解決前端常見問題:競態(tài)條件
大廠技術(shù)??高級前端??Node進階
點擊上方?程序員成長指北,關(guān)注公眾號
回復1,加入高級Node交流群
| 導語?競態(tài)條件一詞翻譯自英語 "race conditions"。當我們在開發(fā)前端 web 時,最常見的邏輯就是從后臺服務(wù)器獲取并處理數(shù)據(jù)然后渲染到瀏覽器頁面上,過程中有不少的細節(jié)需要注意,其中一個就是數(shù)據(jù)競態(tài)條件問題,本文會基于 React 并結(jié)合一個小 demo 來解釋何為競態(tài)條件,以及循序漸進地介紹解決競態(tài)條件方法。框架不同解決的方式會不一樣,但不影響理解競態(tài)條件。
獲取數(shù)據(jù)
下面是一個小 demo:前端獲取文章數(shù)據(jù),并渲染到頁面上
App.tsx
import React from 'react';
import { Routes, Route } from 'react-router-dom';
import Article from './Article';
function App() {
return (
<Routes>
<Route path="/articles/:articleId" element={<Article />} />
Routes>
);
}
export default App;
Article.tsx
import React from 'react';
import useArticleLoading from './useArticleLoading';
const Article = () => {
const { article, isLoading } = useArticleLoading();
if (!article || isLoading) {
return<div>Loading...div>;
}
return (
<div>
<p>{article.id}p>
<p>{article.title}p>
<p>{article.body}p>
div>
);
};
export default Article;
在上述的 Article 組件中,我們把相關(guān)的數(shù)據(jù)請求封裝到了自定義 hook "useArticleLoading" 中,為了頁面的使用體驗,我們要么顯示獲取的數(shù)據(jù),要么顯示加載中。這里加上了加載態(tài)的判斷。
useArticleLoading.tsx
import { useParams } from 'react-router-dom';
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
interface Article {
?id: number;
?title: string;
?body: string;
}
function useArticleLoading() {
?const { articleId } = useParams<{ articleId: string }>();
?const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);
?const [article, setArticle] = useStatenull>(null);
?useEffect(() => {
setIsLoading(true);
fetch(`https://get.a.article.com/articles/${articleId}`)
? ? ?.then((response) => {
? ? ? ?if (response.ok) {
? ? ? ? ?return response.json();
? ? ? ?}
? ? ? ?return Promise.reject();
? ? ?})
? ? ?.then((fetchedArticle: Article) => {
? ? ? ?setArticle(fetchedArticle);
? ? ?})
? ? ?.finally(() => {
? ? ? ?setIsLoading(false);
? ? ?});
?}, [articleId]);
?return {
? ?article,
? ?isLoading,
?};
}
export default useArticleLoading;
在這個自定義 hook 中,我們管理了加載態(tài)以及數(shù)據(jù)請求
當我們 url 訪問 /articles/1 時,會發(fā)出 get 請求獲取對應 articleId 為 1 的文章內(nèi)容
競態(tài)條件出現(xiàn)場景
上面是我們非常常見的獲取數(shù)據(jù)的方法,但是讓我們考慮以下情況(時間順序):
訪問 articles/1 查看第一個文章內(nèi)容
瀏覽器開始請求后臺服務(wù)器,獲取文章 1 的內(nèi)容
網(wǎng)絡(luò)連接出現(xiàn)問題
articles/1 請求未響應,數(shù)據(jù)未渲染到頁面中
不等待 articles/1 了,訪問 articles/2
瀏覽器開始請求后臺服務(wù)器,獲取文章 2 的內(nèi)容
網(wǎng)絡(luò)連接沒有問題
articles/2 請求立即響應了,數(shù)據(jù)渲染到頁面中
articles/1 的請求響應了
通過 setArticles (fetchedArticles) 覆蓋了當前的文章內(nèi)容
當前 url 應該顯示 articles/2,卻顯示了 articles/1
需要理解的一點就是,網(wǎng)絡(luò)請求的過程是復雜的,且響應時間是不確定的,訪問同一個目的地址,請求經(jīng)過的網(wǎng)絡(luò)鏈路不一定是一樣的路徑。所以先發(fā)出的請求不一定先響應,如果前端以先發(fā)請求先響應的規(guī)則來開發(fā)的話,那么就可能會導致錯誤的數(shù)據(jù)使用,這就是競態(tài)條件問題。
解決
解決方法也很簡單,當收到響應后,只要判斷當前數(shù)據(jù)是否需要,如果不是則忽略即可。
在 React 中可以很巧妙的通過 useEffect 的執(zhí)行機制來簡潔、方便地做到這點:
useArticlesLoading.tsx
useEffect(() => {
?let didCancel = false;
?setIsLoading(true);
?fetch(`https://get.a.article.com/articles/${articleId}`)
? ?.then((response) => {
? ? ?if (response.ok) {
? ? ? ?return response.json();
? ? ?}
? ? ?return Promise.reject();
? ?})
? ?.then((fetchedArticle: Article) => {
? ? ?if (!didCancel) {
? ? ? ?setArticle(fetchedArticle);
? ? ?}
? ?})
? ?.finally(() => {
? ? ?setIsLoading(false);
? ?});
?return () => {
? ?didCancel = true;
?}
}, [articleId]);
根據(jù) hook 的執(zhí)行機制:每次切換獲取新文章時,執(zhí)行 useEffect 返回的函數(shù),然后再重新執(zhí)行 hook,重新渲染。
現(xiàn)在 bug 不會再出現(xiàn)了:
訪問 articles/1 查看第一個文章內(nèi)容
瀏覽器開始請求后臺服務(wù)器,獲取文章 1 的內(nèi)容
網(wǎng)絡(luò)連接出現(xiàn)問題
