@Component,@Service等注解是如何被解析的?
來源:my.oschina.net/floor/blog/4325651
前言
@Component和@Service都是工作中常用的注解,Spring如何解析?
1.@Component解析流程
找入口
Spring Framework2.0開始,引入可擴(kuò)展的XML編程機(jī)制,該機(jī)制要求XML Schema命名空間需要與Handler建立映射關(guān)系。
該關(guān)系配置在相對(duì)于classpath下的/META-INF/spring.handlers中。
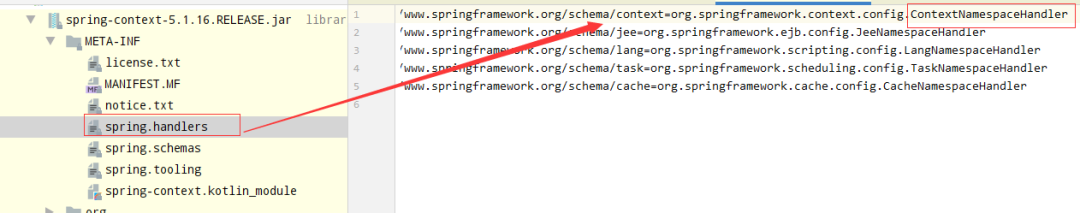
如上圖所示 ContextNamespaceHandler對(duì)應(yīng)context:... 分析的入口。
找核心方法
瀏覽ContextNamespaceHandler
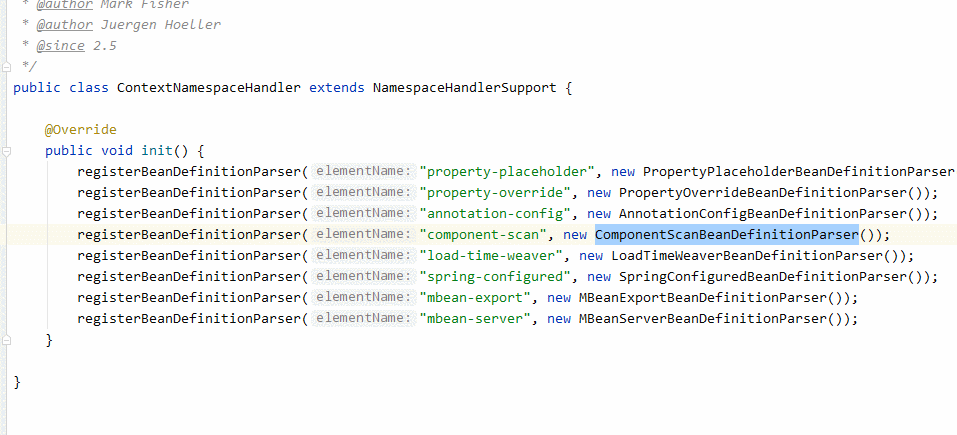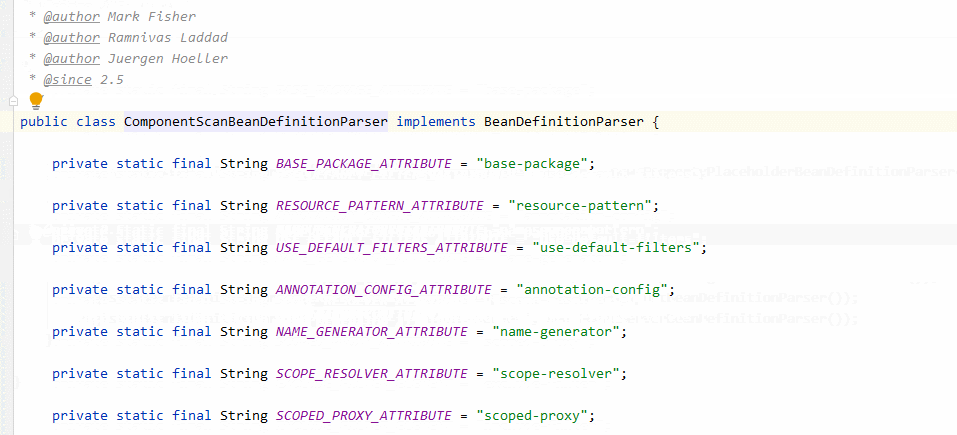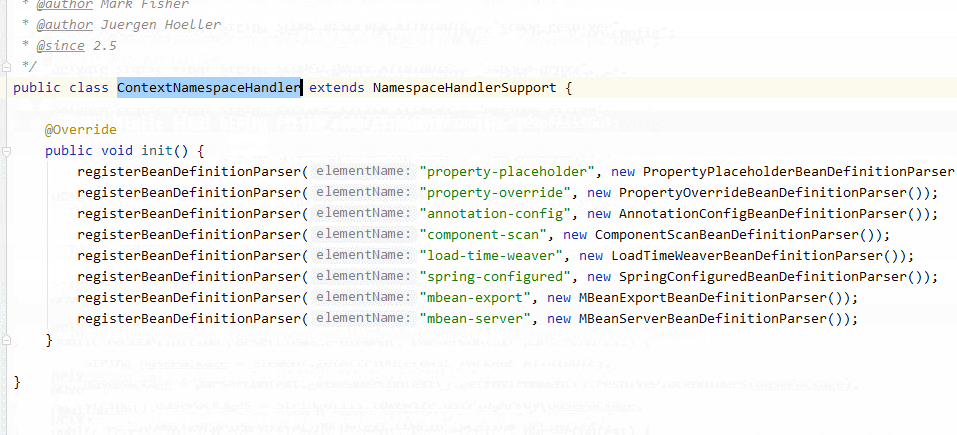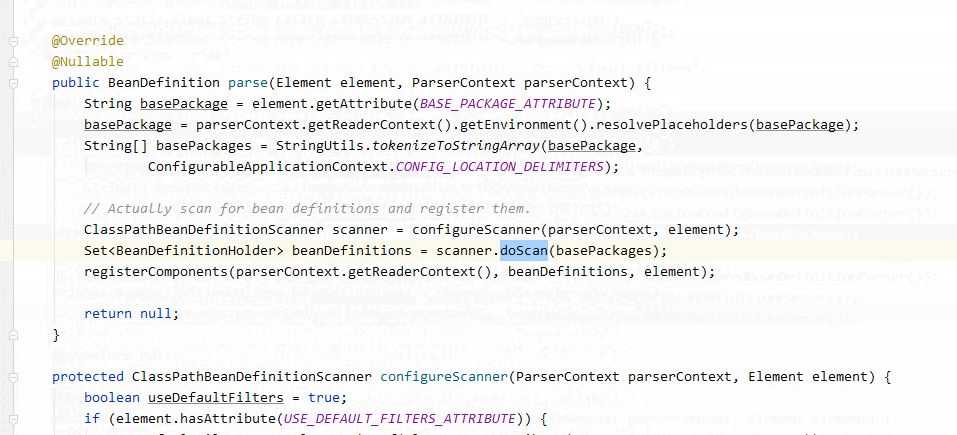
在parse中有一個(gè)很重要的注釋
// Actually scan for bean definitions and register them.
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = configureScanner(parserContext, element);
大意是:ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#doScan是掃描BeanDefinition并注冊(cè)的實(shí)現(xiàn) 。
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 的源碼如下:
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
//findCandidateComponents 讀資源裝換為BeanDefinition
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder =
AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
上邊的代碼,從方法名,猜測(cè):
findCandidateComponents:從classPath掃描組件,并轉(zhuǎn)換為備選BeanDefinition,也就是要做的解析@Component的核心方法。推薦:Java面試練題寶典
概要分析
findCandidateComponents在其父類ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider 中。
public class ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider implements EnvironmentCapable, ResourceLoaderAware {
//省略其他代碼
public Set<BeanDefinition> findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
if (this.componentsIndex != null && indexSupportsIncludeFilters()) {
