JDK核心源碼深入剖析(synchronized和ConcurrentHashMap)
點(diǎn)擊上方藍(lán)色字體,選擇“標(biāo)星公眾號”
優(yōu)質(zhì)文章,第一時間送達(dá)
1 同步鎖synchronized追本溯源
1.1 synchronized場景回顧
public synchronized void test() {
//
}
public void test() {
synchronized (this) {
}
}
public static synchronized void test() {
//
}
public void test() {
synchronized (xx.class) {
}
}
1.2 反匯編尋找鎖實(shí)現(xiàn)原理
public class BTest {
private static Object object = new Object();
public synchronized void testMethod() {
System.out.println("Hello World -synchronized method ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
synchronized (object) {
System.out.println("Hello World -synchronized block ");
}
}
}
javap -v -c BTest.class
Last modified 2021-6-4; size 898 bytes
MD5 checksum 57342c74c29e2a57a799cd2b6b2a9de5
Compiled from "BTest.java"
public class com.syn.BTest
minor version: 0
major version: 52
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_SUPER
Constant pool:
#1 = Methodref #7.#30 // java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
#2 = Fieldref #31.#32 // java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#3 = String #33 // Hello World -synchronized method
#4 = Methodref #34.#35 // java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#5 = Fieldref #8.#36 // com/syn/BTest.object:Ljava/lang/Object;
#6 = String #37 // Hello World -synchronized block
#7 = Class #38 // java/lang/Object
#8 = Class #39 // com/syn/BTest
#9 = Utf8 object
#10 = Utf8 Ljava/lang/Object;
#11 = Utf8 <init>
#12 = Utf8 ()V
#13 = Utf8 Code
#14 = Utf8 LineNumberTable
#15 = Utf8 LocalVariableTable
#16 = Utf8 this
#17 = Utf8 Lcom/syn/BTest;
#18 = Utf8 testMethod
#19 = Utf8 main
#20 = Utf8 ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
#21 = Utf8 args
#22 = Utf8 [Ljava/lang/String;
#23 = Utf8 StackMapTable
#24 = Class #22 // "[Ljava/lang/String;"
#25 = Class #38 // java/lang/Object
#26 = Class #40 // java/lang/Throwable
#27 = Utf8 <clinit>
#28 = Utf8 SourceFile
#29 = Utf8 BTest.java
#30 = NameAndType #11:#12 // "<init>":()V
#31 = Class #41 // java/lang/System
#32 = NameAndType #42:#43 // out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#33 = Utf8 Hello World -synchronized method
#34 = Class #44 // java/io/PrintStream
#35 = NameAndType #45:#46 // println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#36 = NameAndType #9:#10 // object:Ljava/lang/Object;
#37 = Utf8 Hello World -synchronized block
#38 = Utf8 java/lang/Object
#39 = Utf8 com/syn/BTest
#40 = Utf8 java/lang/Throwable
#41 = Utf8 java/lang/System
#42 = Utf8 out
#43 = Utf8 Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#44 = Utf8 java/io/PrintStream
#45 = Utf8 println
#46 = Utf8 (Ljava/lang/String;)V
{
public com.syn.BTest();
descriptor: ()V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC
Code:
stack=1, locals=1, args_size=1
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
4: return
LineNumberTable:
line 3: 0
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 5 0 this Lcom/syn/BTest;
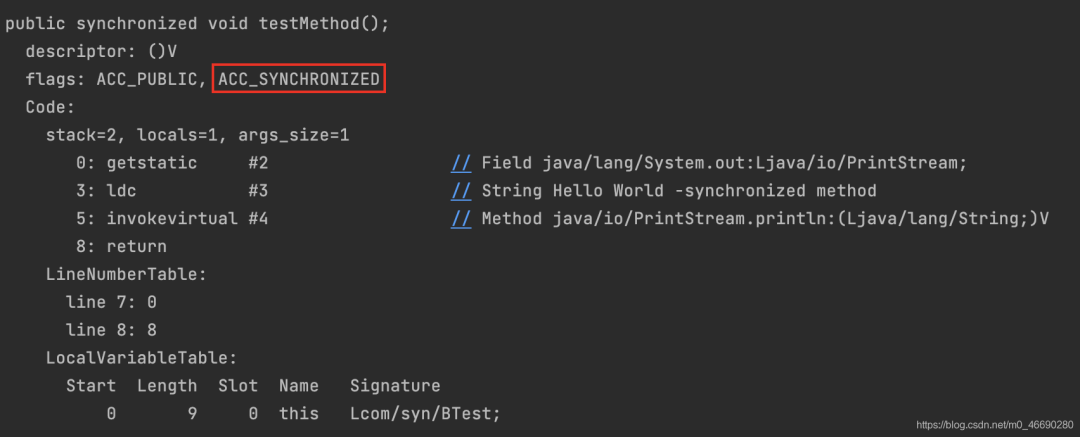
