14 個(gè)你必須知道的JavaScript 函數(shù)
英文 | https://javascript.plainenglish.io/you-must-understand-these-14-javasript-functions-1f4fa1c620e2
翻譯 | 楊小愛
1、確定任意對象的具體類型
眾所周知,JavaScript 中有六種原始數(shù)據(jù)類型(Boolean、Number、String、Null、Undefined、Symbol)和一個(gè)對象數(shù)據(jù)類型。 但是你知道對象數(shù)據(jù)類型可以細(xì)分為很多種子類型嗎? 一個(gè)對象可能是數(shù)組、函數(shù)、map等,如果我們要獲取對象的具體類型,應(yīng)該怎么做呢?
代碼:
function toRawType (value) {let _toString = Object.prototype.toString;let str = _toString.call(value)return str.slice(8, -1)}
解釋
ECMAScript 有以下規(guī)則:

對于不同的對象,調(diào)用 Object.prototype.toString() 時(shí)會返回不同的結(jié)果。
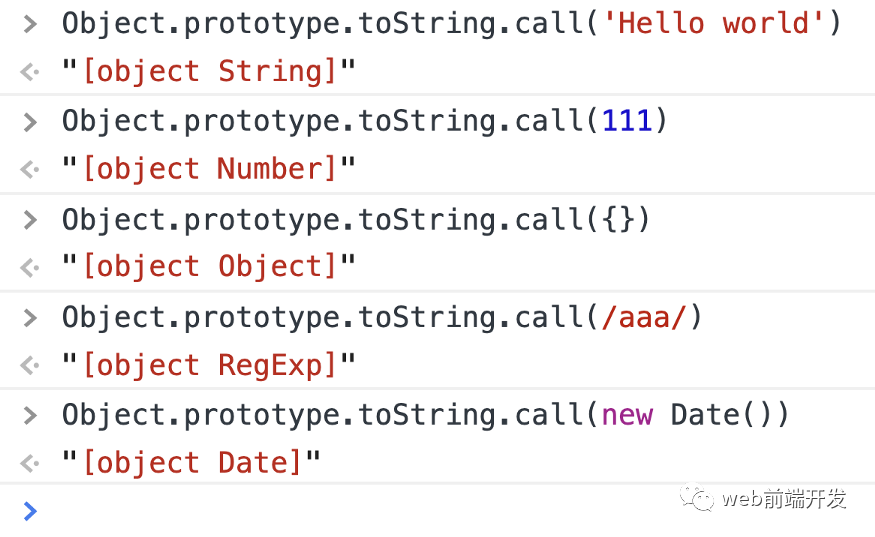
而且,Object.prototype.toString() 的返回值總是‘[object’+‘tag’+‘]’的格式。 如果我們只想要中間的標(biāo)簽,我們可以通過正則表達(dá)式或者String.prototype.slice()刪除兩邊的字符。
例子:
toRawType(null)// "Null"toRawType(/sdfsd/)//"RegExp"
2、緩存函數(shù)計(jì)算結(jié)果
如果有這樣的功能:
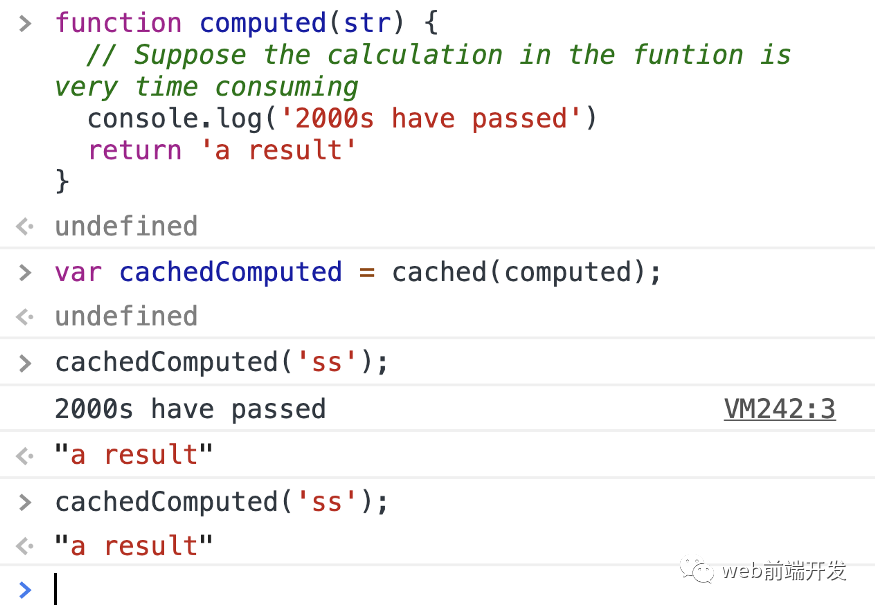
function computed(str) {// Suppose the calculation in the funtion is very time consumingconsole.log('2000s have passed')return 'a result'}
我們要緩存函數(shù)操作的結(jié)果, 稍后調(diào)用時(shí),如果參數(shù)相同,則不再執(zhí)行該函數(shù),而是直接返回緩存中的結(jié)果。 我們能做什么?
