這次終于把Java NIO搞懂了
點擊上方藍色字體,選擇“標星公眾號”
優(yōu)質(zhì)文章,第一時間送達
Java NIO 和 IO 的區(qū)別
緩沖區(qū)存取數(shù)據(jù)的兩個核心方法
put:存入數(shù)據(jù)到緩沖區(qū)
get:獲取緩沖區(qū)中的數(shù)據(jù)
緩沖區(qū)的四個核心屬性
capacity:容量,表示緩沖區(qū)中最大存儲數(shù)據(jù)的容量,一旦聲明不能改變
position:位置,表示緩沖區(qū)中正在操作數(shù)據(jù)的位置
limit:界限,表示緩沖區(qū)中可以操作數(shù)據(jù)的大小。(limit后的數(shù)據(jù)不能進行讀寫)
mark:標記,表示記錄當前position的位置,可以通過reset恢復(fù)到mark的位置
0 <= mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
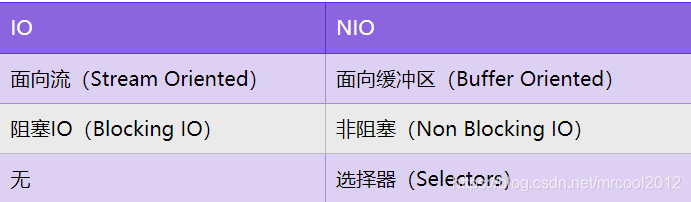
直接緩沖區(qū)與非直接緩沖區(qū)
非直接緩沖區(qū):通過allocate()方法分配的緩沖區(qū),將緩沖區(qū)建立在JVM的內(nèi)存中
直接緩沖區(qū):通過allocateDirect()方法分配的緩沖區(qū),將緩沖區(qū)建立在操作系統(tǒng)的物理內(nèi)存中。可以提高效率
非直接緩沖區(qū)工作原理圖
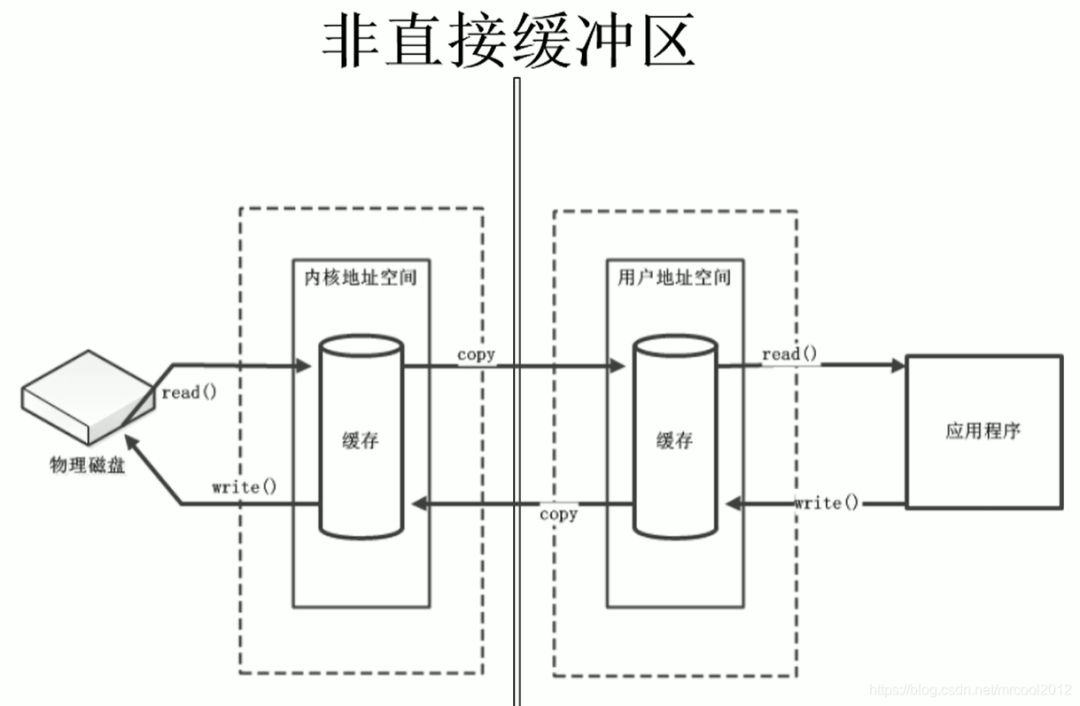
直接緩沖區(qū)工作原理圖

通道
通道(Channel):由java.nio.channels包定義的。channel表示IO源與目標打開的連接。channel類似于傳統(tǒng)的“流”。只不過channel本身不能直接訪問數(shù)據(jù),channel只能與buffer進行交互,在Java NIO中負責緩沖區(qū)數(shù)據(jù)的傳輸。
