前端架構(gòu):萬(wàn)字解析 - 前端監(jiān)控 SDK(干貨)
大廠技術(shù) 高級(jí)前端 Node進(jìn)階
點(diǎn)擊上方 程序員成長(zhǎng)指北,關(guān)注公眾號(hào)
回復(fù)1,加入高級(jí)Node交流群
一個(gè)完整的前端監(jiān)控平臺(tái)包括三個(gè)部分:數(shù)據(jù)采集與上報(bào)、數(shù)據(jù)整理和存儲(chǔ)、數(shù)據(jù)展示。
本文要講的就是其中的第一個(gè)環(huán)節(jié)——數(shù)據(jù)采集與上報(bào)。下圖是本文要講述內(nèi)容的大綱,大家可以先大致了解一下:
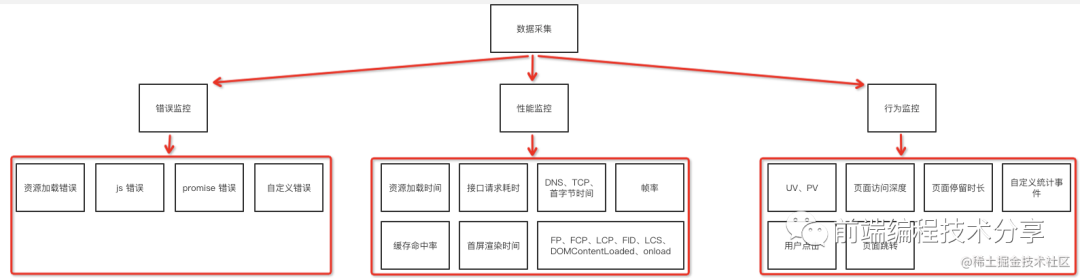
僅看理論知識(shí)是比較難以理解的,為此我結(jié)合本文要講的技術(shù)要點(diǎn)寫了一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的監(jiān)控 SDK[1],可以用它來(lái)寫一些簡(jiǎn)單的 DEMO,幫助加深理解。再結(jié)合本文一起閱讀,效果更好。
性能數(shù)據(jù)采集
chrome 開發(fā)團(tuán)隊(duì)提出了一系列用于檢測(cè)網(wǎng)頁(yè)性能的指標(biāo):
?FP(first-paint),從頁(yè)面加載開始到第一個(gè)像素繪制到屏幕上的時(shí)間?FCP(first-contentful-paint),從頁(yè)面加載開始到頁(yè)面內(nèi)容的任何部分在屏幕上完成渲染的時(shí)間?LCP(largest-contentful-paint),從頁(yè)面加載開始到最大文本塊或圖像元素在屏幕上完成渲染的時(shí)間?CLS(layout-shift),從頁(yè)面加載開始和其生命周期狀態(tài)[2]變?yōu)殡[藏期間發(fā)生的所有意外布局偏移的累積分?jǐn)?shù)
這四個(gè)性能指標(biāo)都需要通過(guò) PerformanceObserver[3] 來(lái)獲取(也可以通過(guò) performance.getEntriesByName() 獲取,但它不是在事件觸發(fā)時(shí)通知的)。PerformanceObserver 是一個(gè)性能監(jiān)測(cè)對(duì)象,用于監(jiān)測(cè)性能度量事件。
FP
FP(first-paint),從頁(yè)面加載開始到第一個(gè)像素繪制到屏幕上的時(shí)間。其實(shí)把 FP 理解成白屏?xí)r間也是沒問(wèn)題的。
測(cè)量代碼如下:
const entryHandler = (list) => {for (const entry of list.getEntries()) {if (entry.name === 'first-paint') {observer.disconnect()}console.log(entry)}}const observer = new PerformanceObserver(entryHandler)// buffered 屬性表示是否觀察緩存數(shù)據(jù),也就是說(shuō)觀察代碼添加時(shí)機(jī)比事情觸發(fā)時(shí)機(jī)晚也沒關(guān)系。observer.observe({ type: 'paint', buffered: true })
通過(guò)以上代碼可以得到 FP 的內(nèi)容:
{duration: 0,entryType: "paint",name: "first-paint",startTime: 359, // fp 時(shí)間}
其中 startTime 就是我們要的繪制時(shí)間。
FCP
FCP(first-contentful-paint),從頁(yè)面加載開始到頁(yè)面內(nèi)容的任何部分在屏幕上完成渲染的時(shí)間。對(duì)于該指標(biāo),"內(nèi)容"指的是文本、圖像(包括背景圖像)、<svg>元素或非白色的<canvas>元素。
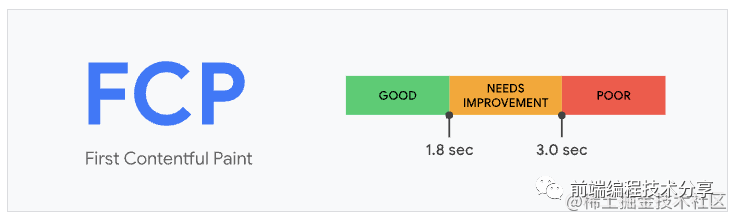
為了提供良好的用戶體驗(yàn),F(xiàn)CP 的分?jǐn)?shù)應(yīng)該控制在 1.8 秒以內(nèi)。
測(cè)量代碼:
const entryHandler = (list) => {for (const entry of list.getEntries()) {if (entry.name === 'first-contentful-paint') {observer.disconnect()}console.log(entry)}}const observer = new PerformanceObserver(entryHandler)observer.observe({ type: 'paint', buffered: true })
通過(guò)以上代碼可以得到 FCP 的內(nèi)容:
{duration: 0,entryType: "paint",name: "first-contentful-paint",startTime: 459, // fcp 時(shí)間}
其中 startTime 就是我們要的繪制時(shí)間。
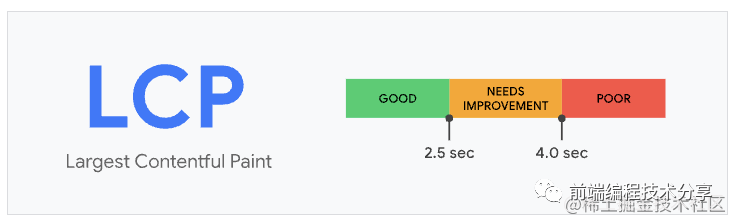
LCP
LCP(largest-contentful-paint),從頁(yè)面加載開始到最大文本塊或圖像元素在屏幕上完成渲染的時(shí)間。LCP 指標(biāo)會(huì)根據(jù)頁(yè)面首次開始加載[4]的時(shí)間點(diǎn)來(lái)報(bào)告可視區(qū)域內(nèi)可見的最大圖像或文本塊[5]完成渲染的相對(duì)時(shí)間。
一個(gè)良好的 LCP 分?jǐn)?shù)應(yīng)該控制在 2.5 秒以內(nèi)。
測(cè)量代碼:
const entryHandler = (list) => {if (observer) {observer.disconnect()}for (const entry of list.getEntries()) {console.log(entry)}}const observer = new PerformanceObserver(entryHandler)observer.observe({ type: 'largest-contentful-paint', buffered: true })
通過(guò)以上代碼可以得到 LCP 的內(nèi)容:
{duration: 0,element: p,entryType: "largest-contentful-paint",id: "",loadTime: 0,name: "",renderTime: 1021.299,size: 37932,startTime: 1021.299,url: "",}
其中 startTime 就是我們要的繪制時(shí)間。element 是指 LCP 繪制的 DOM 元素。
FCP 和 LCP 的區(qū)別是:FCP 只要任意內(nèi)容繪制完成就觸發(fā),LCP 是最大內(nèi)容渲染完成時(shí)觸發(fā)。
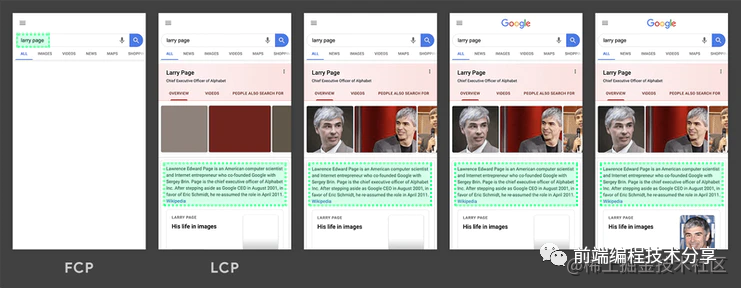
LCP 考察的元素類型為:
?<img>元素?內(nèi)嵌在<svg>元素內(nèi)的<image>元素?<video>元素(使用封面圖像)?通過(guò)url()[6]函數(shù)(而非使用CSS 漸變[7])加載的帶有背景圖像的元素?包含文本節(jié)點(diǎn)或其他行內(nèi)級(jí)文本元素子元素的塊級(jí)元素[8]。
CLS
CLS(layout-shift),從頁(yè)面加載開始和其生命周期狀態(tài)[9]變?yōu)殡[藏期間發(fā)生的所有意外布局偏移的累積分?jǐn)?shù)。
布局偏移分?jǐn)?shù)的計(jì)算方式如下:
布局偏移分?jǐn)?shù) = 影響分?jǐn)?shù) * 距離分?jǐn)?shù)影響分?jǐn)?shù)[10]測(cè)量不穩(wěn)定元素對(duì)兩幀之間的可視區(qū)域產(chǎn)生的影響。
距離分?jǐn)?shù)指的是任何不穩(wěn)定元素在一幀中位移的最大距離(水平或垂直)除以可視區(qū)域的最大尺寸維度(寬度或高度,以較大者為準(zhǔn))。
CLS 就是把所有布局偏移分?jǐn)?shù)加起來(lái)的總和。
當(dāng)一個(gè) DOM 在兩個(gè)渲染幀之間產(chǎn)生了位移,就會(huì)觸發(fā) CLS(如圖所示)。
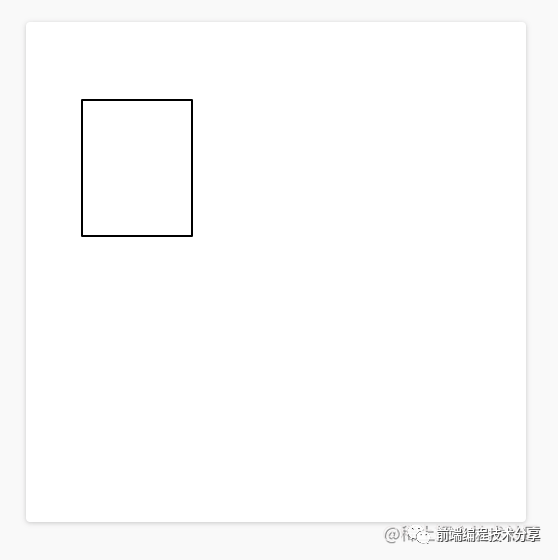