代碼:
function cached(fn){// Create an object to store the results returned after each function execution.const cache = Object.create(null);// Returns the wrapped functionreturn function cachedFn (str) {// If the cache is not hit, the function will be executedif ( !cache[str] ) {let result = fn(str);// Store the result of the function execution in the cachecache[str] = result;}return cache[str]}}
例子:
3、實(shí)現(xiàn)Array.prototype.map
這是 JavaScript 中一個(gè)有用的內(nèi)置方法,你應(yīng)該能夠自己實(shí)現(xiàn)此功能。
代碼:
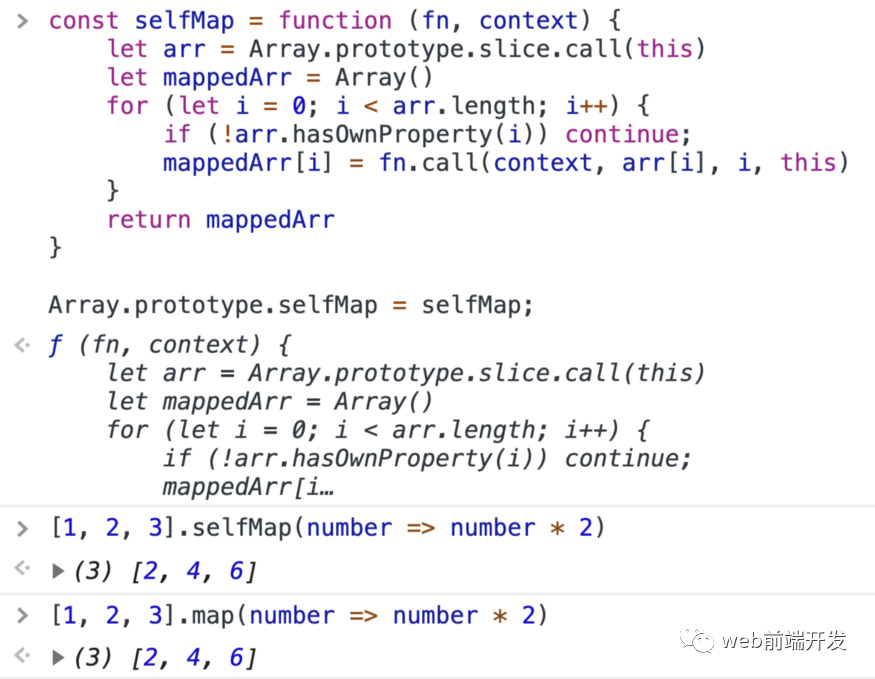
const selfMap = function (fn, context) {let arr = Array.prototype.slice.call(this)let mappedArr = Array()for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {if (!arr.hasOwnProperty(i)) continue;mappedArr[i] = fn.call(context, arr[i], i, this)}return mappedArr}Array.prototype.selfMap = selfMap;
例子:
4、實(shí)現(xiàn)Array.prototype.filter
這是 JavaScript 中一個(gè)有用的內(nèi)置方法,你應(yīng)該能夠自己實(shí)現(xiàn)此功能。
代碼:
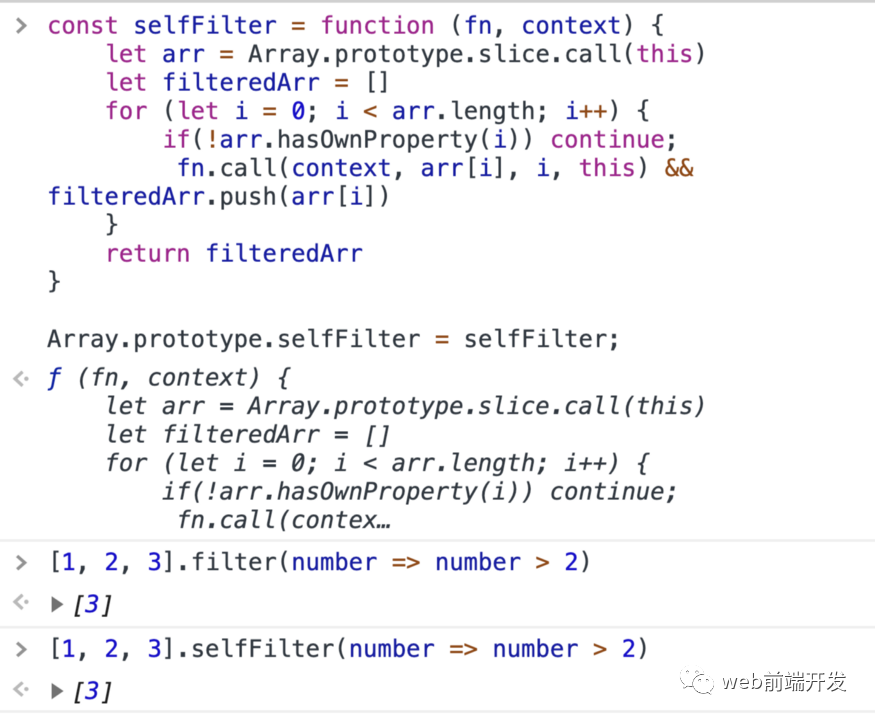
const selfFilter = function (fn, context) {let arr = Array.prototype.slice.call(this)let filteredArr = []for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {if(!arr.hasOwnProperty(i)) continue;fn.call(context, arr[i], i, this) && filteredArr.push(arr[i])}return filteredArr}Array.prototype.selfFilter = selfFilter;
例子:
5、實(shí)現(xiàn) Array.prototype.some
這是 JavaScript 中一個(gè)有用的內(nèi)置方法,你應(yīng)該能夠自己實(shí)現(xiàn)此功能。
代碼:
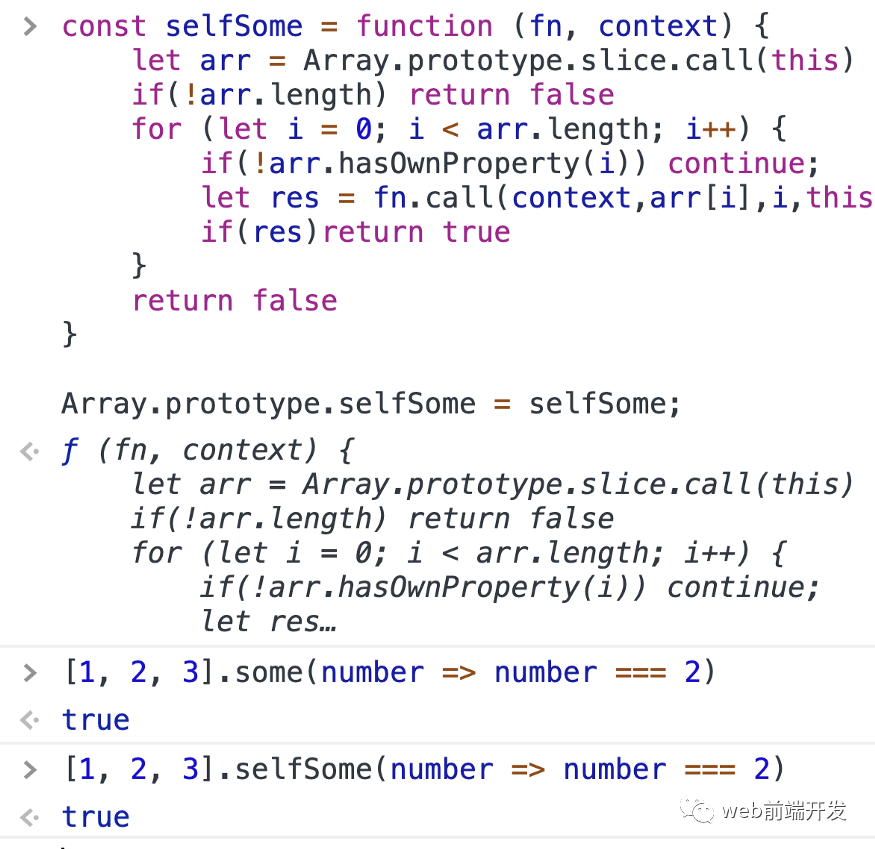
