SpringBoot整合Mybatis原理分析
點擊上方藍色字體,選擇“標星公眾號”
優(yōu)質(zhì)文章,第一時間送達
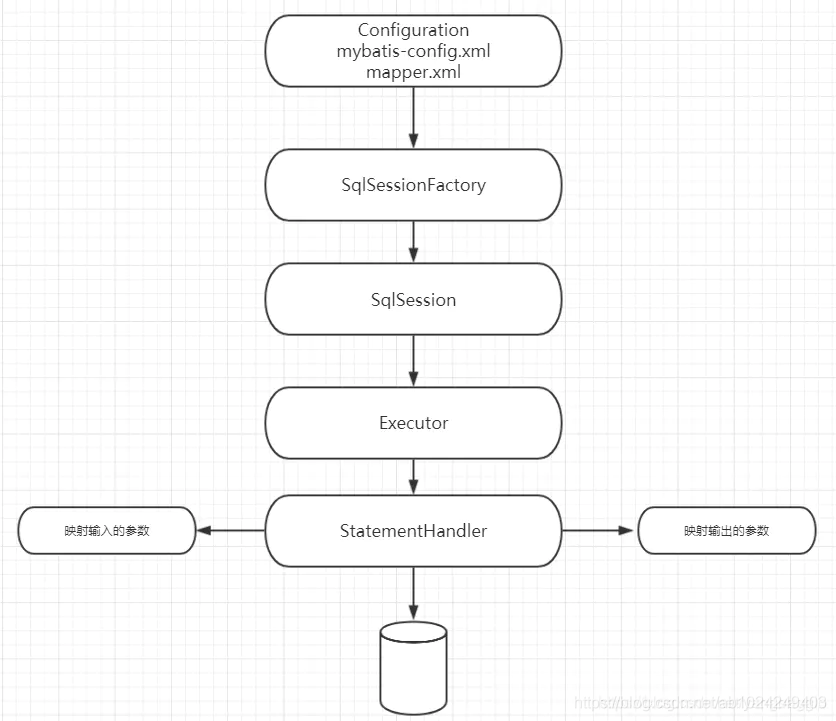
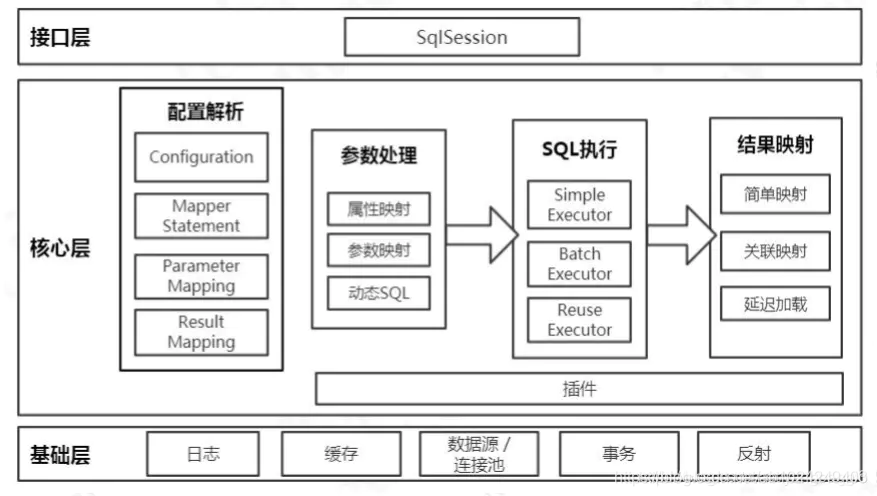
Mybatis核心概念
Configuration 管理mysql-config.xml全局配置關(guān)系類
SqlSessionFactorySession管理工廠接口
Session SqlSession是一個面向用戶(程序員)的接口。SqlSession中提供了很多操作數(shù)據(jù)庫的方法
Executor 執(zhí)行器是一個接口(基本執(zhí)行器、緩存執(zhí)行器)作用:SqlSession 內(nèi)部通過執(zhí)行器操作數(shù)據(jù)庫
MappedStatement 底層封裝對象作用:對操作數(shù)據(jù)庫存儲封裝,包括 sql 語句、輸入輸出參數(shù)
StatementHandler 具體操作數(shù)據(jù)庫相關(guān)的 handler 接口
Mybatis編程式用例
public void testSelect() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // ExecutorType.BATCH
try {
BlogMapper mapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
Blog blog = mapper.selectBlogById(1);
System.out.println(blog);
} finally {
session.close();
}
}
配置掃描解析過程
1、springboot使用自動裝配原理注入SqlSessionFactory,對應(yīng)方法路徑為org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisAutoConfiguration#sqlSessionFactory。如果使用的是mybatis-config.xml進行配置,那么在上述方法中會使用XMLConfigBuilder對mybatis-config.xml文件進行解析,并且會把mybatis-config.xml文件中配置的一個個mapper bean生成相應(yīng)的mapperProxyFactory并且放入mapperRegistry中.MapperRegistry里面維護的其實是一個Map容器,存儲接口和代理工廠的映射關(guān)系。
2、
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(MapperScannerRegistrar.class)
@Repeatable(MapperScans.class)
public @interface MapperScan
@MapperScan是一個復(fù)合注解,其中@Import注解便是起到了掃描注冊第三方組件到springIOC的作用。MapperScannerRegistrar類實現(xiàn)了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,實現(xiàn)了registerBeanDefinitions方法,主要功能用于動態(tài)的注冊某一些具有相同特征的一批類到Spring IoC
3.
@Override
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> "No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages) + "' package. Please check your configuration.");
} else {
processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
}
super.doScan()方法掃描@MapperScan注解中對應(yīng)的Mapper路徑,把該路徑下所有符合候選條件的接口mapper放入ioc容器中。
processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);該方法在doScan()之后進行調(diào)用,將容器中mapper bean的真正類型修改為MapperFactoryBean類型。
