使用 Stream API 高逼格優(yōu)化 Java 代碼!
點(diǎn)擊上方“碼農(nóng)突圍”,馬上關(guān)注 這里是碼農(nóng)充電第一站,回復(fù)“666”,獲取一份專屬大禮包 真愛,請(qǐng)?jiān)O(shè)置“星標(biāo)”或點(diǎn)個(gè)“在看

使用Stream API優(yōu)化代碼
Java8的新特性主要是Lambda表達(dá)式和流,當(dāng)流和Lambda表達(dá)式結(jié)合起來(lái)一起使用時(shí),因?yàn)榱魃昝魇教幚頂?shù)據(jù)集合的特點(diǎn),可以讓代碼變得簡(jiǎn)潔易讀
放大招,流如何簡(jiǎn)化代碼
篩選出卡路里小于400的菜肴 對(duì)篩選出的菜肴進(jìn)行一個(gè)排序 獲取排序后菜肴的名字
菜肴:Dish.java
public class Dish {
private String name;
private boolean vegetarian;
private int calories;
private Type type;
// getter and setter
}
Java8以前的實(shí)現(xiàn)方式
private List<String> beforeJava7(List<Dish> dishList) {
List<Dish> lowCaloricDishes = new ArrayList<>();
//1.篩選出卡路里小于400的菜肴
for (Dish dish : dishList) {
if (dish.getCalories() < 400) {
lowCaloricDishes.add(dish);
}
}
//2.對(duì)篩選出的菜肴進(jìn)行排序
Collections.sort(lowCaloricDishes, new Comparator<Dish>() {
@Override
public int compare(Dish o1, Dish o2) {
return Integer.compare(o1.getCalories(), o2.getCalories());
}
});
//3.獲取排序后菜肴的名字
List<String> lowCaloricDishesName = new ArrayList<>();
for (Dish d : lowCaloricDishes) {
lowCaloricDishesName.add(d.getName());
}
return lowCaloricDishesName;
}
Java8之后的實(shí)現(xiàn)方式
private List<String> afterJava8(List<Dish> dishList) {
return dishList.stream()
.filter(d -> d.getCalories() < 400) //篩選出卡路里小于400的菜肴
.sorted(comparing(Dish::getCalories)) //根據(jù)卡路里進(jìn)行排序
.map(Dish::getName) //提取菜肴名稱
.collect(Collectors.toList()); //轉(zhuǎn)換為L(zhǎng)ist
}
24代碼實(shí)現(xiàn)的功能現(xiàn)在只需5行就可以完成了 不錯(cuò)!基于Springboot 2.0 + LayUI開發(fā)的物流管理系統(tǒng)(已開源)
不錯(cuò)!基于Springboot 2.0 + LayUI開發(fā)的物流管理系統(tǒng)(已開源)對(duì)數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)查詢到的菜肴根據(jù)菜肴種類進(jìn)行分類,返回一個(gè) Map<Type, List<Dish>>的結(jié)果
Java8以前的實(shí)現(xiàn)方式
private static Map<Type, List<Dish>> beforeJdk8(List<Dish> dishList) {
Map<Type, List<Dish>> result = new HashMap<>();
for (Dish dish : dishList) {
//不存在則初始化
if (result.get(dish.getType())==null) {
List<Dish> dishes = new ArrayList<>();
dishes.add(dish);
result.put(dish.getType(), dishes);
} else {
//存在則追加
result.get(dish.getType()).add(dish);
}
}
return result;
}
Java8以后的實(shí)現(xiàn)方式
private static Map<Type, List<Dish>> afterJdk8(List<Dish> dishList) {
return dishList.stream().collect(groupingBy(Dish::getType));
}
Stream API牛批 看到流的強(qiáng)大功能了吧,接下來(lái)將詳細(xì)介紹流 魔都小伙伴們最近要注意的兩件事!