const selfSome = function (fn, context) {let arr = Array.prototype.slice.call(this)if(!arr.length) return falsefor (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {if(!arr.hasOwnProperty(i)) continue;let res = fn.call(context,arr[i],i,this)if(res)return true}return false}Array.prototype.selfSome = selfSome;
例子:
6、實(shí)現(xiàn) Array.prototype.reduce
這是 JavaScript 中一個(gè)有用的內(nèi)置方法,你應(yīng)該能夠自己實(shí)現(xiàn)此功能。
代碼:
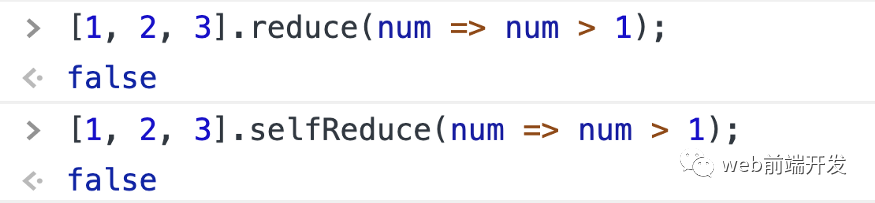
const selfReduce = function (fn, initialValue) {let arr = Array.prototype.slice.call(this)let reslet startIndexif (initialValue === undefined) {for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {if (!arr.hasOwnProperty(i)) continuestartIndex = ires = arr[i]break}} else {res = initialValue}for (let i = ++startIndex || 0; i < arr.length; i++) {if (!arr.hasOwnProperty(i)) continueres = fn.call(null, res, arr[i], i, this)}return res}Array.prototype.selfReduce = selfReduce;
例子:
7、實(shí)現(xiàn) Array.prototype.flat
代碼:
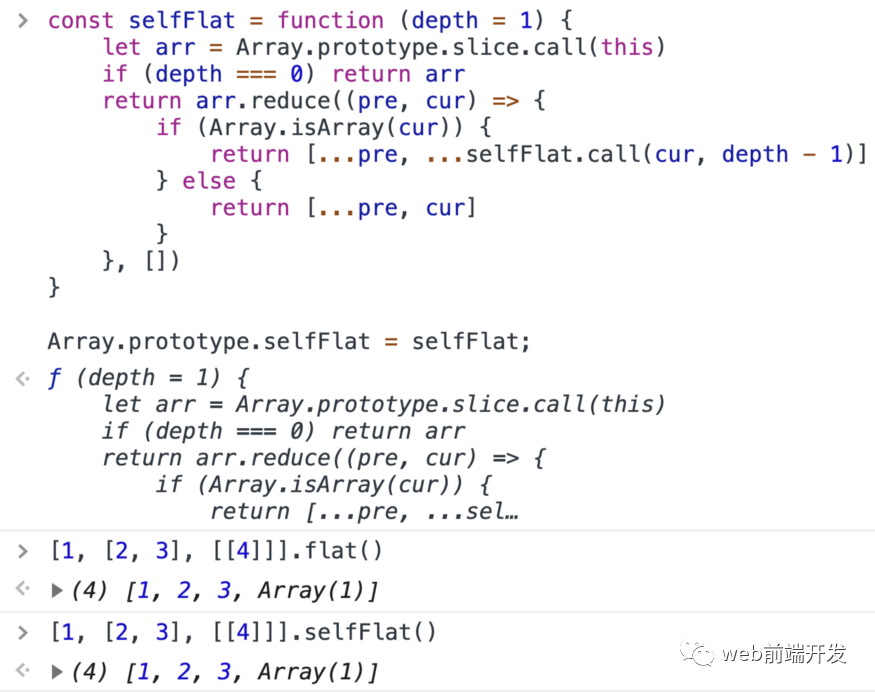
const selfFlat = function (depth = 1) {let arr = Array.prototype.slice.call(this)if (depth === 0) return arrreturn arr.reduce((pre, cur) => {if (Array.isArray(cur)) {return [...pre, ...selfFlat.call(cur, depth - 1)]} else {return [...pre, cur]}}, [])}Array.prototype.selfFlat = selfFlat;
例子:
8、柯里化
柯里化是一種將具有多個(gè)參數(shù)的函數(shù)評估為具有單個(gè)參數(shù)的函數(shù)序列的技術(shù)。
換句話說,當(dāng)一個(gè)函數(shù)不是一次接受所有參數(shù)時(shí),而是接受第一個(gè)參數(shù)并返回一個(gè)新函數(shù),該函數(shù)接受第二個(gè)參數(shù)并返回一個(gè)新函數(shù),該函數(shù)接受第三個(gè)參數(shù),依此類推,直到所有參數(shù)都已履行。
那就是我們將函數(shù)調(diào)用 add(1,2,3) 轉(zhuǎn)換為 add(1)(2)(3) 。 通過使用這種技術(shù),可以輕松地配置和重用小塊。
