Nacos2.0配置灰度發(fā)布原理源碼解析
本文作者:寧與(包冬慶),目前在【阿里云云原生中間件】團(tuán)隊(duì)實(shí)習(xí)
今天分享的是我們組的一個(gè)實(shí)習(xí)生寫(xiě)的一篇源碼解析文章,小伙子實(shí)習(xí)期間在社區(qū)Nacos2.0的基礎(chǔ)上對(duì)灰度發(fā)布的能力進(jìn)行了增強(qiáng),并完成了MSE Nacos2.0上從管控到內(nèi)核的灰度發(fā)布能力的研發(fā)。以下是他對(duì)配置發(fā)布流程的代碼解析,相信看完之后你會(huì)感嘆:現(xiàn)在的實(shí)習(xí)生都有這個(gè)水平了嗎?
說(shuō)到灰度發(fā)布,就不得不提到阿里的安全生產(chǎn)三板斧:可監(jiān)控、可灰度、可回滾。在阿里內(nèi)部,對(duì)于安全生產(chǎn)是高度重視的,灰度可以說(shuō)是發(fā)布之前的必備流程。因此,作為阿里的配置中心,Nacos同樣支持了配置灰度的功能,可以通過(guò)控制臺(tái)進(jìn)行配置的灰度推送、回滾,從而實(shí)現(xiàn)安全的配置發(fā)布。一般來(lái)說(shuō),我們按照下圖所示流程進(jìn)行配置的安全修改。只有在小規(guī)模機(jī)器上驗(yàn)證配置按預(yù)期生效之后才會(huì)正式發(fā)布配置,否則就回滾灰度配置。
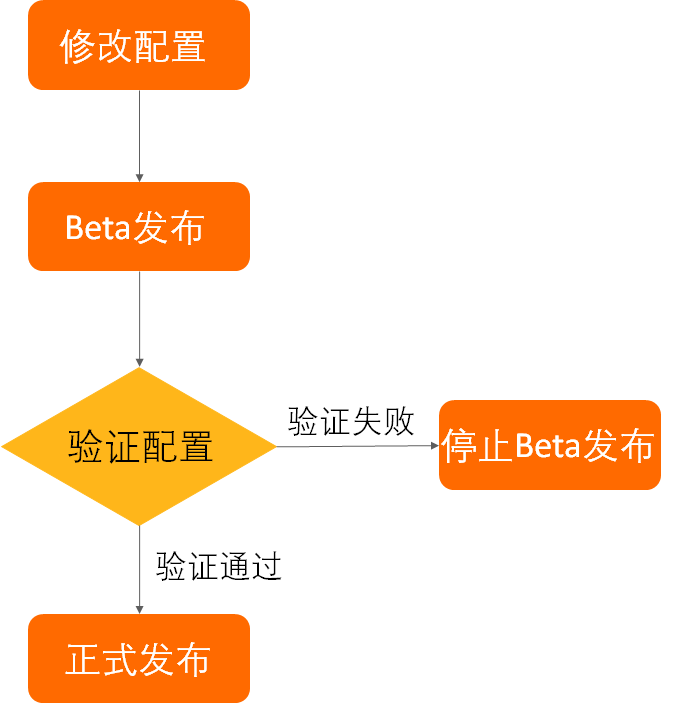
配置灰度發(fā)布流程
社區(qū)Nacos的灰度是基于IP的方式進(jìn)行的,用戶(hù)需要在控制臺(tái),選擇需要灰度的配置,然后新建灰度配置,選擇灰度機(jī)器的IP進(jìn)行配置推送。整個(gè)交互流程如下圖所示。
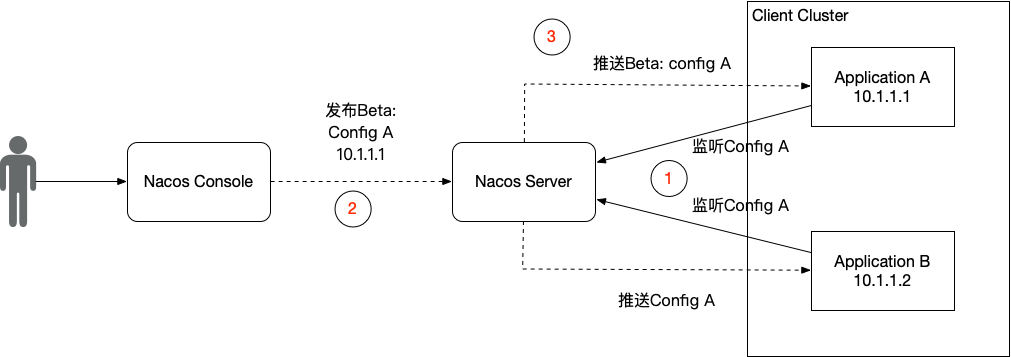
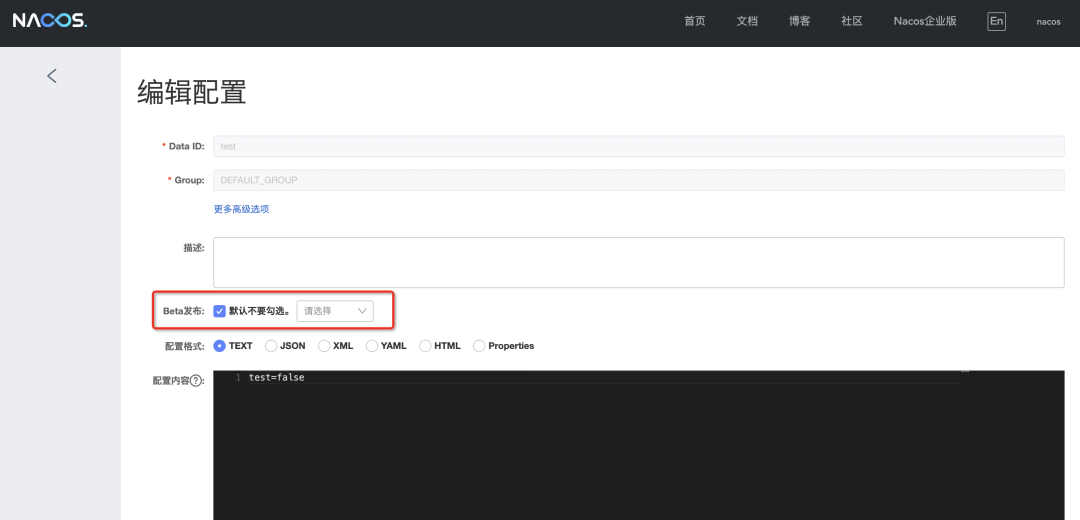
具體的使用方法,如果使用的是自建的社區(qū)Nacos,可以訪問(wèn)http://ip:port/nacos進(jìn)入控制臺(tái),在配置管理的編輯頁(yè)面進(jìn)行配置灰度發(fā)布,如下圖。
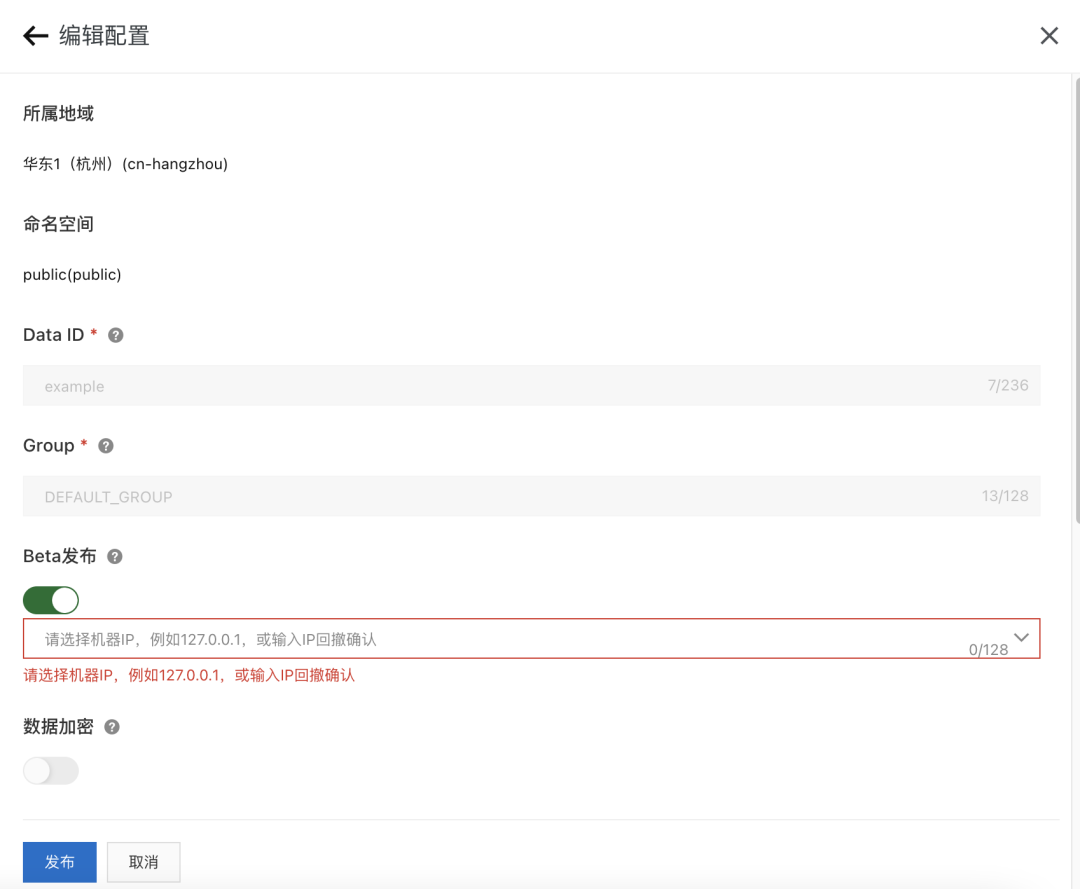
如果使用的是阿里云的MSE微服務(wù)引擎,可以查看MSE配置灰度發(fā)布幫助文檔了解使用方法,目前在Nacos2.0專(zhuān)業(yè)版上已經(jīng)支持灰度功能,在MSE控制臺(tái)打開(kāi)Beta按鈕即可,如下圖所示。