public synchronized void testMethod();
descriptor: ()V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_SYNCHRONIZED
Code:
stack=2, locals=1, args_size=1
0: getstatic #2 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
3: ldc #3 // String Hello World -synchronized method
5: invokevirtual #4 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
8: return
LineNumberTable:
line 7: 0
line 8: 8
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 9 0 this Lcom/syn/BTest;
public static void main(java.lang.String[]);
descriptor: ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATIC
Code:
stack=2, locals=3, args_size=1
0: getstatic #5 // Field object:Ljava/lang/Object;
3: dup
4: astore_1
5: monitorenter
6: getstatic #2 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
9: ldc #6 // String Hello World -synchronized block
11: invokevirtual #4 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
14: aload_1
15: monitorexit
16: goto 24
19: astore_2
20: aload_1
21: monitorexit
22: aload_2
23: athrow
24: return
Exception table:
from to target type
6 16 19 any
19 22 19 any
LineNumberTable:
line 11: 0
line 12: 6
line 13: 14
line 14: 24
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 25 0 args [Ljava/lang/String;
StackMapTable: number_of_entries = 2
frame_type = 255 /* full_frame */
offset_delta = 19
locals = [ class "[Ljava/lang/String;", class java/lang/Object ]
stack = [ class java/lang/Throwable ]
frame_type = 250 /* chop */
offset_delta = 4
static {};
descriptor: ()V
flags: ACC_STATIC
Code:
stack=2, locals=0, args_size=0
0: new #7 // class java/lang/Object
3: dup
4: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
7: putstatic #5 // Field object:Ljava/lang/Object;
10: return
LineNumberTable:
line 4: 0
}
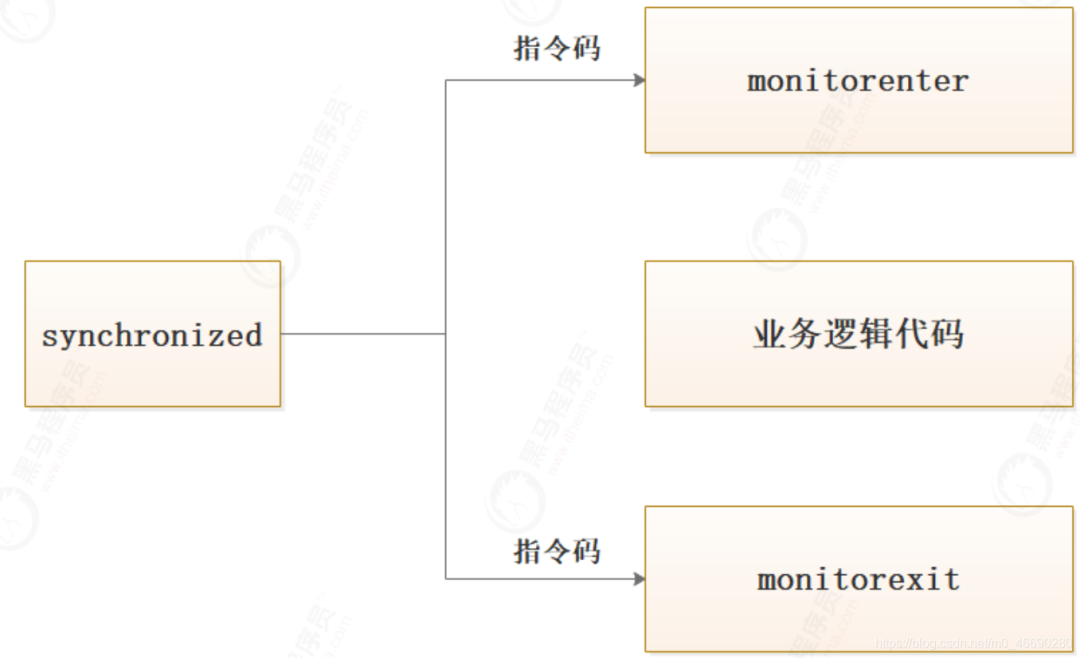
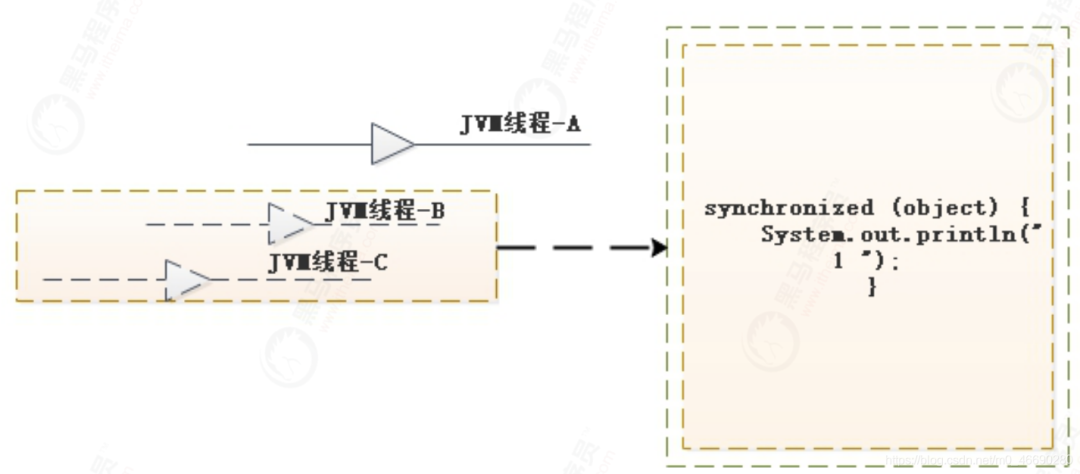
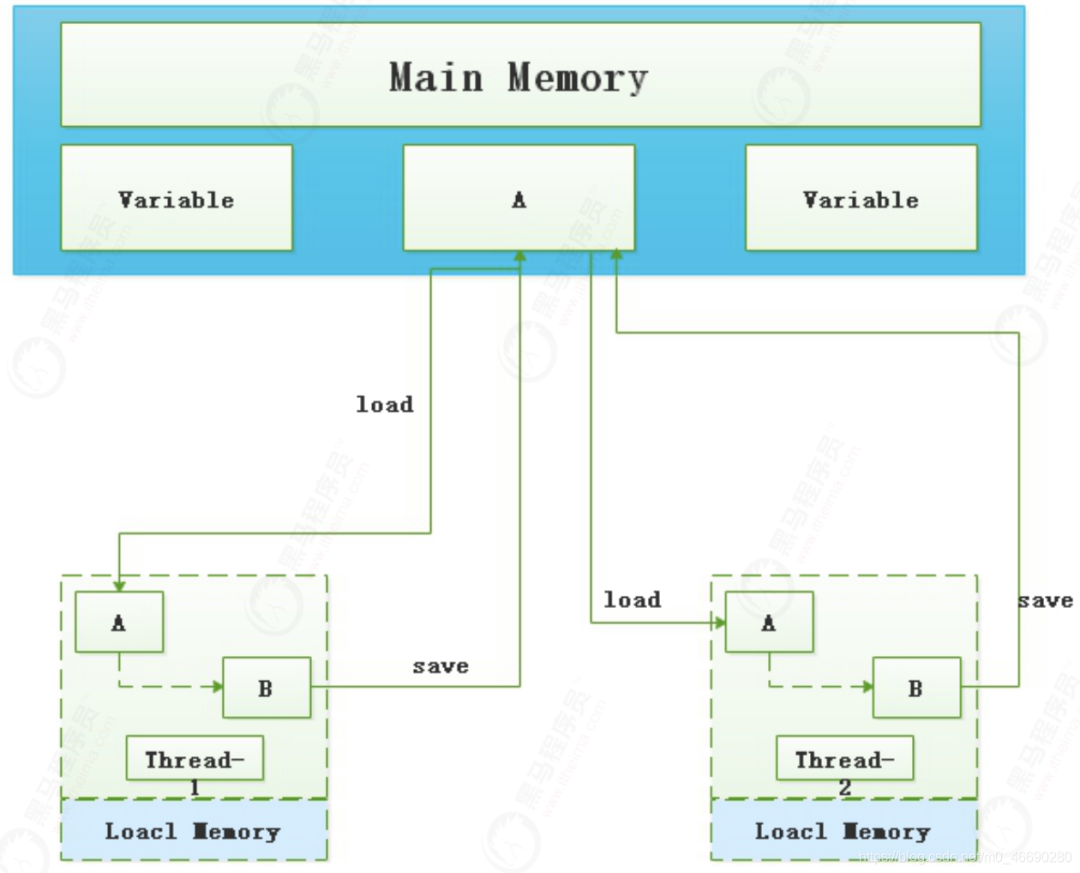
monitorenter :
Each object is associated with a monitor. A monitor is locked if and only if it
has an owner. The thread that executes monitorenter attempts to gain ownership
of the monitor associated with objectref, as follows:
? If the entry count of the monitor associated with objectref is zero, the
thread enters the monitor and sets its entry count to one. The thread is then
the owner of the monitor.
? If the thread already owns the monitor associated with objectref, it reenters
the monitor, incrementing its entry count.
? If another thread already owns the monitor associated with objectref, the
thread blocks until the monitor’s entry count is zero, then tries again to gain
ownership.
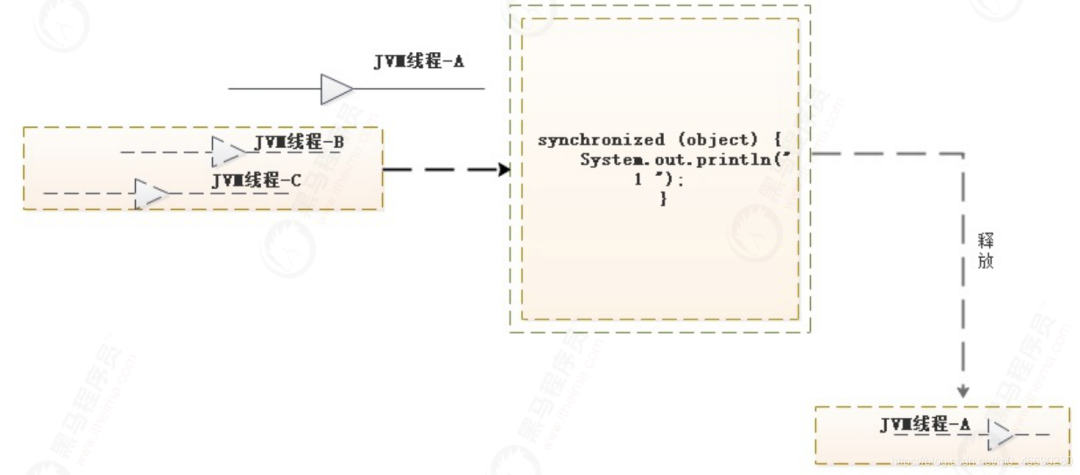
monitorexit:
The thread that executes monitorexit must be the owner of the monitor associated
with the instance referenced by objectref.
The thread decrements the entry count of the monitor associated with objectref.
If as a result the value of the entry count is zero, the thread exits the
monitor and is no longer its owner. Other threads that are blocking to enter the
monitor are allowed to attempt to do so.