魔都小伙伴們最近要注意的兩件事!什么是流
如何生成流
通過(guò)集合生成,應(yīng)用中最常用的一種
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Stream<Integer> stream = integerList.stream();
stream方法生成流通過(guò)數(shù)組生成
int[] intArr = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(intArr);
Arrays.stream方法生成流,并且該方法生成的流是數(shù)值流【即IntStream】而不是Stream<Integer>。補(bǔ)充一點(diǎn)使用數(shù)值流可以避免計(jì)算過(guò)程中拆箱裝箱,提高性能。Stream API提供了mapToInt、mapToDouble、mapToLong三種方式將對(duì)象流【即Stream<T>】轉(zhuǎn)換成對(duì)應(yīng)的數(shù)值流,同時(shí)提供了boxed方法將數(shù)值流轉(zhuǎn)換為對(duì)象流通過(guò)值生成
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Stream的of方法生成流,通過(guò)Stream的empty方法可以生成一個(gè)空流通過(guò)文件生成
Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(Paths.get("data.txt"), Charset.defaultCharset())
Files.line方法得到一個(gè)流,并且得到的每個(gè)流是給定文件中的一行通過(guò)函數(shù)生成 提供了
iterate
generate
iterator
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.iterate(0, n -> n + 2).limit(5);
iterate
iterator
limit
generator
Stream<Double> stream = Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(5);
generate
Supplier<T>
generate
limit
流的操作類型
中間操作 一個(gè)流可以后面跟隨零個(gè)或多個(gè)中間操作。其目的主要是打開流,做出某種程度的數(shù)據(jù)映射/過(guò)濾,然后返回一個(gè)新的流,交給下一個(gè)操作使用。這類操作都是惰性化的,僅僅調(diào)用到這類方法,并沒(méi)有真正開始流的遍歷,真正的遍歷需等到終端操作時(shí),常見的中間操作有下面即將介紹的 filter、map等終端操作 一個(gè)流有且只能有一個(gè)終端操作,當(dāng)這個(gè)操作執(zhí)行后,流就被關(guān)閉了,無(wú)法再被操作,因此一個(gè)流只能被遍歷一次,若想在遍歷需要通過(guò)源數(shù)據(jù)在生成流。終端操作的執(zhí)行,才會(huì)真正開始流的遍歷。如下面即將介紹的 count、collect等
流使用
中間操作
filter篩選
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Stream<Integer> stream = integerList.stream().filter(i -> i > 3);
filter方法進(jìn)行條件篩選,filter的方法參數(shù)為一個(gè)條件distinct去除重復(fù)元素
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Stream<Integer> stream = integerList.stream().distinct();
distinct方法快速去除重復(fù)的元素limit返回指定流個(gè)數(shù)
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Stream<Integer> stream = integerList.stream().limit(3);
limit方法指定返回流的個(gè)數(shù),limit的參數(shù)值必須>=0,否則將會(huì)拋出異常skip跳過(guò)流中的元素
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Stream<Integer> stream = integerList.stream().skip(2);
skip方法跳過(guò)流中的元素,上述例子跳過(guò)前兩個(gè)元素,所以打印結(jié)果為2,3,4,5,skip的參數(shù)值必須>=0,否則將會(huì)拋出異常map流映射
List<String> stringList = Arrays.asList("Java 8", "Lambdas", "In", "Action");
Stream<Integer> stream = stringList.stream().map(String::length);
map方法可以完成映射,該例子完成中String -> Integer的映射,之前上面的例子通過(guò)map方法完成了Dish->String的映射flatMap流轉(zhuǎn)換
List<String> wordList = Arrays.asList("Hello", "World");
List<String> strList = wordList.stream()
.map(w -> w.split(" "))
.flatMap(Arrays::stream)
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
map(w -> w.split(" "))的返回值為Stream<String[]>,我們想獲取Stream<String>,可以通過(guò)flatMap方法完成Stream<String[]> ->Stream<String>的轉(zhuǎn)換元素匹配
allMatch匹配所有
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
if (integerList.stream().allMatch(i -> i > 3)) {