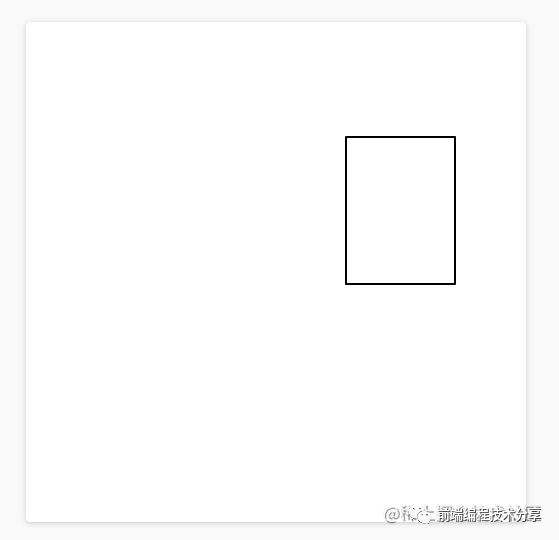
上圖中的矩形從左上角移動(dòng)到了右邊,這就算是一次布局偏移。同時(shí),在 CLS 中,有一個(gè)叫會(huì)話窗口的術(shù)語(yǔ):一個(gè)或多個(gè)快速連續(xù)發(fā)生的單次布局偏移,每次偏移相隔的時(shí)間少于 1 秒,且整個(gè)窗口的最大持續(xù)時(shí)長(zhǎng)為 5 秒。
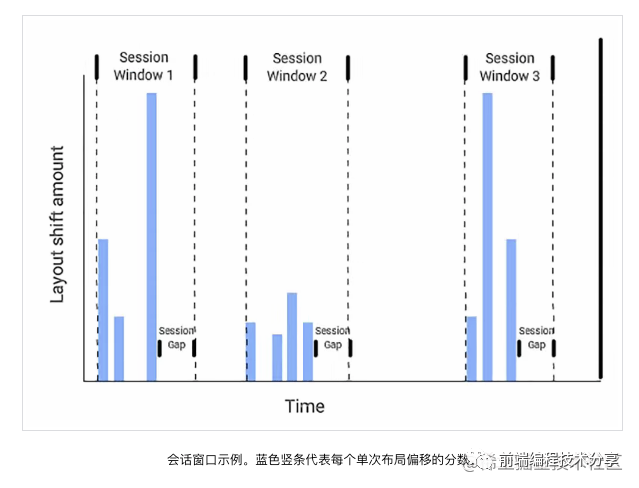
例如上圖中的第二個(gè)會(huì)話窗口,它里面有四次布局偏移,每一次偏移之間的間隔必須少于 1 秒,并且第一個(gè)偏移和最后一個(gè)偏移之間的時(shí)間不能超過(guò) 5 秒,這樣才能算是一次會(huì)話窗口。如果不符合這個(gè)條件,就算是一個(gè)新的會(huì)話窗口。可能有人會(huì)問(wèn),為什么要這樣規(guī)定?其實(shí)這是 chrome 團(tuán)隊(duì)根據(jù)大量的實(shí)驗(yàn)和研究得出的分析結(jié)果 Evolving the CLS metric[11]。
CLS 一共有三種計(jì)算方式:
1.累加2.取所有會(huì)話窗口的平均數(shù)3.取所有會(huì)話窗口中的最大值
累加
也就是把從頁(yè)面加載開始的所有布局偏移分?jǐn)?shù)加在一起。但是這種計(jì)算方式對(duì)生命周期長(zhǎng)的頁(yè)面不友好,頁(yè)面存留時(shí)間越長(zhǎng),CLS 分?jǐn)?shù)越高。
取所有會(huì)話窗口的平均數(shù)
這種計(jì)算方式不是按單個(gè)布局偏移為單位,而是以會(huì)話窗口為單位。將所有會(huì)話窗口的值相加再取平均值。但是這種計(jì)算方式也有缺點(diǎn)。
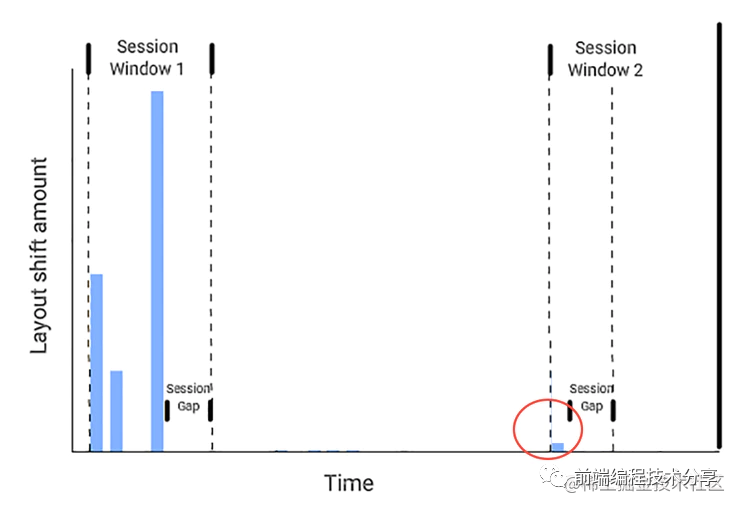
從上圖可以看出來(lái),第一個(gè)會(huì)話窗口產(chǎn)生了比較大的 CLS 分?jǐn)?shù),第二個(gè)會(huì)話窗口產(chǎn)生了比較小的 CLS 分?jǐn)?shù)。如果取它們的平均值來(lái)當(dāng)做 CLS 分?jǐn)?shù),則根本看不出來(lái)頁(yè)面的運(yùn)行狀況。原來(lái)頁(yè)面是早期偏移多,后期偏移少,現(xiàn)在的平均值無(wú)法反映出這種情況。
取所有會(huì)話窗口中的最大值
這種方式是目前最優(yōu)的計(jì)算方式,每次只取所有會(huì)話窗口的最大值,用來(lái)反映頁(yè)面布局偏移的最差情況。詳情請(qǐng)看 Evolving the CLS metric[12]。
下面是第三種計(jì)算方式的測(cè)量代碼:
let sessionValue = 0let sessionEntries = []const cls = {subType: 'layout-shift',name: 'layout-shift',type: 'performance',pageURL: getPageURL(),value: 0,}const entryHandler = (list) => {for (const entry of list.getEntries()) {// Only count layout shifts without recent user input.if (!entry.hadRecentInput) {const firstSessionEntry = sessionEntries[0]const lastSessionEntry = sessionEntries[sessionEntries.length - 1]// If the entry occurred less than 1 second after the previous entry and// less than 5 seconds after the first entry in the session, include the// entry in the current session. Otherwise, start a new session.if (sessionValue&& entry.startTime - lastSessionEntry.startTime < 1000&& entry.startTime - firstSessionEntry.startTime < 5000) {sessionValue += entry.valuesessionEntries.push(formatCLSEntry(entry))} else {sessionValue = entry.valuesessionEntries = [formatCLSEntry(entry)]}// If the current session value is larger than the current CLS value,// update CLS and the entries contributing to it.if (sessionValue > cls.value) {cls.value = sessionValuecls.entries = sessionEntriescls.startTime = performance.now()lazyReportCache(deepCopy(cls))}}}}const observer = new PerformanceObserver(entryHandler)observer.observe({ type: 'layout-shift', buffered: true })
在看完上面的文字描述后,再看代碼就好理解了。一次布局偏移的測(cè)量?jī)?nèi)容如下:
{duration: 0,entryType: "layout-shift",hadRecentInput: false,lastInputTime: 0,name: "",sources: (2) [LayoutShiftAttribution, LayoutShiftAttribution],startTime: 1176.199999999255,value: 0.000005752046026677329,}
代碼中的 value 字段就是布局偏移分?jǐn)?shù)。
DOMContentLoaded、load 事件
當(dāng)純 HTML 被完全加載以及解析時(shí),DOMContentLoaded 事件會(huì)被觸發(fā),不用等待 css、img、iframe 加載完。
當(dāng)整個(gè)頁(yè)面及所有依賴資源如樣式表和圖片都已完成加載時(shí),將觸發(fā) load 事件。
雖然這兩個(gè)性能指標(biāo)比較舊了,但是它們?nèi)匀荒芊从稠?yè)面的一些情況。對(duì)于它們進(jìn)行監(jiān)聽仍然是必要的。
import { lazyReportCache } from '../utils/report'['load', 'DOMContentLoaded'].forEach(type => onEvent(type))function onEvent(type) {function callback() {lazyReportCache({type: 'performance',subType: type.toLocaleLowerCase(),startTime: performance.now(),})window.removeEventListener(type, callback, true)}window.addEventListener(type, callback, true)}
首屏渲染時(shí)間
大多數(shù)情況下,首屏渲染時(shí)間可以通過(guò) load 事件獲取。除了一些特殊情況,例如異步加載的圖片和 DOM。
<script>setTimeout(() => {document.body.innerHTML = `<div><!-- 省略一堆代碼... --></div>`}, 3000)</script>
像這種情況就無(wú)法通過(guò) load 事件獲取首屏渲染時(shí)間了。這時(shí)我們需要通過(guò) MutationObserver[13] 來(lái)獲取首屏渲染時(shí)間。MutationObserver 在監(jiān)聽的 DOM 元素屬性發(fā)生變化時(shí)會(huì)觸發(fā)事件。
首屏渲染時(shí)間計(jì)算過(guò)程:
1.利用 MutationObserver 監(jiān)聽 document 對(duì)象,每當(dāng) DOM 元素屬性發(fā)生變更時(shí),觸發(fā)事件。2.判斷該 DOM 元素是否在首屏內(nèi),如果在,則在 requestAnimationFrame() 回調(diào)函數(shù)中調(diào)用 performance.now() 獲取當(dāng)前時(shí)間,作為它的繪制時(shí)間。3.將最后一個(gè) DOM 元素的繪制時(shí)間和首屏中所有加載的圖片時(shí)間作對(duì)比,將最大值作為首屏渲染時(shí)間。
監(jiān)聽 DOM
const next = window.requestAnimationFrame ? requestAnimationFrame : setTimeoutconst ignoreDOMList = ['STYLE', 'SCRIPT', 'LINK']observer = new MutationObserver(mutationList => {const entry = {children: [],}for (const mutation of mutationList) {if (mutation.addedNodes.length && isInScreen(mutation.target)) {// ...}}if (entry.children.length) {entries.push(entry)next(() => {entry.startTime = performance.now()})}})observer.observe(document, {childList: true,subtree: true,})
上面的代碼就是監(jiān)聽 DOM 變化的代碼,同時(shí)需要過(guò)濾掉 style、script、link 等標(biāo)簽。
判斷是否在首屏
一個(gè)頁(yè)面的內(nèi)容可能非常多,但用戶最多只能看見一屏幕的內(nèi)容。所以在統(tǒng)計(jì)首屏渲染時(shí)間的時(shí)候,需要限定范圍,把渲染內(nèi)容限定在當(dāng)前屏幕內(nèi)。
const viewportWidth = window.innerWidthconst viewportHeight = window.innerHeight// dom 對(duì)象是否在屏幕內(nèi)function isInScreen(dom) {const rectInfo = dom.getBoundingClientRect()if (rectInfo.left < viewportWidth && rectInfo.top < viewportHeight) {return true}return false}
使用 requestAnimationFrame() 獲取 DOM 繪制時(shí)間
當(dāng) DOM 變更觸發(fā) MutationObserver 事件時(shí),只是代表 DOM 內(nèi)容可以被讀取到,并不代表該 DOM 被繪制到了屏幕上。
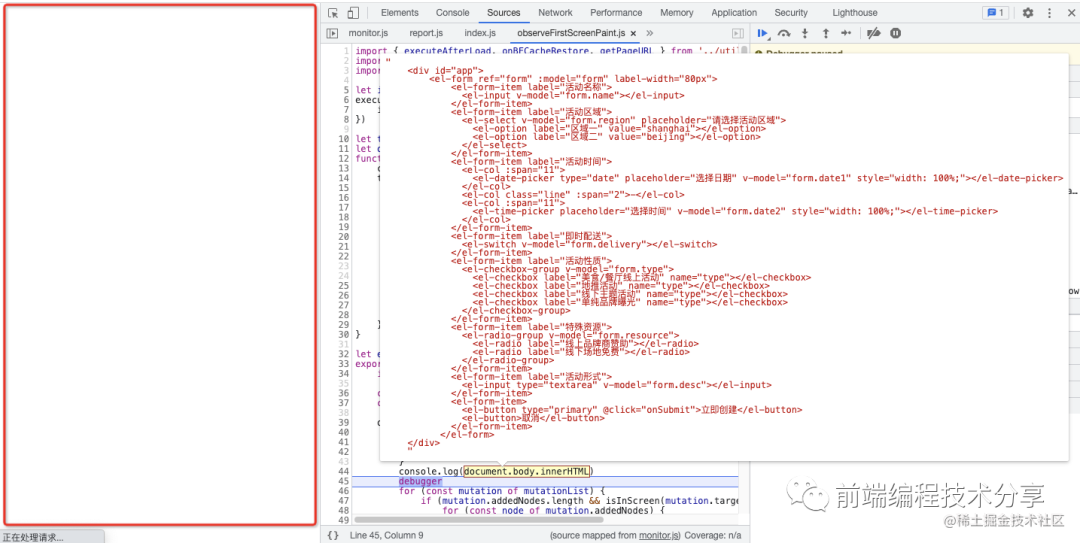
從上圖可以看出,當(dāng)觸發(fā) MutationObserver 事件時(shí),可以讀取到 document.body 上已經(jīng)有內(nèi)容了,但實(shí)際上左邊的屏幕并沒有繪制任何內(nèi)容。所以要調(diào)用 requestAnimationFrame() 在瀏覽器繪制成功后再獲取當(dāng)前時(shí)間作為 DOM 繪制時(shí)間。
和首屏內(nèi)的所有圖片加載時(shí)間作對(duì)比
function getRenderTime() {let startTime = 0entries.forEach(entry => {if (entry.startTime > startTime) {startTime = entry.startTime}})// 需要和當(dāng)前頁(yè)面所有加載圖片的時(shí)間做對(duì)比,取最大值// 圖片請(qǐng)求時(shí)間要小于 startTime,響應(yīng)結(jié)束時(shí)間要大于 startTimeperformance.getEntriesByType('resource').forEach(item => {if (item.initiatorType === 'img'&& item.fetchStart < startTime&& item.responseEnd > startTime) {startTime = item.responseEnd}})return startTime}
優(yōu)化
現(xiàn)在的代碼還沒優(yōu)化完,主要有兩點(diǎn)注意事項(xiàng):
1.什么時(shí)候上報(bào)渲染時(shí)間?2.如果兼容異步添加 DOM 的情況?
第一點(diǎn),必須要在 DOM 不再變化后再上報(bào)渲染時(shí)間,一般 load 事件觸發(fā)后,DOM 就不再變化了。所以我們可以在這個(gè)時(shí)間點(diǎn)進(jìn)行上報(bào)。
第二點(diǎn),可以在 LCP 事件觸發(fā)后再進(jìn)行上報(bào)。不管是同步還是異步加載的 DOM,它都需要進(jìn)行繪制,所以可以監(jiān)聽 LCP 事件,在該事件觸發(fā)后才允許進(jìn)行上報(bào)。
將以上兩點(diǎn)方案結(jié)合在一起,就有了以下代碼:
let isOnLoaded = falseexecuteAfterLoad(() => {isOnLoaded = true})let timerlet observerfunction checkDOMChange() {clearTimeout(timer)timer = setTimeout(() => {// 等 load、lcp 事件觸發(fā)后并且 DOM 樹不再變化時(shí),計(jì)算首屏渲染時(shí)間if (isOnLoaded && isLCPDone()) {observer && observer.disconnect()lazyReportCache({type: 'performance',subType: 'first-screen-paint',startTime: getRenderTime(),pageURL: getPageURL(),})entries = null} else {checkDOMChange()}}, 500)}
checkDOMChange() 代碼每次在觸發(fā) MutationObserver 事件時(shí)進(jìn)行調(diào)用,需要用防抖函數(shù)進(jìn)行處理。
接口請(qǐng)求耗時(shí)
接口請(qǐng)求耗時(shí)需要對(duì) XMLHttpRequest 和 fetch 進(jìn)行監(jiān)聽。
監(jiān)聽 XMLHttpRequest
originalProto.open = function newOpen(...args) {this.url = args[1]this.method = args[0]originalOpen.apply(this, args)}originalProto.send = function newSend(...args) {this.startTime = Date.now()const onLoadend = () => {this.endTime = Date.now()this.duration = this.endTime - this.startTimeconst { status, duration, startTime, endTime, url, method } = thisconst reportData = {status,duration,startTime,endTime,url,method: (method || 'GET').toUpperCase(),success: status >= 200 && status < 300,subType: 'xhr',type: 'performance',}lazyReportCache(reportData)this.removeEventListener('loadend', onLoadend, true)}this.addEventListener('loadend', onLoadend, true)originalSend.apply(this, args)}
如何判斷 XML 請(qǐng)求是否成功?可以根據(jù)他的狀態(tài)碼是否在 200~299 之間。如果在,那就是成功,否則失敗。
監(jiān)聽 fetch