Nacos灰度原理
Nacos的灰度發(fā)布原理其實(shí)并不復(fù)雜,本質(zhì)就如同下面這張流程圖。

乍一看,這個(gè)流程好復(fù)雜,實(shí)際上定睛一看,好像也沒(méi)啥。整個(gè)過(guò)程就是Client、Server和Console之間的交互。Client端監(jiān)聽(tīng)Server上的配置,建立長(zhǎng)連接并上報(bào)自己的客戶(hù)端信息,例如IP地址。Console負(fù)責(zé)進(jìn)行配置灰度的調(diào)用,將用戶(hù)所需要的灰度配置請(qǐng)求發(fā)送到Server端。然后Server端根據(jù)用戶(hù)的灰度配置請(qǐng)求中的IP地址,過(guò)濾與客戶(hù)端的長(zhǎng)連接,然后將灰度配置定向推送到對(duì)應(yīng)IP的客戶(hù)端中即可。下面筆者從長(zhǎng)連接的建立到配置灰度,進(jìn)行詳細(xì)的源碼分析。
長(zhǎng)連接建立
在Nacos2.0版本之前,Nacos主要采用長(zhǎng)輪詢(xún)的方式在客戶(hù)端拉取服務(wù)端的配置信息。而在Nacos2.0版本中,引入了基于gRPC的長(zhǎng)連接模型來(lái)提升配置監(jiān)聽(tīng)的性能,客戶(hù)端和服務(wù)端會(huì)建立長(zhǎng)連接來(lái)監(jiān)聽(tīng)配置的變更,一旦服務(wù)端有配置變更,就會(huì)將配置信息推送到客戶(hù)端中。在Nacos源碼中,這一過(guò)程主要涉及到兩個(gè)組件之間的交互,即com.alibaba.nacos.common.remote.client.grpc包下的GrpcSdkClient類(lèi)和com.alibaba.nacos.core.remote.grpc包下的GrpcBiStreamRequestAcceptor類(lèi)。然而,GrpcSdkClient中沒(méi)有定義具體的連接邏輯,其主要邏輯在其父類(lèi)GrpcClient中。下面這段代碼就是客戶(hù)端連接服務(wù)端的核心代碼,位于GrpcClient的connectToServer方法。
@Override
public Connection connectToServer(ServerInfo serverInfo) {
try {
// ......