為什么有用?
柯里化可以幫助您避免一次又一次地傳遞相同的變量。
它有助于創(chuàng)建高階函數(shù),它對事件處理非常有幫助。
小部件可以輕松配置和重用。
讓我們看一個(gè)簡單的添加函數(shù)。 它接受三個(gè)操作數(shù)作為參數(shù),并返回所有三個(gè)操作數(shù)的總和作為結(jié)果。
function add(a,b,c){return a + b + c;}
你可以用太少(結(jié)果奇怪)或太多(多余的參數(shù)被忽略)來調(diào)用它。
add(1,2,3) --> 6add(1,2) --> NaNadd(1,2,3,4) --> 6 //Extra parameters will be ignored.
如何將現(xiàn)有函數(shù)轉(zhuǎn)換為 curried 版本?
代碼:
function curry(fn) {if (fn.length <= 1) return fn;const generator = (...args) => {if (fn.length === args.length) {return fn(...args)} else {return (...args2) => {return generator(...args, ...args2)}}}return generator}
例子:
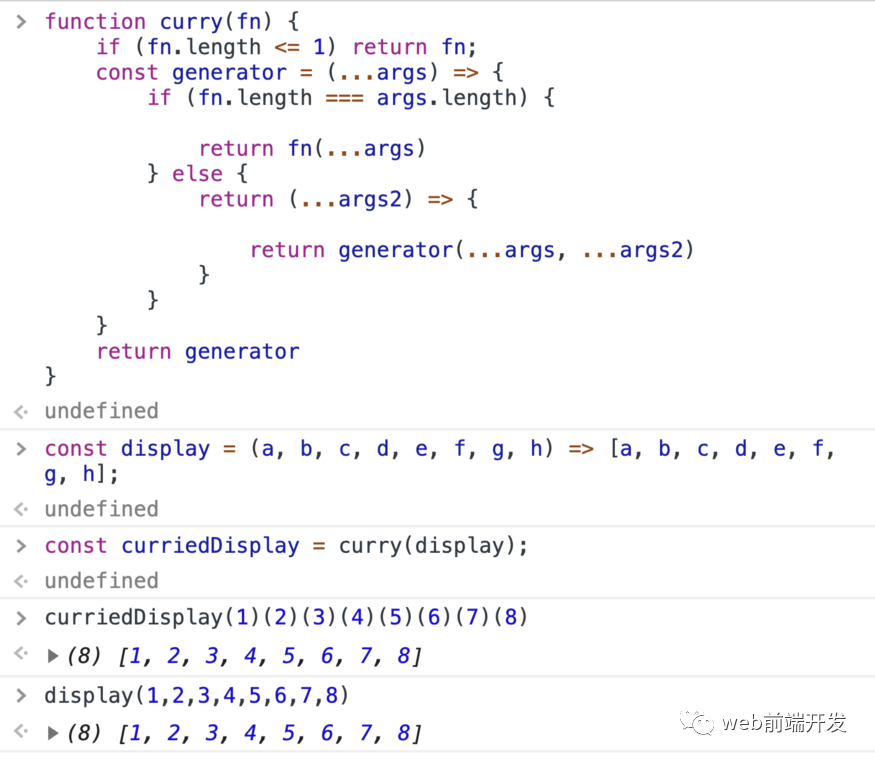
9、去抖動
去抖動只不過是減少不必要的耗時(shí)計(jì)算,以提高瀏覽器性能。在某些情況下,某些功能需要更多時(shí)間來執(zhí)行某個(gè)操作。例如,以電子商務(wù)網(wǎng)站上的搜索欄為例。
假設(shè)用戶想要獲得“Tutorix 學(xué)習(xí)套件”。他在搜索欄中鍵入產(chǎn)品的每個(gè)字符。輸入每個(gè)字符后,從瀏覽器到服務(wù)器都會進(jìn)行一次 Api 調(diào)用,以獲取所需的產(chǎn)品。由于他想要“Tutorix 學(xué)習(xí)套件”,用戶必須從瀏覽器到服務(wù)器進(jìn)行 17 次 Api 調(diào)用。
想象一個(gè)場景,當(dāng)數(shù)百萬人進(jìn)行相同的搜索從而調(diào)用數(shù)十億個(gè) Api 時(shí)。所以一次調(diào)用數(shù)十億個(gè) Api 肯定會導(dǎo)致瀏覽器性能變慢。為了減少這個(gè)缺點(diǎn),去抖動出現(xiàn)了。
在這種情況下,去抖動將在兩次擊鍵之間設(shè)置一個(gè)時(shí)間間隔,假設(shè)為 2 秒。如果兩次擊鍵之間的時(shí)間超過 2 秒,則只會進(jìn)行 Api 調(diào)用。在這 2 秒內(nèi),用戶可以輸入至少一些字符,從而減少 Api 調(diào)用的這些字符。由于 Api 調(diào)用減少,瀏覽器性能將提高。必須注意,每次擊鍵都會更新 Debouncing 功能。
代碼:
const debounce = (func, time = 17, options = {leading: true,context: null}) => {let timer;const _debounce = function (...args) {if (timer) {clearTimeout(timer)}if (options.leading && !timer) {timer = setTimeout(null, time)func.apply(options.context, args)}else{timer = setTimeout(() => {func.apply(options.context, args)timer = null}, time)}};_debounce.cancel = function () {clearTimeout(timer)timer = null};return _debounce};
10、 節(jié)流
節(jié)流將以這樣一種方式更改函數(shù),即它可以在一個(gè)時(shí)間間隔內(nèi)最多觸發(fā)一次。 例如,無論用戶單擊按鈕多少次,限制將在 1000 毫秒內(nèi)僅執(zhí)行一次該功能。

代碼:
const throttle = (func, time = 17, options = {leading: true,trailing: false,context: null}) => {let previous = new Date(0).getTime()let timer;const _throttle = function (...args) {let now = new Date().getTime();if (!options.leading) {if (timer) returntimer = setTimeout(() => {timer = nullfunc.apply(options.context, args)}, time)} else if (now - previous > time) {func.apply(options.context, args)previous = now} else if (options.trailing) {clearTimeout(timer)timer = setTimeout(() => {func.apply(options.context, args)}, time)}};_throttle.cancel = () => {previous = 0;clearTimeout(timer);timer = null};return _throttle};
11、 延遲加載圖片
延遲加載圖片意味著在網(wǎng)站上異步加載圖片——也就是說,在首屏內(nèi)容完全加載之后,甚至有條件地,只有當(dāng)它們出現(xiàn)在瀏覽器的視口中時(shí)。
這意味著如果用戶不一直向下滾動,則放置在頁面底部的圖像甚至不會被加載。
代碼:
// getBoundingClientRectlet imgList1 = [...document.querySelectorAll(".get_bounding_rect")]let num = imgList1.lengthlet lazyLoad1 = (function () {let count = 0return function () {let deleteIndexList = []imgList1.forEach((img,index) => {let rect = img.getBoundingClientRect()if (rect.top < window.innerHeight) {img.src = img.dataset.src// Add picture to delete list after loading successfullydeleteIndexList.push(index)count++if (count === num) {//When all pictures are loaded, unbind scroll eventdocument.removeEventListener('scroll',lazyLoad1)}}})// Delete loaded picturesimgList1 = imgList1.filter((_,index)=>!deleteIndexList.includes(index))}})()
