代碼層面探索前端性能

性能優(yōu)化可分為以下幾個維度:代碼層面、構(gòu)建層面、網(wǎng)絡(luò)層面。
本文主要是從代碼層面探索前端性能,主要分為以下 4 個小節(jié)。
-
使用 CSS 替代 JS -
深度剖析 JS -
前端算法 -
計算機(jī)底層
CSS 動畫
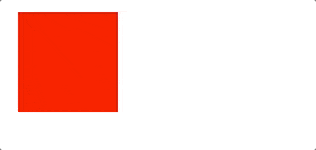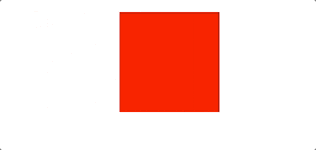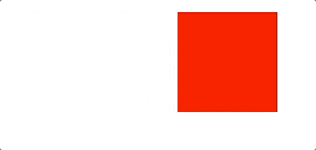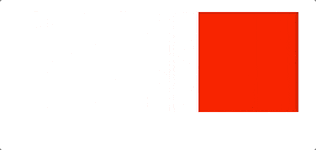
let redBox = document.getElementById('redBox')let l = 10setInterval(() => {l+=3redBox.style.left = `${l}px`}, 50)
-
過渡(Transition) - 過渡是 CSS3 中常用的動畫效果之一,通過對一個元素的某些屬性進(jìn)行變換,使元素在一段時間內(nèi)從一個狀態(tài)平滑地過渡到另一個狀態(tài)。 -
動畫(Animation) - 動畫是 CSS3 中另一個常用的動畫效果,其用于為一個元素添加一些復(fù)雜的動畫效果,可以通過關(guān)鍵幀(@keyframes)來定義一串動畫序列。 -
變換(Transform) - 變換是 CSS3 中用于實現(xiàn) 2D/3D 圖形變換效果的一種技術(shù),包括旋轉(zhuǎn)、縮放、移動、斜切等效果。
#redBox {animation: mymove 5s infinite;}@keyframes mymove{from {left: 0;}to {left: 200px;}}
CSS 組件
在一些知名的組件庫中,有些組件的大部分 props 是通過修改 CSS 樣式實現(xiàn)的,比如 Vant 的 Space 組件。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
再比如 Ant Design 的 Space 組件。
Props |
功能 |
CSS樣式 |
align |
對齊方式 |
align-items: xxx; |
direction |
間距方向 |
flex-direction: column; |
size |
間距大小 |
gap: xxx; |
wrap |
是否自動換行 |
flex-wrap: wrap; |
這類組件完全可以封裝成 SCSS 的 mixin 實現(xiàn)(LESS 也一樣),既能減少項目的構(gòu)建體積(兩個庫的 Space 組件 gzip 后的大小分別為 5.4k 和 22.9k),又能提高性能。
查看組件庫某個組件的體積,可訪問連接:https://bundlephobia.com/。
比如下面的 space mixin:
/** 間距* size: 間距大小,默認(rèn)是 8px* align: 對齊方式,默認(rèn)是 center,可選 start、end、baseline、center* direction: 間距方向,默認(rèn)是 horizontal,可選 horizontal、vertical* wrap: 是否自動換行,僅在 horizontal 時有效,默認(rèn)是 false*/@mixin space($size: 8px, $direction: horizontal, $align: center, $wrap: false) {display: inline-flex;gap: $size;@if ($direction == 'vertical') {flex-direction: column;}@if ($align == 'center') {align-items: center;}@if ($align == 'start') {align-items: flex-start;}@if ($align == 'end') {align-items: flex-end;}@if ($align == 'baseline') {align-items: baseline;}@if ($wrap == true) {@if $direction == 'horizontal' {flex-wrap: wrap;}}}
-
優(yōu)先考慮只使用樣式實現(xiàn) -
僅靠樣式滿足不了,就先增加一個標(biāo)簽,通過這個標(biāo)簽和它的兩個偽元素 ::before 和 ::after 實現(xiàn) -
一個標(biāo)簽實在不夠,再考慮增加額外的標(biāo)簽
