圖解 history api 和 React Router 實(shí)現(xiàn)原理
點(diǎn)擊上方 全站前端精選,關(guān)注公眾號
回復(fù)1,加入高級前段交流
Router 是開發(fā) React 應(yīng)用的必備功能,那 React Router 是怎么實(shí)現(xiàn)的呢?
今天我們就來讀一下 React Router 的源碼吧!
首先,我們來學(xué)一下 History API,這是基礎(chǔ)。
什么是 history 呢?
就是這個東西:
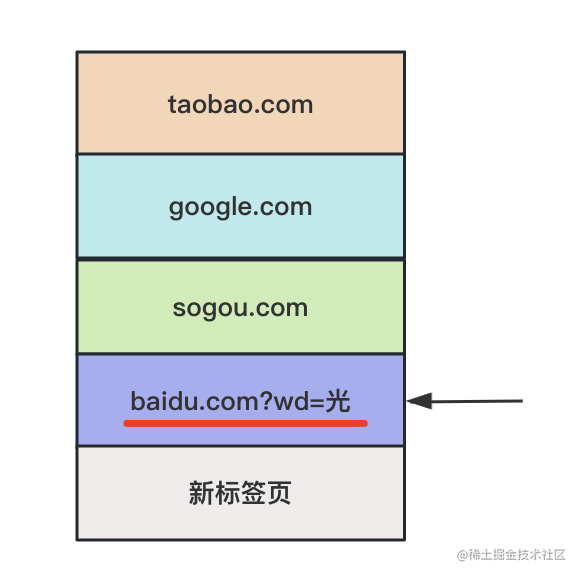
我打開了一個新的標(biāo)簽頁、然后訪問 baidu.com、sougou.com、taobao.com。
長按后退按鈕,就會列出歷史記錄,這就是 history。
現(xiàn)在在這里:
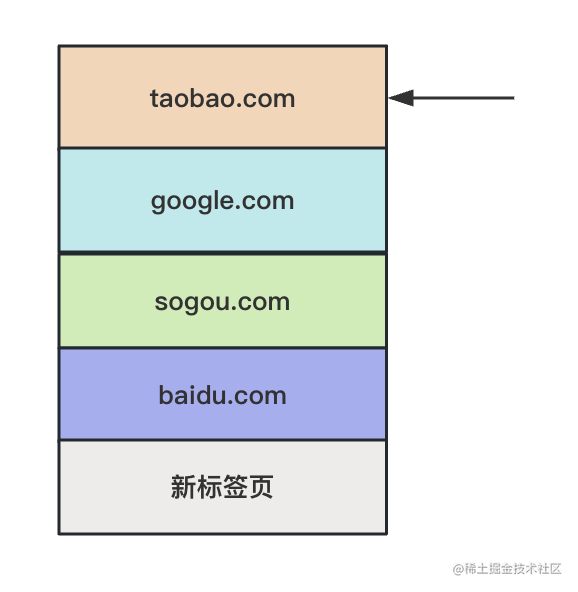
history.length 是 5
點(diǎn)擊兩次后退按鈕,或者執(zhí)行兩次 history.back()
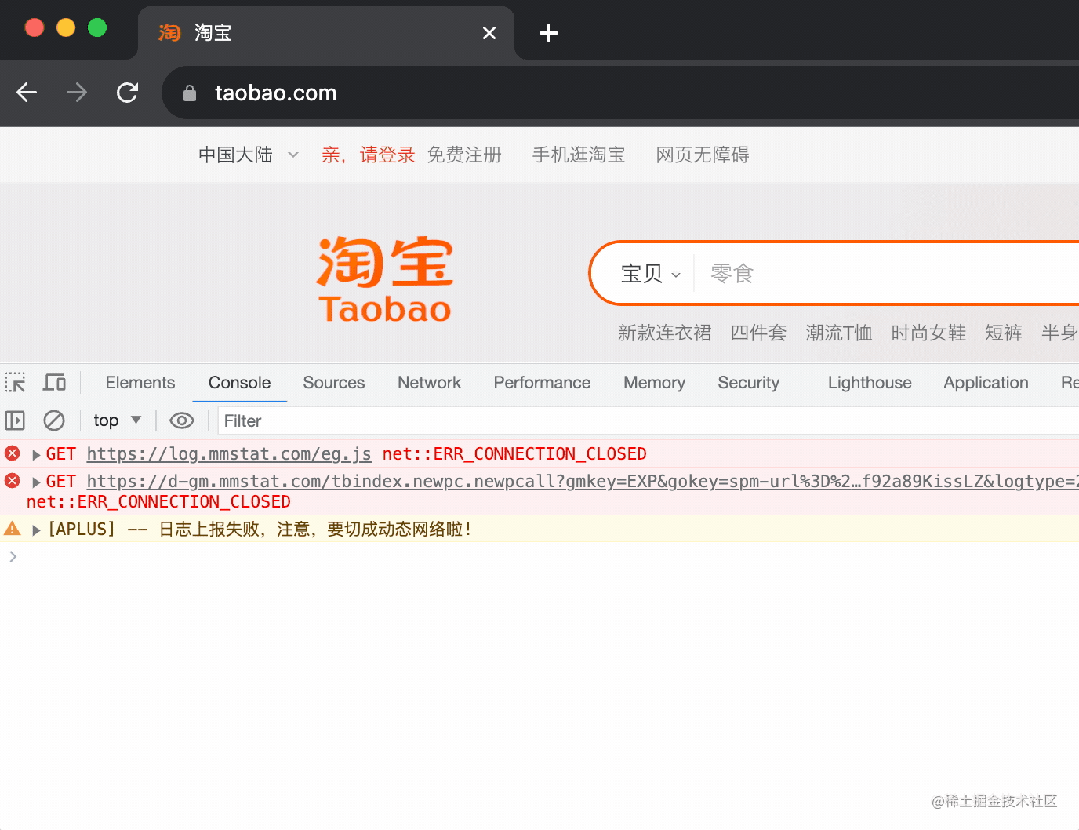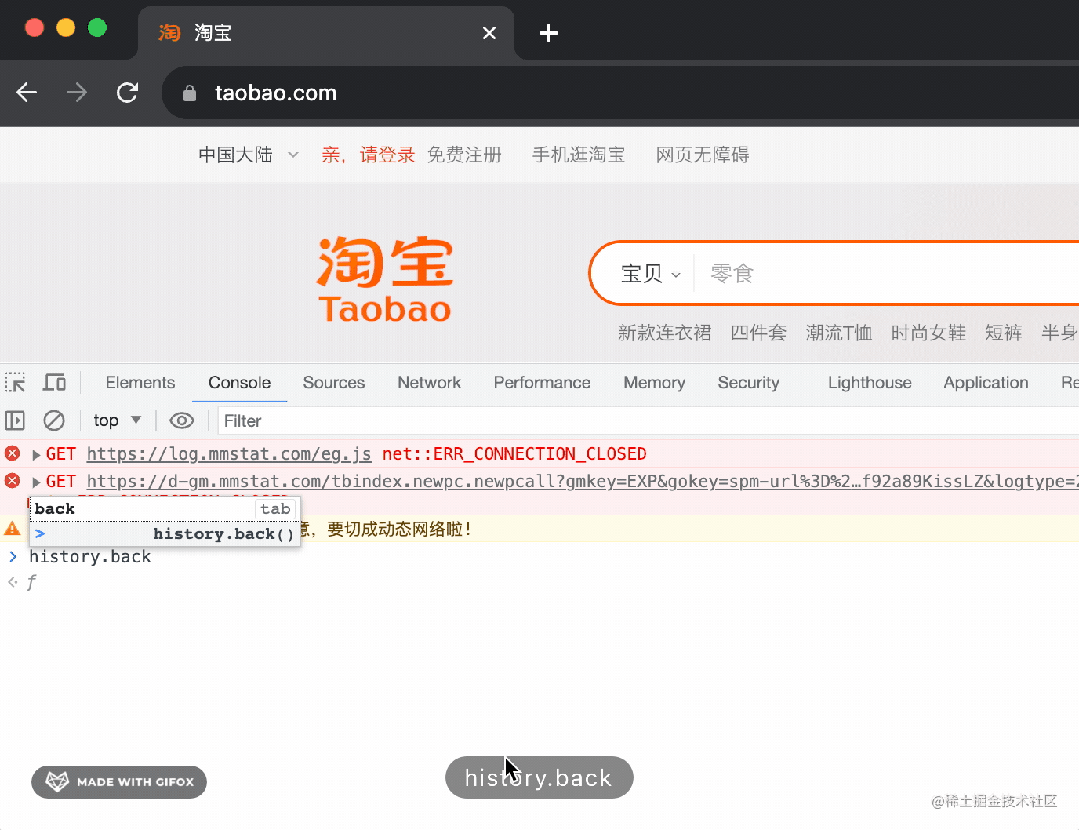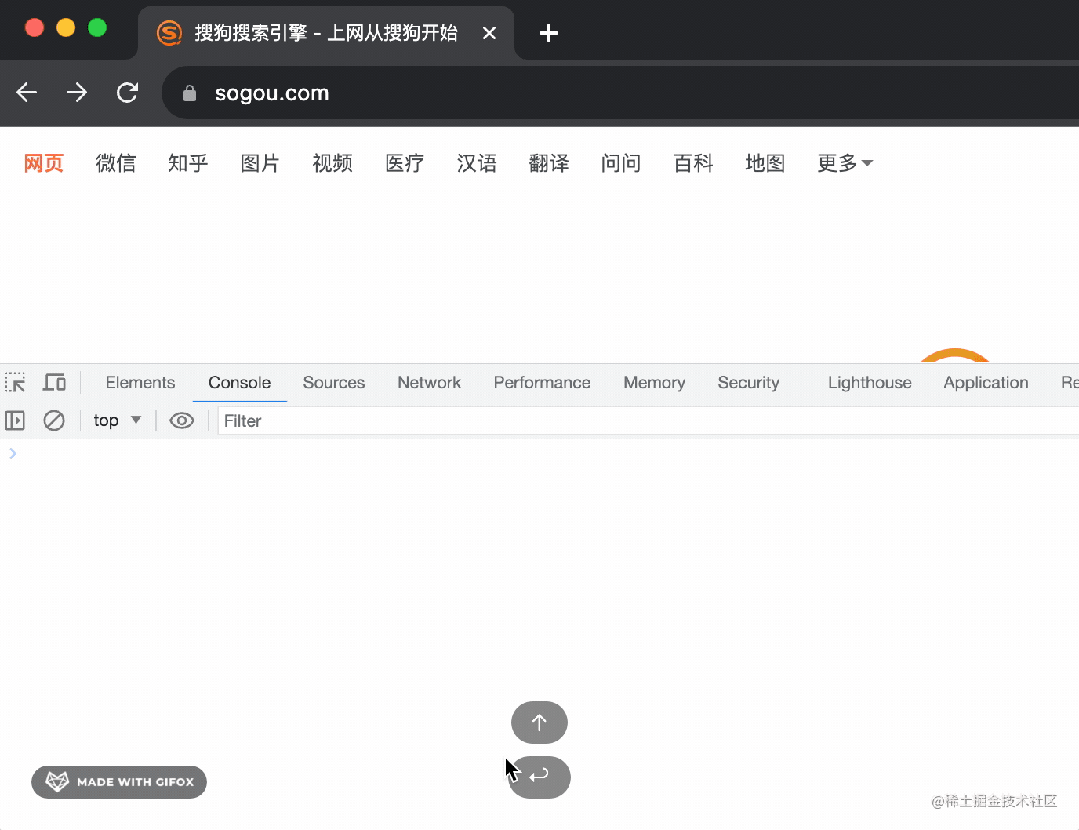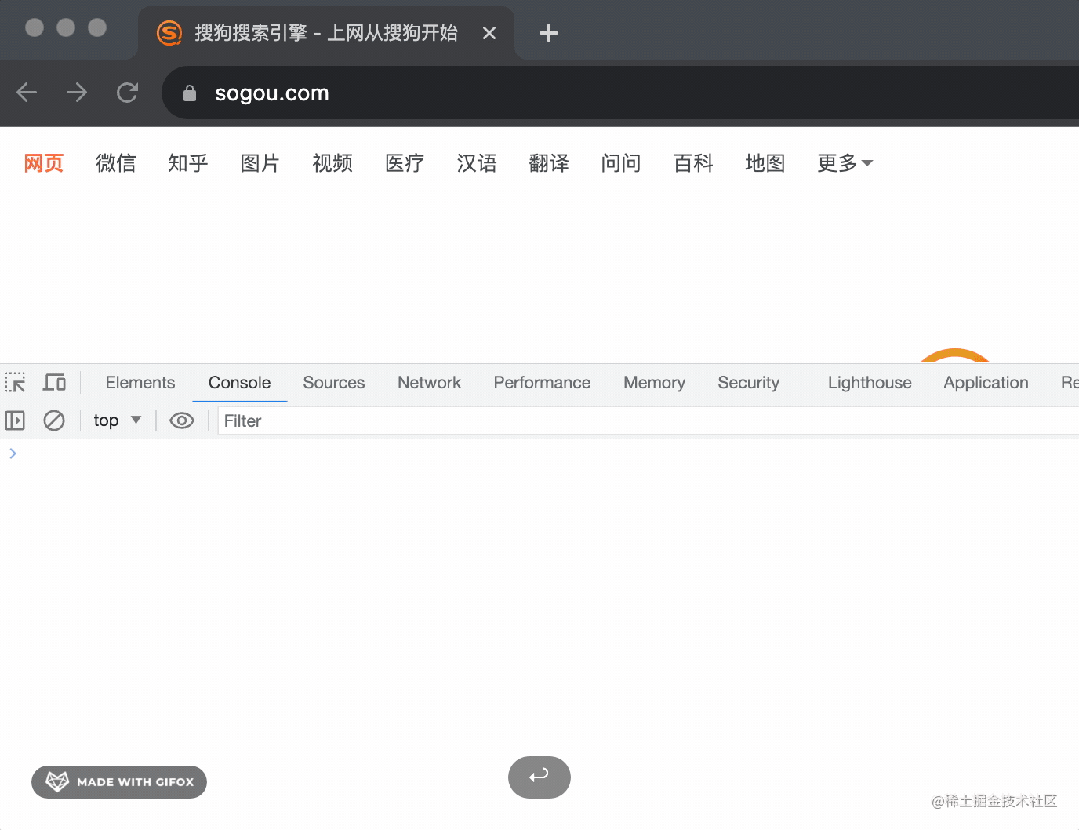