const originalFetch = window.fetchfunction overwriteFetch() {window.fetch = function newFetch(url, config) {const startTime = Date.now()const reportData = {startTime,url,method: (config?.method || 'GET').toUpperCase(),subType: 'fetch',type: 'performance',}return originalFetch(url, config).then(res => {reportData.endTime = Date.now()reportData.duration = reportData.endTime - reportData.startTimeconst data = res.clone()reportData.status = data.statusreportData.success = data.oklazyReportCache(reportData)return res}).catch(err => {reportData.endTime = Date.now()reportData.duration = reportData.endTime - reportData.startTimereportData.status = 0reportData.success = falselazyReportCache(reportData)throw err})}}
對(duì)于 fetch,可以根據(jù)返回?cái)?shù)據(jù)中的的 ok 字段判斷請(qǐng)求是否成功,如果為 true 則請(qǐng)求成功,否則失敗。
注意,監(jiān)聽到的接口請(qǐng)求時(shí)間和 chrome devtool 上檢測(cè)到的時(shí)間可能不一樣。這是因?yàn)?chrome devtool 上檢測(cè)到的是 HTTP 請(qǐng)求發(fā)送和接口整個(gè)過(guò)程的時(shí)間。但是 xhr 和 fetch 是異步請(qǐng)求,接口請(qǐng)求成功后需要調(diào)用回調(diào)函數(shù)。事件觸發(fā)時(shí)會(huì)把回調(diào)函數(shù)放到消息隊(duì)列,然后瀏覽器再處理,這中間也有一個(gè)等待過(guò)程。
資源加載時(shí)間、緩存命中率
通過(guò) PerformanceObserver 可以監(jiān)聽 resource 和 navigation 事件,如果瀏覽器不支持 PerformanceObserver,還可以通過(guò) performance.getEntriesByType(entryType) 來(lái)進(jìn)行降級(jí)處理。
當(dāng) resource 事件觸發(fā)時(shí),可以獲取到對(duì)應(yīng)的資源列表,每個(gè)資源對(duì)象包含以下一些字段:
從這些字段中我們可以提取到一些有用的信息:
{name: entry.name, // 資源名稱subType: entryType,type: 'performance',sourceType: entry.initiatorType, // 資源類型duration: entry.duration, // 資源加載耗時(shí)dns: entry.domainLookupEnd - entry.domainLookupStart, // DNS 耗時(shí)tcp: entry.connectEnd - entry.connectStart, // 建立 tcp 連接耗時(shí)redirect: entry.redirectEnd - entry.redirectStart, // 重定向耗時(shí)ttfb: entry.responseStart, // 首字節(jié)時(shí)間protocol: entry.nextHopProtocol, // 請(qǐng)求協(xié)議responseBodySize: entry.encodedBodySize, // 響應(yīng)內(nèi)容大小responseHeaderSize: entry.transferSize - entry.encodedBodySize, // 響應(yīng)頭部大小resourceSize: entry.decodedBodySize, // 資源解壓后的大小isCache: isCache(entry), // 是否命中緩存startTime: performance.now(),}
判斷該資源是否命中緩存
在這些資源對(duì)象中有一個(gè) transferSize 字段,它表示獲取資源的大小,包括響應(yīng)頭字段和響應(yīng)數(shù)據(jù)的大小。如果這個(gè)值為 0,說(shuō)明是從緩存中直接讀取的(強(qiáng)制緩存)。如果這個(gè)值不為 0,但是 encodedBodySize 字段為 0,說(shuō)明它走的是協(xié)商緩存(encodedBodySize 表示請(qǐng)求響應(yīng)數(shù)據(jù) body 的大小)。
function isCache(entry) {// 直接從緩存讀取或 304return entry.transferSize === 0 || (entry.transferSize !== 0 && entry.encodedBodySize === 0)}
不符合以上條件的,說(shuō)明未命中緩存。然后將所有命中緩存的數(shù)據(jù)/總數(shù)據(jù)就能得出緩存命中率。
瀏覽器往返緩存 BFC(back/forward cache)
bfcache 是一種內(nèi)存緩存,它會(huì)將整個(gè)頁(yè)面保存在內(nèi)存中。當(dāng)用戶返回時(shí)可以馬上看到整個(gè)頁(yè)面,而不用再次刷新。據(jù)該文章 bfcache[14] 介紹,firfox 和 safari 一直支持 bfc,chrome 只有在高版本的移動(dòng)端瀏覽器支持。但我試了一下,只有 safari 瀏覽器支持,可能我的 firfox 版本不對(duì)。
但是 bfc 也是有缺點(diǎn)的,當(dāng)用戶返回并從 bfc 中恢復(fù)頁(yè)面時(shí),原來(lái)頁(yè)面的代碼不會(huì)再次執(zhí)行。為此,瀏覽器提供了一個(gè) pageshow 事件,可以把需要再次執(zhí)行的代碼放在里面。
window.addEventListener('pageshow', function(event) {// 如果該屬性為 true,表示是從 bfc 中恢復(fù)的頁(yè)面if (event.persisted) {console.log('This page was restored from the bfcache.');} else {console.log('This page was loaded normally.');}});
從 bfc 中恢復(fù)的頁(yè)面,我們也需要收集他們的 FP、FCP、LCP 等各種時(shí)間。
onBFCacheRestore(event => {requestAnimationFrame(() => {['first-paint', 'first-contentful-paint'].forEach(type => {lazyReportCache({startTime: performance.now() - event.timeStamp,name: type,subType: type,type: 'performance',pageURL: getPageURL(),bfc: true,})})})})
上面的代碼很好理解,在 pageshow 事件觸發(fā)后,用當(dāng)前時(shí)間減去事件觸發(fā)時(shí)間,這個(gè)時(shí)間差值就是性能指標(biāo)的繪制時(shí)間。注意,從 bfc 中恢復(fù)的頁(yè)面的這些性能指標(biāo),值一般都很小,一般在 10 ms 左右。所以要給它們加個(gè)標(biāo)識(shí)字段 bfc: true。這樣在做性能統(tǒng)計(jì)時(shí)可以對(duì)它們進(jìn)行忽略。
FPS
利用 requestAnimationFrame() 我們可以計(jì)算當(dāng)前頁(yè)面的 FPS。
const next = window.requestAnimationFrame? requestAnimationFrame : (callback) => { setTimeout(callback, 1000 / 60) }const frames = []export default function fps() {let frame = 0let lastSecond = Date.now()function calculateFPS() {frame++const now = Date.now()if (lastSecond + 1000 <= now) {// 由于 now - lastSecond 的單位是毫秒,所以 frame 要 * 1000const fps = Math.round((frame * 1000) / (now - lastSecond))frames.push(fps)frame = 0lastSecond = now}// 避免上報(bào)太快,緩存一定數(shù)量再上報(bào)if (frames.length >= 60) {report(deepCopy({frames,type: 'performace',subType: 'fps',}))frames.length = 0}next(calculateFPS)}calculateFPS()}