int port = serverInfo.getServerPort() + rpcPortOffset();
// 創(chuàng)建一個(gè)Grpc的Stub
RequestGrpc.RequestFutureStub newChannelStubTemp = createNewChannelStub(serverInfo.getServerIp(), port);
if (newChannelStubTemp != null) {
// 檢查服務(wù)端是否可用
Response response = serverCheck(serverInfo.getServerIp(), port, newChannelStubTemp);
if (response == null || !(response instanceof ServerCheckResponse)) {
shuntDownChannel((ManagedChannel) newChannelStubTemp.getChannel());
return null;
}
// 創(chuàng)建一個(gè)Grpc的Stream
BiRequestStreamGrpc.BiRequestStreamStub biRequestStreamStub = BiRequestStreamGrpc
.newStub(newChannelStubTemp.getChannel());
// 創(chuàng)建連接信息,保存Grpc的連接信息,也就是長(zhǎng)連接的一個(gè)holder
GrpcConnection grpcConn = new GrpcConnection(serverInfo, grpcExecutor);
grpcConn.setConnectionId(((ServerCheckResponse) response).getConnectionId());
// 創(chuàng)建stream請(qǐng)求同時(shí)綁定到當(dāng)前連接中
StreamObserver<Payload> payloadStreamObserver = bindRequestStream(biRequestStreamStub, grpcConn);
// 綁定Grpc相關(guān)連接信息
grpcConn.setPayloadStreamObserver(payloadStreamObserver);
grpcConn.setGrpcFutureServiceStub(newChannelStubTemp);
grpcConn.setChannel((ManagedChannel) newChannelStubTemp.getChannel());
// 發(fā)送一個(gè)初始化連接請(qǐng)求,用于上報(bào)客戶(hù)端的一些信息,例如標(biāo)簽、客戶(hù)端版本等
ConnectionSetupRequest conSetupRequest = new ConnectionSetupRequest();
conSetupRequest.setClientVersion(VersionUtils.getFullClientVersion());
conSetupRequest.setLabels(super.getLabels());
conSetupRequest.setAbilities(super.clientAbilities);
conSetupRequest.setTenant(super.getTenant());
grpcConn.sendRequest(conSetupRequest);
// 等待連接建立成功
Thread.sleep(100L);
return grpcConn;
}
return null;
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("[{}]Fail to connect to server!,error={}", GrpcClient.this.getName(), e);
}
return null;
}
上面這段代碼主要功能有兩個(gè),一個(gè)是與服務(wù)端建立gRPC的長(zhǎng)連接,另一個(gè)功能主要是初始化連接,后者是實(shí)現(xiàn)配置灰度發(fā)布的前提。在上文中有提到,配置灰度發(fā)布的過(guò)程中,需要根據(jù)控制臺(tái)的灰度配置請(qǐng)求中的IP信息過(guò)濾長(zhǎng)連接,在服務(wù)端就是根據(jù)連接建立初始化時(shí)上報(bào)的信息實(shí)現(xiàn)的過(guò)濾。從上面的代碼中可以看到,ConnectionSetupRequest作為一個(gè)初始化請(qǐng)求,攜帶著客戶(hù)端版本、標(biāo)簽等信息,但是好像并沒(méi)有攜帶IP地址的信息。實(shí)際上,ConnectionSetupRequest也確實(shí)沒(méi)有攜帶IP地址信息。因?yàn)樵贜acos設(shè)計(jì)中,采用Request來(lái)表明客戶(hù)端的請(qǐng)求信息,而IP地址更像是屬于連接層的信息,應(yīng)該屬于連接的元信息,因此并沒(méi)有放在Request中進(jìn)行顯式的設(shè)置,而是在發(fā)送請(qǐng)求時(shí)自動(dòng)的作為Metadata信息發(fā)送到服務(wù)端中。可以看一下com.alibaba.nacos.common.remote.client.grpc包下的GrpcConnection的sendRequest方法,該方法接收一個(gè)Request請(qǐng)求作為參數(shù),將請(qǐng)求發(fā)送給服務(wù)端。
public void sendRequest(Request request) {
// 將request轉(zhuǎn)換為Grpc的Payload
Payload convert = GrpcUtils.convert(request);
// 通過(guò)Grpc的流發(fā)送請(qǐng)求
payloadStreamObserver.onNext(convert);
}
IP地址的設(shè)置,就在com.alibaba.nacos.common.remote.client.grpc包下的GrpcUtils的convert方法中,該方法主要將一個(gè)Request轉(zhuǎn)換為gRPC的Payload。
/**
* convert request to payload.
*
* @param request request.
* @return payload.
*/
public static Payload convert(Request request) {
// 設(shè)置元信息
Metadata newMeta = Metadata.newBuilder().setType(request.getClass().getSimpleName())
.setClientIp(NetUtils.localIP()).putAllHeaders(request.getHeaders()).build();
request.clearHeaders();
// 轉(zhuǎn)換為json
String jsonString = toJson(request);
Payload.Builder builder = Payload.newBuilder();
// 創(chuàng)建Payload
return builder
.setBody(Any.newBuilder().setValue(ByteString.copyFrom(jsonString, Charset.forName(Constants.ENCODE))))
.setMetadata(newMeta).build();
}
可以看到,這里通過(guò)NetUtils.localIP()方法獲取客戶(hù)端的IP信息,并存入到Metadata中,跟隨Payload一起上報(bào)給服務(wù)端。到這里,客戶(hù)端這里的連接過(guò)程就暫時(shí)完成了,下面介紹一下服務(wù)端接收到連接請(qǐng)求的響應(yīng)過(guò)程。
在服務(wù)端,主要通過(guò)GrpcBiStreamRequestAcceptor的requestBiStream方法接收客戶(hù)端請(qǐng)求,如下所示。
@Override
public StreamObserver<Payload> requestBiStream(StreamObserver<Payload> responseObserver) {
StreamObserver<Payload> streamObserver = new StreamObserver<Payload>() {
final String connectionId = CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_ID.get();
final Integer localPort = CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_LOCAL_PORT.get();
final int remotePort = CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_REMOTE_PORT.get();
String remoteIp = CONTEXT_KEY_CONN_REMOTE_IP.get();
String clientIp = "";
@Override
public void onNext(Payload payload) {
// 獲取客戶(hù)端IP
clientIp = payload.getMetadata().getClientIp();
traceDetailIfNecessary(payload);
Object parseObj;
try {
parseObj = GrpcUtils.parse(payload);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
Loggers.REMOTE_DIGEST
.warn("[{}]Grpc request bi stream,payload parse error={}", connectionId, throwable);
return;
}
if (parseObj == null) {
Loggers.REMOTE_DIGEST
.warn("[{}]Grpc request bi stream,payload parse null ,body={},meta={}", connectionId,
payload.getBody().getValue().toStringUtf8(), payload.getMetadata());
return;
}
// 處理初始化請(qǐng)求
if (parseObj instanceof ConnectionSetupRequest) {
ConnectionSetupRequest setUpRequest = (ConnectionSetupRequest) parseObj;
Map<String, String> labels = setUpRequest.getLabels();
String appName = "-";
if (labels != null && labels.containsKey(Constants.APPNAME)) {
appName = labels.get(Constants.APPNAME);
}
ConnectionMeta metaInfo = new ConnectionMeta(connectionId, payload.getMetadata().getClientIp(),
remoteIp, remotePort, localPort, ConnectionType.GRPC.getType(),
setUpRequest.getClientVersion(), appName, setUpRequest.getLabels());
metaInfo.setTenant(setUpRequest.getTenant());
// 服務(wù)端的長(zhǎng)連接信息holder
Connection connection = new GrpcConnection(metaInfo, responseObserver, CONTEXT_KEY_CHANNEL.get());
connection.setAbilities(setUpRequest.getAbilities());
boolean rejectSdkOnStarting = metaInfo.isSdkSource() && !ApplicationUtils.isStarted();
// 注冊(cè)connection到connectionManager中
if (rejectSdkOnStarting || !connectionManager.register(connectionId, connection)) {
//Not register to the connection manager if current server is over limit or server is starting.
try {
Loggers.REMOTE_DIGEST.warn("[{}]Connection register fail,reason:{}", connectionId,
rejectSdkOnStarting ? " server is not started" : " server is over limited.");
connection.request(new ConnectResetRequest(), 3000L);
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
//Do nothing.
if (connectionManager.traced(clientIp)) {
Loggers.REMOTE_DIGEST
.warn("[{}]Send connect reset request error,error={}", connectionId, e);
}
}
}
} else if (parseObj instanceof Response) {
Response response = (Response) parseObj;
if (connectionManager.traced(clientIp)) {
Loggers.REMOTE_DIGEST
.warn("[{}]Receive response of server request ,response={}", connectionId, response);
}
RpcAckCallbackSynchronizer.ackNotify(connectionId, response);
connectionManager.refreshActiveTime(connectionId);
} else {
Loggers.REMOTE_DIGEST
.warn("[{}]Grpc request bi stream,unknown payload receive ,parseObj={}", connectionId,
parseObj);
}
}
// ......