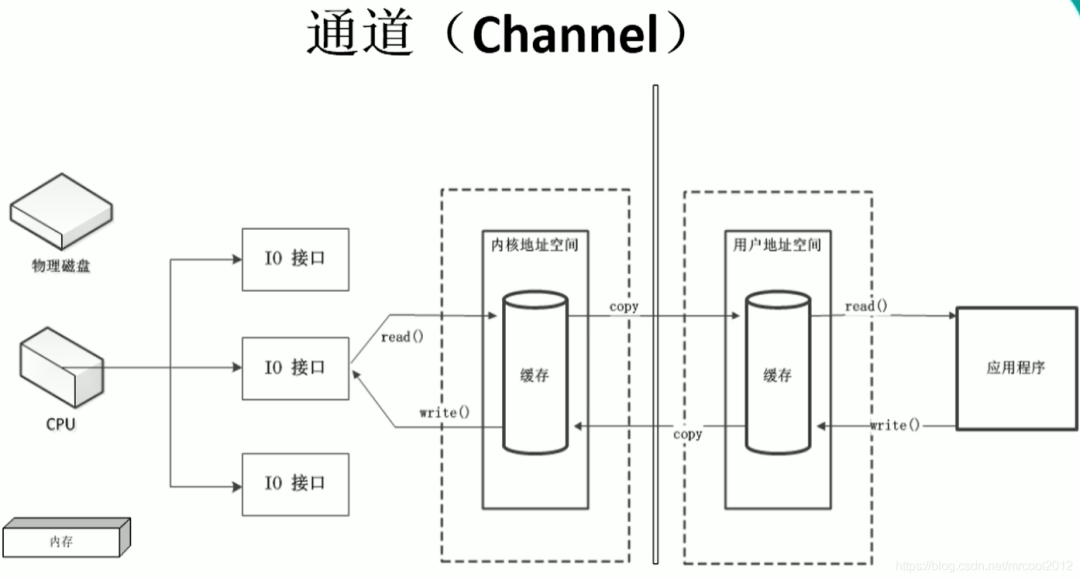
應(yīng)用程序向系統(tǒng)發(fā)起讀寫請求,調(diào)用操作系統(tǒng)的IO接口,IO接口由CPU統(tǒng)一調(diào)配,當讀寫請求過大,會大大占用CPU的資源,會嚴重影響效率,CPU要處理大量的IO請求,分配IO接口,就沒法做其他事情了。
CPU:中央處理器

進行了修改,添加了DMA,直接存儲器;當應(yīng)用程序向操作系統(tǒng)發(fā)起IO請求,首先DMA會向CPU申請權(quán)限,如果CPU給與權(quán)限,那么后續(xù)的讀寫請求就全權(quán)由DMA負責操作;這樣的好處就是在執(zhí)行IO請求時,CPU可以不進行干預(yù),去處理其他事情
但是DMA仍然有缺點,比如當一個大型的應(yīng)用程序發(fā)起大量的IO請求,DMA仍然要向CPU請求資源,影響效率
在IO接口和內(nèi)存之間,會有一個DMA傳輸數(shù)據(jù)總線
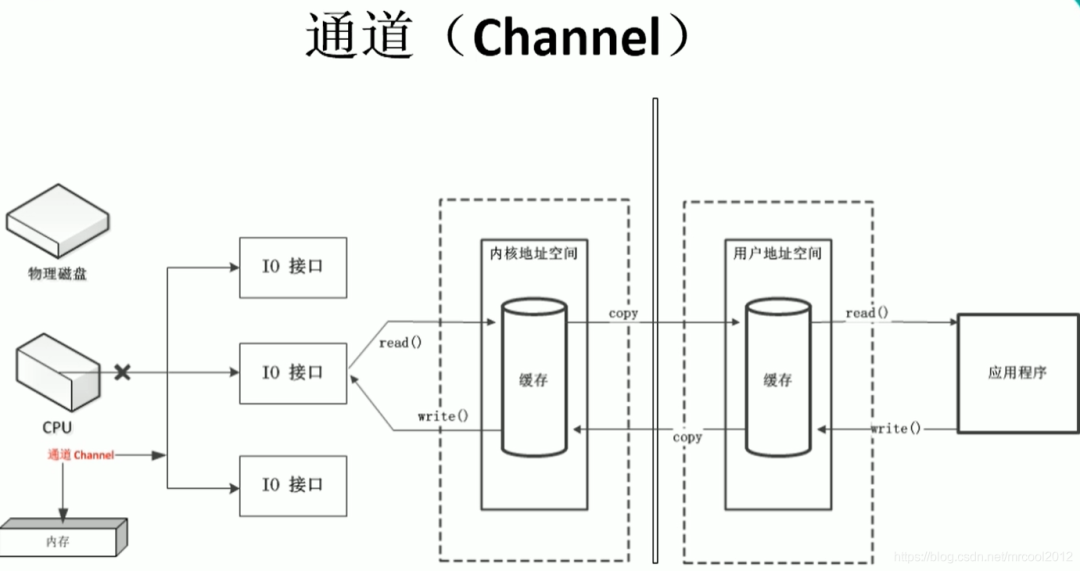
通道,可以理解為一個完全獨立的處理器,專門用于IO操作;通道仍然依附于CPU,但是它有自己的一套指令,是獨立的處理器
通道的主要實現(xiàn)類
在java.nio.channels.Channel接口:
? ? |--FileChannel:文件通道,專門用于操作本地文件,用于本地文件傳輸
? ? |--SocketChannel
? ? |--ServerSocketChannel
? ? |--DatagramChannel
?
SocketChannel 和 ServerSocketChannel 用于TCP;DatagramChannel 用于UDP(UDP,User Datagram Protocol)
