MapReduce源碼解析之MapTask
Mapper 源碼
分析了MapReduce提交任務過程中主要的切片計算之后,接下來就要看計算程序到達切片所在數(shù)據(jù)節(jié)點后,該如何進行工作。
public class Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> {
/**
* The Context passed on to the {@link Mapper} implementations.
*/
public abstract class Context
implements MapContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> {
}
/**
* Called once at the beginning of the task.
*/
protected void setup(Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// NOTHING
}
/**
* Called once for each key/value pair in the input split. Most applications
* should override this, but the default is the identity function.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void map(KEYIN key, VALUEIN value,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write((KEYOUT) key, (VALUEOUT) value);
}
/**
* Called once at the end of the task.
*/
protected void cleanup(Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// NOTHING
}
/**
* Expert users can override this method for more complete control over the
* execution of the Mapper.
* @param context
* @throws IOException
*/
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
setup(context);
try {
while (context.nextKeyValue()) {
map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context);
}
} finally {
cleanup(context);
}
}
}MapTask源碼
是否有Reduce
第一步先判斷是否有reduce任務,如果沒有,那么就單純只是一個map任務,走map分支。如果有reduce任務,那么就是67%map任務,有33%是排序任務,之前分析過排序?qū)τ诤罄m(xù)reduce拉取數(shù)據(jù)的影響極大。排序能夠極大的減少reduce任務IO次數(shù)。
public void run(final JobConf job, final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
this.umbilical = umbilical;
if (isMapTask()) {
// If there are no reducers then there won't be any sort. Hence the map
// phase will govern the entire attempt's progress.
if (conf.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {
mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 1.0f);
} else {
// If there are reducers then the entire attempt's progress will be
// split between the map phase (67%) and the sort phase (33%).
mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 0.667f);
sortPhase = getProgress().addPhase("sort", 0.333f);
}
}
TaskReporter reporter = startReporter(umbilical);
boolean useNewApi = job.getUseNewMapper();
initialize(job, getJobID(), reporter, useNewApi);
// check if it is a cleanupJobTask
if (jobCleanup) {
runJobCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (jobSetup) {
runJobSetupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (taskCleanup) {
runTaskCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (useNewApi) {
runNewMapper(job, splitMetaInfo, umbilical, reporter);
} else {
runOldMapper(job, splitMetaInfo, umbilical, reporter);
}
done(umbilical, reporter);
}Run方法
接下來我們就需要看任務運行的細節(jié)了。主要過程一般都會包含在try catch代碼塊中。其中調(diào)用了上述Mapper的run方法。整體流程是,初始化輸入,map計算,排序,然后輸出。
private <INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>
void runNewMapper(final JobConf job,
final TaskSplitIndex splitIndex,
final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
TaskReporter reporter
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException,
InterruptedException {
// make a task context so we can get the classes
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext taskContext =
new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl(job,
getTaskID(),
reporter);
// make a mapper
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> mapper =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getMapperClass(), job);
// make the input format
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE> inputFormat =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getInputFormatClass(), job);
// rebuild the input split
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit split = null;
split = getSplitDetails(new Path(splitIndex.getSplitLocation()),
splitIndex.getStartOffset());
LOG.info("Processing split: " + split);
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE> input =
new NewTrackingRecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE>