};
return streamObserver;
}
這里我們主要看onNext方法,其負(fù)責(zé)處理客戶(hù)端的請(qǐng)求信息,即Payload信息。如果是初始化連接的請(qǐng)求ConnectionSetupRequest,就會(huì)記錄與客戶(hù)端之間的長(zhǎng)連接信息,并注冊(cè)到ConnectionManager中。ConnectionManager是服務(wù)端維護(hù)所有客戶(hù)端連接信息的類(lèi),持有所有的長(zhǎng)連接信息,后續(xù)的配置推送等都需要通過(guò)ConnectionManager獲取長(zhǎng)連接信息。可以簡(jiǎn)單看一下ConnectionManager的源碼,在com.alibaba.nacos.core.remote包下,如下所示。
/**
* connect manager.
*
* @author liuzunfei
* @version $Id: ConnectionManager.java, v 0.1 2020年07月13日 7:07 PM liuzunfei Exp $
*/
@Service
public class ConnectionManager extends Subscriber<ConnectionLimitRuleChangeEvent> {
// ......
Map<String, Connection> connections = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Connection>();
// ......
/**
* register a new connect.
*
* @param connectionId connectionId
* @param connection connection
*/
public synchronized boolean register(String connectionId, Connection connection) {
if (connection.isConnected()) {
if (connections.containsKey(connectionId)) {
return true;
}
if (!checkLimit(connection)) {
return false;
}
if (traced(connection.getMetaInfo().clientIp)) {
connection.setTraced(true);
}
// 注冊(cè)connection
connections.put(connectionId, connection);
connectionForClientIp.get(connection.getMetaInfo().clientIp).getAndIncrement();
clientConnectionEventListenerRegistry.notifyClientConnected(connection);
Loggers.REMOTE_DIGEST
.info("new connection registered successfully, connectionId = {},connection={} ", connectionId,
connection);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// ......
}
可以看到,在ConnectionManager中,維護(hù)了一個(gè)Map。在調(diào)用register方法時(shí),將Connection注冊(cè)到Map中,以供后續(xù)的邏輯使用。這里有一個(gè)細(xì)節(jié),注冊(cè)到ConnectionManager中的GrpcConnection與客戶(hù)端持有的GrpcConnection不是一個(gè)類(lèi)。這里的GrpcConnection位于com.alibaba.nacos.core.remote.grpc包,而客戶(hù)端的GrpcConnection位于com.alibaba.nacos.common.remote.client.grpc包。事實(shí)上與客戶(hù)端有關(guān)的gRPC相關(guān)的類(lèi)都在com.alibaba.nacos.common.remote.client.grpc。com.alibaba.nacos.core.remote.grpc則是服務(wù)端的相關(guān)實(shí)現(xiàn)。
到這里,長(zhǎng)連接建立的核心流程已經(jīng)介紹完了,接下來(lái)筆者將詳細(xì)介紹一下配置灰度的推送過(guò)程,由于Nacos在這里使用了發(fā)布訂閱模式以及異步的方法調(diào)用,理解起來(lái)可能稍微要麻煩一點(diǎn)。
灰度推送
在Nacos中,提供了一組OpenAPI進(jìn)行配置的管理,配置灰度發(fā)布也是其中一個(gè)功能,可以在com.alibaba.nacos.config.server.controller包下的ConfigController中查看,包括了BetaConfig的發(fā)布、停止和查詢(xún),接下來(lái)筆者將會(huì)一一介紹他們的原理。
創(chuàng)建BetaConfig
創(chuàng)建BetaConfig的API代碼如下,一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的Web的API。
/**
* Adds or updates non-aggregated data.
*
* @throws NacosException NacosException.
*/
@PostMapping
@Secured(action = ActionTypes.WRITE, parser = ConfigResourceParser.class)
public Boolean publishConfig(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@RequestParam(value = "dataId") String dataId, @RequestParam(value = "group") String group,
@RequestParam(value = "tenant", required = false, defaultValue = StringUtils.EMPTY) String tenant,
@RequestParam(value = "content") String content, @RequestParam(value = "tag", required = false) String tag,
@RequestParam(value = "appName", required = false) String appName,
@RequestParam(value = "src_user", required = false) String srcUser,
@RequestParam(value = "config_tags", required = false) String configTags,
@RequestParam(value = "desc", required = false) String desc,
@RequestParam(value = "use", required = false) String use,
@RequestParam(value = "effect", required = false) String effect,
@RequestParam(value = "type", required = false) String type,
@RequestParam(value = "schema", required = false) String schema) throws NacosException {
final String srcIp = RequestUtil.getRemoteIp(request);
final String requestIpApp = RequestUtil.getAppName(request);
srcUser = RequestUtil.getSrcUserName(request);
//check type
if (!ConfigType.isValidType(type)) {
type = ConfigType.getDefaultType().getType();
}
// check tenant
ParamUtils.checkTenant(tenant);
ParamUtils.checkParam(dataId, group, "datumId", content);
ParamUtils.checkParam(tag);
Map<String, Object> configAdvanceInfo = new HashMap<String, Object>(10);
MapUtil.putIfValNoNull(configAdvanceInfo, "config_tags", configTags);
MapUtil.putIfValNoNull(configAdvanceInfo, "desc", desc);
MapUtil.putIfValNoNull(configAdvanceInfo, "use", use);
MapUtil.putIfValNoNull(configAdvanceInfo, "effect", effect);
MapUtil.putIfValNoNull(configAdvanceInfo, "type", type);
MapUtil.putIfValNoNull(configAdvanceInfo, "schema", schema);
ParamUtils.checkParam(configAdvanceInfo);
if (AggrWhitelist.isAggrDataId(dataId)) {
LOGGER.warn("[aggr-conflict] {} attempt to publish single data, {}, {}", RequestUtil.getRemoteIp(request),
dataId, group);
throw new NacosException(NacosException.NO_RIGHT, "dataId:" + dataId + " is aggr");
}
final Timestamp time = TimeUtils.getCurrentTime();
// 目標(biāo)灰度機(jī)器的IP地址。
String betaIps = request.getHeader("betaIps");
ConfigInfo configInfo = new ConfigInfo(dataId, group, tenant, appName, content);
configInfo.setType(type);
if (StringUtils.isBlank(betaIps)) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(tag)) {
persistService.insertOrUpdate(srcIp, srcUser, configInfo, time, configAdvanceInfo, false);
ConfigChangePublisher
.notifyConfigChange(new ConfigDataChangeEvent(false, dataId, group, tenant, time.getTime()));
} else {
persistService.insertOrUpdateTag(configInfo, tag, srcIp, srcUser, time, false);
ConfigChangePublisher.notifyConfigChange(
new ConfigDataChangeEvent(false, dataId, group, tenant, tag, time.getTime()));
}
} else {
// 發(fā)布Beta 配置
persistService.insertOrUpdateBeta(configInfo, betaIps, srcIp, srcUser, time, false);
// 通知配置變更
ConfigChangePublisher