System.out.println("值都大于3");
}
allMatch方法實(shí)現(xiàn)anyMatch匹配其中一個(gè)
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
if (integerList.stream().anyMatch(i -> i > 3)) {
System.out.println("存在大于3的值");
}
for (Integer i : integerList) {
if (i > 3) {
System.out.println("存在大于3的值");
break;
}
}
java8中通過(guò)anyMatch方法實(shí)現(xiàn)這個(gè)功能noneMatch全部不匹配
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
if (integerList.stream().noneMatch(i -> i > 3)) {
System.out.println("值都小于3");
}
noneMatch
終端操作
統(tǒng)計(jì)流中元素個(gè)數(shù)
通過(guò)count
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Long result = integerList.stream().count();
count方法統(tǒng)計(jì)出流中元素個(gè)數(shù)通過(guò)counting
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Long result = integerList.stream().collect(counting());
collect聯(lián)合使用的時(shí)候特別有用查找
findFirst查找第一個(gè)
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Optional<Integer> result = integerList.stream().filter(i -> i > 3).findFirst();
findFirst方法查找到第一個(gè)大于三的元素并打印findAny隨機(jī)查找一個(gè)
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Optional<Integer> result = integerList.stream().filter(i -> i > 3).findAny();
findAny方法查找到其中一個(gè)大于三的元素并打印,因?yàn)閮?nèi)部進(jìn)行優(yōu)化的原因,當(dāng)找到第一個(gè)滿足大于三的元素時(shí)就結(jié)束,該方法結(jié)果和findFirst方法結(jié)果一樣。提供findAny方法是為了更好的利用并行流,findFirst方法在并行上限制更多【本篇文章將不介紹并行流】reduce將流中的元素組合起來(lái)
jdk8之前
int sum = 0;
for (int i : integerList) {
sum += i;
}
jdk8之后通過(guò)reduce進(jìn)行處理
int sum = integerList.stream().reduce(0, (a, b) -> (a + b));
int sum = integerList.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);
reduce接受兩個(gè)參數(shù),一個(gè)初始值這里是0,一個(gè)BinaryOperator<T> accumulator 來(lái)將兩個(gè)元素結(jié)合起來(lái)產(chǎn)生一個(gè)新值, 另外reduce方法還有一個(gè)沒(méi)有初始化值的重載方法獲取流中最小最大值
通過(guò)min/max獲取最小最大值
Optional<Integer> min = menu.stream().map(Dish::getCalories).min(Integer::compareTo);
Optional<Integer> max = menu.stream().map(Dish::getCalories).max(Integer::compareTo);
OptionalInt min = menu.stream().mapToInt(Dish::getCalories).min();
OptionalInt max = menu.stream().mapToInt(Dish::getCalories).max();
min
max
Comparator<? super T> comparator
通過(guò)minBy/maxBy獲取最小最大值
Optional<Integer> min = menu.stream().map(Dish::getCalories).collect(minBy(Integer::compareTo));
Optional<Integer> max = menu.stream().map(Dish::getCalories).collect(maxBy(Integer::compareTo));
minBy
maxBy
Comparator<? super T> comparator
通過(guò)reduce獲取最小最大值
Optional<Integer> min = menu.stream().map(Dish::getCalories).reduce(Integer::min);
Optional<Integer> max = menu.stream().map(Dish::getCalories).reduce(Integer::max);
求和
通過(guò)summingInt
int sum = menu.stream().collect(summingInt(Dish::getCalories));
double
long
summingDouble
summingLong
通過(guò)reduce
int sum = menu.stream().map(Dish::getCalories).reduce(0, Integer::sum);
通過(guò)sum
int sum = menu.stream().mapToInt(Dish::getCalories).sum();