就會回到這里:
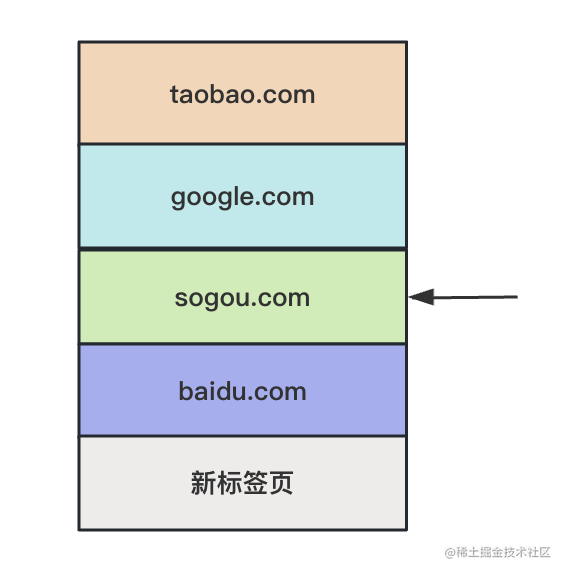
這時候 history.length 依然是 5

因?yàn)榍昂蟮?history 都還保留著:
除了用 history.back、history.forward 在 history 之間切換外,還可以用 history.go
參數(shù)值是 delta:
history.go(0) 是刷新當(dāng)前頁面。
history.go(1) 是前進(jìn)一個,相當(dāng)于 history.forward()
history.go(-1) 是后退一個,相當(dāng)于 history.back()
當(dāng)然,你還可以 history.go(-2)、histroy.go(3) 這種。
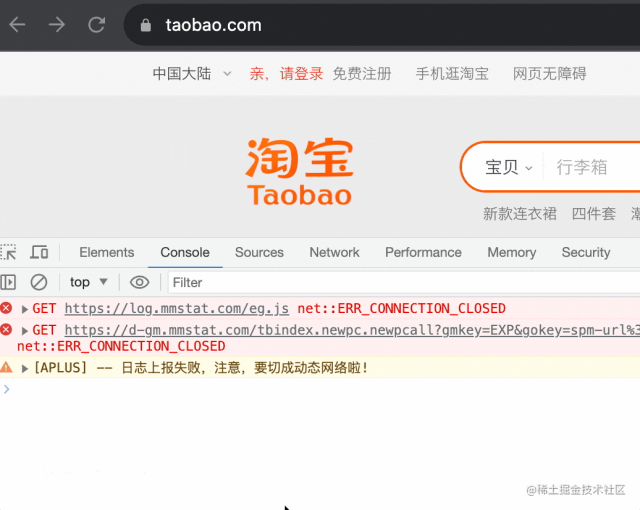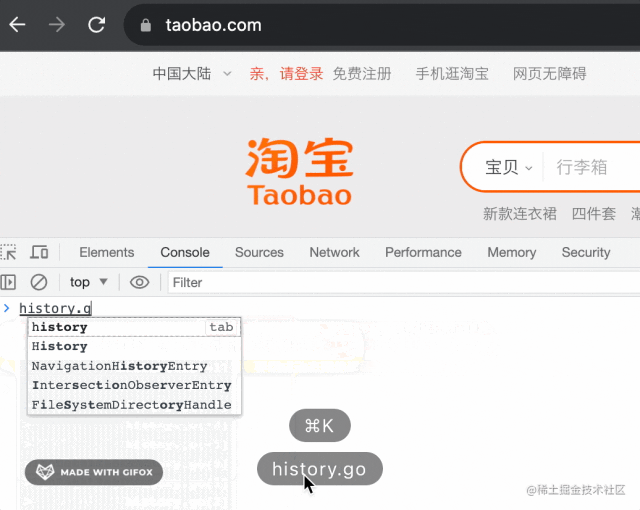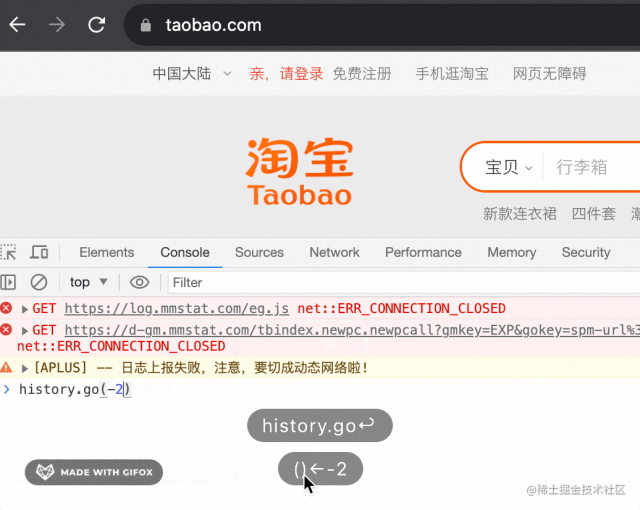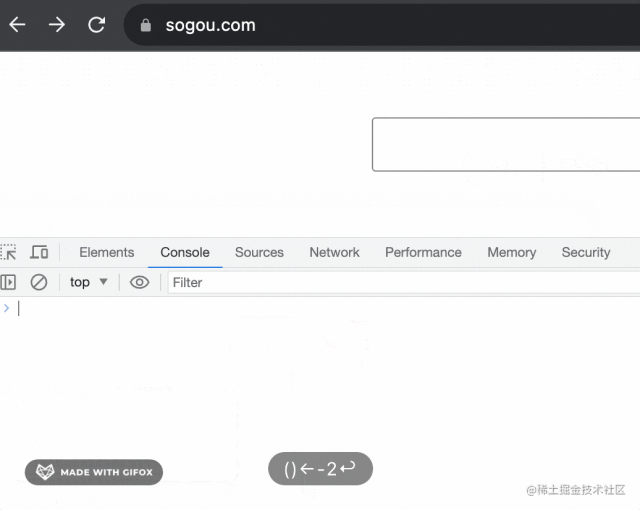
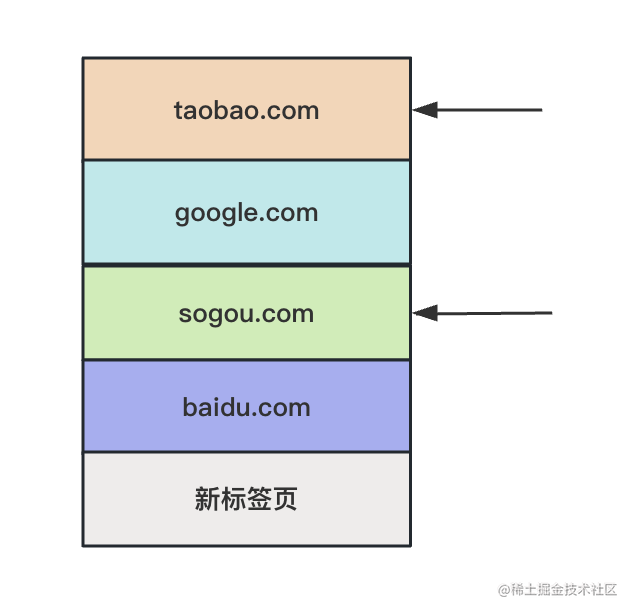
比如當(dāng)我執(zhí)行 history.go(-2) 的時候,能直接從 taobao.com 跳到 sogou.com