articles/1 請求未響應,數(shù)據(jù)未渲染到頁面中
不等待 articles/1 了,訪問 articles/2
useArticleLoading 重新渲染執(zhí)行,重新渲染前執(zhí)行了上一次的 useEffect 返回函數(shù),把 didCancel 設(shè)置為 true
網(wǎng)絡(luò)連接沒有問題
articles/2 請求立即響應了,數(shù)據(jù)渲染到頁面中
articles/1 的請求響應了
由于 didCancel 變量,setArticles (fetchedArticles) 沒有執(zhí)行。
處理完后,當我們再次切換文章時,didCancel 為 true,就不會再處理上一個文章的數(shù)據(jù),以及 setArticles。
AbortController 解決
雖然上述通過變量的解決方案解決了問題,但它并不是最優(yōu)的。瀏覽器仍然等待請求完成,但忽略其結(jié)果。這樣仍然浪費占用著資源。為了改進這一點,我們可以使用 AbortController。
通過 AbortController,我們可以中止一個或多個請求。使用方法很簡單,創(chuàng)建 AbortController 實例,并在發(fā)出請求時使用它:
useEffect(() => {
const abortController = new AbortController();
setIsLoading(true);
fetch(`https://get.a.rticle.com/articles/${articleId}`, {
signal: abortController.signal,
})
.then((response) => {
if (response.ok) {
return response.json();
}
return Promise.reject();
})
.then((fetchedArticle: Article) => {
setArticle(fetchedArticle);
})
.finally(() => {
setIsLoading(false);
});
return () => {
abortController.abort();
};
}, [articleId]);
通過傳遞 abortController.signal,我們可以很容易的使用 abortController.abort() 來終止請求(也可以使用相同的 signal 傳遞給多個請求,這樣可以終止多個請求)
使用 abortController 后,再來看看效果:
訪問 articles/1
請求服務(wù)器獲取 articles/1 數(shù)據(jù)
不等待響應,再訪問 articles/2
重新渲染 hook,useEffect 執(zhí)行返回函數(shù),執(zhí)行 abortController.abort ()
請求服務(wù)器獲取 articles/2 數(shù)據(jù)
獲取到 articles/2 數(shù)據(jù)并渲染到頁面上
第一個文章從未完成加載,因為我們手動終止了請求
可以在開發(fā)工具中查看手動中斷的請求:
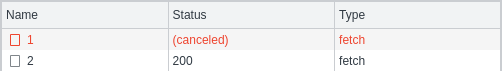
調(diào)用 abortController.abort () 有一個問題,就是其會導致 promise 被拒絕,可能會導致未捕獲的錯誤:

為了避免,我們可以加個捕獲錯誤處理:
useEffect(() => {
?const abortController = new AbortController();
?setIsLoading(true);
?fetch(`https://get.a.article.com/articles/${articleId}`, {
? ?signal: abortController.signal,
?})
? ?.then((response) => {
? ? ?if (response.ok) {
? ? ? ?return response.json();
? ? ?}
? ? ?return Promise.reject();
? ?})
? ?.then((fetchedArticle: Article) => {
? ? ?setArticle(fetchedArticle);
? ?})
? ?.catch(() => {
? ? ?if (abortController.signal.aborted) {
? ? ? ?console.log('The user aborted the request');
? ? ?} else {
? ? ? ?console.error('The request failed');
? ? ?}
? ?})
? ?.finally(() => {
? ? ?setIsLoading(false);
? ?});
?return () => {
? ?abortController.abort();
?};
}, [articleId]);
停止其他 promises
AbortController 不止可以停止異步請求,在函數(shù)中也是可以使用的:
function wait(time: number) {
return new Promise<void>((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, time);
});
}
wait(5000).then(() => {
console.log('5 seconds passed');
});
function wait(time: number, signal?: AbortSignal) {
return new Promise<void>((resolve, reject) => {
const timeoutId = setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, time);
signal?.addEventListener('abort', () => {
clearTimeout(timeoutId);
reject();
});
});
}
const abortController = new AbortController();
setTimeout(() => {
abortController.abort();
}, 1000);
wait(5000, abortController.signal)
.then(() => {
console.log('5 seconds passed');
})
.catch(() => {
console.log('Waiting was interrupted');
});
傳遞 signal 給 wait 來終止 promise。
其他
關(guān)于 AbortController 兼容性:
除了 IE,其他可以放心使用。
總結(jié)
本文討論了 React 中的競態(tài)條件,解釋了競態(tài)條件問題。為了解決這個問題,我們學習了 AbortController 背后的思想,并擴展了解決方案。除此之外,我們還學習了如何將 AbortController 用于其他目的。它需要我們更深入地挖掘并更好地理解 AbortController 是如何工作的。對于前端,可以選擇自己最合適的解決方案。
Node 社群
我組建了一個氛圍特別好的 Node.js 社群,里面有很多 Node.js小伙伴,如果你對Node.js學習感興趣的話(后續(xù)有計劃也可以),我們可以一起進行Node.js相關(guān)的交流、學習、共建。下方加 考拉 好友回復「Node」即可。
如果你覺得這篇內(nèi)容對你有幫助,我想請你幫我2個小忙:
1. 點個「在看」,讓更多人也能看到這篇文章 2. 訂閱官方博客?www.inode.club?讓我們一起成長 點贊和在看就是最大的支持??