return addCandidateComponentsFromIndex(this.componentsIndex, basePackage);
}
else {
return scanCandidateComponents(basePackage);
}
}
private Set<BeanDefinition> scanCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>();
try {
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + '/' + this.resourcePattern;
Resource[] resources = getResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath);
//省略部分代碼
for (Resource resource : resources) {
//省略部分代碼
if (resource.isReadable()) {
try {
MetadataReader metadataReader = getMetadataReaderFactory().getMetadataReader(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setSource(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
candidates.add(sbd);
//省略部分代碼
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {//省略部分代碼 }
return candidates;
}
}
findCandidateComponents大體思路如下:
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + '/' + this.resourcePattern;將package轉(zhuǎn)化為ClassLoader類資源搜索路徑packageSearchPath,例如:com.wl.spring.boot轉(zhuǎn)化為classpath*:com/wl/spring/boot/**/*.classResource[] resources = getResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath);加載搜素路徑下的資源。isCandidateComponent判斷是否是備選組件candidates.add(sbd);添加到返回結(jié)果的list
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider#isCandidateComponent其源碼如下:
protected boolean isCandidateComponent(MetadataReader metadataReader) throws IOException {
//省略部分代碼
for (TypeFilter tf : this.includeFilters) {
if (tf.match(metadataReader, getMetadataReaderFactory())) {
return isConditionMatch(metadataReader);
}
}
return false;
}
includeFilters由registerDefaultFilters()設(shè)置初始值,有@Component,沒有@Service啊?