————————————————
版權(quán)聲明:本文為CSDN博主「Ybb_studyRecord」的原創(chuàng)文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版權(quán)協(xié)議,轉(zhuǎn)載請附上原文出處鏈接及本聲明。
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_46690280/article/details/117553508
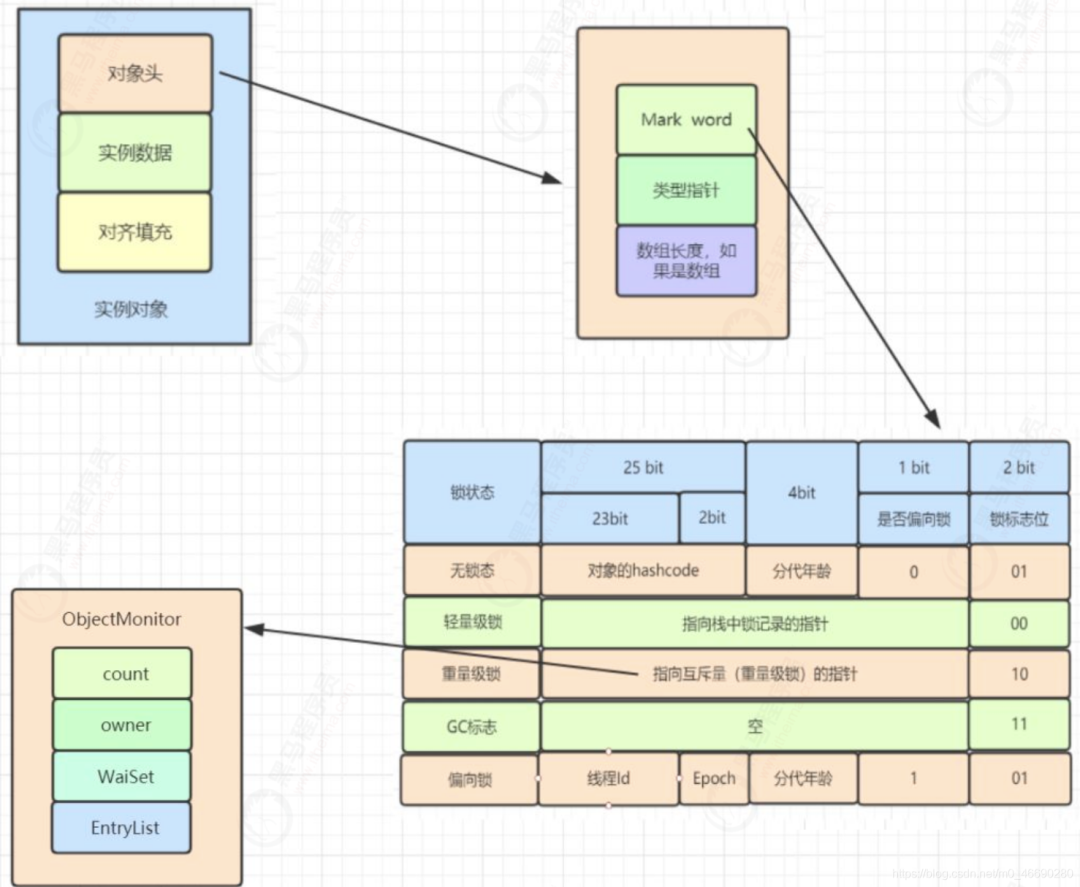
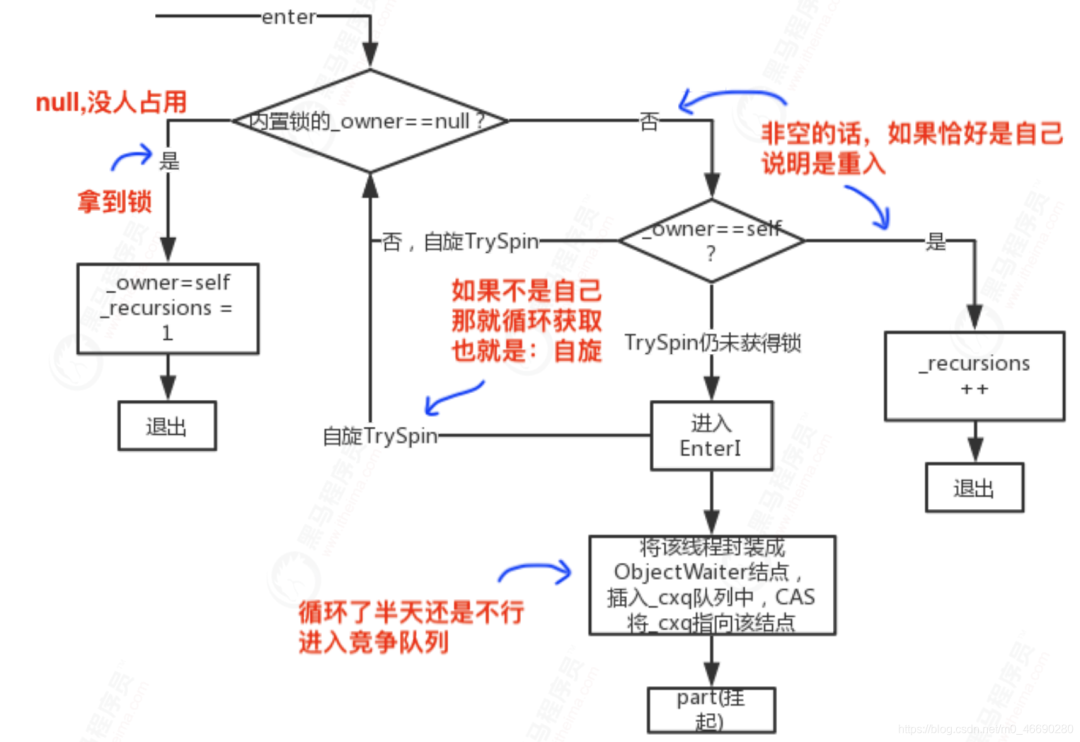
1.3 Monitor詳解
//構(gòu)造器
ObjectMonitor() {
_header = NULL;
_count = 0;
_waiters = 0,
_recursions = 0; // 遞歸;線程的重入次數(shù),典型的System.out.println
_object = NULL; // 對應(yīng)synchronized (object)對應(yīng)里面的object
_owner = NULL; // 標(biāo)識擁有該monitor的線程
_WaitSet = NULL; // 因?yàn)檎{(diào)用object.wait()方法而被阻塞的線程會被放在該隊(duì)列中
_WaitSetLock = 0 ;
_Responsible = NULL;
_succ = NULL;
_cxq = NULL; // 競爭隊(duì)列,所有請求鎖的線程首先會被放在這個隊(duì)列中
FreeNext = NULL;
_EntryList = NULL; // 阻塞;第二輪競爭鎖仍然沒有搶到的線程(偏向/可重入)
_SpinFreq = 0;
_SpinClock = 0;
OwnerIsThread = 0;
}
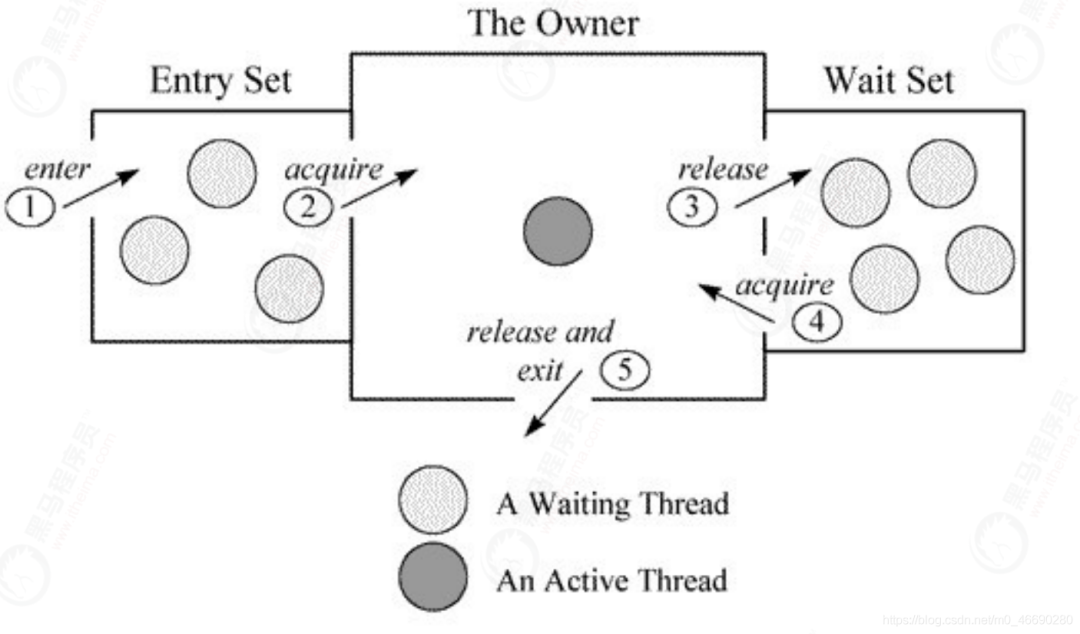
1.3.2 Monitor競爭
1.3.3 Monitor釋放
2 并發(fā)容器線程安全應(yīng)對之道
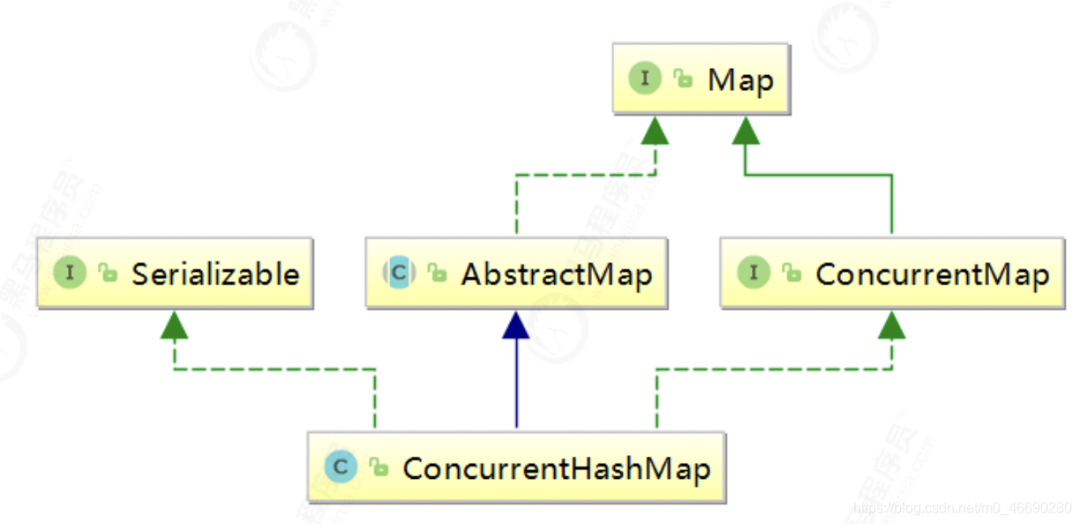
2.1 并發(fā)容器總體概述
2.2 并發(fā)容器數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)與繼承
2.3 并發(fā)容器源碼深度剖析
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, Integer> m = new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
m.put(i, i);//正常新增(演示)
} else if (i == 11) {
m.put(i, i);//擴(kuò)容(演示)
} else if (i == 10) {
m.put(27, 27);
m.put(43, 43);
} else if (i == 9) {
} else {
m.put(i, i);//正常新增
}
}
m.get(8);
System.out.println(m);
}
2.3.1 并發(fā)容器成員變量
private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; //table最大容量:
2^30=1073741824
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16; //默認(rèn)容量,必須是2的冪數(shù)
static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; 數(shù)組的建議最大值
private static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16; //并發(fā)級別,遺留下來的,為兼容以前的版本
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;// 鏈表轉(zhuǎn)紅黑樹閥值,> 8 鏈表轉(zhuǎn)換為紅黑樹
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;// 樹轉(zhuǎn)鏈表閥值
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;// 轉(zhuǎn)化為紅黑樹的表的最小容量
private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16;// 每次進(jìn)行轉(zhuǎn)移的最小值
2.3.2 并發(fā)容器構(gòu)造器
public ConcurrentHashMap() { }
private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity < 0) // 初始容量小于0,拋出異常
