Lombok 安裝及使用指南
本文已收錄至:https://cunyu1943.blog.csdn.net/
1簡介
為了減少寫一些 get/set/toString 方法,讓項目代碼更加整潔,提高開發(fā)效率,發(fā)現(xiàn)大家都開始采用 Lombok 這個工具。Lombok 是一個 Java 類庫,它會自動插入編輯器和構(gòu)建工具,用于幫助開發(fā)人員消除 Java 中冗長樣板代碼。而我們開發(fā)人員所要做的,僅僅是添加幾個 Lombok 中的注解,就可以替換掉原來的多行 get/set/toString 方法代碼,既簡潔也易于維護(hù)。下面我們就來看看,如何安裝并使用這一工具。
2安裝 Lombok
日常開發(fā)中,相信大多數(shù)人現(xiàn)在使用的都是 IDEA 這個 Java 神器了,如果你還在使用 Eclipse 或者 MyEclipse 等工具,那強(qiáng)烈推薦你去體驗一把 IDEA,相信你一用上它就會愛上他它的強(qiáng)大!下面我就以在 IDEA 中使用 Lombok 為例,看看如何安裝并使用它。
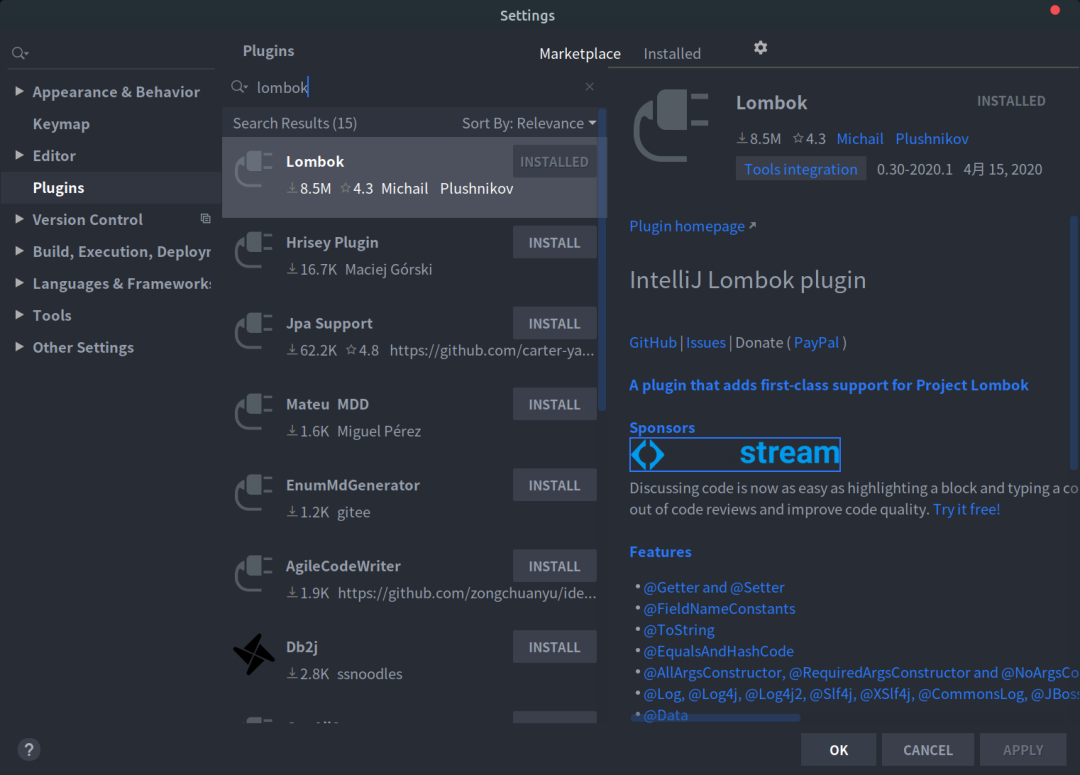
在先前 IDEA 的版本中,Lombok 是需要通過插件來安裝的,安裝方法如下:依次進(jìn)入File -> Settings -> Plugins,然后搜索 Lombok ,最后進(jìn)行安裝即可。而在新版本的 IDEA 中,Lombok 已經(jīng)被集成到 IDEA 中,我們不用再去安裝它就可以直接使用,可以說是十分方便了。
老版本 IDEA 安裝 Lombok
新版本中集成了 Lombok
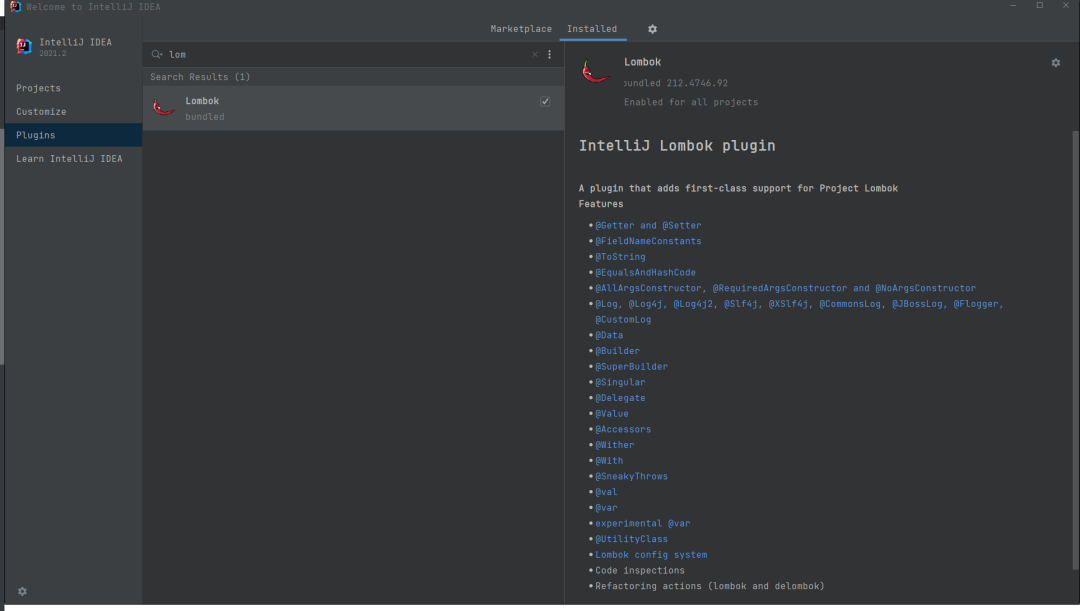
以上就是 Lombok 的安裝過程了,是不是十分簡單?那接下來我們就來看看,如何在我們的項目中使用 Lombok!
3Lombok 使用
現(xiàn)在大家進(jìn)行項目管理時用的工具大多應(yīng)該都是 Maven,所以我們直接在需要使用 Lombok 的項目中加入 Lombok 編譯支持,也就是在 pom.xml 文件中加入以下依賴。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
導(dǎo)入相關(guān)依賴之后,接下來就是具體使用過程了。
具體使用
在需要的實體類中引入相關(guān)注解即可,只不過注解不同它們所對應(yīng)的功能也不同,而且同一個注解可能在不同位置的功能也不一樣。如下圖;
常用注解
@Data
注解在 類 上:給類的所有屬性提供 get 和 set 方法,此外還有 equals、canEqual、hashCode、toString 方法以及 默認(rèn)參數(shù)為空的構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public Long getId() {
return this.id;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public String getEmail() {
return this.email;
}
public void setId(final Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(final String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(final Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setEmail(final String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public boolean equals(final Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof User)) {
return false;
} else {
User other = (User)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
} else {
label59: {
Object this$id = this.getId();
Object other$id = other.getId();
if (this$id == null) {
if (other$id == null) {
break label59;
}
} else if (this$id.equals(other$id)) {
break label59;
}
return false;
}
Object this$age = this.getAge();
Object other$age = other.getAge();
if (this$age == null) {
if (other$age != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$age.equals(other$age)) {
return false;
}
Object this$name = this.getName();
Object other$name = other.getName();
if (this$name == null) {
if (other$name != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$name.equals(other$name)) {
return false;
}
Object this$email = this.getEmail();
Object other$email = other.getEmail();
if (this$email == null) {
if (other$email != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$email.equals(other$email)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
protected boolean canEqual(final Object other) {
return other instanceof User;
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
Object $id = this.getId();
int result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode());
Object $age = this.getAge();
result = result * 59 + ($age == null ? 43 : $age.hashCode());
Object $name = this.getName();
result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode());
Object $email = this.getEmail();
result = result * 59 + ($email == null ? 43 : $email.hashCode());
