Java中的值傳遞和引用傳遞,看完這篇終于終于明白了!

當(dāng)一個(gè)對(duì)象被當(dāng)作參數(shù)傳遞到一個(gè)方法后,此方法可改變這個(gè)對(duì)象的屬性,并可返回變化后的結(jié)果,那么這里到底是值傳遞還是引用傳遞??
答:是值傳遞。Java 編程語(yǔ)言只有值傳遞參數(shù)。當(dāng)一個(gè)對(duì)象實(shí)例作為一個(gè)參數(shù)被傳遞到方法中時(shí),參數(shù)的值就是該對(duì)象的引用一個(gè)副本。指向同一個(gè)對(duì)象,對(duì)象的內(nèi)容可以在被調(diào)用的方法中改變,但對(duì)象的引用(不是引用的副本)是永遠(yuǎn)不會(huì)改變的。
? ? ??
Java參數(shù),不管是原始類型還是引用類型,傳遞的都是副本(有另外一種說(shuō)法是傳值,但是說(shuō)傳副本更好理解吧,傳值通常是相對(duì)傳址而言)。
? ? ??
如果參數(shù)類型是原始類型,那么傳過(guò)來(lái)的就是這個(gè)參數(shù)的一個(gè)副本,也就是這個(gè)原始參數(shù)的值,這個(gè)跟之前所談的傳值是一樣的。如果在函數(shù)中改變了副本的值不會(huì)改變?cè)嫉闹?。
? ? ??
如果參數(shù)類型是引用類型,那么傳過(guò)來(lái)的就是這個(gè)引用參數(shù)的副本,這個(gè)副本存放的是參數(shù)的地址。如果在函數(shù)中沒(méi)有改變這個(gè)副本的地址,而是改變了地址中的值,那么在函數(shù)內(nèi)的改變會(huì)影響到傳入的參數(shù)。如果在函數(shù)中改變了副本的地址,如new一個(gè),那么副本就指向了一個(gè)新的地址,此時(shí)傳入的參數(shù)還是指向原來(lái)的 地址,所以不會(huì)改變參數(shù)的值。
package?com.demo.test;
public?class?Employee?{
????
????private?String name;
????private?double?salary;
????
????public?Employee(String name,double?salary){
????????this.name = name;
????????this.salary = salary;
????}
????public?String getName()?{
????????return?name;
????}
????public?void?setName(String name)?{
????????this.name = name;
????}
????public?double?getSalary()?{
????????return?salary;
????}
????public?void?setSalary(double?salary)?{
????????this.salary = salary;
????}
}package com.demo.test;
public?class?ParamTest?{
????public?static?void?main(String[] args) {
????????/**
?????????* Test 1: Methods can't modify numeric parameters
?????????*/
????????System.out.println("Testing tripleValue:");
????????double?percent = 10;
????????System.out.println("Before: percent="?+ percent);
????????tripleValue(percent);
????????System.out.println("After: percent="?+ percent);
????????/**
?????????* Test 2: Methods can change the state of object parameters
?????????*/
????????System.out.println("\nTesting tripleSalary:");
????????Employee harry = new?Employee("Harry", 50000);
????????System.out.println("Before: salary="?+ harry.getSalary());
????????tripleSalary(harry);
????????System.out.println("After: salary="?+ harry.getSalary());
????????/**
?????????* Test 3: Methods can't attach new objects to object parameters
?????????*/
????????System.out.println("\nTesting swap:");
????????Employee a = new?Employee("Alice", 70000);
????????Employee b = new?Employee("Bob", 60000);
????????System.out.println("Before: a="?+ a.getName());
????????System.out.println("Before: b="?+ b.getName());
????????swap(a, b);
????????System.out.println("After: a="?+ a.getName());
????????System.out.println("After: b="?+ b.getName());
????}
????private?static?void?swap(Employee x, Employee y) {