后三個都是用于網(wǎng)絡(luò)IO
?
獲取通道
JDK1.7以后有三種方式
1、Java針對支持通道的類提供了getChannel()方法
?? ?? ? 本地IO:FileInputStream/FileOutputStream/RandomAccessFile
?? ?? ? 網(wǎng)絡(luò)IO:Socket/ServerSocket/DatagramSocket
2、在JDK1.7中的NIO.2 針對各個通道提供了一個靜態(tài)方法 open()
3、在JDK1.7中的NIO.2 的Files工具欄的newByteChannel()
//用非直接通道完成文件的傳輸
@Test
public?void?test5(){
????FileInputStream?fis?=?null;
????FileOutputStream?fos?=?null;
????FileChannel?inChannel?=?null;
????FileChannel?outChannel?=?null;
????try?{
????????//獲取文件流
????????fis?=?new?FileInputStream("E:\\休閑生活\\桌面壁紙\\王麗坤.jpg");
????????fos?=?new?FileOutputStream("E:\\休閑生活\\桌面壁紙\\2.jpg");
?
?
????????//?1.?獲取通道
????????inChannel?=?fis.getChannel();
????????outChannel?=?fos.getChannel();
?
?
????????//?2.?分配緩沖區(qū)
????????ByteBuffer?buf?=?ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
?
?