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1));
// 初始化
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
public ConcurrentHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.sizeCtl = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
putAll(m);
}
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, 1);
}
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many bins
initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads
long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);
int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
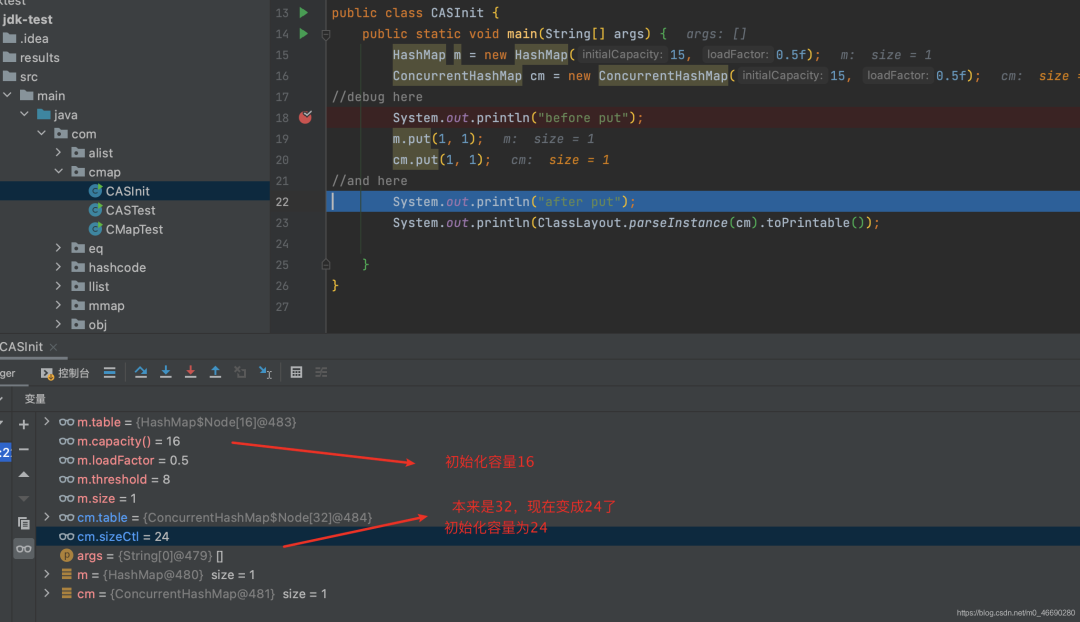
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap m = new HashMap(15, 0.5f);
ConcurrentHashMap cm = new ConcurrentHashMap(15, 0.5f);
//debug here
System.out.println("before put");
m.put(1, 1);
cm.put(1, 1);
//and here
System.out.println("after put");
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(cm).toPrintable());
}
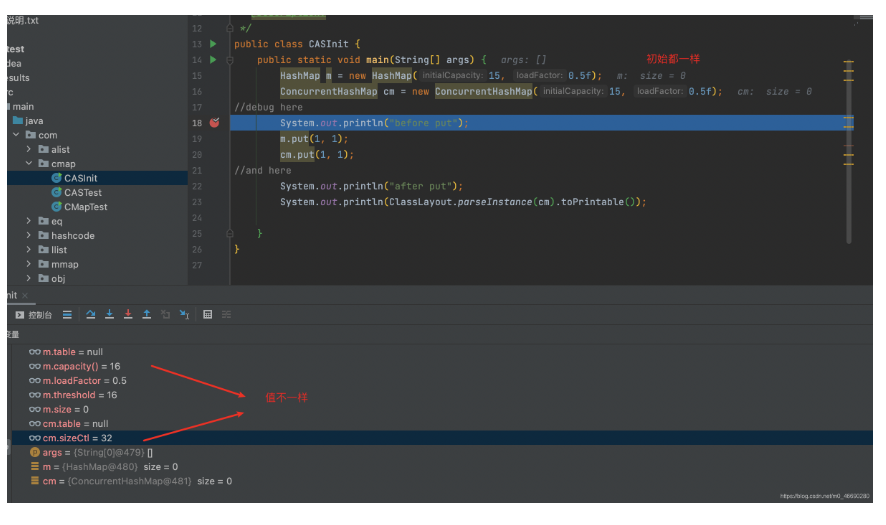
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many bins
initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads
//initial = 15, size = 31
long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);
//所以tableSizeFor做滿1運(yùn)算前,并不是15本身,而是size,也就是31
//運(yùn)算后,cap=32 , 不是16
int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
//開始之初,table為null,在put時,會觸發(fā)table的初始化,也就是以下方法
//從put方法的入口可以追蹤到
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
//sc = 原來的sizeCtl也就是 32
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//創(chuàng)建node數(shù)組,長度為n,也就是32
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
//創(chuàng)建完復(fù)制給table,初始化完成,也就是我們看到的32長度的數(shù)組
table = tab = nt;
// n >>> 2 ,相當(dāng)于n除以4是8, 32-8=24
//實(shí)際效果相當(dāng)于,n* 3/4 , 也就是 n*0.75 , 你指定的0.5在這里 沒什么用!
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
//在finally中將它賦給了sizeCtl,也就是我們最終看到的24
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
/**
* Table initialization and resizing control. When negative, the
* table is being initialized or resized: -1 for initialization,
* else -(1 + the number of active resizing threads). Otherwise,
* when table is null, holds the initial table size to use upon
* creation, or 0 for default. After initialization, holds the
* next element count value upon which to resize the table.