(split, inputFormat, reporter, taskContext);
job.setBoolean(JobContext.SKIP_RECORDS, isSkipping());
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter output = null;
// get an output object
if (job.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {
output =
new NewDirectOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
} else {
output = new NewOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.MapContext<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>
mapContext =
new MapContextImpl<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>(job, getTaskID(),
input, output,
committer,
reporter, split);
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>.Context
mapperContext =
new WrappedMapper<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>().getMapContext(
mapContext);
try {
input.initialize(split, mapperContext);
mapper.run(mapperContext);
mapPhase.complete();
setPhase(TaskStatus.Phase.SORT);
statusUpdate(umbilical);
input.close();
input = null;
output.close(mapperContext);
output = null;
} finally {
closeQuietly(input);
closeQuietly(output, mapperContext);
}
}獲取任務配置
通過獲取任務配置,得到Java編譯的class文件,后續(xù)則可以通過反射來創(chuàng)建我們所寫的Mapper類對象。然后會根據(jù)客戶端輸入的參數(shù),獲取輸入格式化數(shù)據(jù)類型InputFormat。
// make a task context so we can get the classes
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext taskContext =
new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl(job,
getTaskID(),
reporter);
// make a mapper
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> mapper =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getMapperClass(), job);
// make the input format
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE> inputFormat =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getInputFormatClass(), job);
// rebuild the input split
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit split = null;
split = getSplitDetails(new Path(splitIndex.getSplitLocation()),
splitIndex.getStartOffset());INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR 這個常量就是我們用來指定輸入數(shù)據(jù)類型的 KEY,通過此常量來獲取我們的輸入?yún)?shù)的配置。
public Class extends InputFormat> getInputFormatClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException;
public Class extends InputFormat> getInputFormatClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException {
return (Class extends InputFormat>)
conf.getClass(INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR, TextInputFormat.class);
}
public static final String INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR = "mapreduce.job.inputformat.class";獲取到自己相應的split(切片)
// rebuild the input split
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit split = null;
split = getSplitDetails(new Path(splitIndex.getSplitLocation()),
splitIndex.getStartOffset());
LOG.info("Processing split: " + split);記錄讀取器
我們知道m(xù)ap是從切片中一條一條讀取數(shù)據(jù)的,根據(jù)上述參數(shù)配置,及切片信息獲取,我們就可以創(chuàng)建一個對應的記錄讀取器。因為讀取數(shù)據(jù)的數(shù)據(jù)類型不一樣,記錄讀取器的讀取方式自然也會不一樣。因此就會出現(xiàn)各種各樣的默認實現(xiàn)類。
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE> input =
new NewTrackingRecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE>
(split, inputFormat, reporter, taskContext);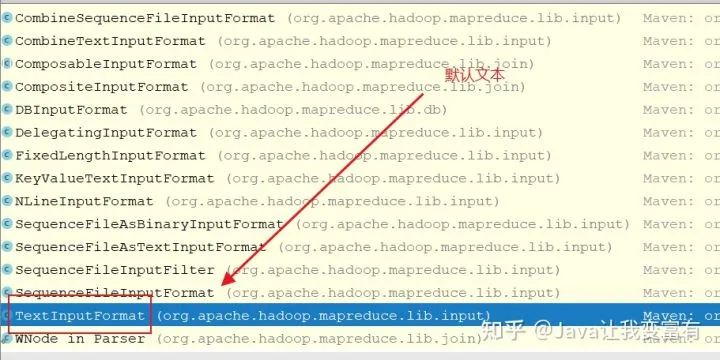
TextInputFormat獲取的是行記錄讀取器。
@Override
public RecordReader<LongWritable, Text>
createRecordReader(InputSplit split,
TaskAttemptContext context) {
String delimiter = context.getConfiguration().get(
"textinputformat.record.delimiter");
byte[] recordDelimiterBytes = null;
if (null != delimiter)
recordDelimiterBytes = delimiter.getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8);
return new LineRecordReader(recordDelimiterBytes);
}Map run方法
map的run方法是一個循環(huán)讀取context記錄的過程。實際上就是input中的LineRecordReader來獲取一條一條的記錄。
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.MapContext<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>
mapContext =
new MapContextImpl<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>(job, getTaskID(),
input, output,
committer,
reporter, split);