/* 三角形 */@mixin triangle($borderWidth: 10, $shapeColor: #666, $direction: up) {width: 0;height: 0;border: if(type-of($borderWidth) == 'number', #{$borderWidth} + 'px', #{$borderWidth}) solid transparent;$doubleBorderWidth: 2 * $borderWidth;$borderStyle: if(type-of($doubleBorderWidth) == 'number', #{$doubleBorderWidth} + 'px', #{$doubleBorderWidth}) solid #{$shapeColor};@if($direction == 'up') {border-bottom: $borderStyle;}@if($direction == 'down') {border-top: $borderStyle;}@if($direction == 'left') {border-right: $borderStyle;}@if($direction == 'right') {border-left: $borderStyle;}}
if-else 語句的優(yōu)化
const a = 2const b = 10let cif (a > 3) {c = a + belse {c = 2 * a}
function check(age, sex) {let msg = ''if (age > 18) {if (sex === 1) {msg = '符合條件'} else {msg = ' 不符合條件'}} else {msg = '不符合條件'}}
function check(age, sex){if (age > 18 && sex ==1) return '符合條件'return '不符合條件'}
Switch 語句的優(yōu)化
參考以下代碼:
function getPrice(level) {if (level > 10) return 100if (level > 9) return 80if (level > 6) return 50if (level > 1) return 20return 10}
function getPrice(level) {switch(level)case 10: return 100case 9: return 80case 8:case 7:case 6: return 50case 5:case 4:case 3:case 2:case 1: return 20default: return 10}
循環(huán)語句的優(yōu)化
function findUserByName(users) {let user = nullfor (let i = 0; i < users.length; i++) {if (users[i].name === '張三') {user = users[i]}}return user}
function findUserByName(users) {for (let i = 0; i < users.length; i++) {if (users[i].name === '章三') return users[i]}}
function findUserByName(users) {let length = users.lengthfor (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {if (users[i].name === '章三') return users[i]}}
let a = 10let b = 11function sum (a, b) {return a + b}
diff 算法
-
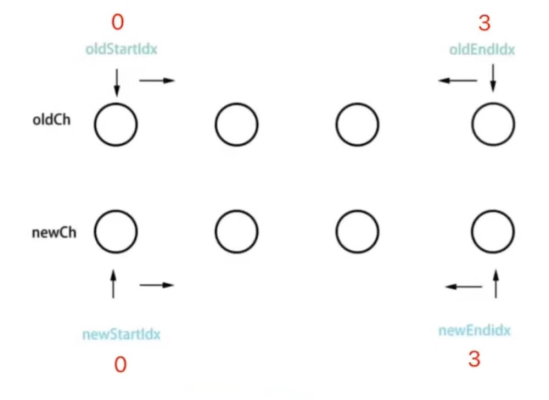
定義 4 個變量,分別為:oldStartIdx、oldEndIdx、newStartIdx 和 newEndIdx -
判斷 oldStartIdx 和 newStartIdx 是否相等 -
判斷 oldEndIdx 和 newEndIdx 是否相等 -
判斷 oldStartIdx 和 newEndIdx 是否相等 -
判斷 oldEndIdx 和 newStartIdx 是否相等 -
同時 oldStartIdx 和 newStartIdx 向右移動;oldEndIdx 和 newEndIdx 向左移動
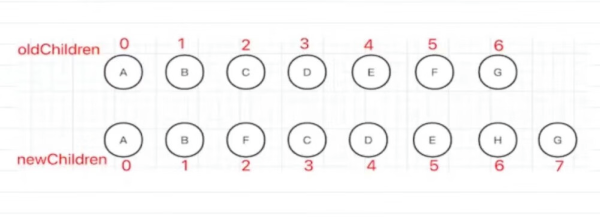
-
先進(jìn)行雙端比較,發(fā)現(xiàn)前面兩個節(jié)點(A 和 B)和最后一個節(jié)點(G)是一樣的,不需要移動 -