*/
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
2.3.3 put方法
(U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1))
static final int HASH_BITS = 0x7fffffff; // usable bits of normal node hash
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, Integer> m = new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
m.put(i, i);//正常新增(演示)
} else if (i == 11) {
m.put(i, i);//擴(kuò)容(演示)
} else if (i == 10) {
m.put(27, 27);
m.put(43, 43);
} else if (i == 9) {
} else {
m.put(i, i);//正常新增
}
}
m.get(8);
System.out.println(m);
}
//哈希沖突
static void testHashCode() {
System.out.println((16 - 1) & spread(new Integer(27).hashCode()));
System.out.println((16 - 1) & spread(new Integer(43).hashCode()));
System.out.println((16 - 1) & spread(new Integer(11).hashCode()));
}
static final int spread(int h) {
return (h ^ (h >>> 16)) & HASH_BITS;
}
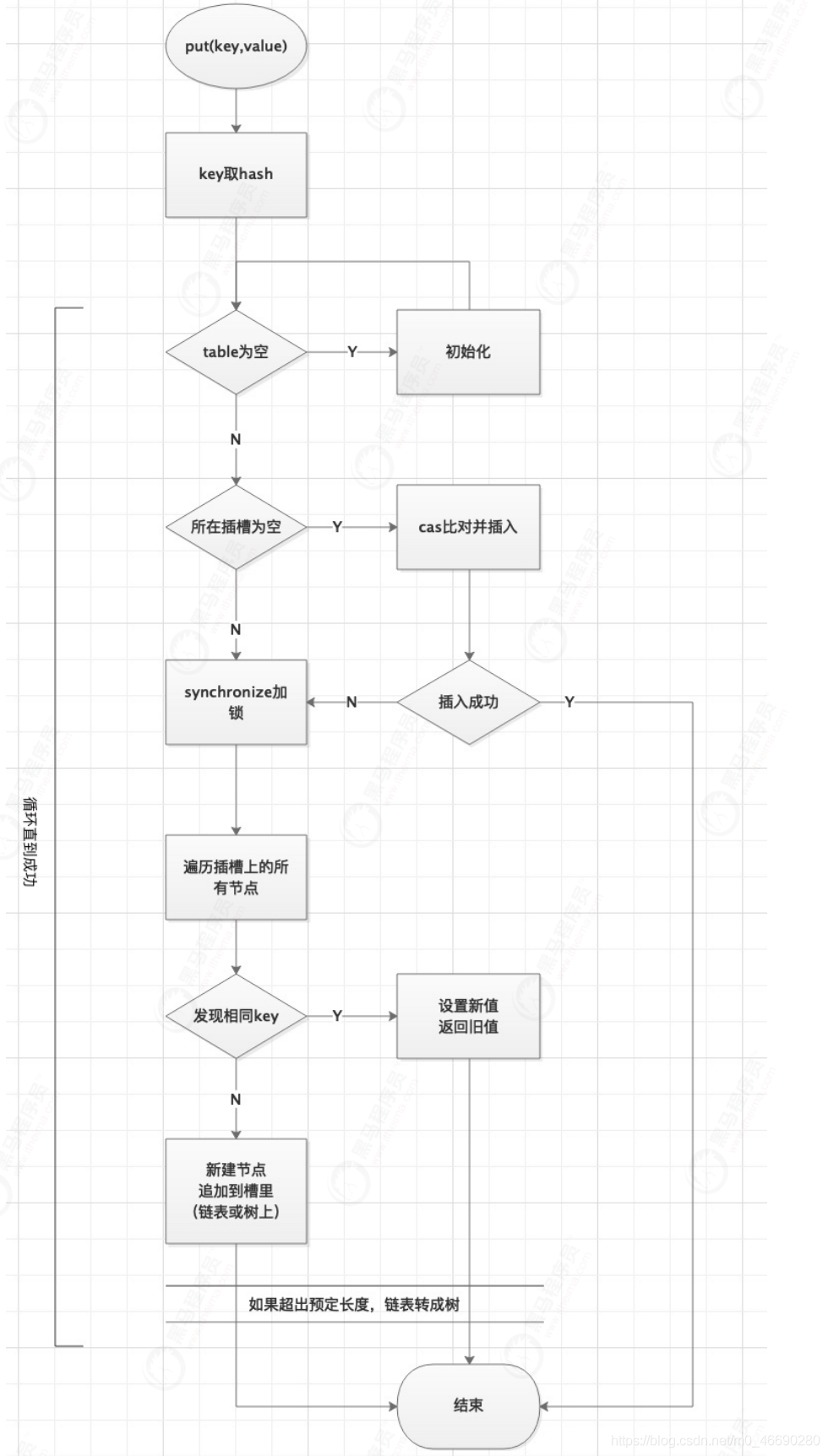
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); //key取hash擾動
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { //循環(huán)直到成功
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable(); //表為空的話,初始化表,下面會詳細(xì)介紹
//尋址,找到頭結(jié)點(diǎn)f
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
//cas在這里!!!
//插槽為空,cas插入元素
//比較是否為null,如果null才會設(shè)置并break,否則到else
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
//插入成功,break終止即可,如果不成功,會進(jìn)入下一輪for
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
//helpTransfer() 擴(kuò)容。下小節(jié)詳細(xì)講,一個個來……
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
//synchronized 在這里!!!
//插槽不為空,說明被別的線程put搶占了槽
//那就加鎖,鎖的是當(dāng)前插槽上的頭節(jié)點(diǎn)f(類似分段鎖)
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
//沿著當(dāng)前插槽的Node鏈往后找
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
//如果找到相同key,說明之前put過
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
//abset參數(shù)來決定要不要覆 蓋,默認(rèn)是覆蓋
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
//否則,新key,新Node插入到最后
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
//如果是紅黑樹,說明已經(jīng)轉(zhuǎn)化過,按樹的規(guī)則放入Node
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
//如果節(jié)點(diǎn)數(shù)達(dá)到臨界值,鏈表轉(zhuǎn)成樹
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount); //統(tǒng)計size
return null;
}
//compareAndSetObject,比較并插入,典型CAS操作
static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i,
Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v) {
return U.compareAndSwapObject(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, c, v);
}
//注意點(diǎn):先以單線程看業(yè)務(wù)流程,再類比多個線程操作下的并發(fā)是如何處理的?
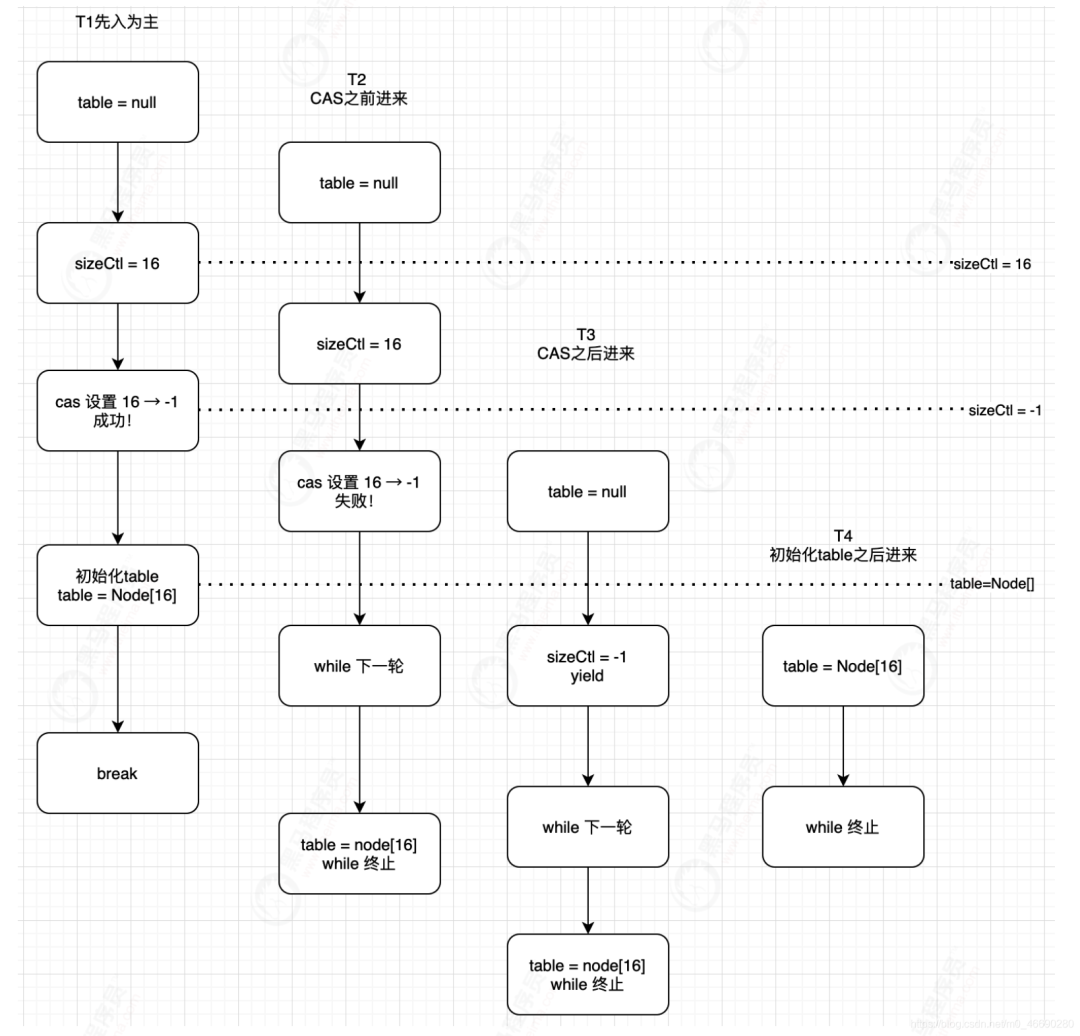
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { //自旋
//第1個線程這個if不成立,會進(jìn)入下面,設(shè)置為-1
//第2個線程來的時候if成立,注意理解多線程在跑。
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0) //注意回顧上面的值,小于0表示正在初始化,或擴(kuò)容
Thread.yield(); //有線程在操作,將當(dāng)前線程yield讓出時間片。喚醒后進(jìn)入下 一輪while
// lost initialization race; just spin
//CAS操作來設(shè)置SIZECTL為-1,如果設(shè)置成功,表示當(dāng)前線程獲得初始化的資格
//傳入對象 & 內(nèi)存地址 & 期望值 & 將修改的值
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {//table是null,還沒初始化
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {//默認(rèn)容量16
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
//初始化 table //給table賦值,注意這個table是volatile的,會被其他線程及時看 到!
