Java Bean 轉(zhuǎn) Map 的巨坑,注意了!!!
作者:明明如月學(xué)長(zhǎng)
鏈接:https://juejin.cn/post/7118073840999071751
一、背景
有些業(yè)務(wù)場(chǎng)景下需要將 Java Bean 轉(zhuǎn)成 Map 再使用。本以為很簡(jiǎn)單場(chǎng)景,但是坑很多。
二、那些坑
2.0 測(cè)試對(duì)象
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
public class MockObject extends MockParent{
private Integer aInteger;
private Long aLong;
private Double aDouble;
private Date aDate;
}
父類
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class MockParent {
private Long parent;
}
2.1 JSON 反序列化了類型丟失
2.1.1 問(wèn)題復(fù)現(xiàn)
將 Java Bean 轉(zhuǎn) Map 最常見的手段就是使用 JSON 框架,如 fastjson 、 gson、jackson 等。但使用 JSON 將 Java Bean 轉(zhuǎn) Map 會(huì)導(dǎo)致部分?jǐn)?shù)據(jù)類型丟失。如使用 fastjson ,當(dāng)屬性為 Long 類型但數(shù)字小于 Integer 最大值時(shí),反序列成 Map 之后,將變?yōu)? Integer 類型。最新面試題整理好了,點(diǎn)擊Java面試庫(kù)小程序在線刷題。
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/fastjson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>2.0.8</version>
</dependency>
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Map;
public class JsonDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MockObject mockObject = new MockObject();
mockObject.setAInteger(1);
mockObject.setALong(2L);
mockObject.setADate(new Date());
mockObject.setADouble(3.4D);
mockObject.setParent(3L);
String json = JSON.toJSONString(mockObject);
Map<String,Object> map = JSON.parseObject(json, new TypeReference<Map<String,Object>>(){});
System.out.println(map);
}
}
{"parent":3,"ADouble":3.4,"ALong":2,"AInteger":1,"ADate":1657299916477}
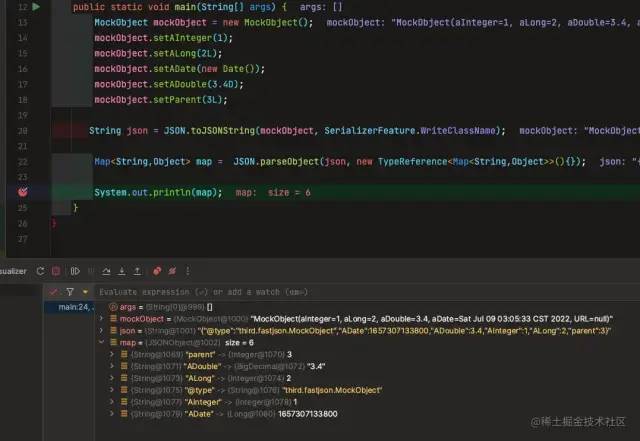
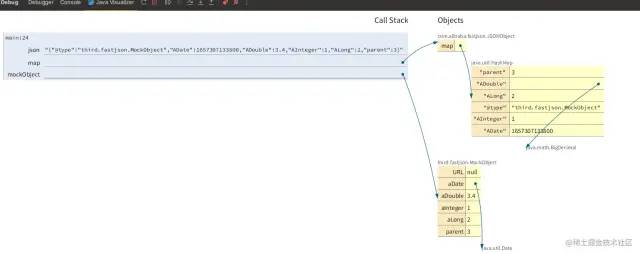
通過(guò) Java Visualizer 插件進(jìn)行可視化查看:
2.2.2 問(wèn)題描述
存在兩個(gè)問(wèn)題
(1) 通過(guò) fastjson 將 Java Bean 轉(zhuǎn)為 Map ,類型會(huì)發(fā)生轉(zhuǎn)變。如 Long 變成 Integer ,Date 變成 Long, Double 變成 Decimal 類型等。
(2)在某些場(chǎng)景下,Map 的 key 并非和屬性名完全對(duì)應(yīng),像是通過(guò) get set 方法“推斷”出來(lái)的屬性名。
2.2 BeanMap 轉(zhuǎn)換屬性名錯(cuò)誤
2.2.1 commons-beanutils 的 BeanMap
maven 版本:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-beanutils/commons-beanutils -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-beanutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-beanutils</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
代碼示例:
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanMap;
import third.fastjson.MockObject;
import java.util.Date;