????????Employee temp = x;
????????x = y;
????????y = temp;
????????System.out.println("End of method: x="?+ x.getName());
????????System.out.println("End of method: y="?+ y.getName());
????}
????private?static?void?tripleSalary(Employee x) {
????????x.setSalary(x.getSalary()*3);
????????System.out.println("End of method: salary="?+ x.getSalary());
????}
????private?static?void?tripleValue(double?x) {
????????x = 3?* x;
????????System.out.println("End of Method X= "?+ x);
????}
}運(yùn)行結(jié)果:
Testing tripleValue:
Before: percent=10.0
End?of?Method X= 30.0
After: percent=10.0
Testing tripleSalary:
Before: salary=50000.0
End?of?method: salary=150000.0
After: salary=150000.0
Testing swap:
Before: a=Alice
Before: b=Bob
End?of?method: x=Bob //可見(jiàn)引用的副本進(jìn)行了交換
End?of?method: y=Alice
After: a=Alice //引用本身沒(méi)有交換
After: b=Bob首先要說(shuō)明的是java中是沒(méi)有指針的,java中只存在值傳遞,只存在值傳遞!!! ?然而我們經(jīng)常看到對(duì)于對(duì)象(數(shù)組,類,接口)的傳遞似乎有點(diǎn)像引用傳遞,可以改變對(duì)象中某個(gè)屬性的值。但是不要被這個(gè)假象所蒙蔽,實(shí)際上這個(gè)傳入函數(shù)的值是對(duì)象引用的拷貝,即傳遞的是引用的地址值,所以還是按值傳遞。
示例1:
public?class?Test?{
????public?static?void?change(int?a){
????????a=50;
????}
????public?static?void?main(String[] args) {
????????int?a=10;
????????System.out.println(a);
????????change(a);
????????System.out.println(a);
????}
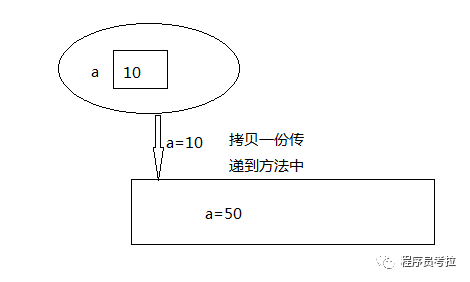
}很顯然輸出的 是10,10。傳遞的是值的一份拷貝,這份拷貝與原來(lái)的值沒(méi)什么關(guān)系。
內(nèi)存分析:
示例2:
public?class?Test?{
????public?static?void?change(int?[]a){
????????a[0]=50;
????}
????public?static?void?main(String[] args) {
????????int?[]a={10,20};
????????System.out.println(a[0]);
????????change(a);
????????System.out.println(a[0]);
????}
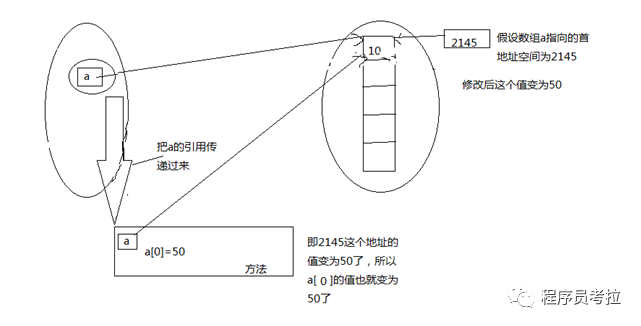
}顯然輸出結(jié)果為10 ? 50。實(shí)際傳遞的是引用的地址值。
內(nèi)存分析:
示例3:
class?Emp?{
????public?int?age;
}
public?class?Test?{
????public?static?void?change(Emp emp)
????{
????????emp.age = 50;
????????emp = new?Emp();//再創(chuàng)建一個(gè)對(duì)象
????????emp.age=100;
????}
????
????public?static?void?main(String[] args) {
????????Emp emp = new?Emp();
????????emp.age = 100;
????????System.out.println(emp.age);
????????change(emp);
????????System.out.println(emp.age);
????????System.out.println(emp.age);
????}
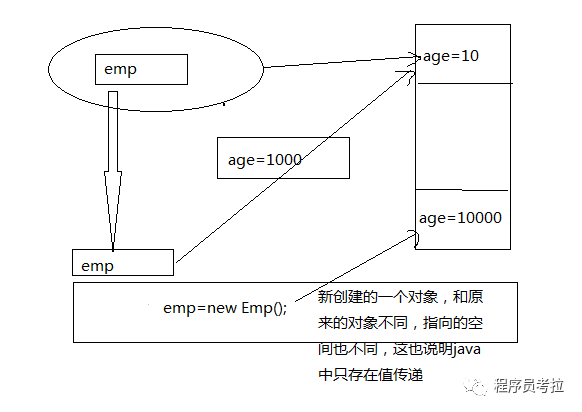
}輸出為:100 ?50 ?50.
內(nèi)存分析:
對(duì)于String類:
public?class?Test?{
????public?static?void?change(String s){
????????s="zhangsan";
????}
????
????public?static?void?main(String[] args) {
????????String s=new?String("lisi");
????????System.out.println(s);
????????change(s);
????????System.out.println(s);
????}
}輸出為:lisi ? lisi,由于String類是final修飾的,不可變,它會(huì)在內(nèi)存中在開(kāi)辟一塊新空間。
原文鏈接:cnblogs.com/xiaoxi/p/7400633.html