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>.Context
mapperContext =
new WrappedMapper<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>().getMapContext(
mapContext);public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
setup(context);
try {
while (context.nextKeyValue()) {
map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context);
}
} finally {
cleanup(context);
}
}輸入
LineRecordReader讀取下一條記錄。
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
long bytesInPrev = getInputBytes(fsStats);
boolean result = real.nextKeyValue();
long bytesInCurr = getInputBytes(fsStats);
if (result) {
inputRecordCounter.increment(1);
}
fileInputByteCounter.increment(bytesInCurr - bytesInPrev);
reporter.setProgress(getProgress());
return result;
}讀取過程中,一遍判斷改行記錄又沒有值,同時一邊賦值記錄下來。之后通過getCurrentKey和getCurrentValue來獲取當前取得的key和value。其中key對應的就是每一行字符串自己第一個字符面向源文件的偏移量。
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException {
if (key == null) {
key = new LongWritable();
}
key.set(pos);
if (value == null) {
value = new Text();
}
int newSize = 0;
// We always read one extra line, which lies outside the upper
// split limit i.e. (end - 1)
while (getFilePosition() <= end || in.needAdditionalRecordAfterSplit()) {
if (pos == 0) {
newSize = skipUtfByteOrderMark();
} else {
newSize = in.readLine(value, maxLineLength, maxBytesToConsume(pos));
pos += newSize;
}
if ((newSize == 0) || (newSize < maxLineLength)) {
break;
}
// line too long. try again
LOG.info("Skipped line of size " + newSize + " at pos " +
(pos - newSize));
}
if (newSize == 0) {
key = null;
value = null;
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
@Override
public LongWritable getCurrentKey() {
return key;
}
@Override
public Text getCurrentValue() {
return value;
}反觀初始化
map切片對應
上述過程中,保障分布式計算的代碼,實際上就在初始化這一步。通過獲取切片位置,以及長度,然后打開相應的文件,同時seek到切片的起始位置。每個map就對應到了自己得切皮上。
public void initialize(InputSplit genericSplit,
TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException {
FileSplit split = (FileSplit) genericSplit;
Configuration job = context.getConfiguration();
this.maxLineLength = job.getInt(MAX_LINE_LENGTH, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
start = split.getStart();
end = start + split.getLength();
final Path file = split.getPath();
// open the file and seek to the start of the split
final FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(job);
fileIn = fs.open(file);
CompressionCodec codec = new CompressionCodecFactory(job).getCodec(file);
if (null!=codec) {
isCompressedInput = true;
decompressor = CodecPool.getDecompressor(codec);
if (codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec) {
final SplitCompressionInputStream cIn =
((SplittableCompressionCodec)codec).createInputStream(
fileIn, decompressor, start, end,
SplittableCompressionCodec.READ_MODE.BYBLOCK);
in = new CompressedSplitLineReader(cIn, job,
this.recordDelimiterBytes);
start = cIn.getAdjustedStart();
end = cIn.getAdjustedEnd();
filePosition = cIn;
} else {
in = new SplitLineReader(codec.createInputStream(fileIn,
decompressor), job, this.recordDelimiterBytes);
filePosition = fileIn;
}
} else {
fileIn.seek(start);
in = new UncompressedSplitLineReader(
fileIn, job, this.recordDelimiterBytes, split.getLength());
filePosition = fileIn;
}
// If this is not the first split, we always throw away first record
// because we always (except the last split) read one extra line in
// next() method.
if (start != 0) {
start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, maxBytesToConsume(start));
}
this.pos = start;
}切斷的數(shù)據(jù)
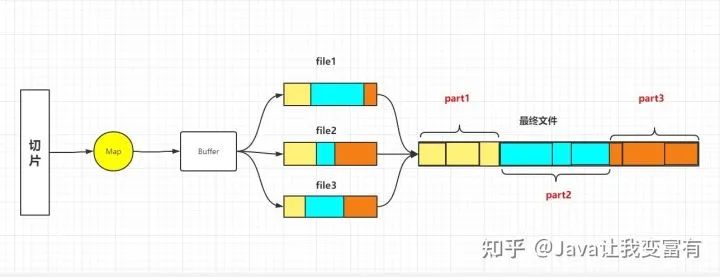
切斷數(shù)據(jù)的解決方式,就是每個不是第一個切片的split,肯定是可能出現(xiàn)第一行數(shù)據(jù)被截斷的。因此就直接讀取一行,然后丟棄,從第二行開始讀取。而每一個切片讀取到最后一行之后,并不直接結(jié)束讀取,而是去找下一個切片的第一行,把下一個切片丟棄的第一行拼接到自己的最后一行。這樣就完成了切斷數(shù)據(jù)拼接的工作,同時還能做到不重復,不丟失。不過此時如果下一個切片在不同的數(shù)據(jù)節(jié)點,那么就需要再遠程請求一次,單獨為了那一行數(shù)據(jù)。
// If this is not the first split, we always throw away first record
// because we always (except the last split) read one extra line in
// next() method.
