FP8 量化:原理、實(shí)現(xiàn)與誤差分析



2.1 浮點(diǎn)數(shù)表示法:
在計(jì)算機(jī)中我們使用符號(hào)位、指數(shù)、底數(shù)三部分表示一個(gè)浮點(diǎn)數(shù)。符號(hào)位只占用1bit,用來表達(dá)數(shù)的正負(fù),0-表示整數(shù),1-表示負(fù)數(shù)。這也意味著在浮點(diǎn)數(shù)中0有兩種表達(dá)方式:
接下來我們討論浮點(diǎn)表示中的指數(shù)部分:
最后我們討論浮點(diǎn)數(shù)中的底數(shù)部分:

2.2 數(shù)的浮點(diǎn)量化
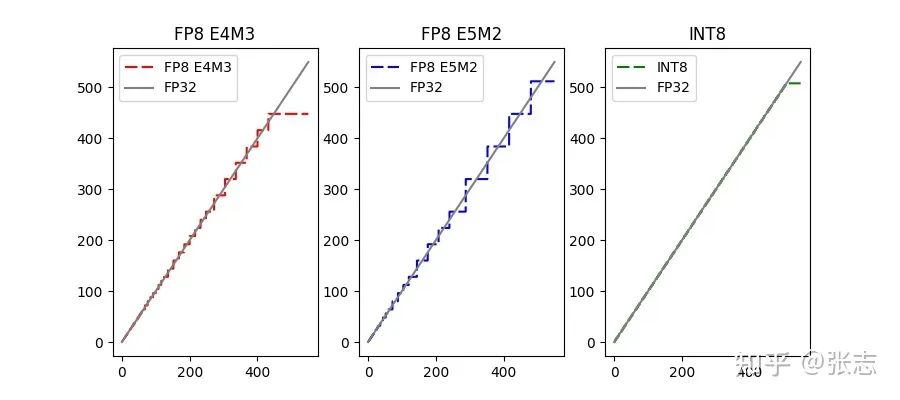
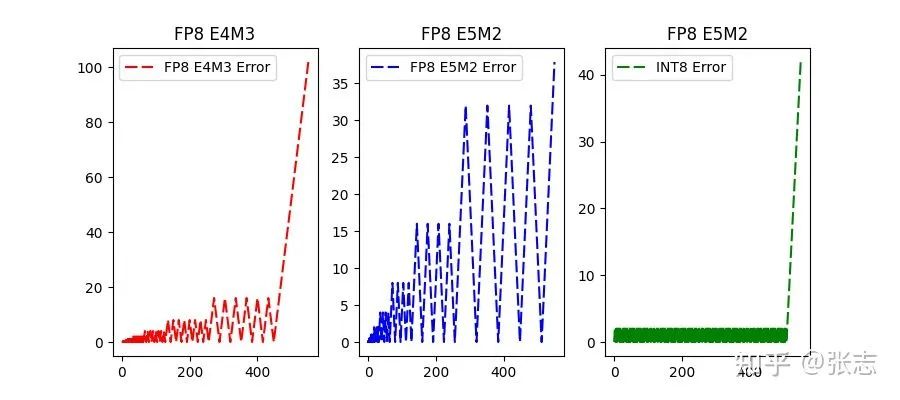
2.3 FP32 到 FP8 的數(shù)據(jù)格式轉(zhuǎn)換
Unscaled FP32 = FP32 / scale
FP8 = Convert(Unscaled FP32)
當(dāng) Unscaled FP32 數(shù)據(jù)已經(jīng)超出 FP8 的表示范圍,即 Unscaled FP32 的幅值大于 448,那么直接進(jìn)行截?cái)啵藭r(shí)為浮點(diǎn)上溢出。
當(dāng) Unscaled FP32 數(shù)據(jù)范圍在 FP8 的表示范圍內(nèi),且幅值大于 FP8 能夠表達(dá)的最小值,此時(shí)需要移去多余的底數(shù)位,并對(duì)底數(shù)進(jìn)行四舍五入。
當(dāng) Unscaled FP32 數(shù)據(jù)小于 FP8 能夠表達(dá)的最小值,此時(shí)浮點(diǎn)下溢出,只需判斷能否四舍五入為 (0 0000 001),若不能則直接為0。
union FPConvertHelper {
float value;
uint32_t data;
};
template<typename Dtype, typename Stype, typename Otype>
__device__ __inline__
float QuantizeScalarFloating(
const Dtype value, const Stype scale, const Otype offset,
const int exponent, const int mantissa,
const float clip_min, const float clip_max,
const Rounding rounding){
/**
* PPQ Quantization Function implementation.
* This function convert an float value to low-precision float
*/
FPConvertHelper helper; FPConvertHelper rounding_helper;
helper.value = static_cast<float>(value) / scale;
// Following code will Split float32 into sign, exp, mantissa
/* IEEE 754 Standard: 1 bit sign, 8 bit exponent, 23 bit mantissa */
/* In binary 10000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 = 0x80000000 in Hex */
/* In binary 01111111 10000000 00000000 00000000 = 0x7F800000 in Hex */
/* In binary 00000000 01111111 11111111 11111111 = 0x007FFFFF in Hex */
/* Tool: https://www.h-schmidt.net/FloatConverter/IEEE754.html */
uint32_t fp32_sign = helper.data & 0x80000000;
int32_t fp32_exp = helper.data & 0x7F800000;
int32_t fp32_mantissa = helper.data & 0x007FFFFF;
int32_t exponent_min = -(1 << (exponent - 1)) + mantissa;
int32_t exponent_max = (1 << (exponent - 1));
// Float Overflow.
if (value > clip_max) return clip_max;
if (value < clip_min) return clip_min;
// Following code will process Float underflow
/* Float underflow means fp32_exp is smaller than exponent_min */
/* Where exponent_min is the minimum exponent value of quantized float. */
/* For FP8 E4M3, the minimum exponent value should be -9. */
if (((fp32_exp >> 23) - 127) < exponent_min){
if (((fp32_exp >> 23) - 127) == (exponent_min - 1)){
// there is a chance to round
rounding_helper.data = (fp32_mantissa & 0x007FFFFF) + 0x3F800000;
if (_round2int(rounding_helper.value - 1, rounding)) {
helper.data = fp32_sign + ((exponent_min + 127) << 23) + (1 << (23 - mantissa));
return helper.value;
}
}
return 0.0f;
}
if ((fp32_exp >> 23) - 127 > exponent_max){
if (fp32_sign) return clip_min;
else return clip_max;
}
/* high precision mantissa convert to low precision mantissa requires rounding */
/* Here we apply a tricky method to round mantissa: */
/* We create another float, which sign = 0, exponent = 127, mantissa = fp32_mantissa << (23 - mantissa) */
/* Then we directly round this float to int, result here is what we want, you can prove it by yourself */
rounding_helper.data = ((fp32_mantissa << (mantissa)) & 0x007FFFFF) + 0x3F800000;
uint32_t round_bit = _round2int(rounding_helper.value - 1, rounding);
// process mantissa
fp32_mantissa = ((fp32_mantissa >> (23 - mantissa)) + round_bit) << (23 - mantissa);
helper.data = fp32_sign + fp32_mantissa + fp32_exp;
return CLIP<float>(helper.value + offset, clip_min, clip_max);
}