public class BeanUtilsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MockObject mockObject = new MockObject();
mockObject.setAInteger(1);
mockObject.setALong(2L);
mockObject.setADate(new Date());
mockObject.setADouble(3.4D);
mockObject.setParent(3L);
BeanMap beanMap = new BeanMap(mockObject);
System.out.println(beanMap);
}
}
調(diào)試截圖:
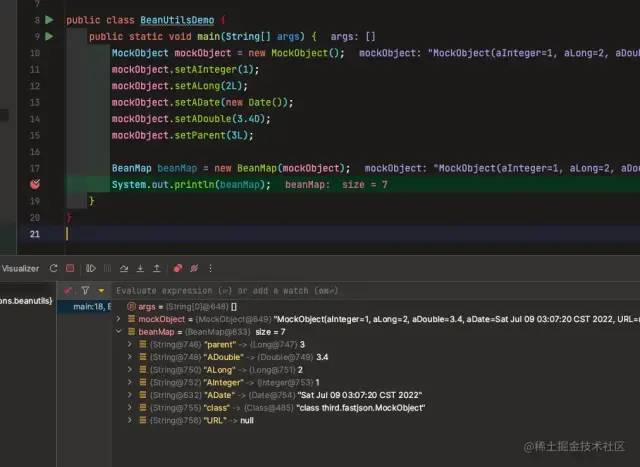 存在和 cglib 一樣的問(wèn)題,雖然類型沒(méi)問(wèn)題但是屬性名還是不對(duì)。
存在和 cglib 一樣的問(wèn)題,雖然類型沒(méi)問(wèn)題但是屬性名還是不對(duì)。
原因分析:
/**
* Constructs a new <code>BeanMap</code> that operates on the
* specified bean. If the given bean is <code>null</code>, then
* this map will be empty.
*
* @param bean the bean for this map to operate on
*/
public BeanMap(final Object bean) {
this.bean = bean;
initialise();
}
關(guān)鍵代碼:
private void initialise() {
if(getBean() == null) {
return;
}
final Class<? extends Object> beanClass = getBean().getClass();
try {
//BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo( bean, null );
final BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo( beanClass );
final PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
if ( propertyDescriptors != null ) {
for (final PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) {
if ( propertyDescriptor != null ) {
final String name = propertyDescriptor.getName();
final Method readMethod = propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod();
final Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod();
final Class<? extends Object> aType = propertyDescriptor.getPropertyType();
if ( readMethod != null ) {
readMethods.put( name, readMethod );
}
if ( writeMethod != null ) {
writeMethods.put( name, writeMethod );
}
types.put( name, aType );
}
}
}
}
catch ( final IntrospectionException e ) {
logWarn( e );
}
}
調(diào)試一下就會(huì)發(fā)現(xiàn),問(wèn)題出在 BeanInfo 里面 PropertyDescriptor 的 name 不正確。
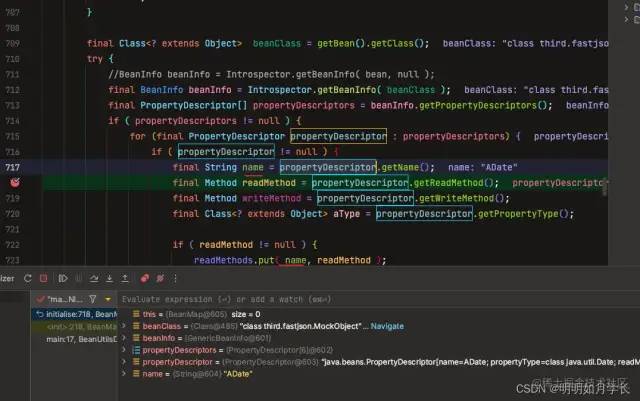
經(jīng)過(guò)分析會(huì)發(fā)現(xiàn) java.beans.Introspector#getTargetPropertyInfo 方法是字段解析的關(guān)鍵
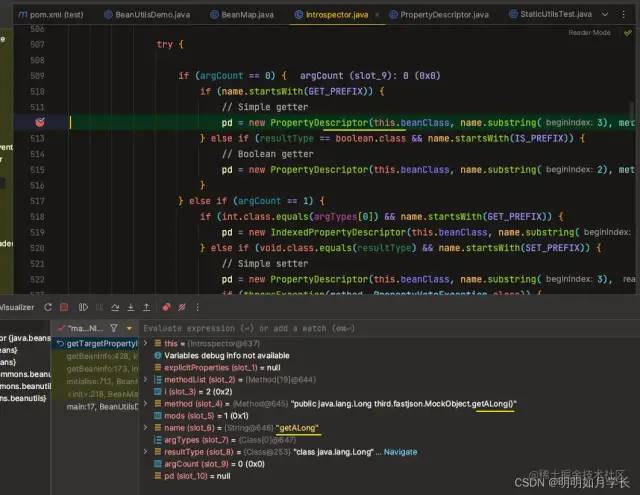 對(duì)于無(wú)參的以 get 開頭的方法名從 index =3 處截取,如 getALong 截取后為 ALong, 如 getADouble 截取后為 ADouble。
對(duì)于無(wú)參的以 get 開頭的方法名從 index =3 處截取,如 getALong 截取后為 ALong, 如 getADouble 截取后為 ADouble。
最新面試題整理好了,點(diǎn)擊Java面試庫(kù)小程序在線刷題。
然后去構(gòu)造 PropertyDescriptor:
/**
* Creates <code>PropertyDescriptor</code> for the specified bean
* with the specified name and methods to read/write the property value.