你還可以通過 history.replaceState 來替換當(dāng)前 history:
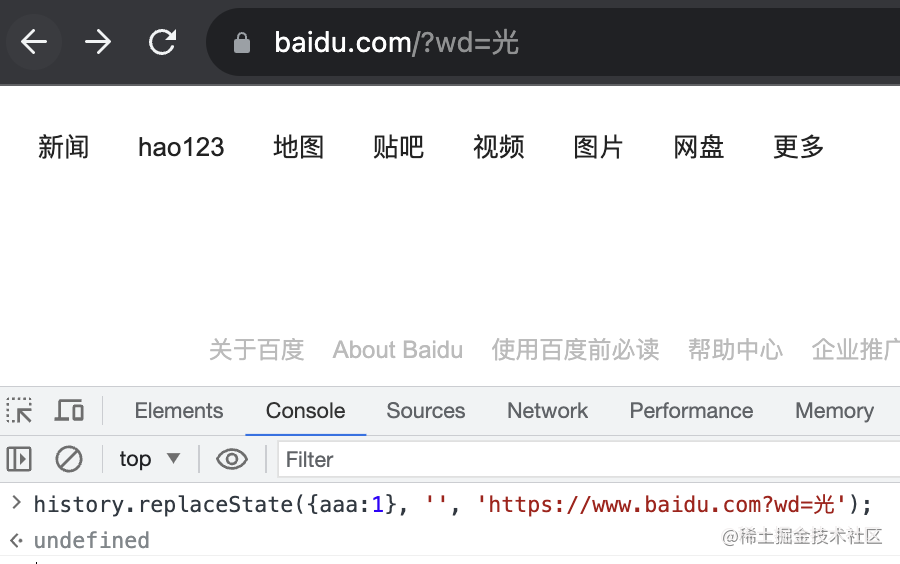
history.replaceState({aaa:1}, '', 'https://www.baidu.com?wd=光')
第一個參數(shù)是 state、第二個參數(shù)是 title,第三個是替換的 url。
不過第二個參數(shù)基本都不支持,state 倒是能拿到。
比如我在 https://www.baidu.com 那頁 replaceState 為一個新的 url:
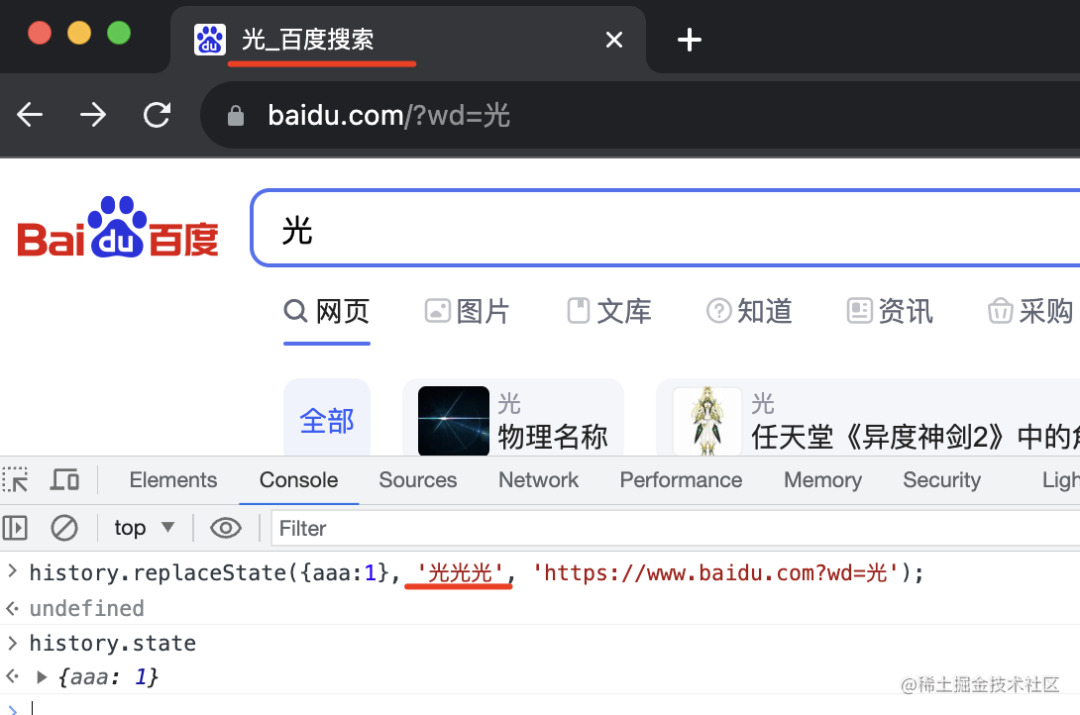
前后 history 都沒變,只有當(dāng)前的變了:
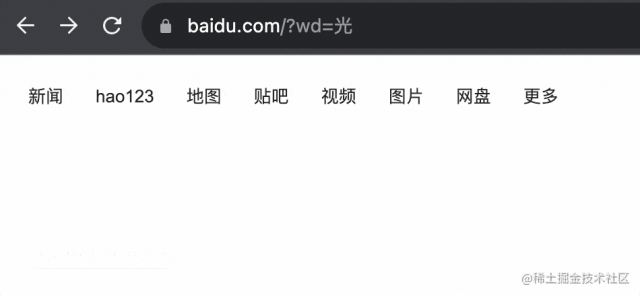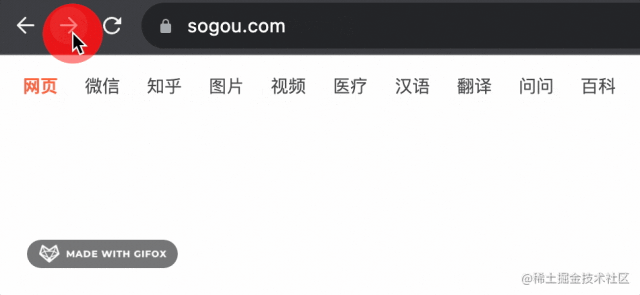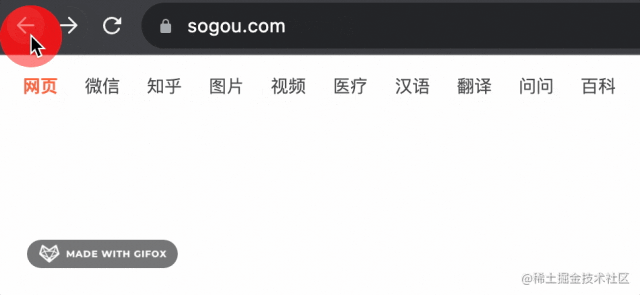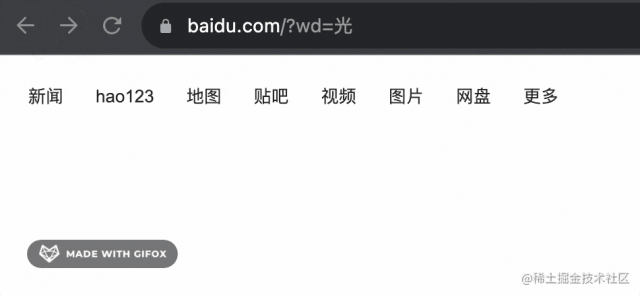
也就是這樣:
當(dāng)然,你還可以用 history.pushState 來添加一個新的 history:
history.pushState({bbb:1}, '', 'https://www.baidu.com?wd=東');