return result;
}
public String toString() {
Long var10000 = this.getId();
return "User(id=" + var10000 + ", name=" + this.getName() + ", age=" + this.getAge() + ", email=" + this.getEmail() + ")";
}
}
使用后
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : zhangliang
* @version : 1.0
* @project : User
* @package : com.cunyu.user.entity
* @className : User
* @createTime : 2021/8/6 17:14
* @description : 用戶實體類
*/
@Data
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
@Setter
注解在 類 上:為該類所有屬性均提供 set 方法,同時提供 默認(rèn)構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public void setId(final Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(final String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(final Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setEmail(final String email) {
this.email = email;
}
}
使用后
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
import lombok.Setter;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : zhangliang
* @version : 1.0
* @project : User
* @package : com.cunyu.user.entity
* @className : User
* @createTime : 2021/8/6 17:14
* @description : 用戶實體類
*/
@Setter
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
注解在 屬性 上:為該屬性提供 set 方法,同時提供 默認(rèn)構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public void setId(final Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
使用后
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
import lombok.Setter;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : zhangliang
* @version : 1.0
* @project : User
* @package : com.cunyu.user.entity
* @className : User
* @createTime : 2021/8/6 17:14
* @description : 用戶實體類
*/
public class User {
@Setter
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
@Getter
注解在 類 上:為該類所有屬性均提供 get 方法,同時提供 默認(rèn)構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public Long getId() {
return this.id;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public String getEmail() {
return this.email;
}
}
使用后
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
import lombok.Getter;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : zhangliang
* @version : 1.0
* @project : User
* @package : com.cunyu.user.entity
* @className : User
* @createTime : 2021/8/6 17:14
* @description : 用戶實體類
*/
@Getter
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
注解在 屬性 上:為該屬性提供 get 方法,同時提供 默認(rèn)構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public Long getId() {
return this.id;
}
}
使用后
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
import lombok.Getter;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : zhangliang
* @version : 1.0
* @project : User
* @package : com.cunyu.user.entity
* @className : User
* @createTime : 2021/8/6 17:14
* @description : 用戶實體類
*/
public class User {
@Getter
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
@ToString
注解在 類 上:生成所有參數(shù)的 toString() 方法,同時提供 默認(rèn)構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public String toString() {
return "User(id=" + this.id + ", name=" + this.name + ", age=" + this.age + ", email=" + this.email + ")";
}
}
使用后
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
import lombok.ToString;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : zhangliang
* @version : 1.0