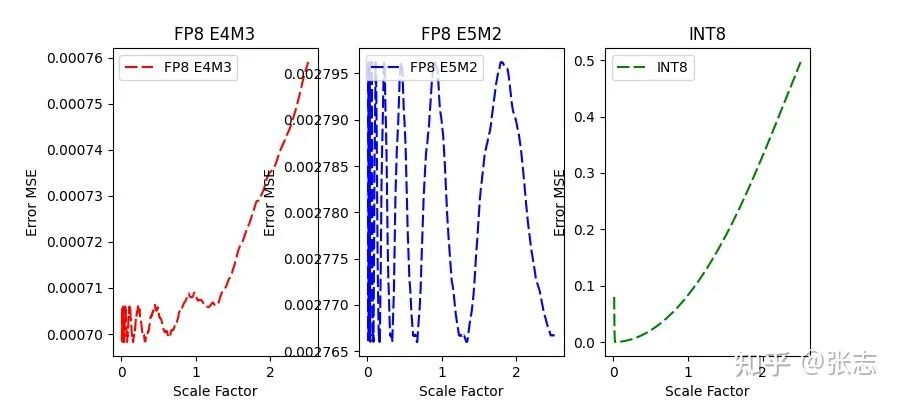
| FP8 E4M3 | FP8 E5M2 | INT8 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.06% | 0.2% | 0.008% |


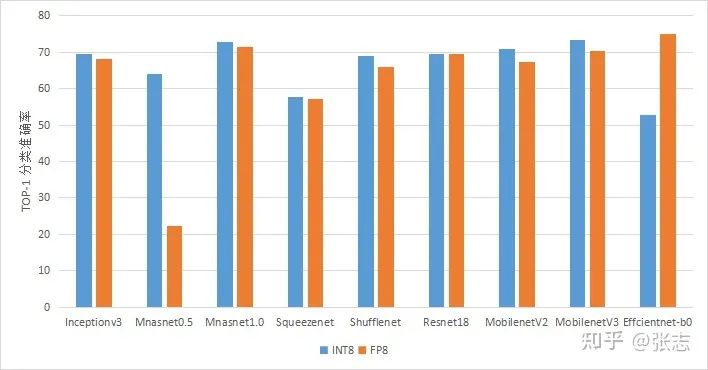
| INT8 | FP8 | |
|---|---|---|
| Inceptionv3 | 69.4 | 68.2 |
| mnasnet | 63.9 | 22.3 |
| mnasnet | 72.8 | 71.3 |
| squeezenet | 57.8 | 57.1 |
| shufflenet | 68.8 | 66.0 |
| resnet18 | 69.6 | 69.4 |
| mobilenetv2 | 70.9 | 67.2 |
| mobilenetv3 | 73.3 | 70.3 |
| efficientnet-b0 | 52.8 | 74.9 |

FP8的量化并不精確
FP8的量化具有良好的寬容度,我們期待他在QAT中取得更好的表現(xiàn)
FP8良好的寬容度可以量化一些奇怪的網(wǎng)絡(luò),例如Effcientnet。
· https://github.com/openppl-public/ppq/tree/master/ppq
· https://github.com/openppl-public/ppq/pull/274
· https://www.graphcore.ai/posts/graphcore-and-amd-propose-8-bit-fp-ai-standard-with-qualcomm-support
· 本文部分內(nèi)容翻譯自:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2209.05433.pdf

推薦閱讀
輔助模塊加速收斂,精度大幅提升!移動(dòng)端實(shí)時(shí)的NanoDet-Plus來了!
SSD的torchvision版本實(shí)現(xiàn)詳解
機(jī)器學(xué)習(xí)算法工程師
一個(gè)用心的公眾號(hào)