*
* @param bean the type of the target bean
* @param base the base name of the property (the rest of the method name)
* @param read the method used for reading the property value
* @param write the method used for writing the property value
* @exception IntrospectionException if an exception occurs during introspection
*
* @since 1.7
*/
PropertyDescriptor(Class<?> bean, String base, Method read, Method write) throws IntrospectionException {
if (bean == null) {
throw new IntrospectionException("Target Bean class is null");
}
setClass0(bean);
setName(Introspector.decapitalize(base));
setReadMethod(read);
setWriteMethod(write);
this.baseName = base;
}
底層使用 java.beans.Introspector#decapitalize 進(jìn)行解析:
/**
* Utility method to take a string and convert it to normal Java variable
* name capitalization. This normally means converting the first
* character from upper case to lower case, but in the (unusual) special
* case when there is more than one character and both the first and
* second characters are upper case, we leave it alone.
* <p>
* Thus "FooBah" becomes "fooBah" and "X" becomes "x", but "URL" stays
* as "URL".
*
* @param name The string to be decapitalized.
* @return The decapitalized version of the string.
*/
public static String decapitalize(String name) {
if (name == null || name.length() == 0) {
return name;
}
if (name.length() > 1 && Character.isUpperCase(name.charAt(1)) &&
Character.isUpperCase(name.charAt(0))){
return name;
}
char chars[] = name.toCharArray();
chars[0] = Character.toLowerCase(chars[0]);
return new String(chars);
}
從代碼中我們可以看出 (1) 當(dāng) name 的長(zhǎng)度 > 1,且第一個(gè)字符和第二個(gè)字符都大寫時(shí),直接返回參數(shù)作為PropertyDescriptor name。(2) 否則將 name 轉(zhuǎn)為首字母小寫
這種處理本意是為了不讓屬性為類似 URL 這種縮略詞轉(zhuǎn)為 uRL ,結(jié)果“誤傷”了我們這種場(chǎng)景。關(guān)注Java核心技術(shù),推送更多 Java 干貨!
2.2.2 使用 cglib 的 BeanMap
cglib 依賴
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/cglib/cglib -->
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib-nodep</artifactId>
<version>3.2.12</version>
</dependency>
代碼示例:
import net.sf.cglib.beans.BeanMap;
import third.fastjson.MockObject;
import java.util.Date;
public class BeanMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MockObject mockObject = new MockObject();
mockObject.setAInteger(1);
mockObject.setALong(2L);
mockObject.setADate(new Date());
mockObject.setADouble(3.4D);
mockObject.setParent(3L);
BeanMap beanMapp = BeanMap.create(mockObject);
System.out.println(beanMapp);
}
}
結(jié)果展示:
我們發(fā)現(xiàn)類型對(duì)了,但是屬性名依然不對(duì)。
關(guān)鍵代碼:net.sf.cglib.core.ReflectUtils#getBeanGetters 底層也會(huì)用到 java.beans.Introspector#decapitalize 所以屬性名存在一樣的問(wèn)題就不足為奇了。
三、解決辦法
3.1 解決方案
解決方案有很多,本文提供一個(gè)基于 dubbo的解決方案。
推薦一個(gè) Spring Boot 基礎(chǔ)實(shí)戰(zhàn)教程:https://github.com/javastacks/spring-boot-best-practice