* @project : User
* @package : com.cunyu.user.entity
* @className : User
* @createTime : 2021/8/6 17:14
* @description : 用戶實體類
*/
@ToString
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
@Value
注解在 類 上:生成 get 方法,以及 equals、hashCode、toString 方法,同時提供 含所有參數(shù)的構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
public final class User {
private final Long id;
private final String name;
private final Integer age;
private final String email;
public User(final Long id, final String name, final Integer age, final String email) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.email = email;
}
public Long getId() {
return this.id;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public String getEmail() {
return this.email;
}
public boolean equals(final Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof User)) {
return false;
} else {
User other;
label56: {
other = (User)o;
Object this$id = this.getId();
Object other$id = other.getId();
if (this$id == null) {
if (other$id == null) {
break label56;
}
} else if (this$id.equals(other$id)) {
break label56;
}
return false;
}
label49: {
Object this$age = this.getAge();
Object other$age = other.getAge();
if (this$age == null) {
if (other$age == null) {
break label49;
}
} else if (this$age.equals(other$age)) {
break label49;
}
return false;
}
Object this$name = this.getName();
Object other$name = other.getName();
if (this$name == null) {
if (other$name != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$name.equals(other$name)) {
return false;
}
Object this$email = this.getEmail();
Object other$email = other.getEmail();
if (this$email == null) {
if (other$email != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$email.equals(other$email)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
Object $id = this.getId();
int result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode());
Object $age = this.getAge();
result = result * 59 + ($age == null ? 43 : $age.hashCode());
Object $name = this.getName();
result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode());
Object $email = this.getEmail();
result = result * 59 + ($email == null ? 43 : $email.hashCode());
return result;
}
public String toString() {
Long var10000 = this.getId();
return "User(id=" + var10000 + ", name=" + this.getName() + ", age=" + this.getAge() + ", email=" + this.getEmail() + ")";
}
}
使用后
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
import lombok.Value;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : zhangliang
* @version : 1.0
* @project : User
* @package : com.cunyu.user.entity
* @className : User
* @createTime : 2021/8/6 17:14
* @description : 用戶實體類
*/
@Value
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
@AllArgsConstructor
注解在 類 上:為類提供一個 全參構(gòu)造方法,但此時不再提供默認(rèn)構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
public User(final Long id, final String name, final Integer age, final String email) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.email = email;
}
}
使用后
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : zhangliang
* @version : 1.0
* @project : User
* @package : com.cunyu.user.entity
* @className : User
* @createTime : 2021/8/6 17:14
* @description : 用戶實體類
*/
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