collect、reduce、min/max/sum方法,推薦使用min、max、sum方法。因?yàn)樗詈?jiǎn)潔易讀,同時(shí)通過(guò)mapToInt將對(duì)象流轉(zhuǎn)換為數(shù)值流,避免了裝箱和拆箱操作通過(guò)averagingInt求平均值
double average = menu.stream().collect(averagingInt(Dish::getCalories));
double、long,則通過(guò)averagingDouble、averagingLong方法進(jìn)行求平均通過(guò)summarizingInt同時(shí)求總和、平均值、最大值、最小值
IntSummaryStatistics intSummaryStatistics = menu.stream().collect(summarizingInt(Dish::getCalories));
double average = intSummaryStatistics.getAverage(); //獲取平均值
int min = intSummaryStatistics.getMin(); //獲取最小值
int max = intSummaryStatistics.getMax(); //獲取最大值
long sum = intSummaryStatistics.getSum(); //獲取總和
double、long,則通過(guò)summarizingDouble、summarizingLong方法通過(guò)foreach進(jìn)行元素遍歷
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
integerList.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
for (int i : integerList) {
System.out.println(i);
}
返回集合
List<String> strings = menu.stream().map(Dish::getName).collect(toList());
Set<String> sets = menu.stream().map(Dish::getName).collect(toSet());
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<>();
Set<String> stringSet = new HashSet<>();
for (Dish dish : menu) {
stringList.add(dish.getName());
stringSet.add(dish.getName());
}
通過(guò)joining拼接流中的元素
String result = menu.stream().map(Dish::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
map方法進(jìn)行映射處理拼接的toString方法返回的字符串,joining的方法參數(shù)為元素的分界符,如果不指定生成的字符串將是一串的,可讀性不強(qiáng)進(jìn)階通過(guò)groupingBy進(jìn)行分組
Map<Type, List<Dish>> result = dishList.stream().collect(groupingBy(Dish::getType));
collect方法中傳入groupingBy進(jìn)行分組,其中groupingBy的方法參數(shù)為分類函數(shù)。還可以通過(guò)嵌套使用groupingBy進(jìn)行多級(jí)分類Map<Type, List<Dish>> result = menu.stream().collect(groupingBy(Dish::getType,
groupingBy(dish -> {
if (dish.getCalories() <= 400) return CaloricLevel.DIET;
else if (dish.getCalories() <= 700) return CaloricLevel.NORMAL;
else return CaloricLevel.FAT;
})));
進(jìn)階通過(guò)partitioningBy進(jìn)行分區(qū)
Map<Boolean, List<Dish>> result = menu.stream().collect(partitioningBy(Dish :: isVegetarian))
Map<Boolean, List<Dish>> result = menu.stream().collect(groupingBy(Dish :: isVegetarian))
List<Integer> integerList = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Map<Boolean, List<Integer>> result = integerList.stream().collect(partitioningBy(i -> i < 3));
總結(jié)
Stream API可以簡(jiǎn)化代碼,同時(shí)提高了代碼可讀性,趕緊在項(xiàng)目里用起來(lái)。講道理在沒(méi)學(xué)Stream API之前,誰(shuí)要是給我在應(yīng)用里寫很多Lambda,Stream API,飛起就想給他一腳。我想,我現(xiàn)在可能愛上他了【嘻嘻】。同時(shí)使用的時(shí)候注意不要將聲明式和命令式編程混合使用,前幾天刷segment刷到一條: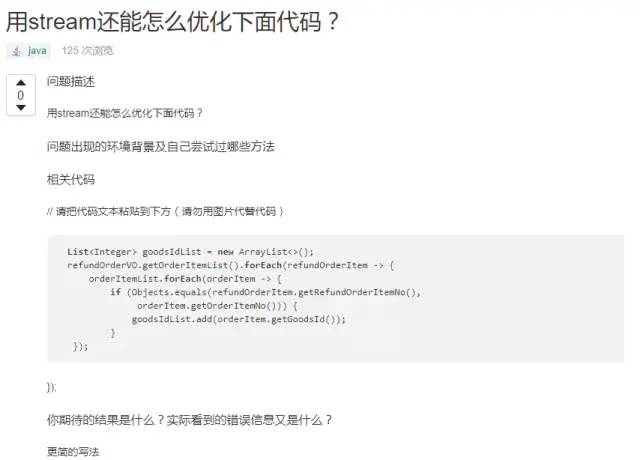
imango老哥說(shuō)的很對(duì),別用聲明式編程的語(yǔ)法干命令式編程的勾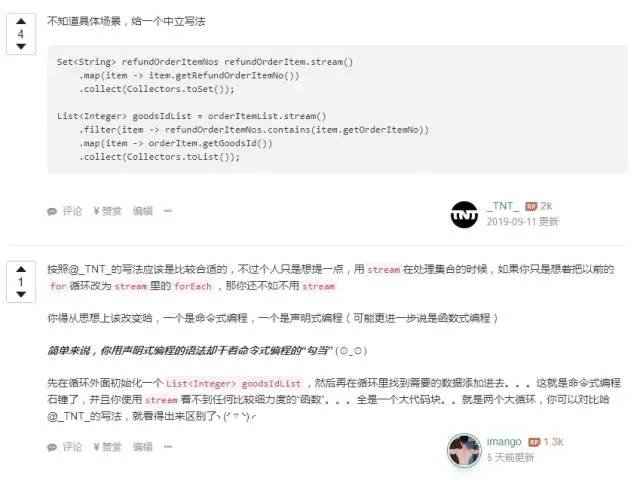
- END - 最近熱文
? 如果把14億中國(guó)人都拉到一個(gè)微信群。。。 ? 再見 Win10!下一代操作系統(tǒng)要來(lái)了! ? 女友回老家了!沒(méi)吊事,手把手帶你搭建一臺(tái)服務(wù)器! ? 尼瑪,Github上最邪惡的開源項(xiàng)目了!未滿18或者女孩子勿進(jìn)哦~
評(píng)論
圖片
表情