但有個現(xiàn)象,就是之后的 history 都沒了:

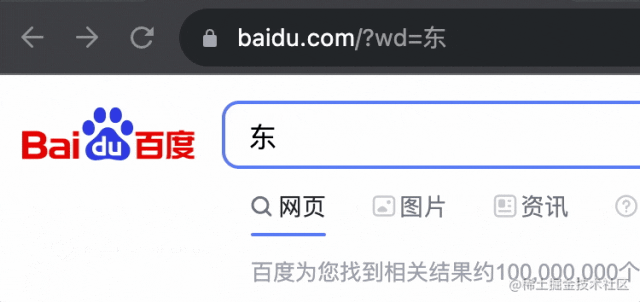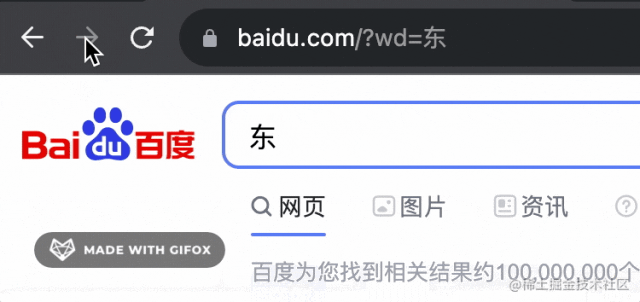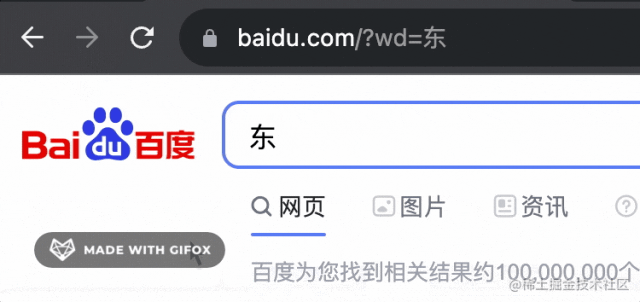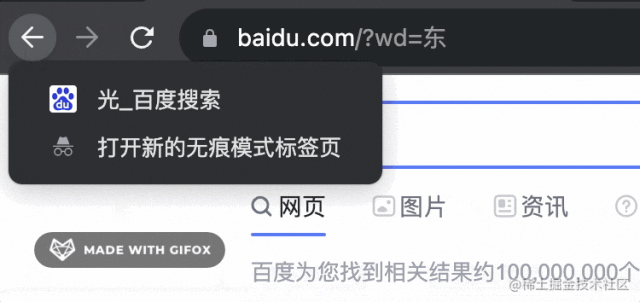
也就是變成了這樣:
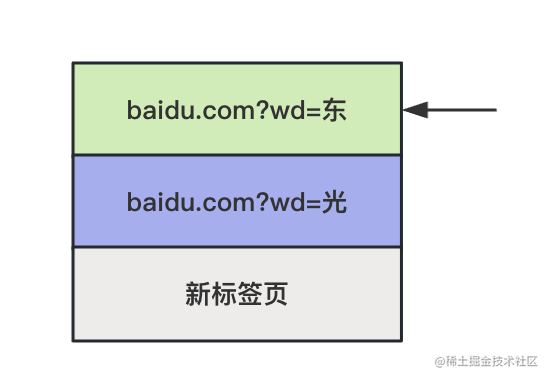
為什么呢?
因?yàn)槟闶?history.pushState 的時候,和后面的 history 沖突了,也就是分叉了:
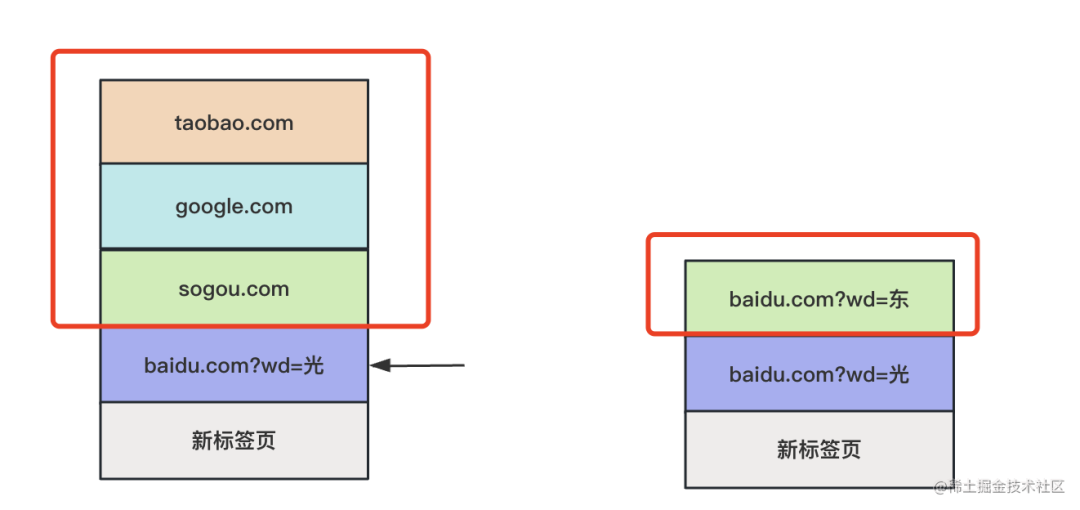
這時候自然只能保留一個分支,也就是最新的那個。
這時候 history.length 就是 3 了。
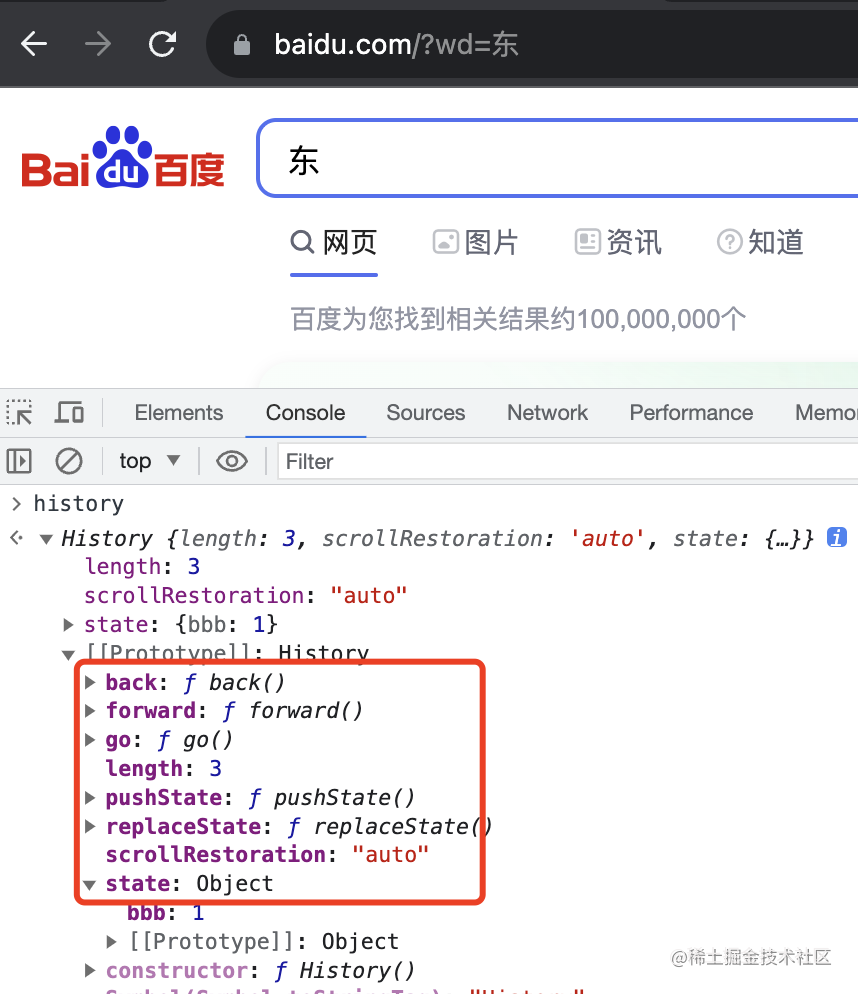
至此,history 的 length、go、back、forward、pushState、replaceState、state 這些 api 我們就用了一遍了。
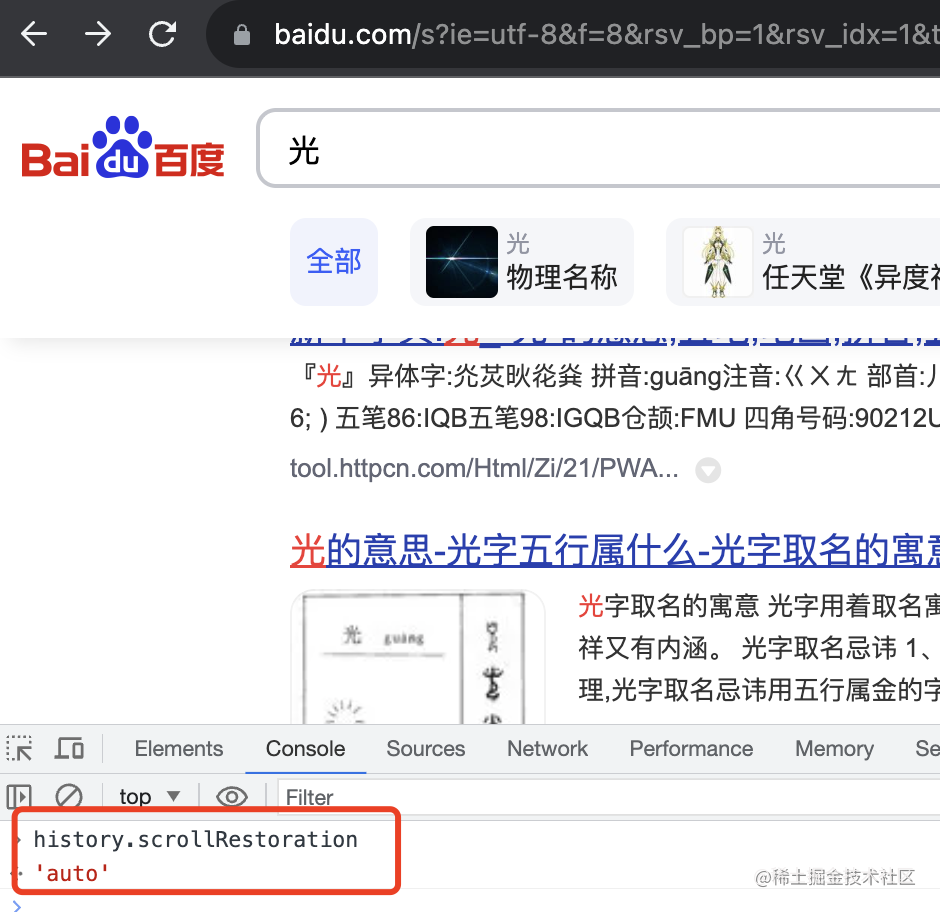
還有個 history.scrollRestoration 是用來保留滾動位置的:
有兩個值 auto、manual,默認(rèn)是 auto,也就是會自動定位到上次滾動位置,設(shè)置為 manual 就不會了。
比如我訪問百度到了這個位置:
打開個新頁面,再退回來:

依然是在上次滾動到的位置。
這是因?yàn)樗?history.scrollRestoration 是 auto
我們把它設(shè)置為 manual 試試看:
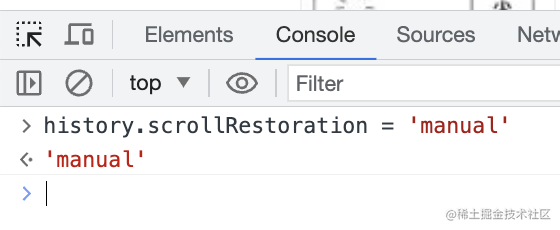

這時候就算滾動到了底部,再切回來也會回到最上面。
此外,與 history 相關(guān)的還有個事件:popstate
當(dāng)你在 history 中導(dǎo)航時,popstate 就會觸發(fā),比如 history.forwad、histroy.back、history.go。
但是 history.pushState、history.replaceState 這種并不會觸發(fā) popstate。
我們測試下:
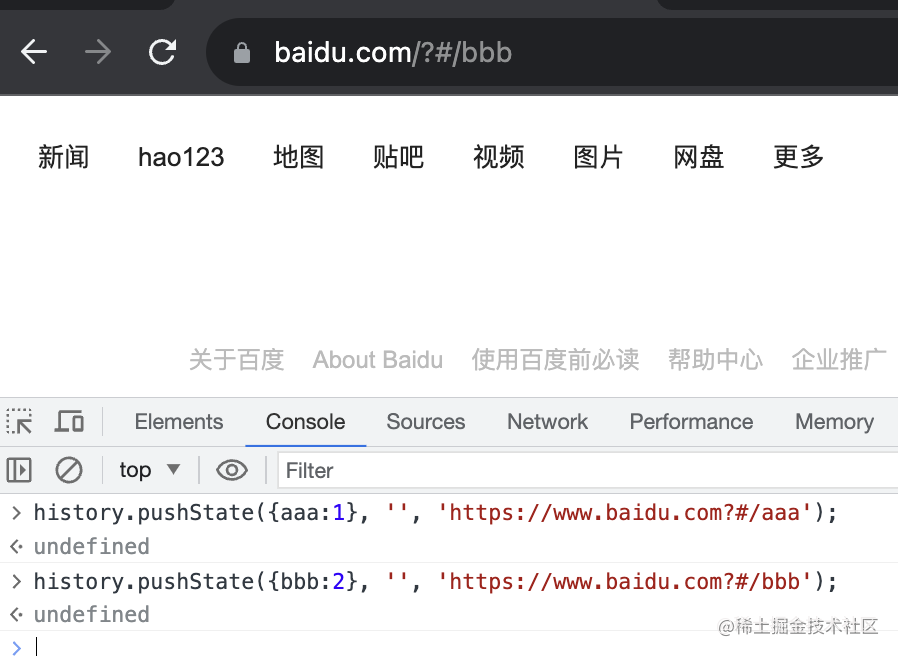
history.pushState({aaa:1}, '', 'https://www.baidu.com?#/aaa');
history.pushState({bbb:2}, '', 'https://www.baidu.com?#/bbb');
我在 www.baidu.com 這個頁面 pushState 添加了兩個 history。