找到最長遞增子序列 C、D、E(新舊 children 都包含的,最長的順序沒有發(fā)生變化的一組節(jié)點) -
把子序列當(dāng)成一個整體,內(nèi)部不用進(jìn)行任何操作,只需要把 F 移動到它的前面,H 插入到它的后面即可
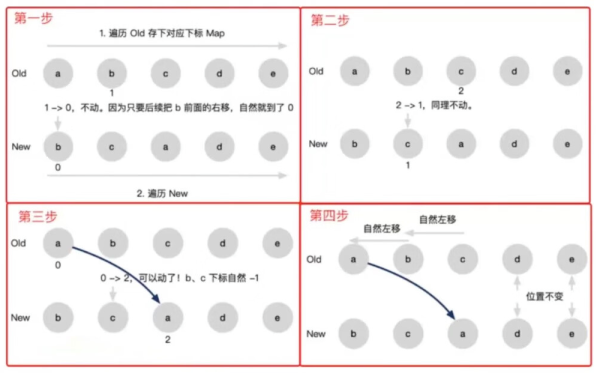
-
遍歷 Old 存下對應(yīng)下標(biāo) Map -
遍歷 New,b 的下標(biāo)從 1 變成了 0,不動(是左移不是右移) -
c 的下標(biāo)從 2 變成了 1,不動(也是左移不是右移) -
a 的下標(biāo)從 0 變成了 2,向右移動,b、c 下標(biāo)都減 1 -
d 和 e 位置沒變,不需要移動
-
只比較同一層級,不跨級比較 -
Tag 不同則刪掉重建(不再去比較內(nèi)部的細(xì)節(jié)) -
子節(jié)點通過 key 區(qū)分(key 的重要性)
setState 真的是異步嗎
clickHandler = () => {console.log('--- start ---')Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('promise then'))this.setState({val: 1}, () => {console.log('state...', this.state.val)})console.log('--- end ---')}render() {return <div onClick={this.clickHandler}>setState</div>}
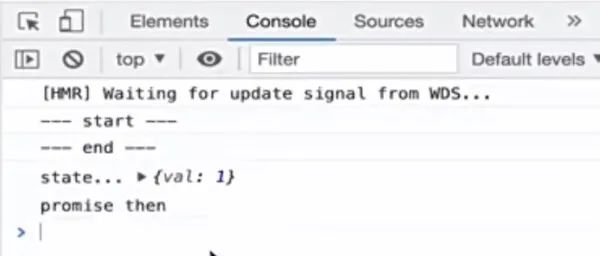
JSX 里的事件,比如 onClick={() => {}},其實叫合成事件,區(qū)別于我們常說的自定義事件:
// 自定義事件document.getElementById('app').addEventListener('click', () => {})
function fn() { // fn 是合成事件函數(shù),內(nèi)部事件同步執(zhí)行// 前置clickHandler()// 后置,執(zhí)行 setState 的 callback}
友情提示:算法一般都是針對大數(shù)據(jù)量而言,區(qū)別于日常開發(fā)。
能用值類型就不用引用類型
function findPalindromeNumbers1(max) {const res = []if (max <= 0) return resfor (let i = 1; i <= max; i++) {// 轉(zhuǎn)換為字符串,轉(zhuǎn)換為數(shù)組,再反轉(zhuǎn),比較const s = i.toString()if (s === s.split('').reverse().join('')) {res.push(i)}}return res}
function findPalindromeNumbers2(max) {const res = []if (max <= 0) return resfor (let i = 1; i <= max; i++) {const s = i.toString()const length = s.length// 字符串頭尾比較let flag = truelet startIndex = 0 // 字符串開始let endIndex = length - 1 // 字符串結(jié)束while (startIndex < endIndex) {if (s[startIndex] !== s[endIndex]) {flag = falsebreak} else {// 繼續(xù)比較startIndex++endIndex--}}if (flag) res.push(res)}return res}
function findPalindromeNumbers3(max) {const res = []if (max <= 0) return resfor (let i = 1; i <= max; i++) {let n = ilet rev = 0 // 存儲翻轉(zhuǎn)數(shù)// 生成翻轉(zhuǎn)數(shù)while (n > 0) {rev = rev * 10 + n % 10n = Math.floor(n / 10)}if (i === rev) res.push(i)}return res}
思路 1- 看似是 O(n),但數(shù)組轉(zhuǎn)換、操作都需要時間,所以慢
思路 2 VS 思路3 - 操作數(shù)字更快(電腦原型就是計算器)