protected void registerDefaultFilters() {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class));
ClassLoader cl = ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.class.getClassLoader();
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.annotation.ManagedBean", cl)), false));
logger.trace("JSR-250 'javax.annotation.ManagedBean' found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-250 1.1 API (as included in Java EE 6) not available - simply skip.
}
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Named", cl)), false));
logger.trace("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Named' annotation found and supported for component scanning");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}
Spring如何處理@Service的注解的呢????
2.查文檔找思路
查閱官方文檔,下面這話:
https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/5.0.17.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/core.html#beans-meta-annotations
@Component is a generic stereotype for any Spring-managed component. @Repository, @Service, and @Controller are specializations of @Component
大意如下:
@Component是任何Spring管理的組件的通用原型。@Repository、@Service和@Controller是派生自@Component。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
// @Service 派生自@Component
@Component
public @interface Service {
/**
* The value may indicate a suggestion for a logical component name,
* to be turned into a Spring bean in case of an autodetected component.
* @return the suggested component name, if any (or empty String otherwise)
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = Component.class)
String value() default "";
}
@Component是@Service的元注解,Spring 大概率,在讀取@Service,也讀取了它的元注解,并將@Service作為@Component處理。
3. 探尋@Component派生性流程
回顧C(jī)lassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider 中的關(guān)鍵的代碼片段如下:
private Set<BeanDefinition> scanCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
//省略其他代碼
MetadataReader metadataReader
=getMetadataReaderFactory().getMetadataReader(resource);
if(isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)){
//....
}
}
public final MetadataReaderFactory getMetadataReaderFactory() {