.notifyConfigChange(new ConfigDataChangeEvent(true, dataId, group, tenant, time.getTime()));
}
ConfigTraceService
.logPersistenceEvent(dataId, group, tenant, requestIpApp, time.getTime(), InetUtils.getSelfIP(),
ConfigTraceService.PERSISTENCE_EVENT_PUB, content);
return true;
}
該方法接收一個(gè)創(chuàng)建配置的請(qǐng)求,包括配置的data-id、content等信息。從代碼中可以看出,該方法是通過(guò)判斷請(qǐng)求的Header中有無(wú)betaIps的值來(lái)確定是發(fā)布正式配置還是Beta配置的。如果betaIps的值不為空,則表明待發(fā)布的配置是一個(gè)Beta配置。而配置發(fā)布的過(guò)程,實(shí)際上就是把配置插入或者更新到數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)中。在Nacos中,正式配置和灰度配置是分別存儲(chǔ)在不同的表中的,一旦發(fā)布就會(huì)通過(guò)ConfigChangePublisher發(fā)布一個(gè)ConfigDataChangeEvent事件,然后由訂閱了該事件的監(jiān)聽(tīng)者推送配置信息到客戶(hù)端。ConfigDataChangeEvent的監(jiān)聽(tīng)者是AsyncNotifyService類(lèi),位于com.alibaba.nacos.config.server.service.notify包下,該類(lèi)主要用作執(zhí)行集群之間的數(shù)據(jù)Dump操作。該類(lèi)在初始化的時(shí)候,會(huì)向事件中心NotifyCenter注冊(cè)一個(gè)監(jiān)聽(tīng)者,用以監(jiān)聽(tīng)數(shù)據(jù)變更事件并異步執(zhí)行數(shù)據(jù)的Dump操作,如下所示。
/**
* Async notify service.
*
* @author Nacos
*/
@Service
public class AsyncNotifyService {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AsyncNotifyService.class);
private final NacosAsyncRestTemplate nacosAsyncRestTemplate = HttpClientManager.getNacosAsyncRestTemplate();
private static final int MIN_RETRY_INTERVAL = 500;
private static final int INCREASE_STEPS = 1000;
private static final int MAX_COUNT = 6;
@Autowired
private DumpService dumpService;
@Autowired
private ConfigClusterRpcClientProxy configClusterRpcClientProxy;
private ServerMemberManager memberManager;
@Autowired
public AsyncNotifyService(ServerMemberManager memberManager) {
this.memberManager = memberManager;
// Register ConfigDataChangeEvent to NotifyCenter.
NotifyCenter.registerToPublisher(ConfigDataChangeEvent.class, NotifyCenter.ringBufferSize);
// Register A Subscriber to subscribe ConfigDataChangeEvent.
NotifyCenter.registerSubscriber(new Subscriber() {
@Override
public void onEvent(Event event) {
// Generate ConfigDataChangeEvent concurrently
if (event instanceof ConfigDataChangeEvent) {
ConfigDataChangeEvent evt = (ConfigDataChangeEvent) event;
long dumpTs = evt.lastModifiedTs;
String dataId = evt.dataId;
String group = evt.group;
String tenant = evt.tenant;
String tag = evt.tag;
Collection<Member> ipList = memberManager.allMembers();
// In fact, any type of queue here can be
Queue<NotifySingleTask> httpQueue = new LinkedList<NotifySingleTask>();
Queue<NotifySingleRpcTask> rpcQueue = new LinkedList<NotifySingleRpcTask>();
for (Member member : ipList) {
// 判斷是否是長(zhǎng)輪詢(xún)
if (!MemberUtil.isSupportedLongCon(member)) {
// 添加一個(gè)長(zhǎng)輪詢(xún)的異步dump任務(wù)
httpQueue.add(new NotifySingleTask(dataId, group, tenant, tag, dumpTs, member.getAddress(),
evt.isBeta));
} else {
// 添加一個(gè)長(zhǎng)連接的異步dump任務(wù)
rpcQueue.add(
new NotifySingleRpcTask(dataId, group, tenant, tag, dumpTs, evt.isBeta, member));
}
}
// 判斷并執(zhí)行長(zhǎng)輪詢(xún)的異步dump任務(wù)
if (!httpQueue.isEmpty()) {
ConfigExecutor.executeAsyncNotify(new AsyncTask(nacosAsyncRestTemplate, httpQueue));
}
// 判斷并執(zhí)行長(zhǎng)連接的異步dump任務(wù)
if (!rpcQueue.isEmpty()) {
ConfigExecutor.executeAsyncNotify(new AsyncRpcTask(rpcQueue));
}
}
}
@Override
public Class<? extends Event> subscribeType() {
return ConfigDataChangeEvent.class;
}
});
}
}
在接收到ConfigDataChangeEvent之后,如果Nacos2.0以上的版本,會(huì)創(chuàng)建一個(gè)RpcTask用以執(zhí)行配置變更的通知,由內(nèi)部類(lèi)AsyncRpcTask執(zhí)行,AsyncRpcTask具體邏輯如下所示。
class AsyncRpcTask implements Runnable {
private Queue<NotifySingleRpcTask> queue;
public AsyncRpcTask(Queue<NotifySingleRpcTask> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
NotifySingleRpcTask task = queue.poll();
// 創(chuàng)建配置變更請(qǐng)求
ConfigChangeClusterSyncRequest syncRequest = new ConfigChangeClusterSyncRequest();
syncRequest.setDataId(task.getDataId());
syncRequest.setGroup(task.getGroup());
syncRequest.setBeta(task.isBeta);
syncRequest.setLastModified(task.getLastModified());
syncRequest.setTag(task.tag);
syncRequest.setTenant(task.getTenant());
Member member = task.member;
// 如果是自身的數(shù)據(jù)變更,直接執(zhí)行dump操作
if (memberManager.getSelf().equals(member)) {
if (syncRequest.isBeta()) {
// 同步Beta配置
dumpService.dump(syncRequest.getDataId(), syncRequest.getGroup(), syncRequest.getTenant(),
syncRequest.getLastModified(), NetUtils.localIP(), true);
} else {
// 同步正式配置
dumpService.dump(syncRequest.getDataId(), syncRequest.getGroup(), syncRequest.getTenant(),
syncRequest.getTag(), syncRequest.getLastModified(), NetUtils.localIP());
}
continue;
}
// 通知其他服務(wù)端進(jìn)行dump
if (memberManager.hasMember(member.getAddress())) {
// start the health check and there are ips that are not monitored, put them directly in the notification queue, otherwise notify
boolean unHealthNeedDelay = memberManager.isUnHealth(member.getAddress());
if (unHealthNeedDelay) {
// target ip is unhealthy, then put it in the notification list
ConfigTraceService.logNotifyEvent(task.getDataId(), task.getGroup(), task.getTenant(), null,
task.getLastModified(), InetUtils.getSelfIP(), ConfigTraceService.NOTIFY_EVENT_UNHEALTH,
0, member.getAddress());
// get delay time and set fail count to the task
asyncTaskExecute(task);
} else {
if (!MemberUtil.isSupportedLongCon(member)) {
asyncTaskExecute(
new NotifySingleTask(task.getDataId(), task.getGroup(), task.getTenant(), task.tag,
task.getLastModified(), member.getAddress(), task.isBeta));
} else {
try {
configClusterRpcClientProxy
.syncConfigChange(member, syncRequest, new AsyncRpcNotifyCallBack(task));
} catch (Exception e) {
MetricsMonitor.getConfigNotifyException().increment();
asyncTaskExecute(task);
}
}
}
} else {
//No nothig if member has offline.