if (start != 0) {
start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, maxBytesToConsume(start));
}
this.pos = start;根據(jù)reduce的操作
如下代碼可以看到我們曾經(jīng)提到的分區(qū)概念,有多少reduce就會有多少分區(qū)(partitions)。每個分區(qū)可以對應若干組。
NewOutputCollector(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobContext jobContext,
JobConf job,
TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
TaskReporter reporter
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
collector = createSortingCollector(job, reporter);
partitions = jobContext.getNumReduceTasks();
if (partitions > 1) {
partitioner = (org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(jobContext.getPartitionerClass(), job);
} else {
partitioner = new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>() {
@Override
public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numPartitions) {
return partitions - 1;
}
};
}
}判定分區(qū)
判定key的分區(qū)采用的哈希算法,和我們學習過的HashMap一樣。形同的key的hashcode一定相同,與上Integer的最大值獲取非負整數(shù),同時取模分區(qū)的大小,那么分區(qū)下標一定會落在這個范圍內(nèi),并且相同的key分區(qū)下標將會相同。
public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> {
/** Use {@link Object#hashCode()} to partition. */
public int getPartition(K key, V value,
int numReduceTasks) {
return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
}
}輸出
前邊我們知道輸入采取的LineRecordReader,輸出采用的是MapOutputCollector的collect方法。整個鏈條如下
// get an output object
if (job.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {
output =
new NewDirectOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
} else {
output = new NewOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
}MapTask的內(nèi)部私有類
private class NewOutputCollector<K,V>
extends org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter<K,V> {
private final MapOutputCollector<K,V> collector;
private final org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V> partitioner;
private final int partitions;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
NewOutputCollector(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobContext jobContext,
JobConf job,
TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
TaskReporter reporter
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
collector = createSortingCollector(job, reporter);
partitions = jobContext.getNumReduceTasks();
if (partitions > 1) {
partitioner = (org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(jobContext.getPartitionerClass(), job);
} else {
partitioner = new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>() {
@Override
public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numPartitions) {
return partitions - 1;
}
};
}
}
@Override
public void write(K key, V value) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
collector.collect(key, value,
partitioner.getPartition(key, value, partitions));
}
@Override
public void close(TaskAttemptContext context
) throws IOException,InterruptedException {
try {
collector.flush();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cnf) {
throw new IOException("can't find class ", cnf);
}
collector.close();
}
}map每次取到key,value的時候,都會調(diào)用寫入方法,如下所示。
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
setup(context);
try {
while (context.nextKeyValue()) {
map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context);
}
} finally {
cleanup(context);
}
}而寫入方法的內(nèi)部,調(diào)用的寫入實現(xiàn)類,在本節(jié)內(nèi)容中是NewOutputCollector。
我們可以看到不僅寫入了key和value,同時還寫入每個key value的所屬分區(qū),最終這些key,value要根據(jù)相應的分區(qū)號進入相應的reduce。
@Override
public void write(K key, V value) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
collector.collect(key, value,
partitioner.getPartition(key, value, partitions));
}
寫入緩沖區(qū)
最終會由MapOutputBuffer寫入緩沖區(qū)。同時我們可以看到,key,value會經(jīng)過序列化放到緩沖區(qū)中。
public synchronized void collect(K key, V value, final int partition
) throws IOException {
reporter.progress();
if (key.getClass() != keyClass) {
throw new IOException("Type mismatch in key from map: expected "
+ keyClass.getName() + ", received "
+ key.getClass().getName());
}
if (value.getClass() != valClass) {
throw new IOException("Type mismatch in value from map: expected "
+ valClass.getName() + ", received "
+ value.getClass().getName());
}
if (partition < 0 || partition >= partitions) {
throw new IOException("Illegal partition for " + key + " (" +
partition + ")");
}
checkSpillException();
bufferRemaining -= METASIZE;
if (bufferRemaining <= 0) {
// start spill if the thread is not running and the soft limit has been
// reached
spillLock.lock();
try {
do {
if (!spillInProgress) {
final int kvbidx = 4 * kvindex;
final int kvbend = 4 * kvend;
// serialized, unspilled bytes always lie between kvindex and
// bufindex, crossing the equator. Note that any void space
// created by a reset must be included in "used" bytes
final int bUsed = distanceTo(kvbidx, bufindex);
final boolean bufsoftlimit = bUsed >= softLimit;
if ((kvbend + METASIZE) % kvbuffer.length !=
equator - (equator % METASIZE)) {
// spill finished, reclaim space
resetSpill();
bufferRemaining = Math.min(
distanceTo(bufindex, kvbidx) - 2 * METASIZE,
softLimit - bUsed) - METASIZE;
continue;
} else if (bufsoftlimit && kvindex != kvend) {
// spill records, if any collected; check latter, as it may
// be possible for metadata alignment to hit spill pcnt
startSpill();
final int avgRec = (int)
(mapOutputByteCounter.getCounter() /
mapOutputRecordCounter.getCounter());
// leave at least half the split buffer for serialization data
// ensure that kvindex >= bufindex
final int distkvi = distanceTo(bufindex, kvbidx);
final int newPos = (bufindex +
Math.max(2 * METASIZE - 1,
Math.min(distkvi / 2,
distkvi / (METASIZE + avgRec) * METASIZE)))
% kvbuffer.length;
setEquator(newPos);
bufmark = bufindex = newPos;
final int serBound = 4 * kvend;
// bytes remaining before the lock must be held and limits
// checked is the minimum of three arcs: the metadata space, the
// serialization space, and the soft limit
bufferRemaining = Math.min(
// metadata max
distanceTo(bufend, newPos),
Math.min(
// serialization max
distanceTo(newPos, serBound),
// soft limit
softLimit)) - 2 * METASIZE;
}
}
} while (false);
} finally {
spillLock.unlock();
}
}
try {
// serialize key bytes into buffer
int keystart = bufindex;
keySerializer.serialize(key);
if (bufindex < keystart) {
// wrapped the key; must make contiguous
bb.shiftBufferedKey();
keystart = 0;
}
// serialize value bytes into buffer
final int valstart = bufindex;
valSerializer.serialize(value);
// It's possible for records to have zero length, i.e. the serializer
// will perform no writes. To ensure that the boundary conditions are
// checked and that the kvindex invariant is maintained, perform a
// zero-length write into the buffer. The logic monitoring this could be
// moved into collect, but this is cleaner and inexpensive. For now, it
// is acceptable.