????????//?3.?讀取數(shù)據(jù)
????????while?(inChannel.read(buf)?!=?-1){
????????????//?4.?切換讀模式
????????????buf.flip();
????????????//?5.?寫數(shù)據(jù)
????????????outChannel.write(buf);
????????????buf.clear();????//?緩沖區(qū)循環(huán)重復(fù)讀寫數(shù)據(jù)
????????}
????}?catch?(IOException?e)?{
????????e.printStackTrace();
????}?finally?{
????????//?6.?關(guān)閉通道,關(guān)閉流
????????if(inChannel!=null){
????????????try?{
????????????????inChannel.close();
????????????}?catch?(IOException?e)?{
????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????}
????????}
????????if(outChannel!=null){
????????????try?{
????????????????outChannel.close();
????????????}?catch?(IOException?e)?{
????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????}
????????}
????????if(fis!=null){
????????????try?{
????????????????fis.close();
????????????}?catch?(IOException?e)?{
????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????}
????????}
????????if(fos!=null){
????????????try?{
????????????????fos.close();
????????????}?catch?(IOException?e)?{
????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????}
????????}
????}
}
//用直接通道完成文件的傳輸
@Test
public?void?test6(){
????FileChannel?inChannel?=?null;
????FileChannel?outChannel?=?null;
????try?{
????????//FileChannel.open()的兩個參數(shù):路徑path,模式
????????//StandardOpenOption.READ?讀模式
????????inChannel?=?FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E:\\休閑生活\\桌面壁紙\\王麗坤.jpg"),?StandardOpenOption.READ);
????????//StandardOpenOption.CREATE_NEW?創(chuàng)建模式,當路徑下有同名文件時報錯,沒有就創(chuàng)建
????????//StandardOpenOption.CREATE?創(chuàng)建模式,當路徑下有同名文件時會覆蓋,沒有就創(chuàng)建
????????outChannel?=?FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E:\\休閑生活\\桌面壁紙\\2.jpg"),?StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE_NEW);
?
?
????????//?內(nèi)存映射文件
????????MappedByteBuffer?inMappedBuffer?=?inChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY,?0,?inChannel.size());
????????MappedByteBuffer?outMappedBuffer?=?outChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE,?0,?inChannel.size());
?
?
????????//讀寫文件
????????byte[]?bytes?=?new?byte[inMappedBuffer.limit()];
????????inMappedBuffer.get(bytes);
????????outMappedBuffer.put(bytes);
????}?catch?(IOException?e)?{
????????e.printStackTrace();
????}?finally?{
????????if(inChannel!=null){
????????????try?{
????????????????inChannel.close();
????????????}?catch?(IOException?e)?{
????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????}
????????}
????????if(outChannel!=null){
????????????try?{
????????????????outChannel.close();
????????????}?catch?(IOException?e)?{
????????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????????}
????????}
????}
}
通道間的數(shù)據(jù)傳輸
transferTo()
transferFrom()
????//?通道之間的數(shù)據(jù)傳輸
????@Test
????public?void?test7()?throws?IOException?{
????????FileChannel?inChannel?=?FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E:\\學習視頻\\JavaNIO\\nio\\1.?尚硅谷_NIO_NIO?與?IO?區(qū)別.avi"),?StandardOpenOption.READ);
????????FileChannel?outChannel?=?FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E:\\學習視頻\\JavaNIO\\nio\\1.avi"),StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE_NEW);
?
????????inChannel.transferTo(0,inChannel.size(),outChannel);
//????????outChannel.transferFrom(inChannel,0,inChannel.size());
?