}
}
}
}
這里首先創(chuàng)建了一個(gè)ConfigChangeClusterSyncRequest,并將配置信息寫(xiě)入。然后獲取集群信息,通知相應(yīng)的Server處理的數(shù)據(jù)同步請(qǐng)求。同步配置變更信息的核心邏輯由DumpService來(lái)執(zhí)行。我們主要查看同步Beta配置的操作,DumpService的dump方法如下所示。
/**
* Add DumpTask to TaskManager, it will execute asynchronously.
*/
public void dump(String dataId, String group, String tenant, long lastModified, String handleIp, boolean isBeta) {
String groupKey = GroupKey2.getKey(dataId, group, tenant);
String taskKey = String.join("+", dataId, group, tenant, String.valueOf(isBeta));
dumpTaskMgr.addTask(taskKey, new DumpTask(groupKey, lastModified, handleIp, isBeta));
DUMP_LOG.info("[dump-task] add task. groupKey={}, taskKey={}", groupKey, taskKey);
}
在該方法中,這里會(huì)根據(jù)配置變更信息,提交一個(gè)異步的DumpTask任務(wù),后續(xù)會(huì)由DumpProcessor類(lèi)的process方法進(jìn)行處理,該方法如下所示。
/**
* dump processor.
*
* @author Nacos
* @date 2020/7/5 12:19 PM
*/
public class DumpProcessor implements NacosTaskProcessor {
final DumpService dumpService;
public DumpProcessor(DumpService dumpService) {
this.dumpService = dumpService;
}
@Override
public boolean process(NacosTask task) {
final PersistService persistService = dumpService.getPersistService();
DumpTask dumpTask = (DumpTask) task;
String[] pair = GroupKey2.parseKey(dumpTask.getGroupKey());
String dataId = pair[0];
String group = pair[1];
String tenant = pair[2];
long lastModified = dumpTask.getLastModified();
String handleIp = dumpTask.getHandleIp();
boolean isBeta = dumpTask.isBeta();
String tag = dumpTask.getTag();
ConfigDumpEvent.ConfigDumpEventBuilder build = ConfigDumpEvent.builder().namespaceId(tenant).dataId(dataId)
.group(group).isBeta(isBeta).tag(tag).lastModifiedTs(lastModified).handleIp(handleIp);
if (isBeta) {
// 更新Beta配置的緩存
ConfigInfo4Beta cf = persistService.findConfigInfo4Beta(dataId, group, tenant);
build.remove(Objects.isNull(cf));
build.betaIps(Objects.isNull(cf) ? null : cf.getBetaIps());
build.content(Objects.isNull(cf) ? null : cf.getContent());
return DumpConfigHandler.configDump(build.build());
}
if (StringUtils.isBlank(tag)) {
ConfigInfo cf = persistService.findConfigInfo(dataId, group, tenant);
build.remove(Objects.isNull(cf));
build.content(Objects.isNull(cf) ? null : cf.getContent());
build.type(Objects.isNull(cf) ? null : cf.getType());
} else {
ConfigInfo4Tag cf = persistService.findConfigInfo4Tag(dataId, group, tenant, tag);
build.remove(Objects.isNull(cf));
build.content(Objects.isNull(cf) ? null : cf.getContent());
}
return DumpConfigHandler.configDump(build.build());
}
}
可以看到,如果是Beta配置,則獲取最新的Beta配置信息,然后觸發(fā)DumpConfigHandler的configDump方法。進(jìn)入configDump可以看到,該方法主要用來(lái)更新緩存的配置信息,調(diào)用ConfigCacheService的相關(guān)操作進(jìn)行配置的更新。
/**
* Dump config subscriber.
*
* @author <a href="mailto:[email protected]">liaochuntao</a>
*/
public class DumpConfigHandler extends Subscriber<ConfigDumpEvent> {
/**
* trigger config dump event.
*
* @param event {@link ConfigDumpEvent}
* @return {@code true} if the config dump task success , else {@code false}
*/
public static boolean configDump(ConfigDumpEvent event) {
final String dataId = event.getDataId();
final String group = event.getGroup();
final String namespaceId = event.getNamespaceId();
final String content = event.getContent();
final String type = event.getType();
final long lastModified = event.getLastModifiedTs();
if (event.isBeta()) {
boolean result = false;
// 刪除操作
if (event.isRemove()) {
result = ConfigCacheService.removeBeta(dataId, group, namespaceId);
if (result) {
ConfigTraceService.logDumpEvent(dataId, group, namespaceId, null, lastModified, event.getHandleIp(),
ConfigTraceService.DUMP_EVENT_REMOVE_OK, System.currentTimeMillis() - lastModified, 0);
}
return result;
} else {
// 更新或者發(fā)布
result = ConfigCacheService
.dumpBeta(dataId, group, namespaceId, content, lastModified, event.getBetaIps());
if (result) {
ConfigTraceService.logDumpEvent(dataId, group, namespaceId, null, lastModified, event.getHandleIp(),
ConfigTraceService.DUMP_EVENT_OK, System.currentTimeMillis() - lastModified,
content.length());
}
}
return result;
}
// ......
}
@Override
public void onEvent(ConfigDumpEvent event) {
configDump(event);
}
@Override
public Class<? extends Event> subscribeType() {
return ConfigDumpEvent.class;
}
}
在ConfigCacheService中,會(huì)對(duì)比配置信息,如果配置有變化,則發(fā)布事件LocalDataChangeEvent,觸發(fā)RpcConfigChangeNotifier的configDataChanged方法來(lái)推送配置,configDataChanged方法代碼如下。
/**
* ConfigChangeNotifier.
*
* @author liuzunfei
* @version $Id: ConfigChangeNotifier.java, v 0.1 2020年07月20日 3:00 PM liuzunfei Exp $
*/
@Component(value = "rpcConfigChangeNotifier")
public class RpcConfigChangeNotifier extends Subscriber<LocalDataChangeEvent> {
// ......