加上導(dǎo)航頁一共 4 個:
然后我監(jiān)聽 popstate 事件:
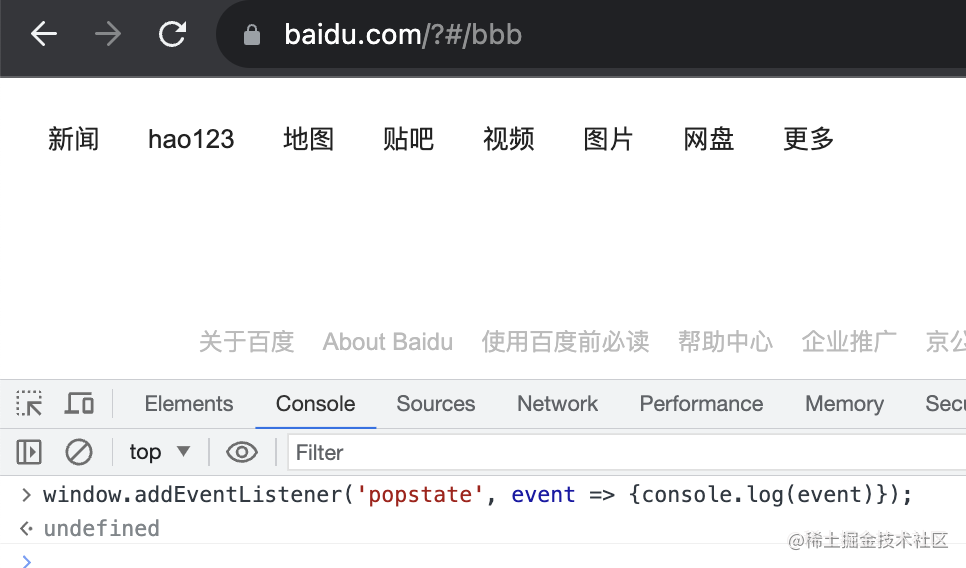
window.addEventListener('popstate', event => {console.log(event)});
執(zhí)行 history.back 和 history.forward 都會觸發(fā) popstate 事件:
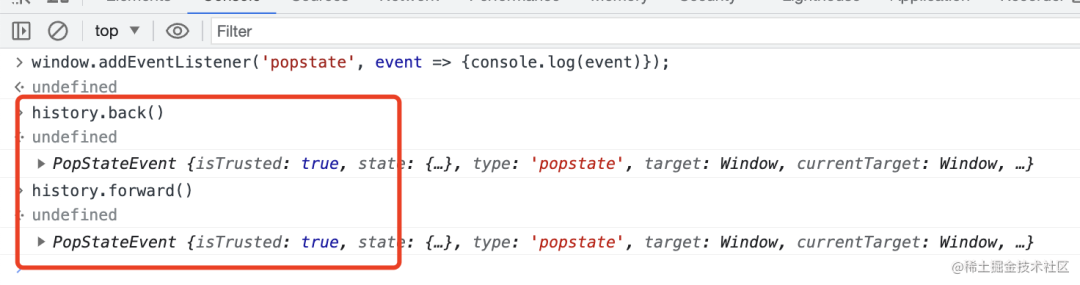
事件包含 state,也可以從 target.location 拿到當(dāng)前 url
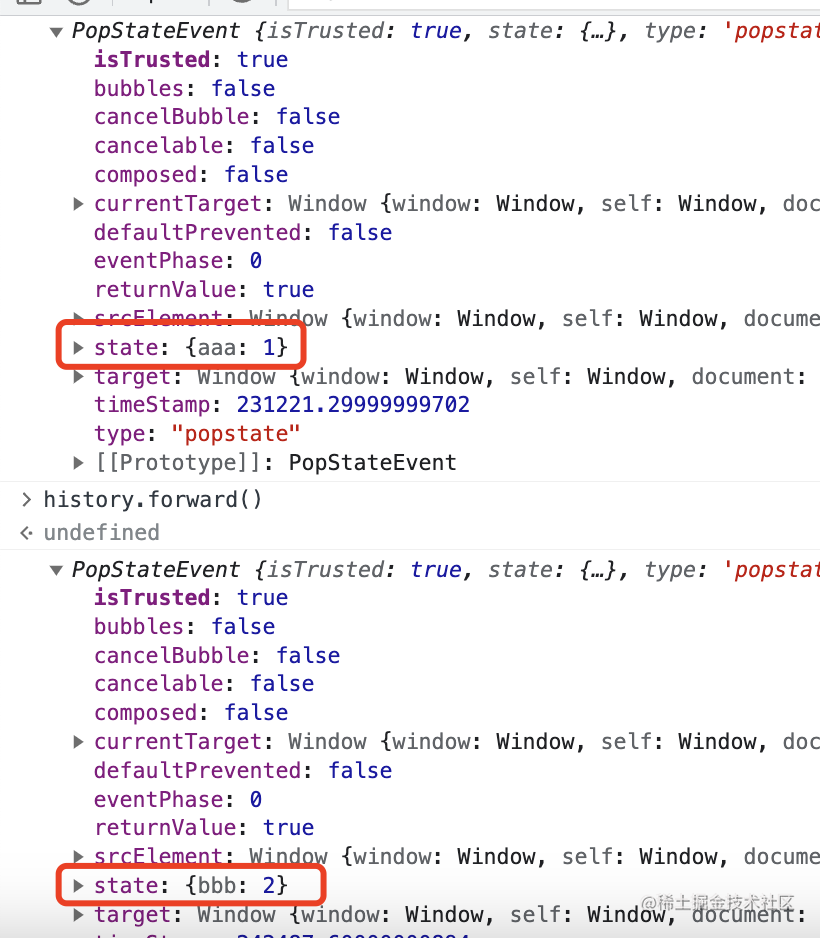
但是當(dāng)你 history.pushState、history.replaceState 并不會觸發(fā)它:
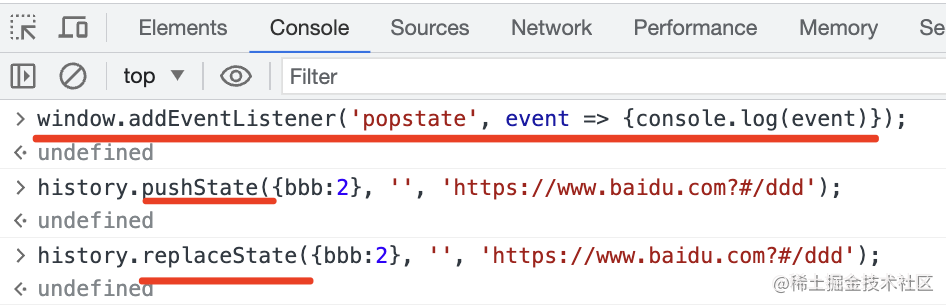
也就是說添加、修改 history 不會觸發(fā) popstate,只有在 state 之間導(dǎo)航才會觸發(fā)。
綜上,history api 和 popstate 事件我們都過了一遍。
基于這些就可以實(shí)現(xiàn) React Router。
有的同學(xué)說,不是還有個 hashchange 事件么?