12、數(shù)組隨機(jī)無序
我們經(jīng)常需要打亂一個(gè)數(shù)組。
代碼:
// Randomly select one of all elements after the current element to exchange with the current elementfunction shuffle(arr) {for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {let randomIndex = i + Math.floor(Math.random() * (arr.length - i));[arr[i], arr[randomIndex]] = [arr[randomIndex], arr[i]]}return arr}// Generate a new array, randomly take an element from the original array and put it into the new arrayfunction shuffle2(arr) {let _arr = []while (arr.length) {let randomIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * (arr.length))_arr.push(arr.splice(randomIndex, 1)[0])}return _arr}
例子:

13、單例模式
單例模式將特定對象的實(shí)例數(shù)限制為一個(gè),這個(gè)單一實(shí)例稱為單例模式。
單例在需要從單個(gè)中心位置協(xié)調(diào)系統(tǒng)范圍的操作的情況下很有用。 一個(gè)例子是數(shù)據(jù)庫連接池。 池管理整個(gè)應(yīng)用程序的所有數(shù)據(jù)庫連接的創(chuàng)建、銷毀和生命周期,確保沒有連接“丟失”。
單例減少了對全局變量的需求,這在 JavaScript 中尤為重要,因?yàn)樗拗屏嗣臻g污染和相關(guān)的名稱沖突風(fēng)險(xiǎn)。
代碼:
function proxy(func) {let instance;let handler = {construct(target, args) {if (!instance) {// Create an instance if there is not existinstance = Reflect.construct(func,args)}return instance}}return new Proxy(func, handler)}// examplefunction Person(name, age) {this.name = namethis.age = age}const SingletonPerson = proxy(Person)let person1 = new SingletonPerson('zhl', 22)let person2 = new SingletonPerson('cyw', 22)console.log(person1 === person2) // true