@Autowired
ConfigChangeListenContext configChangeListenContext;
@Autowired
private RpcPushService rpcPushService;
@Autowired
private ConnectionManager connectionManager;
/**
* adaptor to config module ,when server side config change ,invoke this method.
*
* @param groupKey groupKey
*/
public void configDataChanged(String groupKey, String dataId, String group, String tenant, boolean isBeta,
List<String> betaIps, String tag) {
// 獲取配置的所有監(jiān)聽(tīng)者
Set<String> listeners = configChangeListenContext.getListeners(groupKey);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(listeners)) {
return;
}
int notifyClientCount = 0;
// 遍歷所有監(jiān)聽(tīng)者
for (final String client : listeners) {
// 獲取長(zhǎng)連接信息
Connection connection = connectionManager.getConnection(client);
if (connection == null) {
continue;
}
String clientIp = connection.getMetaInfo().getClientIp();
String clientTag = connection.getMetaInfo().getTag();
// 判斷是否是Beta的Ip
if (isBeta && betaIps != null && !betaIps.contains(clientIp)) {
continue;
}
// tag check
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(tag) && !tag.equals(clientTag)) {
continue;
}
// 配置變更推送請(qǐng)求
ConfigChangeNotifyRequest notifyRequest = ConfigChangeNotifyRequest.build(dataId, group, tenant);
// 執(zhí)行推送任務(wù)
RpcPushTask rpcPushRetryTask = new RpcPushTask(notifyRequest, 50, client, clientIp,
connection.getMetaInfo().getAppName());
push(rpcPushRetryTask);
notifyClientCount++;
}
Loggers.REMOTE_PUSH.info("push [{}] clients ,groupKey=[{}]", notifyClientCount, groupKey);
}
@Override
public void onEvent(LocalDataChangeEvent event) {
String groupKey = event.groupKey;
boolean isBeta = event.isBeta;
List<String> betaIps = event.betaIps;
String[] strings = GroupKey.parseKey(groupKey);
String dataId = strings[0];
String group = strings[1];
String tenant = strings.length > 2 ? strings[2] : "";
String tag = event.tag;
configDataChanged(groupKey, dataId, group, tenant, isBeta, betaIps, tag);
}
// ......
}
到這里,基本上就是配置變更推送的最后一個(gè)步驟了,如代碼中注釋所示,通過(guò)調(diào)用ConnectionManager的getConnection方法,遍歷所有監(jiān)聽(tīng)者的連接,根據(jù)其中的Meta信息判斷是否是Beta推送的目標(biāo),然后執(zhí)行推送任務(wù),也就是執(zhí)行push方法,如下所示。
private void push(RpcPushTask retryTask) {
ConfigChangeNotifyRequest notifyRequest = retryTask.notifyRequest;
// 判斷是否重試次數(shù)達(dá)到限制
if (retryTask.isOverTimes()) {
Loggers.REMOTE_PUSH
.warn("push callback retry fail over times .dataId={},group={},tenant={},clientId={},will unregister client.",
notifyRequest.getDataId(), notifyRequest.getGroup(), notifyRequest.getTenant(),
retryTask.connectionId);
// 主動(dòng)注銷(xiāo)連接
connectionManager.unregister(retryTask.connectionId);
} else if (connectionManager.getConnection(retryTask.connectionId) != null) {
// first time :delay 0s; sencond time:delay 2s ;third time :delay 4s
// 嘗試執(zhí)行配置推送
ConfigExecutor.getClientConfigNotifierServiceExecutor()
.schedule(retryTask, retryTask.tryTimes * 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} else {
// client is already offline,ingnore task.
}
}
這里實(shí)際上也是一個(gè)異步執(zhí)行的過(guò)程,推送任務(wù)RpcPushTask會(huì)被提交到ClientConfigNotifierServiceExecutor來(lái)計(jì)劃執(zhí)行,第一次會(huì)立即推送配置,即調(diào)用RpcPushTask的run方法,如果失敗則延遲重試次數(shù)x2的秒數(shù)再次執(zhí)行,直到超過(guò)重試次數(shù),主動(dòng)注銷(xiāo)當(dāng)前連接。其中,RpcPushTask的定義如下。
class RpcPushTask implements Runnable {
ConfigChangeNotifyRequest notifyRequest;
int maxRetryTimes = -1;
int tryTimes = 0;
String connectionId;
String clientIp;
String appName;
public RpcPushTask(ConfigChangeNotifyRequest notifyRequest, int maxRetryTimes, String connectionId,
String clientIp, String appName) {
this.notifyRequest = notifyRequest;
this.maxRetryTimes = maxRetryTimes;
this.connectionId = connectionId;
this.clientIp = clientIp;
this.appName = appName;
}
public boolean isOverTimes() {
return maxRetryTimes > 0 && this.tryTimes >= maxRetryTimes;
}
@Override
public void run() {
tryTimes++;
if (!tpsMonitorManager.applyTpsForClientIp(POINT_CONFIG_PUSH, connectionId, clientIp)) {
push(this);
} else {
// 推送配置
rpcPushService.pushWithCallback(connectionId, notifyRequest, new AbstractPushCallBack(3000L) {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
tpsMonitorManager.applyTpsForClientIp(POINT_CONFIG_PUSH_SUCCESS, connectionId, clientIp);
}
@Override
public void onFail(Throwable e) {
tpsMonitorManager.applyTpsForClientIp(POINT_CONFIG_PUSH_FAIL, connectionId, clientIp);
Loggers.REMOTE_PUSH.warn("Push fail", e);
push(RpcPushTask.this);
}
}, ConfigExecutor.getClientConfigNotifierServiceExecutor());
}
}
}
可以看到,在RpcPushTask的run方法中,調(diào)用了RpcPushService的pushWithCallback方法,如下所示。
/**
* push response to clients.
*
* @author liuzunfei
* @version $Id: PushService.java, v 0.1 2020年07月20日 1:12 PM liuzunfei Exp $
*/
@Service
public class RpcPushService {
@Autowired
private ConnectionManager connectionManager;
/**
* push response with no ack.
*
* @param connectionId connectionId.
* @param request request.
* @param requestCallBack requestCallBack.
*/
public void pushWithCallback(String connectionId, ServerRequest request, PushCallBack requestCallBack,
Executor executor) {
Connection connection = connectionManager.getConnection(connectionId);
if (connection != null) {
try {
// 執(zhí)行配置推送
connection.asyncRequest(request, new AbstractRequestCallBack(requestCallBack.getTimeout()) {
@Override
public Executor getExecutor() {
return executor;
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Response response) {
if (response.isSuccess()) {
requestCallBack.onSuccess();
} else {
requestCallBack.onFail(new NacosException(response.getErrorCode(), response.getMessage()));
}
}
@Override
public void onException(Throwable e) {
requestCallBack.onFail(e);
}
});
} catch (ConnectionAlreadyClosedException e) {
connectionManager.unregister(connectionId);
requestCallBack.onSuccess();
} catch (Exception e) {
Loggers.REMOTE_DIGEST
.error("error to send push response to connectionId ={},push response={}", connectionId,
request, e);
requestCallBack.onFail(e);
}
} else {
requestCallBack.onSuccess();
}
}
}
其持有ConnectionManager對(duì)象,當(dāng)需要推送配置到客戶(hù)端時(shí),會(huì)獲取相應(yīng)的Connection,然后執(zhí)行asyncRequest將配置推送到客戶(hù)端中。如果連接已經(jīng)關(guān)閉,則注銷(xiāo)連接。在asyncRequest底層即是調(diào)用Grpc建立的Stream的onNext方法,將配置推送給客戶(hù)端,如下。
/**
* grpc connection.