確實(shí),那個就是監(jiān)聽 hash 變化的。
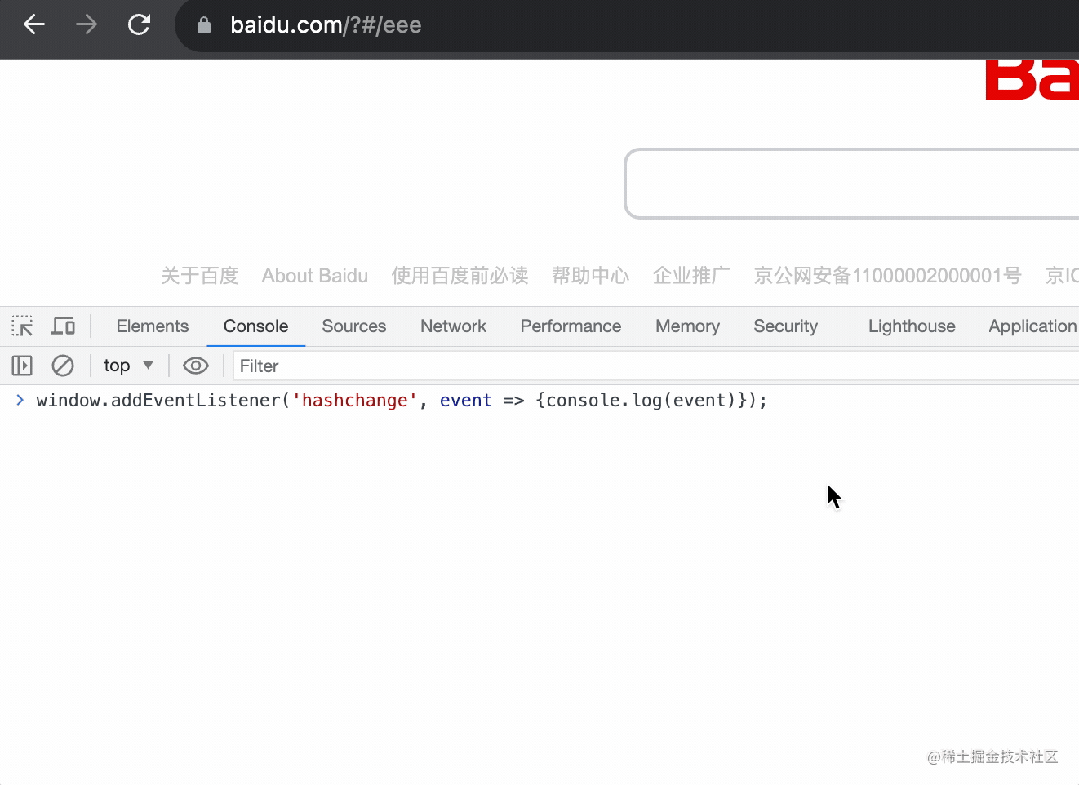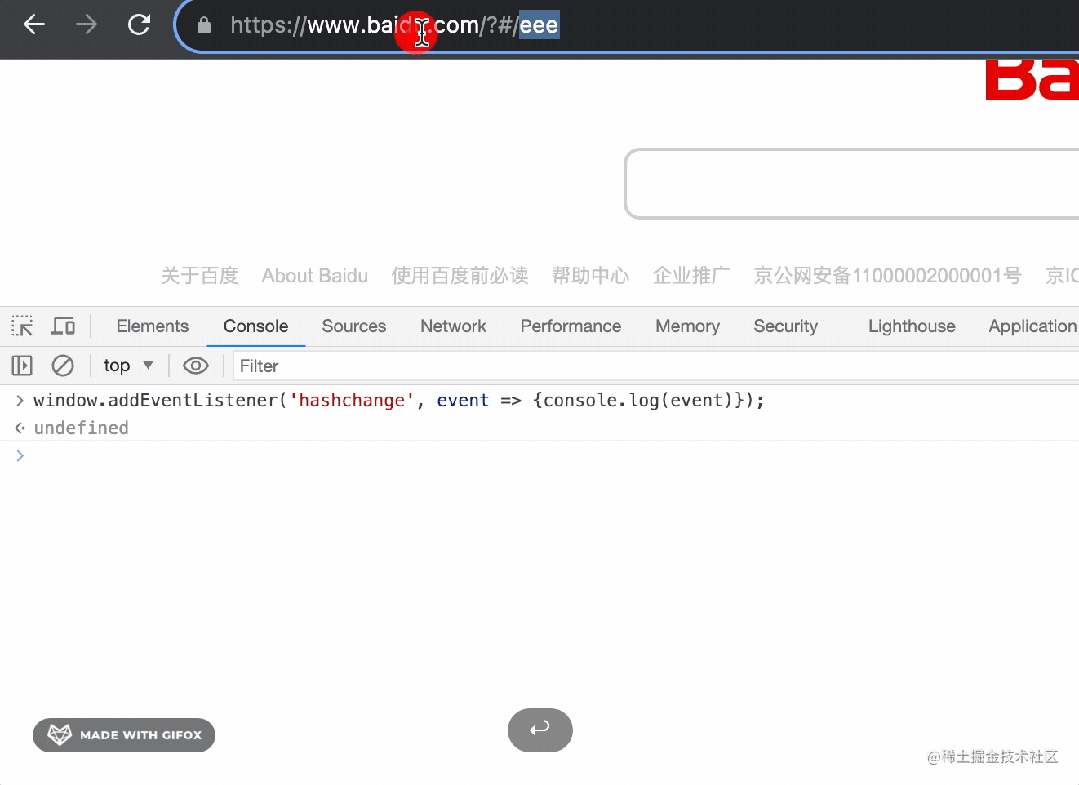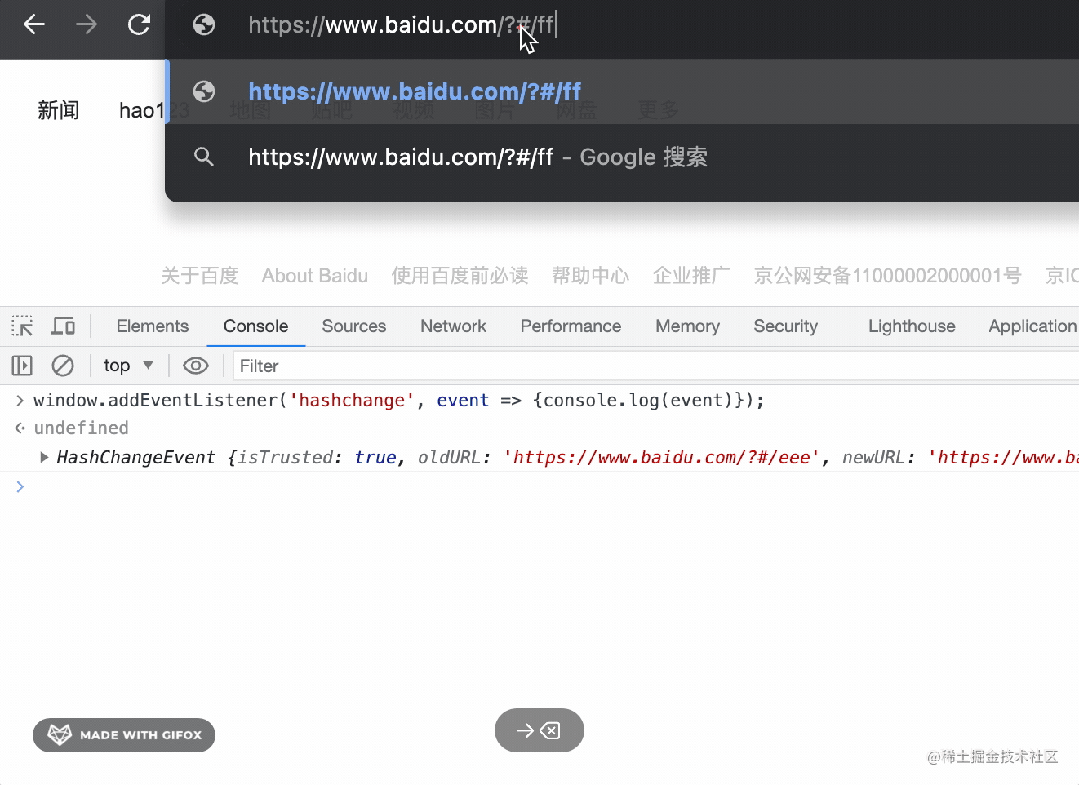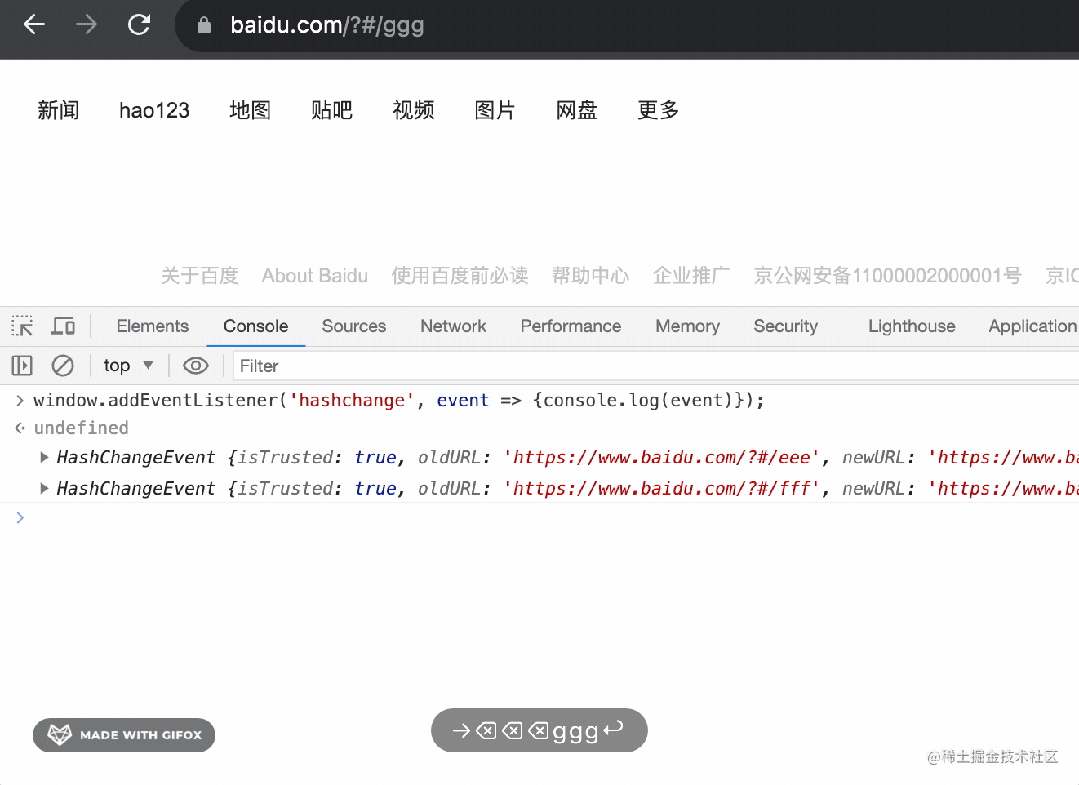
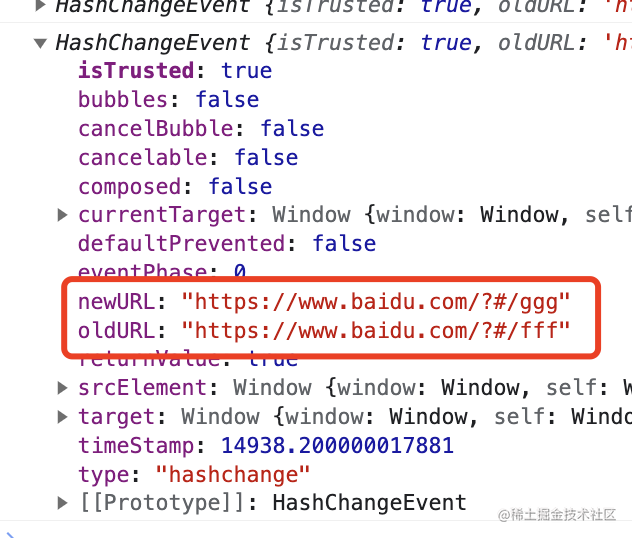
基于它也可以實(shí)現(xiàn) router,但很明顯,hashchange 只能監(jiān)聽 hash 的變化,而 popstate 不只是 hash 變化,功能更多。
所以用 popstate 事件就足夠了。
其實(shí)在 react router 里,就只用到了 popstate 事件,沒用到 hashchange 事件:
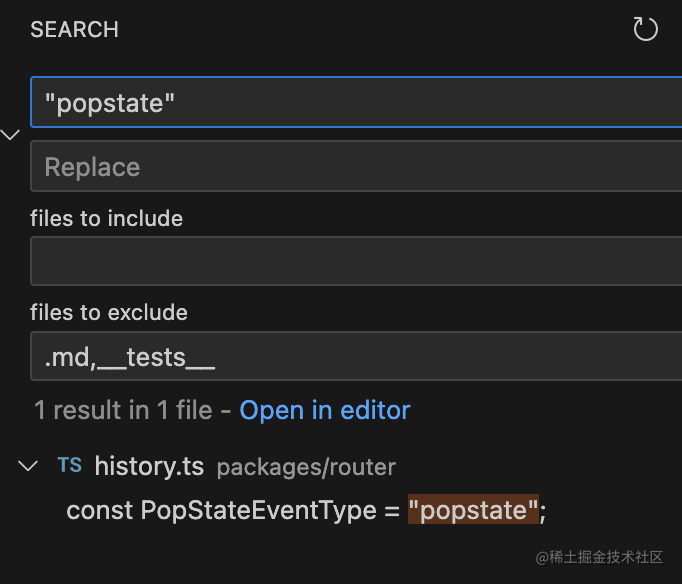
接下來我們就具體來看下 React Router 是怎么實(shí)現(xiàn)的吧。
創(chuàng)建個 react 項(xiàng)目:
npx create-react-app react-router-test
安裝 react-router 的包:
npm install react-router-dom
然后在 index.js 寫如下代碼:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client';
import {
createBrowserRouter,
Link,
Outlet,
RouterProvider,
} from "react-router-dom";
function Aaa() {
return <div>
<p>aaa</p>
<Link to={'/bbb/111'}>to bbb</Link>
<br/>
<Link to={'/ccc'}>to ccc</Link>
<br/>
<Outlet/>
</div>;
}