代碼邏輯如下:
1.先記錄一個(gè)初始時(shí)間,然后每次觸發(fā) requestAnimationFrame() 時(shí),就將幀數(shù)加 1。過(guò)去一秒后用幀數(shù)/流逝的時(shí)間就能得到當(dāng)前幀率。
當(dāng)連續(xù)三個(gè)低于 20 的 FPS 出現(xiàn)時(shí),我們可以斷定頁(yè)面出現(xiàn)了卡頓,詳情請(qǐng)看 如何監(jiān)控網(wǎng)頁(yè)的卡頓[15]。
export function isBlocking(fpsList, below = 20, last = 3) {let count = 0for (let i = 0; i < fpsList.length; i++) {if (fpsList[i] && fpsList[i] < below) {count++} else {count = 0}if (count >= last) {return true}}return false}
Vue 路由變更渲染時(shí)間
首屏渲染時(shí)間我們已經(jīng)知道如何計(jì)算了,但是如何計(jì)算 SPA 應(yīng)用的頁(yè)面路由切換導(dǎo)致的頁(yè)面渲染時(shí)間呢?本文用 Vue 作為示例,講一下我的思路。
export default function onVueRouter(Vue, router) {let isFirst = truelet startTimerouter.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {// 首次進(jìn)入頁(yè)面已經(jīng)有其他統(tǒng)計(jì)的渲染時(shí)間可用if (isFirst) {isFirst = falsereturn next()}// 給 router 新增一個(gè)字段,表示是否要計(jì)算渲染時(shí)間// 只有路由跳轉(zhuǎn)才需要計(jì)算router.needCalculateRenderTime = truestartTime = performance.now()next()})let timerVue.mixin({mounted() {if (!router.needCalculateRenderTime) returnthis.$nextTick(() => {// 僅在整個(gè)視圖都被渲染之后才會(huì)運(yùn)行的代碼const now = performance.now()clearTimeout(timer)timer = setTimeout(() => {router.needCalculateRenderTime = falselazyReportCache({type: 'performance',subType: 'vue-router-change-paint',duration: now - startTime,startTime: now,pageURL: getPageURL(),})}, 1000)})},})}
代碼邏輯如下:
1.監(jiān)聽路由鉤子,在路由切換時(shí)會(huì)觸發(fā) router.beforeEach() 鉤子,在該鉤子的回調(diào)函數(shù)里將當(dāng)前時(shí)間記為渲染開始時(shí)間。2.利用 Vue.mixin() 對(duì)所有組件的 mounted() 注入一個(gè)函數(shù)。每個(gè)函數(shù)都執(zhí)行一個(gè)防抖函數(shù)。3.當(dāng)最后一個(gè)組件的 mounted() 觸發(fā)時(shí),就代表該路由下的所有組件已經(jīng)掛載完畢。可以在 this.$nextTick() 回調(diào)函數(shù)中獲取渲染時(shí)間。
同時(shí),還要考慮到一個(gè)情況。不切換路由時(shí),也會(huì)有變更組件的情況,這時(shí)不應(yīng)該在這些組件的 mounted() 里進(jìn)行渲染時(shí)間計(jì)算。所以需要添加一個(gè) needCalculateRenderTime 字段,當(dāng)切換路由時(shí)將它設(shè)為 true,代表可以計(jì)算渲染時(shí)間了。
錯(cuò)誤數(shù)據(jù)采集
資源加載錯(cuò)誤
使用 addEventListener() 監(jiān)聽 error 事件,可以捕獲到資源加載失敗錯(cuò)誤。
// 捕獲資源加載失敗錯(cuò)誤 js css img...window.addEventListener('error', e => {const target = e.targetif (!target) returnif (target.src || target.href) {const url = target.src || target.hreflazyReportCache({url,type: 'error',subType: 'resource',startTime: e.timeStamp,html: target.outerHTML,resourceType: target.tagName,paths: e.path.map(item => item.tagName).filter(Boolean),pageURL: getPageURL(),})}}, true)
js 錯(cuò)誤
使用 window.onerror 可以監(jiān)聽 js 錯(cuò)誤。
// 監(jiān)聽 js 錯(cuò)誤window.onerror = (msg, url, line, column, error) => {lazyReportCache({msg,line,column,error: error.stack,subType: 'js',pageURL: url,type: 'error',startTime: performance.now(),})}
promise 錯(cuò)誤
使用 addEventListener() 監(jiān)聽 unhandledrejection 事件,可以捕獲到未處理的 promise 錯(cuò)誤。
// 監(jiān)聽 promise 錯(cuò)誤 缺點(diǎn)是獲取不到列數(shù)據(jù)window.addEventListener('unhandledrejection', e => {lazyReportCache({reason: e.reason?.stack,subType: 'promise',type: 'error',startTime: e.timeStamp,pageURL: getPageURL(),})})
sourcemap
一般生產(chǎn)環(huán)境的代碼都是經(jīng)過(guò)壓縮的,并且生產(chǎn)環(huán)境不會(huì)把 sourcemap 文件上傳。所以生產(chǎn)環(huán)境上的代碼報(bào)錯(cuò)信息是很難讀的。因此,我們可以利用 source-map[16] 來(lái)對(duì)這些壓縮過(guò)的代碼報(bào)錯(cuò)信息進(jìn)行還原。
當(dāng)代碼報(bào)錯(cuò)時(shí),我們可以獲取到對(duì)應(yīng)的文件名、行數(shù)、列數(shù):
{line: 1,column: 17,file: 'https:/www.xxx.com/bundlejs',}
然后調(diào)用下面的代碼進(jìn)行還原:
async function parse(error) {const mapObj = JSON.parse(getMapFileContent(error.url))const consumer = await new sourceMap.SourceMapConsumer(mapObj)// 將 webpack://source-map-demo/./src/index.js 文件中的 ./ 去掉const sources = mapObj.sources.map(item => format(item))// 根據(jù)壓縮后的報(bào)錯(cuò)信息得出未壓縮前的報(bào)錯(cuò)行列數(shù)和源碼文件const originalInfo = consumer.originalPositionFor({ line: error.line, column: error.column })// sourcesContent 中包含了各個(gè)文件的未壓縮前的源碼,根據(jù)文件名找出對(duì)應(yīng)的源碼const originalFileContent = mapObj.sourcesContent[sources.indexOf(originalInfo.source)]return {file: originalInfo.source,content: originalFileContent,line: originalInfo.line,column: originalInfo.column,msg: error.msg,error: error.error}}function format(item) {return item.replace(/(\.\/)*/g, '')}function getMapFileContent(url) {return fs.readFileSync(path.resolve(__dirname, `./maps/${url.split('/').pop()}.map`), 'utf-8')}
每次項(xiàng)目打包時(shí),如果開啟了 sourcemap,那么每一個(gè) js 文件都會(huì)有一個(gè)對(duì)應(yīng)的 map 文件。
bundle.jsbundle.js.map
這時(shí) js 文件放在靜態(tài)服務(wù)器上供用戶訪問(wèn),map 文件存儲(chǔ)在服務(wù)器,用于還原錯(cuò)誤信息。source-map 庫(kù)可以根據(jù)壓縮過(guò)的代碼報(bào)錯(cuò)信息還原出未壓縮前的代碼報(bào)錯(cuò)信息。例如壓縮后報(bào)錯(cuò)位置為 1 行 47 列,還原后真正的位置可能為 4 行 10 列。除了位置信息,還可以獲取到源碼原文。

上圖就是一個(gè)代碼報(bào)錯(cuò)還原后的示例。鑒于這部分內(nèi)容不屬于 SDK 的范圍,所以我另開了一個(gè) 倉(cāng)庫(kù)[17] 來(lái)做這個(gè)事,有興趣可以看看。
Vue 錯(cuò)誤
利用 window.onerror 是捕獲不到 Vue 錯(cuò)誤的,它需要使用 Vue 提供的 API 進(jìn)行監(jiān)聽。
Vue.config.errorHandler = (err, vm, info) => {// 將報(bào)錯(cuò)信息打印到控制臺(tái)console.error(err)lazyReportCache({info,error: err.stack,subType: 'vue',type: 'error',startTime: performance.now(),pageURL: getPageURL(),})}
行為數(shù)據(jù)采集
PV、UV
PV(page view) 是頁(yè)面瀏覽量,UV(Unique visitor)用戶訪問(wèn)量。PV 只要訪問(wèn)一次頁(yè)面就算一次,UV 同一天內(nèi)多次訪問(wèn)只算一次。
對(duì)于前端來(lái)說(shuō),只要每次進(jìn)入頁(yè)面上報(bào)一次 PV 就行,UV 的統(tǒng)計(jì)放在服務(wù)端來(lái)做,主要是分析上報(bào)的數(shù)據(jù)來(lái)統(tǒng)計(jì)得出 UV。
export default function pv() {lazyReportCache({type: 'behavior',subType: 'pv',startTime: performance.now(),pageURL: getPageURL(),referrer: document.referrer,uuid: getUUID(),})}
頁(yè)面停留時(shí)長(zhǎng)
用戶進(jìn)入頁(yè)面記錄一個(gè)初始時(shí)間,用戶離開頁(yè)面時(shí)用當(dāng)前時(shí)間減去初始時(shí)間,就是用戶停留時(shí)長(zhǎng)。這個(gè)計(jì)算邏輯可以放在 beforeunload 事件里做。
export default function pageAccessDuration() {onBeforeunload(() => {report({type: 'behavior',subType: 'page-access-duration',startTime: performance.now(),pageURL: getPageURL(),uuid: getUUID(),}, true)})}
頁(yè)面訪問(wèn)深度
記錄頁(yè)面訪問(wèn)深度是很有用的,例如不同的活動(dòng)頁(yè)面 a 和 b。a 平均訪問(wèn)深度只有 50%,b 平均訪問(wèn)深度有 80%,說(shuō)明 b 更受用戶喜歡,根據(jù)這一點(diǎn)可以有針對(duì)性的修改 a 活動(dòng)頁(yè)面。
除此之外還可以利用訪問(wèn)深度以及停留時(shí)長(zhǎng)來(lái)鑒別電商刷單。例如有人進(jìn)來(lái)頁(yè)面后一下就把頁(yè)面拉到底部然后等待一段時(shí)間后購(gòu)買,有人是慢慢的往下滾動(dòng)頁(yè)面,最后再購(gòu)買。雖然他們?cè)陧?yè)面的停留時(shí)間一樣,但明顯第一個(gè)人更像是刷單的。
頁(yè)面訪問(wèn)深度計(jì)算過(guò)程稍微復(fù)雜一點(diǎn):
1.用戶進(jìn)入頁(yè)面時(shí),記錄當(dāng)前時(shí)間、scrollTop 值、頁(yè)面可視高度、頁(yè)面總高度。2.用戶滾動(dòng)頁(yè)面的那一刻,會(huì)觸發(fā) scroll 事件,在回調(diào)函數(shù)中用第一點(diǎn)得到的數(shù)據(jù)算出頁(yè)面訪問(wèn)深度和停留時(shí)長(zhǎng)。3.當(dāng)用戶滾動(dòng)頁(yè)面到某一點(diǎn)時(shí),停下繼續(xù)觀看頁(yè)面。這時(shí)記錄當(dāng)前時(shí)間、scrollTop 值、頁(yè)面可視高度、頁(yè)面總高度。4.重復(fù)第二點(diǎn)...
具體代碼請(qǐng)看:
let timerlet startTime = 0let hasReport = falselet pageHeight = 0let scrollTop = 0let viewportHeight = 0export default function pageAccessHeight() {window.addEventListener('scroll', onScroll)onBeforeunload(() => {const now = performance.now()report({startTime: now,duration: now - startTime,type: 'behavior',subType: 'page-access-height',pageURL: getPageURL(),value: toPercent((scrollTop + viewportHeight) / pageHeight),uuid: getUUID(),}, true)})// 頁(yè)面加載完成后初始化記錄當(dāng)前訪問(wèn)高度、時(shí)間executeAfterLoad(() => {startTime = performance.now()pageHeight = document.documentElement.scrollHeight || document.body.scrollHeightscrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTopviewportHeight = window.innerHeight})}function onScroll() {clearTimeout(timer)const now = performance.now()if (!hasReport) {hasReport = truelazyReportCache({startTime: now,duration: now - startTime,type: 'behavior',subType: 'page-access-height',pageURL: getPageURL(),value: toPercent((scrollTop + viewportHeight) / pageHeight),uuid: getUUID(),})}timer = setTimeout(() => {hasReport = falsestartTime = nowpageHeight = document.documentElement.scrollHeight || document.body.scrollHeightscrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTopviewportHeight = window.innerHeight}, 500)}function toPercent(val) {if (val >= 1) return '100%'return (val * 100).toFixed(2) + '%'}