maven 依賴:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.dubbo/dubbo -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.dubbo</groupId>
<artifactId>dubbo</artifactId>
<version>3.0.9</version>
</dependency>
示例代碼:
import org.apache.dubbo.common.utils.PojoUtils;
import third.fastjson.MockObject;
import java.util.Date;
public class DubboPojoDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MockObject mockObject = new MockObject();
mockObject.setAInteger(1);
mockObject.setALong(2L);
mockObject.setADate(new Date());
mockObject.setADouble(3.4D);
mockObject.setParent(3L);
Object generalize = PojoUtils.generalize(mockObject);
System.out.println(generalize);
}
}
調(diào)試效果:
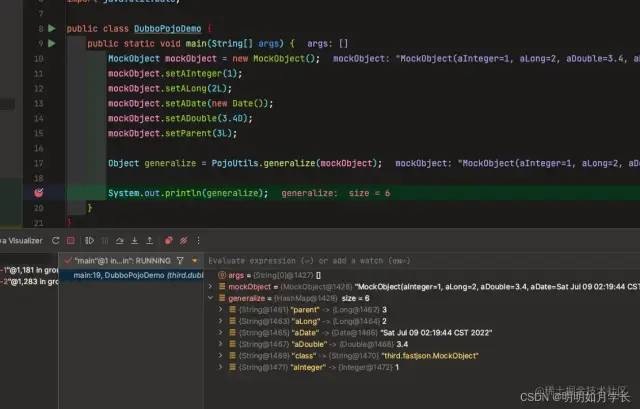 Java Visualizer 效果:
Java Visualizer 效果: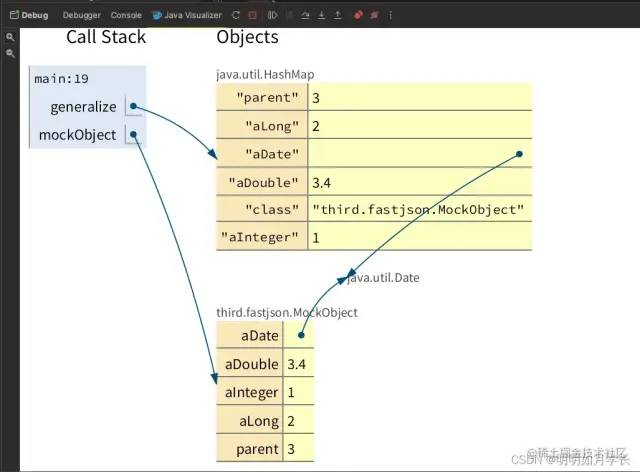
3.2 原理解析
核心代碼:org.apache.dubbo.common.utils.PojoUtils#generalize(java.lang.Object)
public static Object generalize(Object pojo) {
eturn generalize(pojo, new IdentityHashMap());
}
關(guān)鍵代碼:
// pojo 待轉(zhuǎn)換的對(duì)象
// history 緩存 Map,提高性能
private static Object generalize(Object pojo, Map<Object, Object> history) {
if (pojo == null) {
return null;
}
// 枚舉直接返回枚舉名
if (pojo instanceof Enum<?>) {
return ((Enum<?>) pojo).name();
}
// 枚舉數(shù)組,返回枚舉名數(shù)組
if (pojo.getClass().isArray() && Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(pojo.getClass().getComponentType())) {
int len = Array.getLength(pojo);
String[] values = new String[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
values[i] = ((Enum<?>) Array.get(pojo, i)).name();
}
return values;
}
// 基本類型返回 pojo 自身
if (ReflectUtils.isPrimitives(pojo.getClass())) {
return pojo;
}
// Class 返回 name
if (pojo instanceof Class) {
return ((Class) pojo).getName();
}
Object o = history.get(pojo);
if (o != null) {
return o;
}
history.put(pojo, pojo);
// 數(shù)組類型,遞歸
if (pojo.getClass().isArray()) {
int len = Array.getLength(pojo);
Object[] dest = new Object[len];
history.put(pojo, dest);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Object obj = Array.get(pojo, i);
dest[i] = generalize(obj, history);
}
return dest;
}
// 集合類型遞歸
if (pojo instanceof Collection<?>) {
Collection<Object> src = (Collection<Object>) pojo;
int len = src.size();
Collection<Object> dest = (pojo instanceof List<?>) ? new ArrayList<Object>(len) : new HashSet<Object>(len);
history.put(pojo, dest);
for (Object obj : src) {
dest.add(generalize(obj, history));
}
return dest;
}
// Map 類型,直接 對(duì) key 和 value 處理
if (pojo instanceof Map<?, ?>) {
Map<Object, Object> src = (Map<Object, Object>) pojo;
Map<Object, Object> dest = createMap(src);
history.put(pojo, dest);
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> obj : src.entrySet()) {
dest.put(generalize(obj.getKey(), history), generalize(obj.getValue(), history));