@NoArgsConstructor
注解在 類 上:為類提供一個 無參構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
public User() {
}
}
使用后
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : zhangliang
* @version : 1.0
* @project : User
* @package : com.cunyu.user.entity
* @className : User
* @createTime : 2021/8/6 17:14
* @description : 用戶實體類
*/
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
@RequiredArgsConstructor
注解在 類 上:使用類中所有帶 @NonNull 注解的或帶有 final 修飾的成員變量生成對應(yīng)構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
import lombok.NonNull;
public class User {
@NonNull
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
@NonNull
private String email;
public User(@NonNull final Long id, @NonNull final String email) {
if (id == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("id is marked non-null but is null");
} else if (email == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("email is marked non-null but is null");
} else {
this.id = id;
this.email = email;
}
}
}
使用后
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : zhangliang
* @version : 1.0
* @project : User
* @package : com.cunyu.user.entity
* @className : User
* @createTime : 2021/8/6 17:14
* @description : 用戶實體類
*/
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class User {
@NonNull
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
@NonNull
private String email;
}
@NonNull
注解在 屬性 上,自動生成一個關(guān)于該參數(shù)的非空檢查,若參數(shù)為 null,則拋出一個空指針異常,同時提供 默認(rèn)構(gòu)造方法,具體用法可以參照上面的例子;
@EqualsAndHashCode
注解在 類 上,生成 equals、canEquals、hasnCode 方法,同時會生成默認(rèn)構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
public User() {
}
public boolean equals(final Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof User)) {
return false;
} else {
User other = (User)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
} else {
label59: {
Object this$id = this.id;
Object other$id = other.id;
if (this$id == null) {
if (other$id == null) {
break label59;
}
} else if (this$id.equals(other$id)) {
break label59;
}
return false;
}
Object this$age = this.age;
Object other$age = other.age;
if (this$age == null) {
if (other$age != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$age.equals(other$age)) {
return false;
}
Object this$name = this.name;
Object other$name = other.name;
if (this$name == null) {
if (other$name != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$name.equals(other$name)) {
return false;
}
Object this$email = this.email;
Object other$email = other.email;
if (this$email == null) {
if (other$email != null) {
return false;
}
} else if (!this$email.equals(other$email)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
protected boolean canEqual(final Object other) {
return other instanceof User;
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
Object $id = this.id;
int result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode());
Object $age = this.age;
result = result * 59 + ($age == null ? 43 : $age.hashCode());
Object $name = this.name;
result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode());
Object $email = this.email;
result = result * 59 + ($email == null ? 43 : $email.hashCode());
return result;
}
}
使用后
package com.cunyu.user.entity;
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : zhangliang
* @version : 1.0