????????inChannel.close();
????????outChannel.close();
????}
分散(Scatter)與聚集(Gather)
分散讀取:Scattering Reads,將通道中的數(shù)據(jù)分散到多個緩沖區(qū)中
聚集寫入:Gathering Writes,將多個緩沖區(qū)中的數(shù)據(jù)聚集到通道中

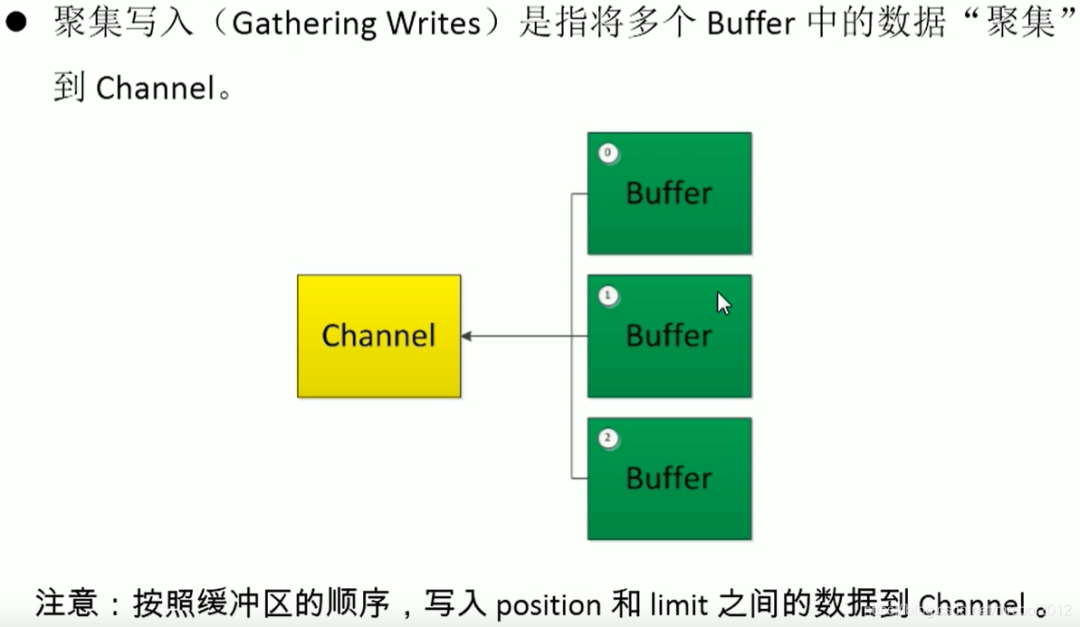
//分散與聚集
@Test
public?void?test8()?throws?IOException?{
????RandomAccessFile?file?=?new?RandomAccessFile("C:\\Users\\FMM.000\\Desktop\\spring?ioc流程.txt","rw");
????//?獲取通道
????FileChannel?fileChannel?=?file.getChannel();
????//?分配指定大小的緩沖區(qū)
????ByteBuffer?buf1?=?ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
????ByteBuffer?buf2?=?ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
????//?分散讀取
????ByteBuffer[]?bufs?=?{buf1,buf2};
????fileChannel.read(bufs);
?
?
????for(ByteBuffer?buffer?:?bufs){
????????buffer.flip();
????}
????System.out.println(new?String(bufs[0].array(),0,bufs[0].limit()));
????System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
????System.out.println(new?String(bufs[1].array(),0,bufs[1].limit()));
?
?
????//?聚集寫入
????RandomAccessFile?file1?=?new?RandomAccessFile("C:\\Users\\FMM.000\\Desktop\\ioc流程.txt","rw");
????FileChannel?fileChannel1?=?file1.getChannel();
????fileChannel1.write(bufs);
????//?關(guān)閉通道
????fileChannel.close();
????fileChannel1.close();
}
字符集Charset
編碼:字符串--->字節(jié)數(shù)組
解碼:字節(jié)數(shù)組--->字符串
//?編碼解碼
@Test
public?void?test10()?throws?CharacterCodingException?{
????Charset?charset?=?Charset.forName("GBK");
????//?獲取編碼器
????CharsetEncoder?encoder?=?charset.newEncoder();
????//?獲取解碼器
????CharsetDecoder?decoder?=?charset.newDecoder();
?
?