bb.write(b0, 0, 0);
// the record must be marked after the preceding write, as the metadata
// for this record are not yet written
int valend = bb.markRecord();
mapOutputRecordCounter.increment(1);
mapOutputByteCounter.increment(
distanceTo(keystart, valend, bufvoid));
// write accounting info
kvmeta.put(kvindex + PARTITION, partition);
kvmeta.put(kvindex + KEYSTART, keystart);
kvmeta.put(kvindex + VALSTART, valstart);
kvmeta.put(kvindex + VALLEN, distanceTo(valstart, valend));
// advance kvindex
kvindex = (kvindex - NMETA + kvmeta.capacity()) % kvmeta.capacity();
} catch (MapBufferTooSmallException e) {
LOG.info("Record too large for in-memory buffer: " + e.getMessage());
spillSingleRecord(key, value, partition);
mapOutputRecordCounter.increment(1);
return;
}
}初始化收集器
看了大部分源碼之后,會發(fā)現(xiàn)hadoop中什么東西其實都是可以進行自定義,我們可以選擇通過參數(shù)指定自己的buffer,當然一開始選擇默認就可以了。
private <KEY, VALUE> MapOutputCollector<KEY, VALUE>
createSortingCollector(JobConf job, TaskReporter reporter)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
MapOutputCollector.Context context =
new MapOutputCollector.Context(this, job, reporter);
Class[] collectorClasses = job.getClasses(
JobContext.MAP_OUTPUT_COLLECTOR_CLASS_ATTR, MapOutputBuffer.class);
int remainingCollectors = collectorClasses.length;
for (Class clazz : collectorClasses) {
try {
if (!MapOutputCollector.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
throw new IOException("Invalid output collector class: " + clazz.getName() +
" (does not implement MapOutputCollector)");
}
Class extends MapOutputCollector> subclazz =
clazz.asSubclass(MapOutputCollector.class);
LOG.debug("Trying map output collector class: " + subclazz.getName());
MapOutputCollector<KEY, VALUE> collector =
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(subclazz, job);
collector.init(context);
LOG.info("Map output collector class = " + collector.getClass().getName());
return collector;
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = "Unable to initialize MapOutputCollector " + clazz.getName();
if (--remainingCollectors > 0) {
msg += " (" + remainingCollectors + " more collector(s) to try)";
}
LOG.warn(msg, e);
}
}
throw new IOException("Unable to initialize any output collector");
}之前在文章中記錄過,緩沖區(qū)也是需要我們排序的,而系統(tǒng)默認的排序方式是快速排序,當然我們可以實現(xiàn)自己的排序類。

public void init(MapOutputCollector.Context context
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
job = context.getJobConf();
reporter = context.getReporter();
mapTask = context.getMapTask();
mapOutputFile = mapTask.getMapOutputFile();
sortPhase = mapTask.getSortPhase();
spilledRecordsCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.SPILLED_RECORDS);
partitions = job.getNumReduceTasks();
rfs = ((LocalFileSystem)FileSystem.getLocal(job)).getRaw();
//sanity checks
final float spillper =
job.getFloat(JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT, (float)0.8);
final int sortmb = job.getInt(JobContext.IO_SORT_MB, 100);
indexCacheMemoryLimit = job.getInt(JobContext.INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT,
INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT_DEFAULT);
if (spillper > (float)1.0 || spillper <= (float)0.0) {
throw new IOException("Invalid \"" + JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT +
"\": " + spillper);
}
if ((sortmb & 0x7FF) != sortmb) {