盡量用“低級”代碼
如,輸入字符串 12aBc34,輸出字符串 12AbC34
function switchLetterCase(s) {let res = ''const length = s.lengthif (length === 0) return resconst reg1 = /[a-z]const reg2 = /[A-Z]for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {const c = s[i]if (reg1.test(c)) {res += c.toUpperCase()} else if (reg2.test(c)) {res += c.toLowerCase()} else {res += c}}return res}
function switchLetterCase2(s) {let res = ''const length = s.lengthif (length === 0) return resfor (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {const c = s[i]const code = c.charCodeAt(0)if (code >= 65 && code <= 90) {res += c.toLowerCase()} else if (code >= 97 && code <= 122) {res += c.toUpperCase()} else {res += c}}return res}
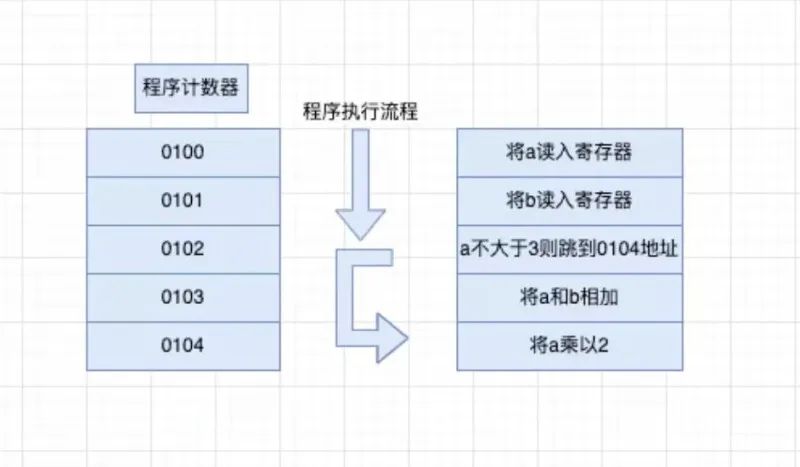
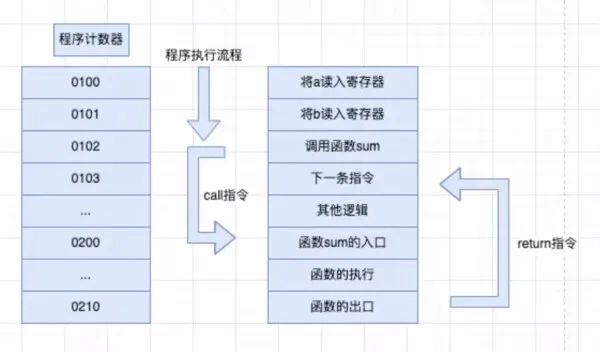
從“內(nèi)存”讀數(shù)據(jù)
寄存器是在 CPU 內(nèi)的,也是 CPU 的一部分,所以 CPU 從寄存器讀寫數(shù)據(jù)非常快。
二進(jìn)制的位運算
function isPowerOfTwo(n) {if (n <= 0) return falselet temp = nwhile (temp > 1) {if (temp % 2 != 0) return falsetemp /= 2}return true}
function isPowerOfTwo(n) {return (n > 0) && ((n & (n - 1)) == 0)}
export const enum ShapeFlags {ELEMENT = 1,FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT = 1 << 1,STATEFUL_COMPONENT = 1 << 2,TEXT_CHILDREN = 1 << 3,ARRAY_CHILDREN = 1 << 4,SLOTS_CHILDREN = 1 << 5,TELEPORT = 1 << 6,SUSPENSE = 1 << 7,COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE = 1 << 8,COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE = 1 << 9,COMPONENT = ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT | ShapeFlags.FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT}if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT || shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TELEPORT) {...}if (hasDynamicKeys) {patchFlag |= PatchFlags.FULL_PROPSelse {if (hasClassBinding) {patchFlag |= PatchFlags.CLASS}if (hasStyleBinding) {patchFlag |= PatchFlags.STYLE}if (dynamicPropNames.length) {patchFlag |= PatchFlags.PROPS}if (hasHydrationEventBinding) {patchFlag |= PatchFlags.HYDRATE_EVENTS}}
-
JS 基礎(chǔ)知識深度剖析 -
框架源碼
-
CSS 動畫、組件 -
算法 -
計算機(jī)底層
評論
圖片
表情