if (this.metadataReaderFactory == null) {
this.metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory();
}
return this.metadataReaderFactory;
}
1. 確定metadataReader
CachingMetadataReaderFactory繼承自 SimpleMetadataReaderFactory,就是對(duì)SimpleMetadataReaderFactory加了一層緩存。
其內(nèi)部的SimpleMetadataReaderFactory#getMetadataReader 為:
public class SimpleMetadataReaderFactory implements MetadataReaderFactory{
@Override
public MetadataReader getMetadataReader(Resource resource) throws IOException {
return new SimpleMetadataReader(resource, this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader());
}
}
這里可以看出
MetadataReader metadataReader =new SimpleMetadataReader(...);
2.查看match方法找重點(diǎn)方法
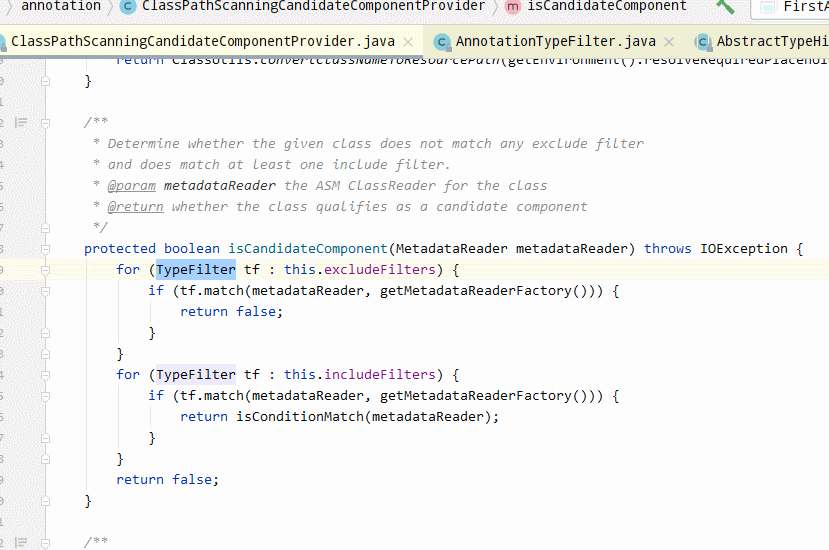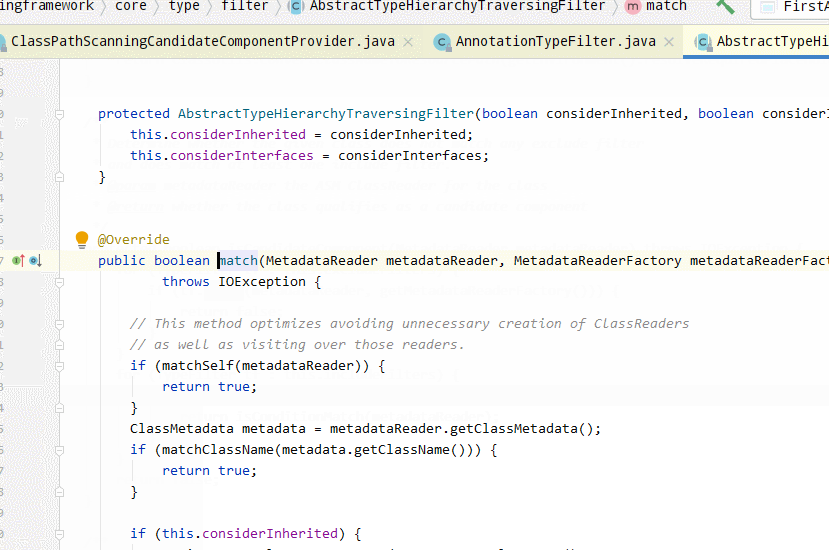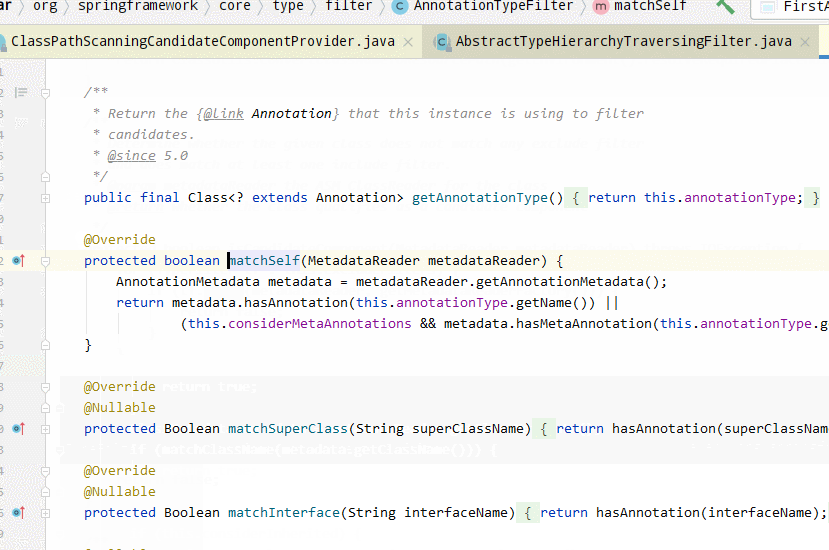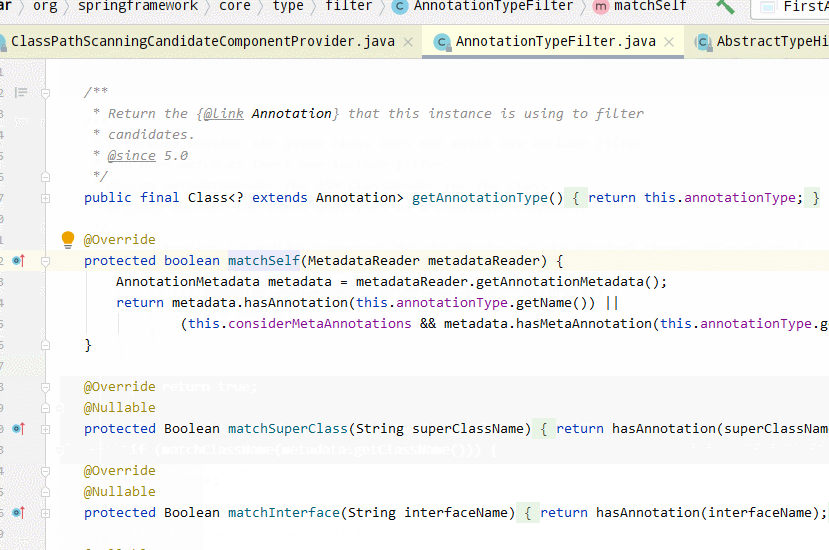
AnnotationTypeFilter#matchself方法如下:
@Override
protected boolean matchSelf(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
AnnotationMetadata metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
return metadata.hasAnnotation(this.annotationType.getName()) ||
(this.considerMetaAnnotations && metadata.hasMetaAnnotation(this.annotationType.getName()));
}
是metadata.hasMetaAnnotation法,從名稱看是處理元注解,我們重點(diǎn)關(guān)注
逐步分析
找metadata.hasMetaAnnotation
metadata=metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
metadataReader =new SimpleMetadataReader(...)
metadata= new SimpleMetadataReader#getAnnotationMetadata()
//SimpleMetadataReader 的構(gòu)造方法
SimpleMetadataReader(Resource resource, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws IOException {
InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(resource.getInputStream());
ClassReader classReader;
try {
classReader = new ClassReader(is);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("ASM ClassReader failed to parse class file - " +
"probably due to a new Java class file version that isn't supported yet: " + resource, ex);
}
finally {
is.close();
}
AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor visitor =
new AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor(classLoader);