用戶點(diǎn)擊
利用 addEventListener() 監(jiān)聽 mousedown、touchstart 事件,我們可以收集用戶每一次點(diǎn)擊區(qū)域的大小,點(diǎn)擊坐標(biāo)在整個(gè)頁(yè)面中的具體位置,點(diǎn)擊元素的內(nèi)容等信息。
export default function onClick() {['mousedown', 'touchstart'].forEach(eventType => {let timerwindow.addEventListener(eventType, event => {clearTimeout(timer)timer = setTimeout(() => {const target = event.targetconst { top, left } = target.getBoundingClientRect()lazyReportCache({top,left,eventType,pageHeight: document.documentElement.scrollHeight || document.body.scrollHeight,scrollTop: document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop,type: 'behavior',subType: 'click',target: target.tagName,paths: event.path?.map(item => item.tagName).filter(Boolean),startTime: event.timeStamp,pageURL: getPageURL(),outerHTML: target.outerHTML,innerHTML: target.innerHTML,width: target.offsetWidth,height: target.offsetHeight,viewport: {width: window.innerWidth,height: window.innerHeight,},uuid: getUUID(),})}, 500)})})}
頁(yè)面跳轉(zhuǎn)
利用 addEventListener() 監(jiān)聽 popstate、hashchange 頁(yè)面跳轉(zhuǎn)事件。需要注意的是調(diào)用history.pushState()或history.replaceState()不會(huì)觸發(fā)popstate事件。只有在做出瀏覽器動(dòng)作時(shí),才會(huì)觸發(fā)該事件,如用戶點(diǎn)擊瀏覽器的回退按鈕(或者在Javascript代碼中調(diào)用history.back()或者history.forward()方法)。同理,hashchange 也一樣。
export default function pageChange() {let from = ''window.addEventListener('popstate', () => {const to = getPageURL()lazyReportCache({from,to,type: 'behavior',subType: 'popstate',startTime: performance.now(),uuid: getUUID(),})from = to}, true)let oldURL = ''window.addEventListener('hashchange', event => {const newURL = event.newURLlazyReportCache({from: oldURL,to: newURL,type: 'behavior',subType: 'hashchange',startTime: performance.now(),uuid: getUUID(),})oldURL = newURL}, true)}
Vue 路由變更
Vue 可以利用 router.beforeEach 鉤子進(jìn)行路由變更的監(jiān)聽。
export default function onVueRouter(router) {router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {// 首次加載頁(yè)面不用統(tǒng)計(jì)if (!from.name) {return next()}const data = {params: to.params,query: to.query,}lazyReportCache({data,name: to.name || to.path,type: 'behavior',subType: ['vue-router-change', 'pv'],startTime: performance.now(),from: from.fullPath,to: to.fullPath,uuid: getUUID(),})next()})}
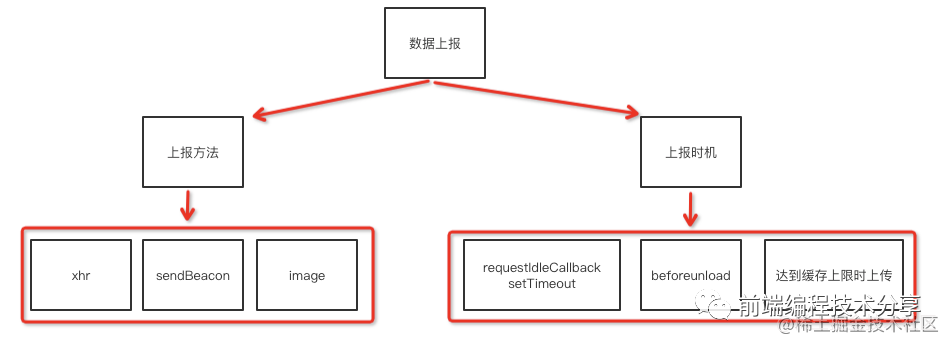
數(shù)據(jù)上報(bào)
上報(bào)方法
數(shù)據(jù)上報(bào)可以使用以下幾種方式:
?sendBeacon[18]?XMLHttpRequest[19]?image
我寫的簡(jiǎn)易 SDK 采用的是第一、第二種方式相結(jié)合的方式進(jìn)行上報(bào)。利用 sendBeacon 來(lái)進(jìn)行上報(bào)的優(yōu)勢(shì)非常明顯。
使用
sendBeacon()方法會(huì)使用戶代理在有機(jī)會(huì)時(shí)異步地向服務(wù)器發(fā)送數(shù)據(jù),同時(shí)不會(huì)延遲頁(yè)面的卸載或影響下一導(dǎo)航的載入性能。這就解決了提交分析數(shù)據(jù)時(shí)的所有的問(wèn)題:數(shù)據(jù)可靠,傳輸異步并且不會(huì)影響下一頁(yè)面的加載。
在不支持 sendBeacon 的瀏覽器下我們可以使用 XMLHttpRequest 來(lái)進(jìn)行上報(bào)。一個(gè) HTTP 請(qǐng)求包含發(fā)送和接收兩個(gè)步驟。其實(shí)對(duì)于上報(bào)來(lái)說(shuō),我們只要確保能發(fā)出去就可以了。也就是發(fā)送成功了就行,接不接收響應(yīng)無(wú)所謂。為此,我做了個(gè)實(shí)驗(yàn),在 beforeunload 用 XMLHttpRequest 傳送了 30kb 的數(shù)據(jù)(一般的待上報(bào)數(shù)據(jù)很少會(huì)有這么大),換了不同的瀏覽器,都可以成功發(fā)出去。當(dāng)然,這和硬件性能、網(wǎng)絡(luò)狀態(tài)也是有關(guān)聯(lián)的。
上報(bào)時(shí)機(jī)
上報(bào)時(shí)機(jī)有三種:
1.采用 requestIdleCallback/setTimeout 延時(shí)上報(bào)。2.在 beforeunload 回調(diào)函數(shù)里上報(bào)。3.緩存上報(bào)數(shù)據(jù),達(dá)到一定數(shù)量后再上報(bào)。
建議將三種方式結(jié)合一起上報(bào):
1.先緩存上報(bào)數(shù)據(jù),緩存到一定數(shù)量后,利用 requestIdleCallback/setTimeout 延時(shí)上報(bào)。2.在頁(yè)面離開時(shí)統(tǒng)一將未上報(bào)的數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行上報(bào)。
總結(jié)
僅看理論知識(shí)是比較難以理解的,為此我結(jié)合本文所講的技術(shù)要點(diǎn)寫了一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的監(jiān)控 SDK[20],可以用它來(lái)寫一些簡(jiǎn)單的 DEMO,幫助加深理解。再結(jié)合本文一起閱讀,效果更好。
