用Qt寫一個簡單的代碼編輯器
關(guān)注、星標公眾號,直達精彩內(nèi)容
來源:技術(shù)讓夢想更偉大
作者:李肖遙
這次的代碼編輯器比較簡單,主要有以下幾個功能:
簡單編輯
顯示行號
突出顯示當前行
如下圖所示,主要來看看怎么實現(xiàn)。
代碼編輯器的實現(xiàn)
代碼編輯器主要是使用了CodeEditor和LineNumberArea,其實現(xiàn)步驟如下:
CodeEditor是繼承QPlainTextEdit的小部件,在CodeEditor(LineNumberArea)中保留一個單獨的小部件,在其上繪制行號。
QPlainTextEdit繼承自QAbstractScrollArea,并且編輯在其viewport()的邊距內(nèi)進行。通過將視口的左邊距設(shè)置為繪制行號所需的尺寸,為行號區(qū)域騰出空間。
在編輯代碼時,我們首選QPlainTextEdit而不是QTextEdit,因為它已針對處理純文本進行了優(yōu)化。
除了用戶可以使用鼠標或鍵盤進行的選擇之外,QPlainTextEdit還允許我們添加選擇,我們使用此功能突出顯示當前行。
LineNumberArea類
在此部件上繪制行號,并將其放置在CodeEditor的viewport()的左邊距區(qū)域上,QWidget類也可以幫助我們對其內(nèi)容進行滾動。另外,如果使用斷點或其他代碼編輯器功能擴展編輯器,單獨的窗口小部件是正確的選擇。
class LineNumberArea : public QWidget
{
public:
LineNumberArea(CodeEditor *editor) : QWidget(editor) {
codeEditor = editor;
}
QSize sizeHint() const {
return QSize(codeEditor->lineNumberAreaWidth(), 0);
}
protected:
void paintEvent(QPaintEvent *event) {
codeEditor->lineNumberAreaPaintEvent(event);
}
private:
CodeEditor *codeEditor;
};
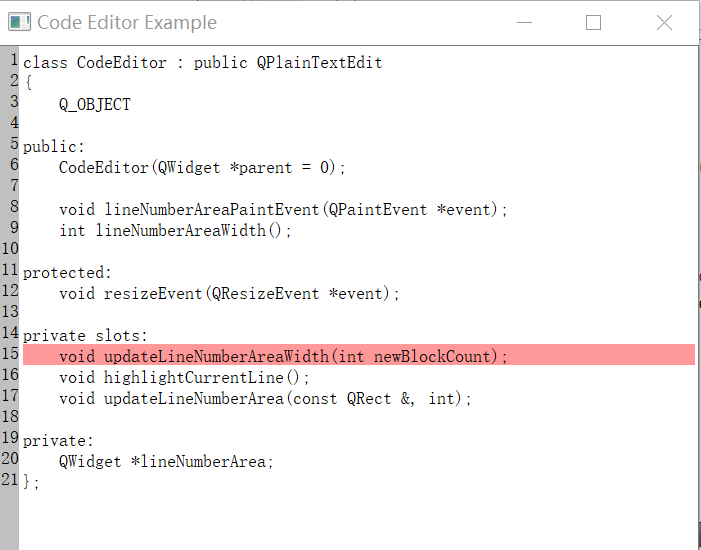
CodeEditor類定義
這是代碼編輯器的類定義:
class CodeEditor : public QPlainTextEdit
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
CodeEditor(QWidget *parent = 0);
void lineNumberAreaPaintEvent(QPaintEvent *event);
int lineNumberAreaWidth();
protected:
void resizeEvent(QResizeEvent *event);
private slots:
void updateLineNumberAreaWidth(int newBlockCount);
void highlightCurrentLine();
void updateLineNumberArea(const QRect &, int);
private:
QWidget *lineNumberArea;
};
在編輯器中,調(diào)整大小并在LineNumberArea上繪制行號,當編輯器中的行數(shù)更改以及滾動編輯器的viewport()時,執(zhí)行此操作,每當光標的位置發(fā)生變化時,會在highlightCurrentLine()中突出顯示當前行。
CodeEditor類的實現(xiàn)
現(xiàn)在,我們將從構(gòu)造函數(shù)開始,通過代碼編輯器實現(xiàn)。
CodeEditor::CodeEditor(QWidget *parent) : QPlainTextEdit(parent)
{
lineNumberArea = new LineNumberArea(this);
connect(this, SIGNAL(blockCountChanged(int)), this, SLOT(updateLineNumberAreaWidth(int)));
connect(this, SIGNAL(updateRequest(QRect,int)), this, SLOT(updateLineNumberArea(QRect,int)));
connect(this, SIGNAL(cursorPositionChanged()), this, SLOT(highlightCurrentLine()));
updateLineNumberAreaWidth(0);
highlightCurrentLine();
}
在構(gòu)造函數(shù)中,我們將插槽連接到QPlainTextEdit中的信號,創(chuàng)建編輯器時,必須計算行號區(qū)域的寬度并突出顯示第一行。
int CodeEditor::lineNumberAreaWidth()
{
int digits = 1;
int max = qMax(1, blockCount());
while (max >= 10) {
max /= 10;
++digits;
}
int space = 3 + fontMetrics().width(QLatin1Char('9')) * digits;
return space;
}
lineNumberAreaWidth()函數(shù)計算LineNumberArea小部件的寬度,在編輯器的最后一行取位數(shù),然后將其乘以位數(shù)的最大寬度。