//一旦其他線程看到不是null,走while循環(huán)發(fā)現(xiàn)table不等于空就 return了
table = tab = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2); //計算下次擴(kuò)容的閾值,容量的0.75,和你指 定的factor無關(guān)
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
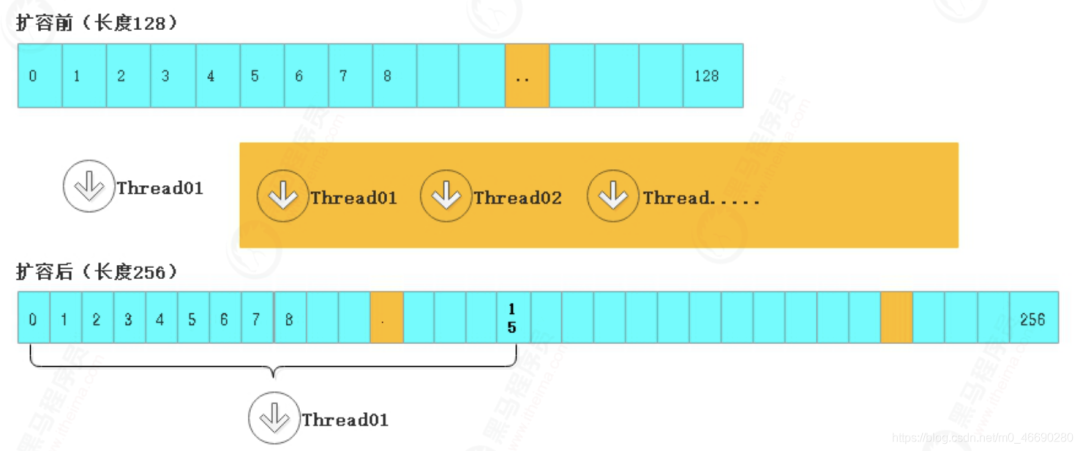
2.3.4 擴(kuò)容
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, Integer> m = new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
m.put(i, i);//正常新增(演示)
} else if (i == 11) {
m.put(i, i);//擴(kuò)容(演示)
} else if (i == 10) {
m.put(27, 27);
m.put(43, 43);
} else if (i == 9) {
} else {
m.put(i, i);//正常新增
}
}
m.get(8);
System.out.println(m);
}
//如果正在擴(kuò)容,上去幫忙 * tab = 舊數(shù)組, f=頭結(jié)點(diǎn),如果正在擴(kuò)容,它是一個ForwardNode類型
final Node<K,V>[] helpTransfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V> f) {
Node<K,V>[] nextTab; int sc;
if (tab != null && (f instanceof ForwardingNode) &&
(nextTab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)f).nextTable) != null) {
int rs = resizeStamp(tab.length);
// sizeCtl < 0 (說明還在擴(kuò)容中)
while (nextTab == nextTable && table == tab &&
(sc = sizeCtl) < 0) {
//一堆條件判斷,不去管它
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || transferIndex <= 0)
break;
// cas將 sizeCtl + 1, (表示增加了一個線程幫助其擴(kuò)容)
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) {
// 找到了,核心在這里!這個內(nèi)部藏著擴(kuò)容的具體操作
transfer(tab, nextTab);
break;
}
}
return nextTab;
}
return table;
}
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
int n = tab.length, stride;
// 將 length / 8 然后除以 CPU核心數(shù)。如果得到的結(jié)果小于 16,那么就使用 16。
// 如果桶較少的話,默認(rèn)一個 CPU(一個線程)處理 16 個桶
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range // 最小16
if (nextTab == null) { // initiating // 新的 table 尚未初始化
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 擴(kuò)容 2 倍
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];
// 賦值給新table
nextTab = nt;
} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
// 更新成員變量
// transferIndex表示沒遷移的桶里最大索引的值,這個會被多個線程瓜分走越來越小。
// 一開始這個值是舊tab的尾部:也就是 n
// 瓜分時,從大索引往后分,也就是順序是 : 15 14 13 12 ....0
nextTable = nextTab;
transferIndex = n; // tag_0
}
// 新 tab 的 length
int nextn = nextTab.length;
// 創(chuàng)建一個 fwd 節(jié)點(diǎn),用于標(biāo)記。當(dāng)別的線程發(fā)現(xiàn)這個槽位中是 fwd 類型的節(jié)點(diǎn),則跳過這個節(jié) 點(diǎn)。
ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);
boolean advance = true; //臨時變量,表示要不要移動槽
boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab //臨時變量,表示當(dāng)前槽有沒有遷移完
for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
//每次for遍歷一個桶來遷移,也就是舊table里的一個 元素
Node<K,V> f; int fh;
while (advance) {
//這里的while是配合tag_3的cas做自旋,只有它可能會觸發(fā)多次循環(huán), 其他倆都是循環(huán)1次結(jié)束
//while比較亂:可以打斷點(diǎn)進(jìn)來調(diào)試查看每次的經(jīng)過
// 第一次for的時候進(jìn) tag_3 確定bound和i,也就是給當(dāng)前線程分配了 bound ~ i 之間的桶
// 以后每次--i,只要不大于bound,都進(jìn) tag_1,也就是啥都不干
// 最后一次,等于bound的時候,說明分配給當(dāng)前線程的桶被它for完了,退出
int nextIndex, nextBound;
if (--i >= bound || finishing)// tag_1
//如果i比bound還大,或者當(dāng)前i下的鏈表沒移動完,--i推動一格
advance = false;
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {// tag_2
//如果transferIndex <=0 說明已遷移完成,沒有桶需要處理了,退出
i = -1;
advance = false;
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
nextIndex - stride : 0))) {// tag_3
// 第一次for的時候會走進(jìn)這里,確定當(dāng)前線程負(fù)責(zé)的桶的范圍,同時cas更新transferIndex
// 也就是,多個線程第一次都會訪問到這里,通過cas來分一部分桶,cas防止并發(fā)下重復(fù)分配
// 注意,來這里之前,經(jīng)過了tag_2的賦值:
// 所以這里在cas前 nextIndex = transferIndex = 16
// cas后, transferIndex = nextBound = (nextIndex - stride) = 0
// 注意,這里不一定是0,只不過舊長度16被一個線程全拿走了,剩下了0個
// 也就是說,transfer是本次分配后,還剩下的桶里最大的索引,別的線程還會繼續(xù)分
bound = nextBound; // 最小下標(biāo)0(舊數(shù)組)
i = nextIndex - 1; //最大下標(biāo)15(舊數(shù)組)
advance = false;
}
}
// 判斷i的范圍,不在可移動插槽的索引范圍內(nèi),說明全部遷移完了!