例子:
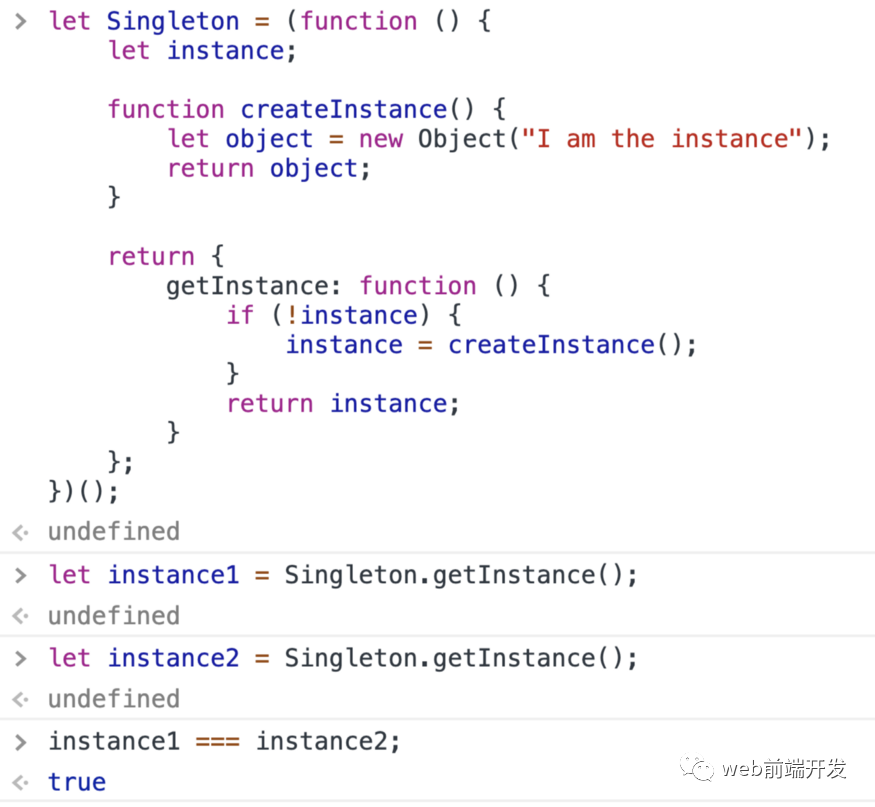
14、實(shí)現(xiàn) JSON.stringify
這是 JavaScript 中一個(gè)有用的內(nèi)置方法,你應(yīng)該能夠自己實(shí)現(xiàn)此功能。
代碼:
const isString = value => typeof value === 'string';const isSymbol = value => typeof value === 'symbol'const isUndefined = value => typeof value === 'undefined'const isDate = obj => Object.prototype.toString.call(obj) === '[object Date]'const isFunction = obj => Object.prototype.toString.call(obj) === '[object Function]';const isComplexDataType = value => (typeof value === 'object' || typeof value === 'function') && value !== null;const isValidBasicDataType = value => value !== undefined && !isSymbol(value);const isValidObj = obj => Array.isArray(obj) || Object.prototype.toString.call(obj) === '[object Object]';const isInfinity = value => value === Infinity || value === -Infinity// Symbol,undefined,function in array will become null// Infinity,NaN will also become nullconst processSpecialValueInArray = value =>isSymbol(value) || isFunction(value) || isUndefined(value) || isInfinity(value) || isNaN(value) ? null : value;// Handling property values according to JSON specificationconst processValue = value => {if (isInfinity(value) || isNaN(value)) {return null}if (isString(value)) {return `"${value}"`}return value};// obj.loop = objconst jsonStringify = (function () {// Closure + WeakMap prevent circular referenceslet wp = new WeakMap();//It is the function in the closure that recursively