void CodeEditor::updateLineNumberAreaWidth(int /* newBlockCount */)
{
setViewportMargins(lineNumberAreaWidth(), 0, 0, 0);
}
當更新行號區(qū)域的寬度時,我們只需調(diào)用QAbstractScrollArea::setViewportMargins()。
void CodeEditor::updateLineNumberArea(const QRect &rect, int dy)
{
if (dy)
lineNumberArea->scroll(0, dy);
else
lineNumberArea->update(0, rect.y(), lineNumberArea->width(), rect.height());
if (rect.contains(viewport()->rect()))
updateLineNumberAreaWidth(0);
}
當編輯器窗口已滾動時,將調(diào)用此函數(shù)來更新重新繪制。
void CodeEditor::resizeEvent(QResizeEvent *e)
{
QPlainTextEdit::resizeEvent(e);
QRect cr = contentsRect();
lineNumberArea->setGeometry(QRect(cr.left(), cr.top(), lineNumberAreaWidth(), cr.height()));
}
當編輯器的大小更改時,還需要調(diào)整行號區(qū)域的大小,代碼如下。
void CodeEditor::highlightCurrentLine()
{
QList<QTextEdit::ExtraSelection> extraSelections;
if (!isReadOnly()) {
QTextEdit::ExtraSelection selection;
QColor lineColor = QColor(Qt::yellow).lighter(160);
selection.format.setBackground(lineColor);
selection.format.setProperty(QTextFormat::FullWidthSelection, true);
selection.cursor = textCursor();
selection.cursor.clearSelection();
extraSelections.append(selection);
}
setExtraSelections(extraSelections);
}
當光標位置更改時,我們突出顯示當前行,即包含光標的行,在此之前需要先清除光標選擇。
使用文本光標設(shè)置選擇,使用FullWidthSelection屬性時,將選擇當前光標文本塊,并根據(jù)設(shè)置的位置移動光標。
void CodeEditor::lineNumberAreaPaintEvent(QPaintEvent *event)
{
QPainter painter(lineNumberArea);
painter.fillRect(event->rect(), Qt::lightGray);
每當LineNumberAreaPaintEvent()收到繪制事件時,就會從LineNumberArea調(diào)用它。函數(shù)如下
QTextBlock block = firstVisibleBlock();
int blockNumber = block.blockNumber();
int top = (int) blockBoundingGeometry(block).translated(contentOffset()).top();
int bottom = top + (int) blockBoundingRect(block).height();
遍歷所有可見線號,在純文本編輯中,每一行將包含一個QTextBlock,獲得第一個文本塊的頂部和底部y坐標,并在循環(huán)的每次迭代中通過當前文本塊的高度調(diào)整這些值。
while (block.isValid() && top <= event->rect().bottom()) {
if (block.isVisible() && bottom >= event->rect().top()) {
QString number = QString::number(blockNumber + 1);
painter.setPen(Qt::black);
painter.drawText(0, top, lineNumberArea->width(), fontMetrics().height(),
Qt::AlignRight, number);
}
block = block.next();
top = bottom;
bottom = top + (int) blockBoundingRect(block).height();
++blockNumber;
}
注意,除了檢查該塊是否在視口區(qū)域之外,我們還要檢查該塊是否可見。
擴展
除了行號之外,還可以在額外的區(qū)域中添加更多內(nèi)容,例如,斷點等等,本文是一個入門級別的編譯器,后續(xù)會增加更多功能
嵌入式編程專輯 Linux 學(xué)習(xí)專輯 C/C++編程專輯 Qt進階學(xué)習(xí)專輯
關(guān)注我的微信公眾號,回復(fù)“加群”按規(guī)則加入技術(shù)交流群。
點擊“閱讀原文”查看更多分享。