classReader.accept(visitor, ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG);
this.annotationMetadata = visitor;
// (since AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor extends ClassMetadataReadingVisitor)
this.classMetadata = visitor;
this.resource = resource;
}
metadata=new SimpleMetadataReader(...).getAnnotationMetadata()= new AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor(。。)
也就是說
metadata.hasMetaAnnotation=AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor#hasMetaAnnotation
其方法如下:
public class AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor{
// 省略部分代碼
@Override
public boolean hasMetaAnnotation(String metaAnnotationType) {
Collection<Set<String>> allMetaTypes = this.metaAnnotationMap.values();
for (Set<String> metaTypes : allMetaTypes) {
if (metaTypes.contains(metaAnnotationType)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
邏輯很簡(jiǎn)單,就是判斷該注解的元注解在,在不在metaAnnotationMap中,如果在就返回true。
這里面核心就是metaAnnotationMap,搜索AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor類,沒有發(fā)現(xiàn)賦值的地方??!。
推薦:Java面試練題寶典
查找metaAnnotationMap賦值
回到SimpleMetadataReader 的方法,
//這個(gè)accept方法,很可疑,在賦值之前執(zhí)行
SimpleMetadataReader(Resource resource, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws IOException {
//省略其他代碼
AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor visitor = new AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor(classLoader);
classReader.accept(visitor, ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG);
this.annotationMetadata = visitor;
}
發(fā)現(xiàn)一個(gè)可疑的語句:classReader.accept。
查看accept方法
public class ClassReader {
//省略其他代碼
public void accept(..省略代碼){
//省略其他代碼
readElementValues(
classVisitor.visitAnnotation(annotationDescriptor, /* visible = */ true),
currentAnnotationOffset,
true,
charBuffer);
}
}
查看readElementValues方法
public class ClassReader{
//省略其他代碼
private int readElementValues(
final AnnotationVisitor annotationVisitor,
final int annotationOffset,
final boolean named,
final char[] charBuffer) {
int currentOffset = annotationOffset;
// Read the num_element_value_pairs field (or num_values field for an array_value).