calls jsonstrify, not the jsonstrify function declared by constreturn function jsonStringify(obj) {if (wp.get(obj)) throw new TypeError('Converting circular structure to JSON');let res = "";if (isComplexDataType(obj)) {if (obj.toJSON) return obj.toJSON;if (!isValidObj(obj)) {return}wp.set(obj, obj);if (Array.isArray(obj)) {res += "[";let temp = [];obj.forEach((value) => {temp.push(isComplexDataType(value) && !isFunction(value) ?jsonStringify(value) :`${processSpecialValueInArray(value, true)}`)});res += `${temp.join(',')}]`} else {res += "{";let temp = [];Object.keys(obj).forEach((key) => {if (isComplexDataType(obj[key])) {if (isValidObj(obj[key])) {temp.push(`"${key}":${jsonStringify(obj[key])}`)} else if (isDate(obj[key])) {temp.push(`"${key}":"${obj[key].toISOString()}"`)} else if (!isFunction(obj[key])) {temp.push(`"${key}":{}`)}} else if (isValidBasicDataType(obj[key])) {temp.push(`"${key}":${processValue(obj[key])}`)}});res += `${temp.join(',')}}`}} else if (isSymbol(obj)) {return} else {return obj}return res}})();// examplelet s = Symbol('s')let obj = {str: "123",arr: [1, {e: 1}, s, () => {}, undefined,Infinity,NaN],obj: {a: 1},Infinity: -Infinity,nan: NaN,undef: undefined,symbol: s,date: new Date(),reg: /123/g,func: () => {},dom: document.querySelector('body'),};console.log(jsonStringify(obj));console.log(JSON.stringify(obj));
例子:

以上就是我與你分享的14個(gè)JavaScript的函數(shù),這些函數(shù)也是我們作為一名web前端開發(fā)人員必須要知道的,希望對你有用,如果覺得對你有幫助的話,請記得點(diǎn)贊我,關(guān)注我,并將它分享給你身邊做開發(fā)的朋友,也許能夠幫助到他。
學(xué)習(xí)更多技能
請點(diǎn)擊下方公眾號
![]()