}
return dest;
}
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
history.put(pojo, map);
// 開啟生成 class 則寫入 pojo 的class
if (GENERIC_WITH_CLZ) {
map.put("class", pojo.getClass().getName());
}
// 處理 get 方法
for (Method method : pojo.getClass().getMethods()) {
if (ReflectUtils.isBeanPropertyReadMethod(method)) {
ReflectUtils.makeAccessible(method);
try {
map.put(ReflectUtils.getPropertyNameFromBeanReadMethod(method), generalize(method.invoke(pojo), history));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
// 處理公有屬性
for (Field field : pojo.getClass().getFields()) {
if (ReflectUtils.isPublicInstanceField(field)) {
try {
Object fieldValue = field.get(pojo);
// 對(duì)象已經(jīng)解析過(guò),直接從緩存里讀提高性能
if (history.containsKey(pojo)) {
Object pojoGeneralizedValue = history.get(pojo);
// 已經(jīng)解析過(guò)該屬性則跳過(guò)(如公有屬性,且有 get 方法的情況)
if (pojoGeneralizedValue instanceof Map
&& ((Map) pojoGeneralizedValue).containsKey(field.getName())) {
continue;
}
}
if (fieldValue != null) {
map.put(field.getName(), generalize(fieldValue, history));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
return map;
}
關(guān)鍵截圖 

org.apache.dubbo.common.utils.ReflectUtils#getPropertyNameFromBeanReadMethod
public static String getPropertyNameFromBeanReadMethod(Method method) {
if (isBeanPropertyReadMethod(method)) {
// get 方法,則從 index =3 的字符小寫 + 后面的字符串
if (method.getName().startsWith("get")) {
return method.getName().substring(3, 4).toLowerCase()
+ method.getName().substring(4);
}
// is 開頭方法, index =2 的字符小寫 + 后面的字符串
if (method.getName().startsWith("is")) {
return method.getName().substring(2, 3).toLowerCase()
+ method.getName().substring(3);
}
}
return null;
}
因此, getALong 方法對(duì)應(yīng)的屬性名被解析為 aLong。
 同時(shí),這么處理也會(huì)存在問(wèn)題。如當(dāng)屬性名叫 URL 時(shí),轉(zhuǎn)為 Map 后 key 就會(huì)被解析成 uRL。
同時(shí),這么處理也會(huì)存在問(wèn)題。如當(dāng)屬性名叫 URL 時(shí),轉(zhuǎn)為 Map 后 key 就會(huì)被解析成 uRL。

從這里看出,當(dāng)屬性名比較特殊時(shí)也很容易出問(wèn)題,但 dubbo 這個(gè)工具類更符合我們的預(yù)期。更多細(xì)節(jié),大家可以根據(jù) DEMO 自行調(diào)試學(xué)習(xí)。最新面試題整理好了,點(diǎn)擊Java面試庫(kù)小程序在線刷題。
如果想嚴(yán)格和屬性保持一致,可以使用反射獲取屬性名和屬性值,加緩存機(jī)制提升解析的效率。
四、總結(jié)
Java Bean 轉(zhuǎn) Map 的坑很多,最常見的就是類型丟失和屬性名解析錯(cuò)誤的問(wèn)題。大家在使用 JSON 框架和 Java Bean 轉(zhuǎn) Map 的框架時(shí)要特別小心。平時(shí)使用某些框架時(shí),多寫一些 DEMO 進(jìn)行驗(yàn)證,多讀源碼,多調(diào)試,少趟坑。
END
推薦閱讀
END
一鍵生成Springboot & Vue項(xiàng)目!【畢設(shè)神器】
Java可視化編程工具系列(一)
Java可視化編程工具系列(二)
順便給大家推薦一個(gè)GitHub項(xiàng)目,這個(gè) GitHub 整理了上千本常用技術(shù)PDF,絕大部分核心的技術(shù)書籍都可以在這里找到,
GitHub地址:https://github.com/javadevbooks/books
電子書已經(jīng)更新好了,你們需要的可以自行下載了,記得點(diǎn)一個(gè)star,持續(xù)更新中..

順便給大家推薦一個(gè)GitHub項(xiàng)目,這個(gè) GitHub 整理了上千本常用技術(shù)PDF,絕大部分核心的技術(shù)書籍都可以在這里找到,
GitHub地址:https://github.com/javadevbooks/books
電子書已經(jīng)更新好了,你們需要的可以自行下載了,記得點(diǎn)一個(gè)star,持續(xù)更新中..