int numElementValuePairs = readUnsignedShort(currentOffset);
currentOffset += 2;
if (named) {
// Parse the element_value_pairs array.
while (numElementValuePairs-- > 0) {
String elementName = readUTF8(currentOffset, charBuffer);
currentOffset =
readElementValue(annotationVisitor, currentOffset + 2, elementName, charBuffer);
}
} else {
// Parse the array_value array.
while (numElementValuePairs-- > 0) {
currentOffset =
readElementValue(annotationVisitor, currentOffset, /* named = */ null, charBuffer);
}
}
if (annotationVisitor != null) {
annotationVisitor.visitEnd();
}
return currentOffset;
}
}
這里面的核心就是 annotationVisitor.visitEnd();
確定annotationVisitor
這里的annotationVisitor=AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor#visitAnnotation
源碼如下,注意這里傳遞了metaAnnotationMap!!
public class AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor{
@Override
public AnnotationVisitor visitAnnotation(String desc, boolean visible) {
String className = Type.getType(desc).getClassName();
this.annotationSet.add(className);
return new AnnotationAttributesReadingVisitor(
className, this.attributesMap,
this.metaAnnotationMap, this.classLoader);
}
}
annotationVisitor=AnnotationAttributesReadingVisitor
查閱annotationVisitor.visitEnd()
annotationVisitor=AnnotationAttributesReadingVisitor#visitEnd()
public class AnnotationAttributesReadingVisitor{
@Override
public void visitEnd() {
super.visitEnd();
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass = this.attributes.annotationType();
if (annotationClass != null) {
List<AnnotationAttributes> attributeList = this.attributesMap.get(this.annotationType);
if (attributeList == null) {
this.attributesMap.add(this.annotationType, this.attributes);
}
else {
attributeList.add(0, this.attributes);
}
if (!AnnotationUtils.isInJavaLangAnnotationPackage(annotationClass.getName())) {
try {
Annotation[] metaAnnotations = annotationClass.getAnnotations();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(metaAnnotations)) {
Set<Annotation> visited = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (Annotation metaAnnotation : metaAnnotations) {
recursivelyCollectMetaAnnotations(visited, metaAnnotation);
}
if (!visited.isEmpty()) {
Set<String> metaAnnotationTypeNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(visited.size());
for (Annotation ann : visited) {
metaAnnotationTypeNames.add(ann.annotationType().getName());
}
this.metaAnnotationMap.put(annotationClass.getName(), metaAnnotationTypeNames);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to introspect meta-annotations on " + annotationClass + ": " + ex);
}
}
}
}
}
}
內(nèi)部方法recursivelyCollectMetaAnnotations 遞歸的讀取注解,與注解的元注解(讀@Service,再讀元注解@Component),并設(shè)置到metaAnnotationMap,也就是AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor 中的metaAnnotationMap中。
總結(jié)
大致如下:
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider#findCandidateComponents
1.將package轉(zhuǎn)化為ClassLoader類資源搜索路徑packageSearchPath
2.加載搜素路徑下的資源。
3.isCandidateComponent 判斷是否是備選組件。
內(nèi)部調(diào)用的TypeFilter的match方法:
AnnotationTypeFilter#matchself中metadata.hasMetaAnnotation處理元注解metadata.hasMetaAnnotation=AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor#hasMetaAnnotation
就是判斷當(dāng)前注解的元注解在不在metaAnnotationMap中。
AnnotationAttributesReadingVisitor#visitEnd()內(nèi)部方法recursivelyCollectMetaAnnotations 遞歸的讀取注解,與注解的元注解(讀@Service,再讀元注解@Component),并設(shè)置到metaAnnotationMap
4.添加到返回結(jié)果的list
最近給大家找了 零基礎(chǔ)學(xué)小程序
資源,怎么領(lǐng)取?
掃二維碼為,加我微信,回復(fù):零基礎(chǔ)學(xué)小程序
注意,不要亂回復(fù) 沒錯(cuò),不是機(jī)器人 記得一定要等待,等待才有好東西