????CharBuffer?charBuffer?=?CharBuffer.allocate(1024);
????charBuffer.put("尚硅谷威武!");
????//?切換讀模式
????charBuffer.flip();
?
?
????//?編碼
????ByteBuffer?buffer?=?encoder.encode(charBuffer);
????for?(int?i?=?0;?i?????????System.out.println(buffer.get());
????}
????//?解碼
????buffer.flip();
????CharBuffer?cb?=?decoder.decode(buffer);
????System.out.println(cb.toString());
????System.out.println("============================");
????buffer.flip();
????Charset?cs?=?Charset.forName("UTF-8");
????CharBuffer?cBuf?=?cs.decode(buffer);
????System.out.println(cBuf.toString());
}
使用NIO完成網(wǎng)絡(luò)通信的三大核心:
1、通道(Channel):負責連接
? ? java.nio.channels.Channel 接口:
?? ?? ? |--SelectableChannel
?? ??? ?? ? |--SocketChannel
?? ??? ?? ? |--ServerSocketChannel? ? //上兩個是TCP
?? ??? ?? ? |--DatagramChannel?? ?? ? //UDP,都是用于網(wǎng)絡(luò) IO
?
?? ??? ?? ? |--Pipe.SinkChannel
?? ??? ?? ? |--Pipi.SourceChannel
?
2、緩沖區(qū)(Buffer):負責數(shù)據(jù)的存取
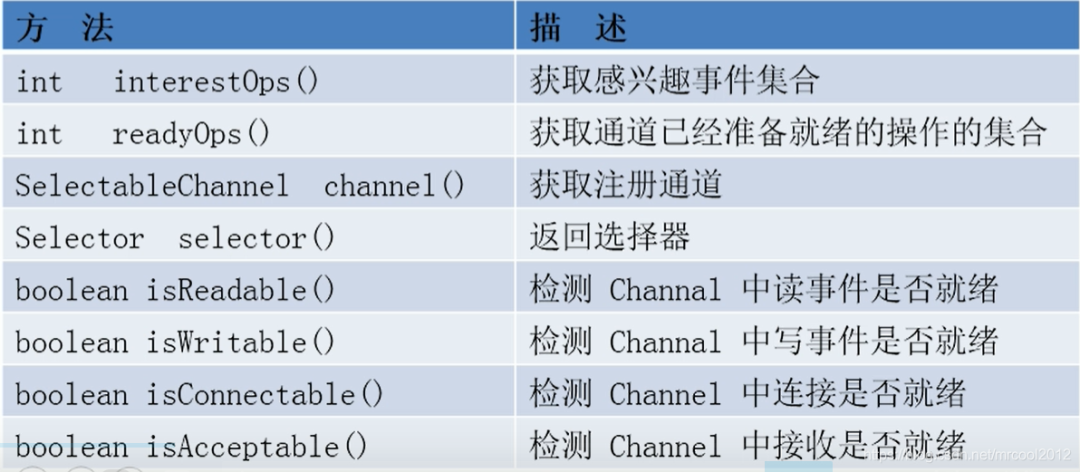
3、選擇器(Selector):是 SelectableChannel 的多路復(fù)用器,用于監(jiān)控 SelectableChannel 的 IO 狀況
?? ?? ? SelectionKey:表示 SelectableChannel 和 Selector 之間的注冊關(guān)系。每次向選擇器注冊通道時就會選澤一個事件(選擇鍵)

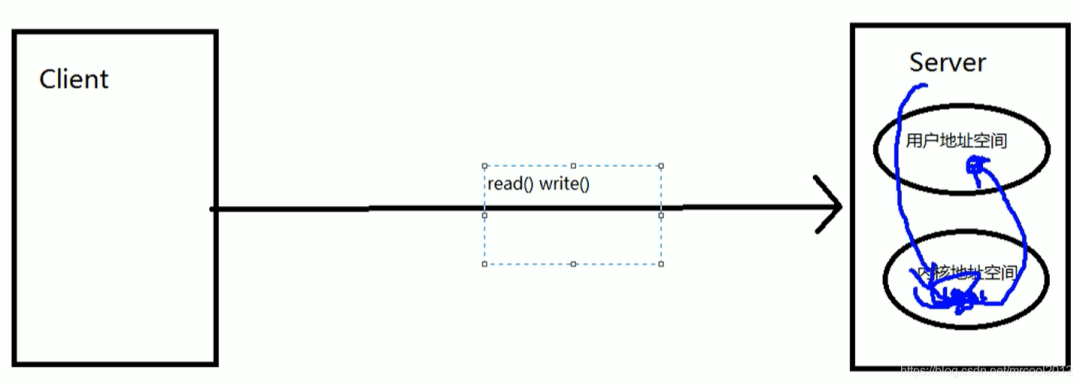
示例1:阻塞式IO
當client端向server端發(fā)送請求時,如果server端不能確定client請求的讀/寫的數(shù)據(jù),server端會處于阻塞狀態(tài),阻塞狀態(tài)下server端下的此線程不能做其他操作,一直等待,當server有client端需要讀/寫的數(shù)據(jù)時,會將數(shù)據(jù)讀/寫給用戶,然后釋放資源
//?模擬網(wǎng)絡(luò)IO,客戶端
@Test
public?void?nioClient(){
????SocketChannel?socketChannel?=?null;
????FileChannel?fileChannel?=?null;
????try?{
????????//?1.?獲取通道
????????socketChannel?=?SocketChannel.open(new?InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9898));
?
????????fileChannel?=?FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E:\\休閑生活\\桌面壁紙\\無情的戰(zhàn)爭.jpg"),?StandardOpenOption.READ);
????????//?2.?分配指定大小緩沖區(qū)