private void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) {
GenericBeanDefinition definition;
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {
definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();
String beanClassName = definition.getBeanClassName();
// the mapper interface is the original class of the bean
// but, the actual class of the bean is MapperFactoryBean
definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(beanClassName); // 構(gòu)造函數(shù)傳參,傳入初始mapper類型
definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);
}
獲得Mapper對象
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T>
1、SqlSessionDaoSupport內(nèi)部持有SqlSession的實現(xiàn)類SqlSessionTemplate;
2、SqlSessionDaoSupport類重寫了checkDaoConfig()方法,這個方法主要用于非mybatis-config.xml方式來注冊mapper的情況,這個方法會確保把所有的mapper bean生成相應(yīng)的mapperProxyFactory并且放入mapperRegistry中。調(diào)用時機:在Bean的屬性值設(shè)置完成時被調(diào)用(InitializingBean接口)
3、上述說到所有的mapper接口在放入spring容器之后,真正的bean類型被修改為MapperFactoryBean,而MapperFactoryBean實現(xiàn)了FactoryBean接口,所以程序中從ioc容器在獲取對應(yīng)的Mapper實例的話,走的是getObject()方法,最終調(diào)用的又是org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperRegistry#getMapper方法;
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
4、可以看到獲取Mapper的代理對象,實際上是從map中獲取對應(yīng)的工廠類后,最終通過JDK動態(tài)代理創(chuàng)建的。實質(zhì)上是獲取了一個MapperProxy的代理對象,MapperProxy中有SqlSession、mapperInterface、methodCache。
執(zhí)行sql
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
1、由于所有的Mapper都是MapperProxy的代理對象,所以任意的方法都是執(zhí)行MapperProxy的invoke()方法。
2、通過Executor、MappedStatement、SqlSession進行sql語句處理,參數(shù)填充等等,最終還是通過JDBC包中的PreparedStatement、ResultSet進行最終的調(diào)用和結(jié)果集處理;
————————————————
版權(quán)聲明:本文為CSDN博主「澎仔」的原創(chuàng)文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版權(quán)協(xié)議,轉(zhuǎn)載請附上原文出處鏈接及本聲明。
原文鏈接:
https://blog.csdn.net/ab1024249403/article/details/113931500
粉絲福利:Java從入門到入土學(xué)習(xí)路線圖
??????

??長按上方微信二維碼 2 秒
感謝點贊支持下哈 