*
* @author liuzunfei
* @version $Id: GrpcConnection.java, v 0.1 2020年07月13日 7:26 PM liuzunfei Exp $
*/
public class GrpcConnection extends Connection {
private StreamObserver streamObserver;
private Channel channel;
public GrpcConnection(ConnectionMeta metaInfo, StreamObserver streamObserver, Channel channel) {
super(metaInfo);
this.streamObserver = streamObserver;
this.channel = channel;
}
@Override
public void asyncRequest(Request request, RequestCallBack requestCallBack) throws NacosException {
sendRequestInner(request, requestCallBack);
}
private DefaultRequestFuture sendRequestInner(Request request, RequestCallBack callBack) throws NacosException {
final String requestId = String.valueOf(PushAckIdGenerator.getNextId());
request.setRequestId(requestId);
DefaultRequestFuture defaultPushFuture = new DefaultRequestFuture(getMetaInfo().getConnectionId(), requestId,
callBack, () -> RpcAckCallbackSynchronizer.clearFuture(getMetaInfo().getConnectionId(), requestId));
RpcAckCallbackSynchronizer.syncCallback(getMetaInfo().getConnectionId(), requestId, defaultPushFuture);
sendRequestNoAck(request);
return defaultPushFuture;
}
private void sendRequestNoAck(Request request) throws NacosException {
try {
//StreamObserver#onNext() is not thread-safe,synchronized is required to avoid direct memory leak.
synchronized (streamObserver) {
Payload payload = GrpcUtils.convert(request);
traceIfNecessary(payload);
streamObserver.onNext(payload);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (e instanceof StatusRuntimeException) {
throw new ConnectionAlreadyClosedException(e);
}
throw e;
}
}
}
主要推送邏輯的代碼如上所示,調(diào)用asyncRequest之后,會(huì)將請(qǐng)求交給sendRequestInner處理,sendRequestInner又會(huì)調(diào)用sendRequestNoAck將推送請(qǐng)求推入gRPC的流中,客戶(hù)端收到配置更新的請(qǐng)求,就會(huì)更新客戶(hù)端的配置了。至此,一個(gè)灰度配置就發(fā)布成功了。
刪除/查詢(xún)BetaConfig
刪除和查詢(xún)BetaConfig的方法都很簡(jiǎn)單,都是簡(jiǎn)單的操作數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)即可。如果是刪除配置,則會(huì)觸發(fā)ConfigDataChangeEvent來(lái)告知客戶(hù)端更新配置,這里筆者就不多加贅述了。
/**
* Execute to remove beta operation.
*
* @param dataId dataId string value.
* @param group group string value.
* @param tenant tenant string value.
* @return Execute to operate result.
*/
@DeleteMapping(params = "beta=true")
@Secured(action = ActionTypes.WRITE, parser = ConfigResourceParser.class)
public RestResult<Boolean> stopBeta(@RequestParam(value = "dataId") String dataId,
@RequestParam(value = "group") String group,
@RequestParam(value = "tenant", required = false, defaultValue = StringUtils.EMPTY) String tenant) {
try {
persistService.removeConfigInfo4Beta(dataId, group, tenant);
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOGGER.error("remove beta data error", e);
return RestResultUtils.failed(500, false, "remove beta data error");
}
ConfigChangePublisher
.notifyConfigChange(new ConfigDataChangeEvent(true, dataId, group, tenant, System.currentTimeMillis()));
return RestResultUtils.success("stop beta ok", true);
}
/**
* Execute to query beta operation.
*
* @param dataId dataId string value.
* @param group group string value.
* @param tenant tenant string value.
* @return RestResult for ConfigInfo4Beta.
*/
@GetMapping(params = "beta=true")
@Secured(action = ActionTypes.READ, parser = ConfigResourceParser.class)
public RestResult<ConfigInfo4Beta> queryBeta(@RequestParam(value = "dataId") String dataId,
@RequestParam(value = "group") String group,
@RequestParam(value = "tenant", required = false, defaultValue = StringUtils.EMPTY) String tenant) {
try {
ConfigInfo4Beta ci = persistService.findConfigInfo4Beta(dataId, group, tenant);
return RestResultUtils.success("stop beta ok", ci);
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOGGER.error("remove beta data error", e);
return RestResultUtils.failed("remove beta data error");
}
}
總結(jié)
Nacos2.0使用長(zhǎng)連接代替了短連接的長(zhǎng)輪詢(xún),性能幾乎提升了10倍。在阿里內(nèi)部,也在逐漸推進(jìn)Nacos2作為統(tǒng)一的配置中心。目前在微服務(wù)引擎(Micro Service Engine,簡(jiǎn)稱(chēng) MSE),Nacos作為注冊(cè)配置中心,提供了純托管的服務(wù),只需要購(gòu)買(mǎi)Nacos專(zhuān)業(yè)版即可享受到10倍的性能提升。
此外,MSE微服務(wù)引擎顧名思義,是一個(gè)面向業(yè)界主流開(kāi)源微服務(wù)生態(tài)的一站式微服務(wù)平臺(tái), 幫助微服務(wù)用戶(hù)更穩(wěn)定、更便捷、更低成本的使用開(kāi)源微服務(wù)技術(shù)構(gòu)建微服務(wù)體系。不但提供注冊(cè)中心、配置中心全托管(兼容 Nacos/ZooKeeper/Eureka),而且提供網(wǎng)關(guān)(兼容 Ingress/Enovy)和無(wú)侵入的開(kāi)源增強(qiáng)服務(wù)治理能力。
在阿里,MSE微服務(wù)引擎已經(jīng)被大規(guī)模的接入使用,經(jīng)歷阿里內(nèi)部生產(chǎn)考驗(yàn)以及反復(fù)淬煉,其中微服務(wù)服務(wù)治理能力支撐了大量的微服務(wù)系統(tǒng),對(duì)包括Spring Cloud、Dubbo等微服務(wù)框架的治理功能增強(qiáng),提供了無(wú)損上下線、金絲雀發(fā)布、離群摘除以及無(wú)損滾動(dòng)升級(jí)的功能。
如果有快速搭建高性能微服務(wù)以及大規(guī)模服務(wù)治理的需求,相比于從零搭建和運(yùn)維,MSE微服務(wù)引擎是一個(gè)不錯(cuò)的選擇。