* @project : User
* @package : com.cunyu.user.entity
* @className : User
* @createTime : 2021/8/6 17:14
* @description : 用戶實體類
*/
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
@Cleanup
注解在 局部變量 前,保證該變量代表的資源使用后自動關(guān)閉,默認(rèn)調(diào)用資源的 close() 方法,若該資源有其它關(guān)閉方法,可用 @Cleanup("方法名") 來指定要調(diào)用的方法,同時提供 默認(rèn)構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
import java.io.*;
public class CleanupExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(args[0]);
try {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(args[1]);
try {
byte[] b = new byte[10000];
while (true) {
int r = in.read(b);
if (r == -1) break;
out.write(b, 0, r);
}
} finally {
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
} finally {
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
}
}
}
使用后
import lombok.Cleanup;
import java.io.*;
public class CleanupExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
@Cleanup InputStream in = new FileInputStream(args[0]);
@Cleanup OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(args[1]);
byte[] b = new byte[10000];
while (true) {
int r = in.read(b);
if (r == -1) break;
out.write(b, 0, r);
}
}
}
@Synchronized
注解在 類方法 或 實例方法:效果與 synchronized 關(guān)鍵字相同,區(qū)別在于鎖對象不同,對于類方法和實例方法,synchronized 關(guān)鍵字的鎖對象分別是 類的 class 對象和 this 對象,而 @Synchronized 的鎖對象分別是 私有靜態(tài) final 對象 lock 和 私有 final 對象 lock,也可以自己指定鎖對象,同時提供默認(rèn)構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
public class SynchronizedExample {
private static final Object $LOCK = new Object[0];
private final Object $lock = new Object[0];
private final Object readLock = new Object();
public static void hello() {
synchronized($LOCK) {
System.out.println("world");
}
}
public int answerToLife() {
synchronized($lock) {
return 42;
}
}
public void foo() {
synchronized(readLock) {
System.out.println("bar");
}
}
}
使用后
import lombok.Synchronized;
public class SynchronizedExample {
private final Object readLock = new Object();
@Synchronized
public static void hello() {
System.out.println("world");
}
@Synchronized
public int answerToLife() {
return 42;
}
@Synchronized("readLock")
public void foo() {
System.out.println("bar");
}
}
@SneakyThrows
注解在 方法 上:將方法中的代碼用 try-catch 語句包裹,捕獲異常并在 catch 中用 Lombok.sneakyThrow(e) 將異常拋出,還可以用 @SneakyThrows(Exception.class) 的形式指定拋出異常類型,同時提供 默認(rèn)構(gòu)造方法;
使用前
import lombok.Lombok;
public class SneakyThrowsExample implements Runnable {
public String utf8ToString(byte[] bytes) {
try {
return new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw Lombok.sneakyThrow(e);
}
}
public void run() {
try {
throw new Throwable();
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw Lombok.sneakyThrow(t);
}
}
}
使用后
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
public class SneakyThrowsExample implements Runnable {
@SneakyThrows(UnsupportedEncodingException.class)
public String utf8ToString(byte[] bytes) {
return new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
}
@SneakyThrows
public void run() {
throw new Throwable();
}
}
@Log
注解在 類 上:主要用于我們記錄日志信息,同時提供 默認(rèn)構(gòu)造方法。它封裝了多個主流 Log 庫,主要有如下幾個;
@Log@Slf4jLog4jLog4j2
4總結(jié)
以上就是關(guān)于 Lombok 的相關(guān)使用小技巧了,如果你還沒有使用過它,那就趕緊去試試吧!
最后,創(chuàng)作不易,如果你覺得我的文章對你有所幫助,那就來個一鍵三連吧!
5參考資料
https://projectlombok.org/features/all