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc;
// 如果完成了擴(kuò)容
if (finishing) {
nextTable = null; // 釋放
table = nextTab; // 更新 table
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1); // 更新閾值
return;// 結(jié)束方法。
}
// 如果沒完成,嘗試使用cas減少sizeCtl,也就是擴(kuò)容的線程數(shù),同時更新標(biāo)記 finishing為true
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) { /
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return;
finishing = advance = true;
i = n; // recheck before commit
}
}
//下面才是真正遷移數(shù)據(jù)的操作!!!
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
// 獲取老 tab i 下標(biāo)位置的變量,如果是 null,就使用 fwd 占位。
// cas成功,advance為true,下次for里while會做--i移動一個下標(biāo)
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)// 如果不是 null 且 hash 值是 MOVED
advance = true; // already processed // 說明別的線程已經(jīng)處理過了,移動一個下標(biāo)
else {
// 到這里,說明這個位置有實(shí)際值了,且不是占位符,那就需要我們遷數(shù)據(jù)了。
// 對這個節(jié)點(diǎn)上鎖。防止別的線程 putVal 的時候向鏈表插入數(shù)據(jù)
synchronized (f) {
// 判斷 i 下標(biāo)處的桶節(jié)點(diǎn)是否和 f 相同 ,確保沒有被別的線程動過
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node<K,V> ln, hn;// 定義 low, height 高位桶,低位桶
// 如果 f 的 hash 值大于 0 屬于常規(guī)hash,開始拆分高低鏈表 // 參考靜態(tài)變量:MOVED -1、TREEBIN -2、RESERVED -3、HASH_BITS > 0
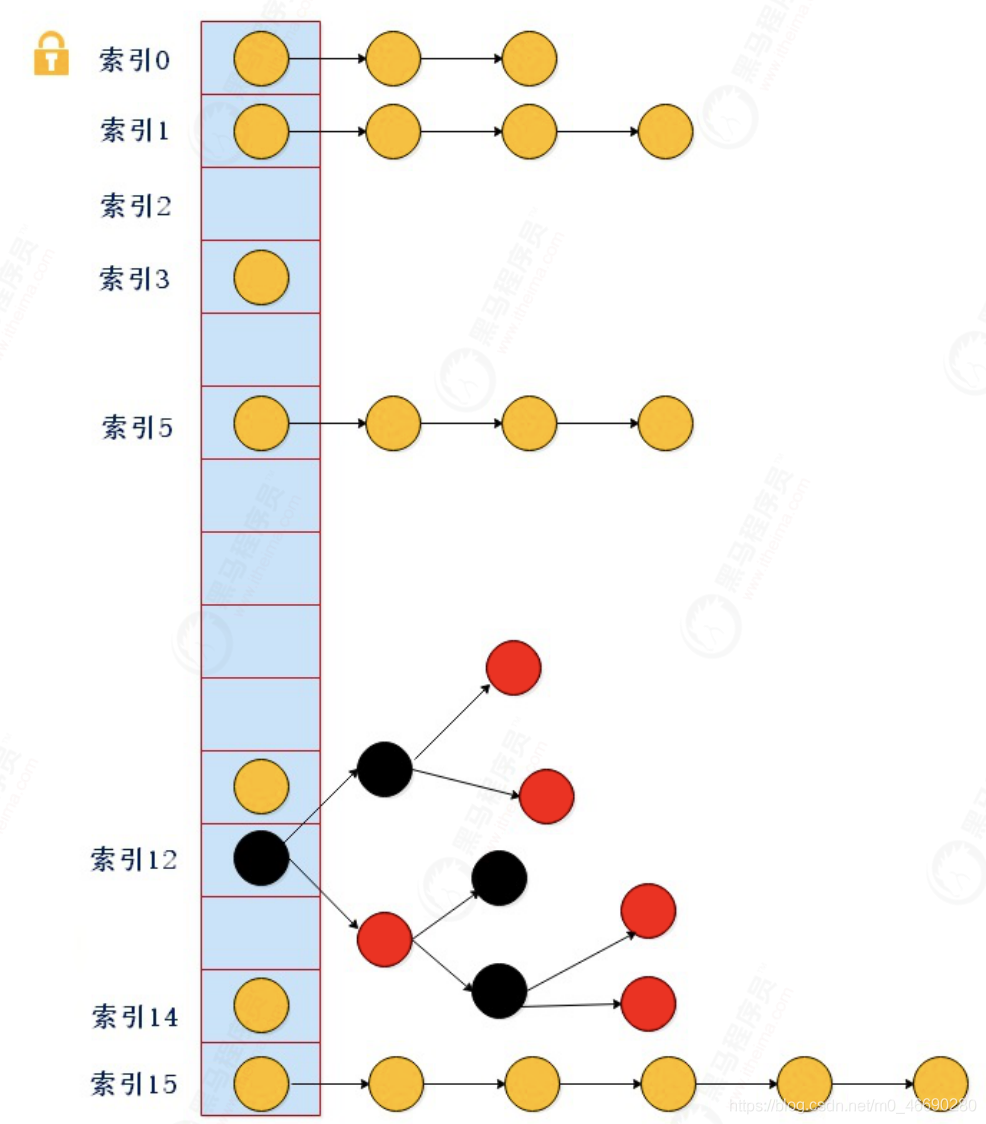
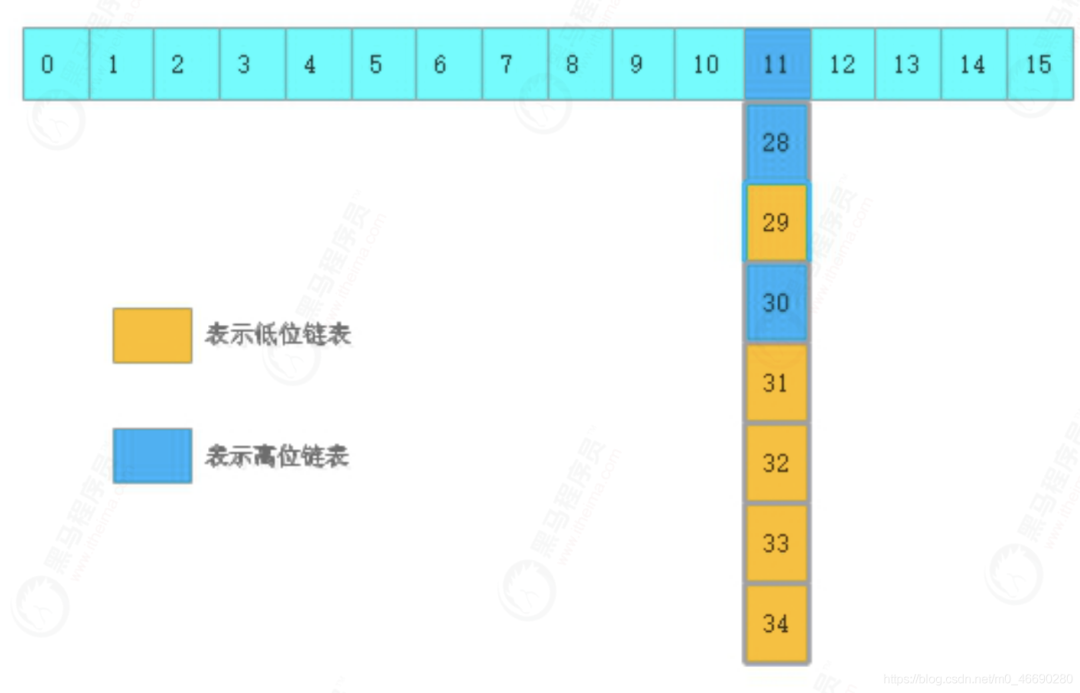
if (fh >= 0) {
// 和老長度進(jìn)行與運(yùn)算,由于 Map 的長度都是 2 的次方(16就是 10000 這類的數(shù)字)
// 那么取與 n 只有 2 種結(jié)果,一種是 0,一種是n
// 如果是結(jié)果是0 ,拆分后,Doug Lea 將其放在低位鏈表,反之放在 高位鏈表
// 這里和HashMap的算法不一樣了!
int runBit = fh & n;
Node<K,V> lastRun = f;
// 遍歷這個桶,注意,這地方有個討巧的操作!往下看 ↓ (可以借助下 面的圖來同步說明)
for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
// 沿著鏈往下走,挨個取與
int b = p.hash & n;
// 如果和上次循環(huán)的值相等,那不動(當(dāng)然第一次的話就是和頭節(jié)點(diǎn) 比較)
if (b != runBit) {
//如果不相等的話,就切換值
runBit = b;// 0遍。
lastRun = p;// 這個 lastRun 保證后面的節(jié)點(diǎn)與自己的 取于值相同,避免后面沒
}
}
//思考一下,經(jīng)過上一輪遍歷完,發(fā)生了什么?