throw new IOException(
"Invalid \"" + JobContext.IO_SORT_MB + "\": " + sortmb);
}
sorter = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getClass("map.sort.class",
QuickSort.class, IndexedSorter.class), job);
// buffers and accounting
int maxMemUsage = sortmb << 20;
maxMemUsage -= maxMemUsage % METASIZE;
kvbuffer = new byte[maxMemUsage];
bufvoid = kvbuffer.length;
kvmeta = ByteBuffer.wrap(kvbuffer)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asIntBuffer();
setEquator(0);
bufstart = bufend = bufindex = equator;
kvstart = kvend = kvindex;
maxRec = kvmeta.capacity() / NMETA;
softLimit = (int)(kvbuffer.length * spillper);
bufferRemaining = softLimit;
LOG.info(JobContext.IO_SORT_MB + ": " + sortmb);
LOG.info("soft limit at " + softLimit);
LOG.info("bufstart = " + bufstart + "; bufvoid = " + bufvoid);
LOG.info("kvstart = " + kvstart + "; length = " + maxRec);
// k/v serialization
comparator = job.getOutputKeyComparator();
keyClass = (Class<K>)job.getMapOutputKeyClass();
valClass = (Class<V>)job.getMapOutputValueClass();
serializationFactory = new SerializationFactory(job);
keySerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(keyClass);
keySerializer.open(bb);
valSerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(valClass);
valSerializer.open(bb);
// output counters
mapOutputByteCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_BYTES);
mapOutputRecordCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_RECORDS);
fileOutputByteCounter = reporter
.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_MATERIALIZED_BYTES);
// compression
if (job.getCompressMapOutput()) {
Class extends CompressionCodec> codecClass =
job.getMapOutputCompressorClass(DefaultCodec.class);
codec = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(codecClass, job);
} else {
codec = null;
}
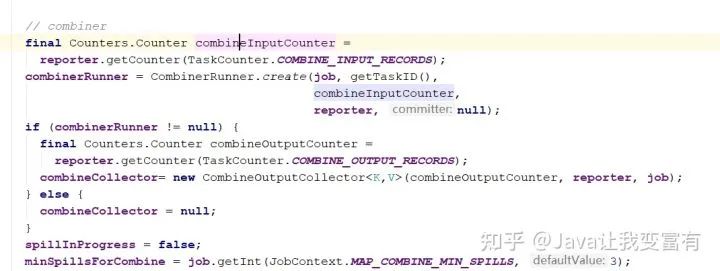
// combiner
final Counters.Counter combineInputCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_INPUT_RECORDS);
combinerRunner = CombinerRunner.create(job, getTaskID(),
combineInputCounter,
reporter, null);
if (combinerRunner != null) {
final Counters.Counter combineOutputCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_OUTPUT_RECORDS);
combineCollector= new CombineOutputCollector<K,V>(combineOutputCounter, reporter, job);
} else {
combineCollector = null;
}
spillInProgress = false;
minSpillsForCombine = job.getInt(JobContext.MAP_COMBINE_MIN_SPILLS, 3);
spillThread.setDaemon(true);
spillThread.setName("SpillThread");
spillLock.lock();
try {
spillThread.start();
while (!spillThreadRunning) {
spillDone.await();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize", e);
} finally {
spillLock.unlock();
}
if (sortSpillException != null) {
throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize",
sortSpillException);
}
}比較器
有了排序方式,我們需要指定對什么東西進行排序。因此就需要用到比較器。如果我們定義了比較器,就用自定義的,如果沒有自定義,就取我們曾經(jīng)設置的key類型的自己的比較器。
public RawComparator getOutputKeyComparator() {
Class extends RawComparator> theClass = getClass(
JobContext.KEY_COMPARATOR, null, RawComparator.class);
if (theClass != null)
return ReflectionUtils.newInstance(theClass, this);
return WritableComparator.get(getMapOutputKeyClass().asSubclass(WritableComparable.class), this);
}合并器
在reduce之前,如果有一些分組的數(shù)據(jù)聚集在一個分片中,我們可以提前對其進行合并,然后再通過reduce調(diào)取合并后的數(shù)據(jù)。可以極大的減少IO的次數(shù)。