????????ByteBuffer?buf?=?ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
????????//?3.?讀取本地文件,并發(fā)送到服務(wù)器
????????while?(fileChannel.read(buf)!=-1){
????????????buf.flip();
????????????socketChannel.write(buf);
????????????buf.clear();
????????}
?
????}?catch?(Exception?e)?{
????????e.printStackTrace();
????}?finally?{
????????//?關(guān)閉通道
????????try?{
????????????if(fileChannel!=null){
????????????????fileChannel.close();
????????????}
????????????if?(socketChannel!=null){
????????????????socketChannel.close();
????????????}
????????}?catch?(IOException?e)?{
????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????}
????}
}
?
?
//?服務(wù)端
@Test
public?void?nioServer(){
????ServerSocketChannel?ssChannel?=?null;
????FileChannel?outChannel?=?null;
????try?{
????????//?1.?獲取通道
????????ssChannel?=?ServerSocketChannel.open();
????????outChannel?=?FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E:\\休閑生活\\桌面壁紙\\2.jpg"),StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
????????//?2.?綁定連接
????????ssChannel.bind(new?InetSocketAddress(9898));
????????//?3.?獲取客戶端通道
????????SocketChannel?sChannel?=?ssChannel.accept();
????????//?4.?分配指定大小的緩沖區(qū)
????????ByteBuffer?buf?=?ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
????????//?5.?接收客戶端數(shù)據(jù),并保存到本地
????????while?(sChannel.read(buf)!=-1){
????????????buf.flip();
????????????outChannel.write(buf);
????????????buf.clear();
????????}
?
?
????}?catch?(IOException?e)?{
????????e.printStackTrace();
????}?finally?{
????????//?關(guān)閉通道
????????try?{
????????????if(outChannel!=null){
????????????????outChannel.close();
????????????}
????????????if(ssChannel!=null){
????????????????ssChannel.close();
????????????}
????????}?catch?(Exception?e){
????????????e.printStackTrace();
????????}
????}
}
非阻塞式IO
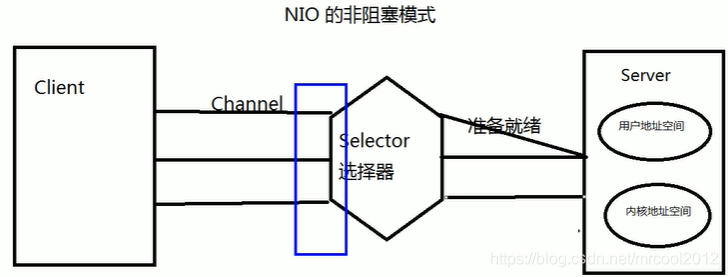
示例1:非阻塞式IO
public?class?TestNonBlockingIO?{
?