// runBit 要么是0 要么是1 ,
// lastRun 指向了最后一次切換的那個節(jié)點(diǎn),它后面再沒發(fā)生或切換
// 也就意味著,lastRun后面所有的節(jié)點(diǎn)和它都具備相同的runBit值
// 想想,可以做什么???
// 對!在lastRun處直接切斷!帶著后面的尾巴,直接當(dāng)做拆分后的高 位,或者低位鏈表
// 這樣就不需要和hashMap一樣挨個斷開指針,再挨個接一遍到新鏈,一 鍋端就行了
if (runBit == 0) { // 如果最后的 runBit 是 0 ,直接當(dāng)?shù)臀绘湵?br> ln = lastRun;
hn = null;
}
else {
hn = lastRun; // 如果最后的 runBit 是 1, 直接當(dāng)高位鏈表
ln = null;
}
// 那么lastRun前面剩下的那些呢?
// 再遍歷一遍就是了,注意,是從頭結(jié)點(diǎn)f遍歷到lastRun,后面的不需 要操心了
for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
if ((ph & n) == 0)
// 如果與運(yùn)算結(jié)果是 0,那么放低位鏈 表,注意是頭插
ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);// 參數(shù)里的ln 是next,頭插!
else // 1 則放高位
hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
}
// 這里往下就類似 hashMap
// 設(shè)置低位鏈表放在新鏈表的 i
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
// 設(shè)置高位鏈表,在原有長度上加 n
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
// 將舊的鏈表設(shè)置成占位符,表示遷移完了!
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
// 繼續(xù)向后推進(jìn)
advance = true;
}
// 如果是紅黑樹
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
// 遍歷
for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {
int h = e.hash;
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>
(h, e.key, e.val, null, null);
// 和鏈表相同的判斷,與運(yùn)算 == 0 的放在低位
if ((h & n) == 0) {
if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
lo = p;
else
loTail.next = p;
loTail = p;
++lc;
}// 不是 0 的放在高位
else {
if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
hi = p;
else
hiTail.next = p;
hiTail = p;
++hc;
}
}
// 如果樹的節(jié)點(diǎn)數(shù)小于等于 6,那么轉(zhuǎn)成鏈表,反之,創(chuàng)建一個新的樹
ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;
hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;
// 低位樹
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
// 高位樹
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
// 舊的設(shè)置成占位符
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
// 繼續(xù)向后推進(jìn)
advance = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
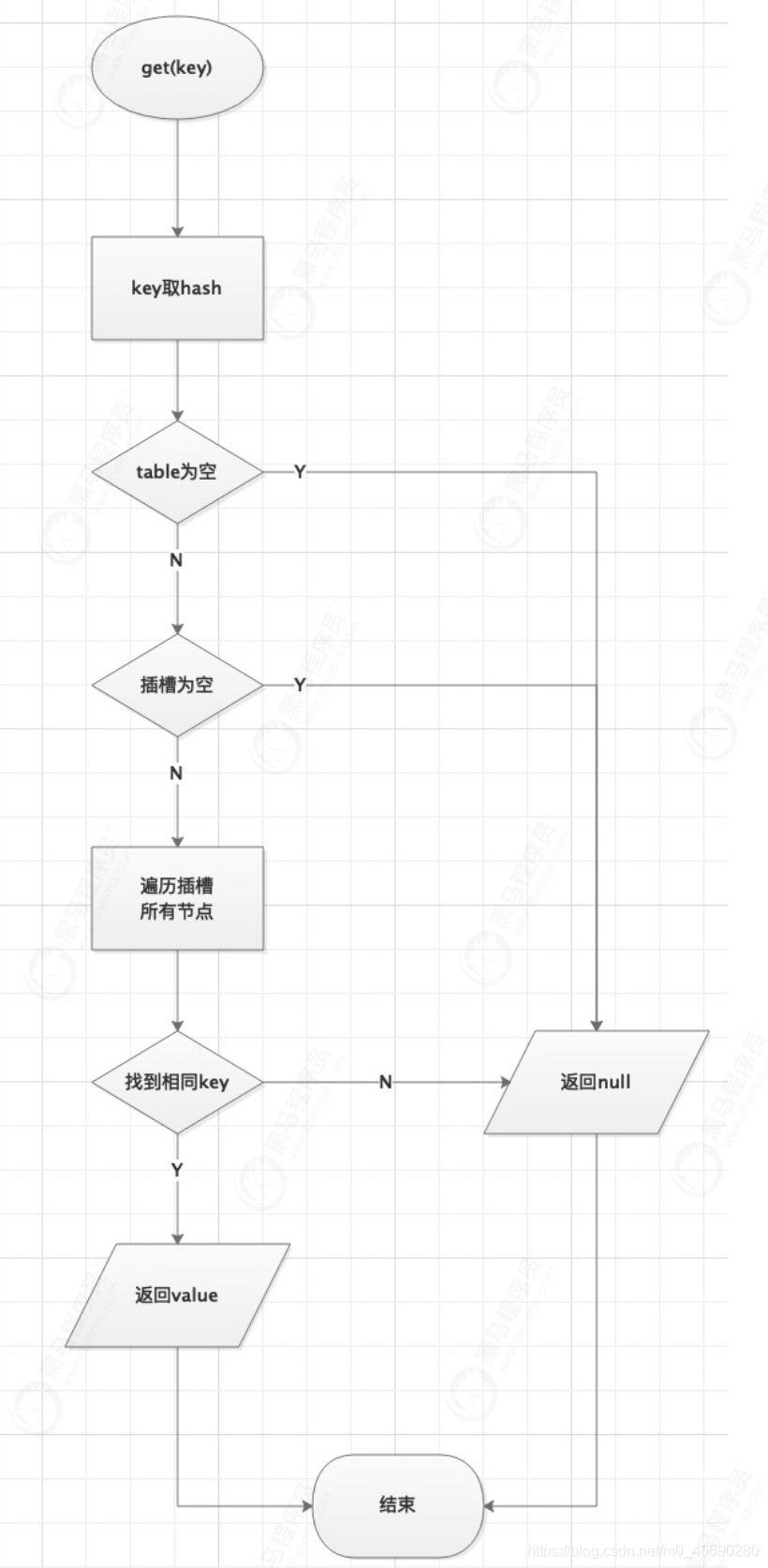
2.3.5 get方法
//get操作無鎖
//因?yàn)镹ode的val和next是用volatile修飾的
//多線程環(huán)境下線程A修改結(jié)點(diǎn)的val或者新增節(jié)點(diǎn)的時候是對線程B可見的
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
//key取hash
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
//1.判斷table是不是空的,2.當(dāng)前桶上是不是空的
//如果為空,返回null
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
//找到對應(yīng)hash槽的第一個node,如果key相等,返回value
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
//hash值為負(fù)值表示正在擴(kuò)容,這個時候查的是ForwardingNode的find方法來定位到 nextTable新表中
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {//既不是首節(jié)點(diǎn)也不是ForwardingNode,那就往下 遍歷
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
//遍歷完還沒找到,返回null
return null;
}
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V val;
volatile Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;
缺點(diǎn):
最大缺點(diǎn)就是ABA問題
ABA:如果一個值原來是A,變成了B,又變成了A,那么使用CAS進(jìn)行檢查時會發(fā)現(xiàn)它的值沒有發(fā)生變化,但 是實(shí)際上卻變化了
解決方案:
1、使用版本號。在變量前面追加上版本號,每次變量更新的時候把版本號加一,那么A-B-A 就會變成 1A-2B-3A
2、從Java1.5開始JDK的atomic包里提供了一個類AtomicStampedReference來解決ABA問題
這個類的compareAndSet方法作用是首先檢查當(dāng)前引用是否等于預(yù)期引用,并且當(dāng)前標(biāo)志是否等于預(yù)期標(biāo) 志,如果全部相等,則更新
版權(quán)聲明:本文為博主原創(chuàng)文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版權(quán)協(xié)議,轉(zhuǎn)載請附上原文出處鏈接和本聲明。
本文鏈接:
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_46690280/article/details/117553508


評論
圖片
表情