我組建了一個(gè)氛圍特別好的 Node.js 社群,里面有很多 Node.js小伙伴,如果你對(duì)Node.js學(xué)習(xí)感興趣的話(后續(xù)有計(jì)劃也可以),我們可以一起進(jìn)行Node.js相關(guān)的交流、學(xué)習(xí)、共建。下方加 考拉 好友回復(fù)「Node」即可。

“分享、點(diǎn)贊、在看” 支持一波??
參考資料
性能監(jiān)控
?Performance API[21]?PerformanceResourceTiming[22]?Using_the_Resource_Timing_API[23]?PerformanceTiming[24]?Metrics[25]?evolving-cls[26]?custom-metrics[27]?web-vitals[28]?PerformanceObserver[29]?Element_timing_API[30]?PerformanceEventTiming[31]?Timing-Allow-Origin[32]?bfcache[33]?MutationObserver[34]?XMLHttpRequest[35]?如何監(jiān)控網(wǎng)頁(yè)的卡頓[36]?sendBeacon[37]
錯(cuò)誤監(jiān)控
?noerror[38]?source-map[39]
行為監(jiān)控
?popstate[40]?hashchange[41]
References
[1] 監(jiān)控 SDK: https://github.com/woai3c/monitor-demo[2] 生命周期狀態(tài): https://developers.google.com/web/updates/2018/07/page-lifecycle-api[3] PerformanceObserver: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/PerformanceObserver[4] 首次開始加載: https://w3c.github.io/hr-time/#timeorigin-attribute[5] 圖像或文本塊: https://web.dev/lcp/#what-elements-are-considered[6] url(): https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/CSS/url()[7] CSS 漸變: https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/CSS/CSS_Images/Using_CSS_gradients[8] 塊級(jí)元素: https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/HTML/Block-level_elements[9] 生命周期狀態(tài): https://developers.google.com/web/updates/2018/07/page-lifecycle-api[10] 影響分?jǐn)?shù): https://github.com/WICG/layout-instability#Impact-Fraction[11] Evolving the CLS metric: https://web.dev/evolving-cls/[12] Evolving the CLS metric: https://web.dev/evolving-cls/[13] MutationObserver: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/MutationObserver/MutationObserver[14] bfcache: https://web.dev/bfcache/[15] 如何監(jiān)控網(wǎng)頁(yè)的卡頓: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/39292837[16] source-map: https://github.com/mozilla/source-map[17] 倉(cāng)庫(kù): https://github.com/woai3c/source-map-demo[18] sendBeacon: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Navigator/sendBeacon[19] XMLHttpRequest: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/XMLHttpRequest[20] 監(jiān)控 SDK: https://github.com/woai3c/monitor-demo[21] Performance API: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Performance_API[22] PerformanceResourceTiming: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/PerformanceResourceTiming[23] Using_the_Resource_Timing_API: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Resource_Timing_API/Using_the_Resource_Timing_API[24] PerformanceTiming: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/PerformanceTiming[25] Metrics: https://web.dev/metrics/[26] evolving-cls: https://web.dev/evolving-cls/[27] custom-metrics: https://web.dev/custom-metrics/[28] web-vitals: https://github.com/GoogleChrome/web-vitals[29] PerformanceObserver: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/PerformanceObserver[30] Element_timing_API: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Element_timing_API[31] PerformanceEventTiming: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/PerformanceEventTiming[32] Timing-Allow-Origin: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Timing-Allow-Origin[33] bfcache: https://web.dev/bfcache/[34] MutationObserver: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/MutationObserver[35] XMLHttpRequest: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/XMLHttpRequest[36] 如何監(jiān)控網(wǎng)頁(yè)的卡頓: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/39292837[37] sendBeacon: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Navigator/sendBeacon[38] noerror: https://github.com/joeyguo/noerror[39] source-map: https://github.com/mozilla/source-map[40] popstate: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Window/popstate_event[41] hashchange: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Window/hashchange_event
