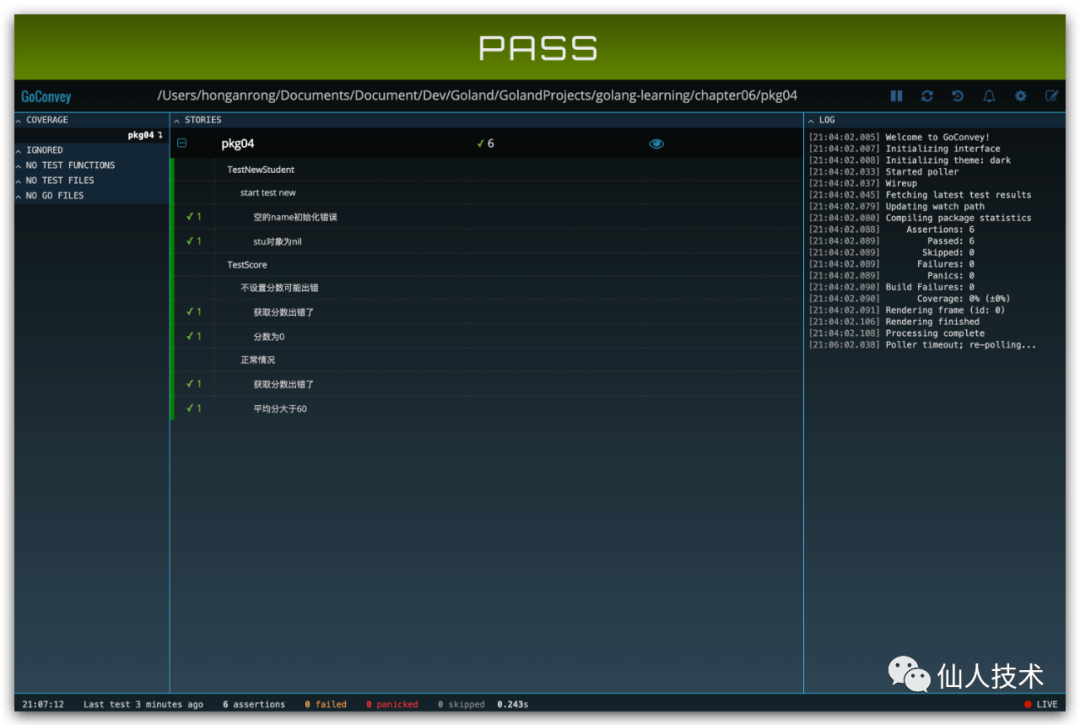
2.3 testify
2.3.1 簡單使用
業(yè)務(wù)代碼cal.go
package pkg05
func Add(x int ) (result int) {
result = x + 2
return result
}
測(cè)試用例cal_test.go
package pkg05
import (
"github.com/stretchr/testify/assert"
"testing"
)
func TestAdd(t *testing.T) {
// assert equality
assert.Equal(t, Add(5), 7, "they should be equal")
}
執(zhí)行測(cè)試
? go test -v .
=== RUN TestAdd
--- PASS: TestAdd (0.00s)
PASS
ok pkg05 1.216s
2.3.2 表驅(qū)動(dòng)測(cè)試
package pkg05
import (
"github.com/stretchr/testify/assert"
"testing"
)
func TestAdd(t *testing.T) {
// assert equality
assert.Equal(t, Add(5), 7, "they should be equal")
}
func TestCal(t *testing.T) {
ass := assert.New(t)
var tests = []struct {
input int
expected int
}{
{2, 4},
{-1, 1},
{0, 2},
{-5, -3},
{999999997, 999999999},
}
for _, test := range tests {
ass.Equal(Add(test.input), test.expected)
}
}
2.3.3 mock 功能
使用 testify/mock隔離第三方依賴或者復(fù)雜調(diào)用testfiy/mock使得偽造對(duì)象的輸入輸出值可以在運(yùn)行時(shí)決定參考:https://github.com/euclidr/testingo
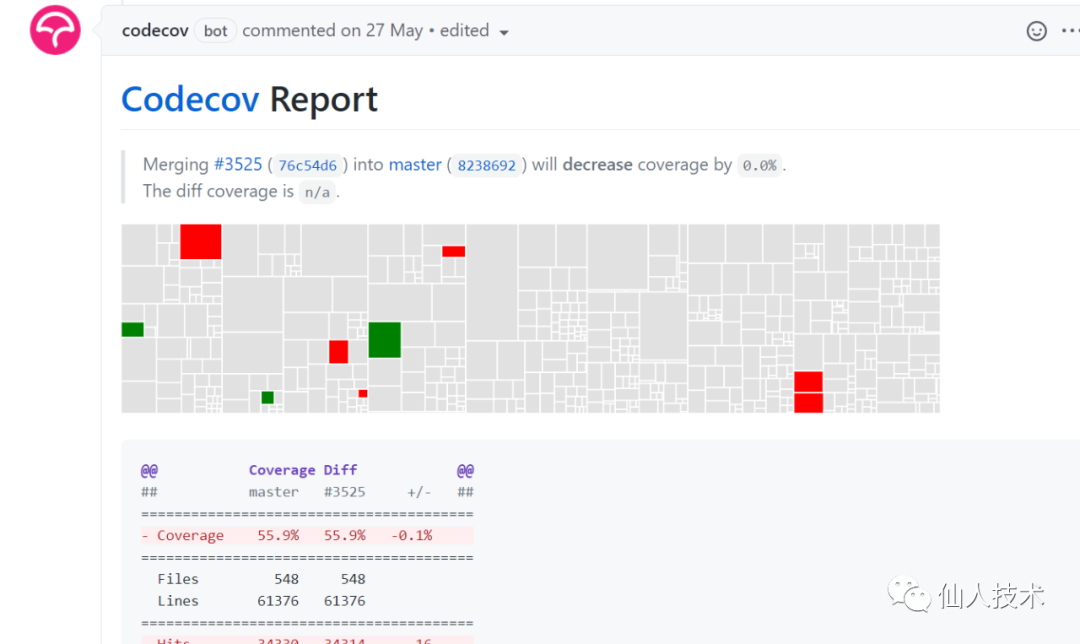
2.3.4 單元測(cè)試覆蓋率應(yīng)用實(shí)例
https://github.com/m3db/m3/pull/3525
參考資料
prometheus 源碼:https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/blob/main/web/api/v1/api_test.go: https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/blob/main/web/api/v1/api_test.go