?
????@Test
????public?void?client()?throws?IOException?{
????????//獲取通道
????????SocketChannel?sChannel?=?SocketChannel.open(new?InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",?9898));
????????//切換成非阻塞式
????????sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
????????//分配指定大小的緩沖區(qū)
????????ByteBuffer?buf?=?ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
????????//發(fā)送數(shù)據(jù)給服務(wù)端
//????????buf.put(LocalDateTime.now().toString().getBytes());
????????Scanner?scanner?=?new?Scanner(System.in);
????????while?(scanner.hasNext()){
????????????String?str?=?scanner.next();
????????????buf.put((new?Date().toString()?+"\n"?+?str).getBytes());
????????????buf.flip();
????????????sChannel.write(buf);
????????????buf.clear();
????????}
?
?
????????//關(guān)閉通道
????????sChannel.close();
????}
?
?
????@Test
????public?void?server()?throws?IOException?{
????????//?1.?獲取通道
????????ServerSocketChannel?ssChannel?=?ServerSocketChannel.open();
????????//?2.?切換非阻塞式
????????ssChannel.configureBlocking(false);
????????//?3.?綁定連接
????????ssChannel.bind(new?InetSocketAddress(9898));
????????//?4.?獲取選擇器
????????Selector?selector?=?Selector.open();
????????//?5.?將通道注冊到選擇器上,并指定“監(jiān)聽連接事件”
????????ssChannel.register(selector,?SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
????????//?6.?輪詢式的獲取選擇器上以及“準備就緒”的事件
????????while?(selector.select()>0){
????????????//?7.?獲取當前選擇器中所有注冊的“選擇鍵(已就緒的監(jiān)聽事件)”
????????????Iterator?it?=?selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
????????????while?(it.hasNext()){
????????????????//?8.?獲取準備“就緒”的事件
????????????????SelectionKey?sk?=?it.next();
????????????????//?9.?判斷具體是什么事件準備就緒
????????????????if(sk.isAcceptable()){
????????????????????//?10.?若“接收就緒”,獲取客戶端連接
????????????????????SocketChannel?sChannel?=?ssChannel.accept();
????????????????????//?11.?切換非阻塞模式
????????????????????sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
????????????????????//?12.?將該通道注冊到選擇器上
????????????????????sChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
????????????????}?else?if(sk.isReadable()){
????????????????????//?13.?獲取當前選擇器上“讀就緒”狀態(tài)的通道
????????????????????SocketChannel?sChannel?=?(SocketChannel)?sk.channel();
????????????????????//?14.?讀取數(shù)據(jù)
????????????????????ByteBuffer?buf?=?ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
????????????????????int?len?=?0;
????????????????????while?((len?=?sChannel.read(buf))>0){
????????????????????????buf.flip();
????????????????????????System.out.println(new?String(buf.array(),0,len));
????????????????????????buf.clear();
????????????????????}
????????????????}
????????????????//?15.?取消選擇鍵,SelectionKey
????????????????it.remove();
????????????}
????????}
????}
}
版權(quán)聲明:本文為博主原創(chuàng)文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版權(quán)協(xié)議,轉(zhuǎn)載請附上原文出處鏈接和本聲明。
本文鏈接:
https://blog.csdn.net/mrcool2012/article/details/108972988
粉絲福利:108本java從入門到大神精選電子書領(lǐng)取
???
?長按上方鋒哥微信二維碼?2 秒 備注「1234」即可獲取資料以及 可以進入java1234官方微信群
感謝點贊支持下哈?