function Bbb() {
return 'bbb';
}
function Ccc() {
return 'ccc';
}
function ErrorPage() {
return 'error';
}
const routes = [
{
path: "/",
element: <Aaa/>,
errorElement: <ErrorPage/>,
children: [
{
path: "bbb/:id",
element: <Bbb />,
},
{
path: "ccc",
element: <Ccc />,
}
],
}
];
const router = createBrowserRouter(routes);
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(<RouterProvider router={router} />);
通過 react-router-dom 包的 createBrowserRouter 創(chuàng)建 router,傳入 routes 配置。
然后把 router 傳入 RouterProvider。
有一個根路由 /、兩個子路由 /bbb/:id 和 /ccc
把開發(fā)服務(wù)跑起來:
npm run start
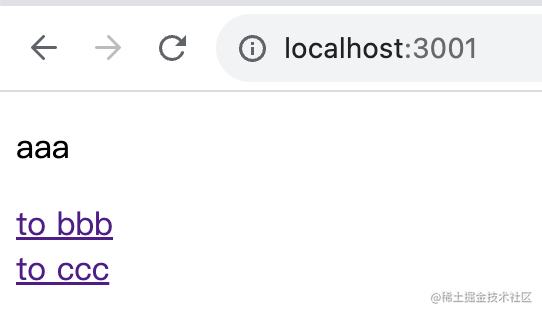
測試下:
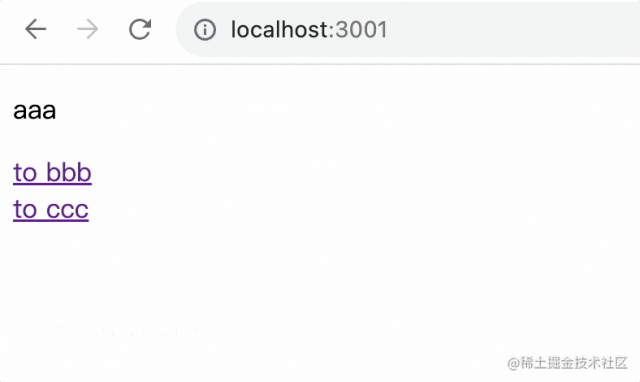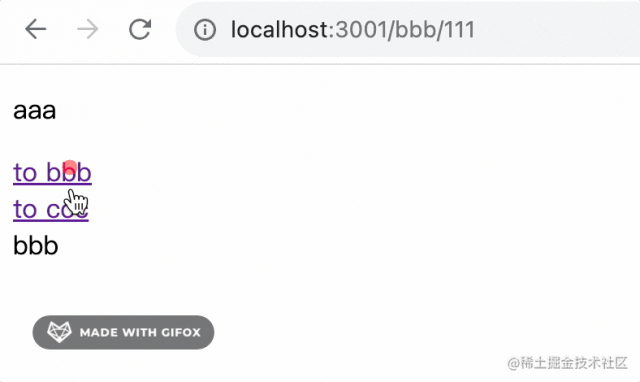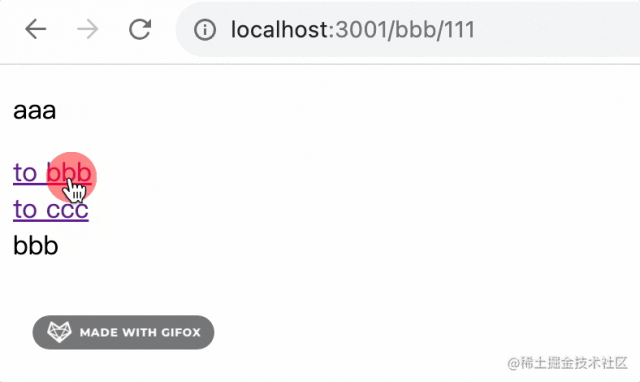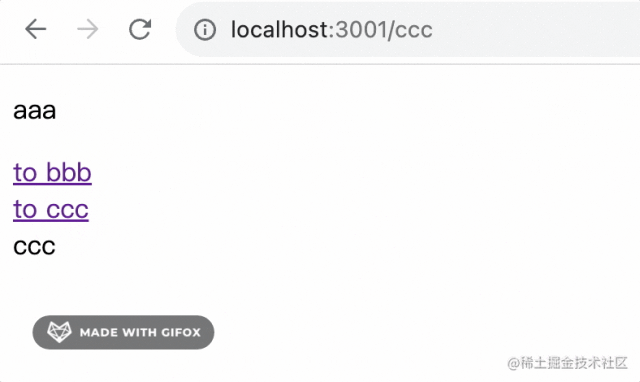
子路由對應(yīng)的組件在
當(dāng)沒有對應(yīng)路由的時候,會返回錯誤頁面:
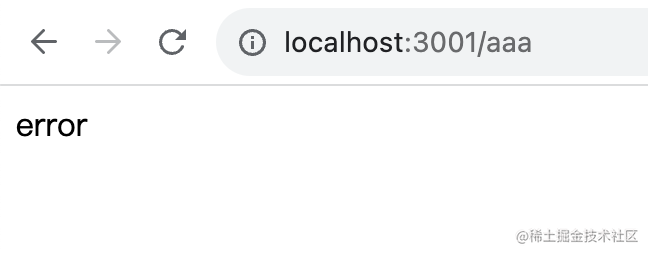
那它是怎么實(shí)現(xiàn)的呢?
我們斷點(diǎn)調(diào)試下:
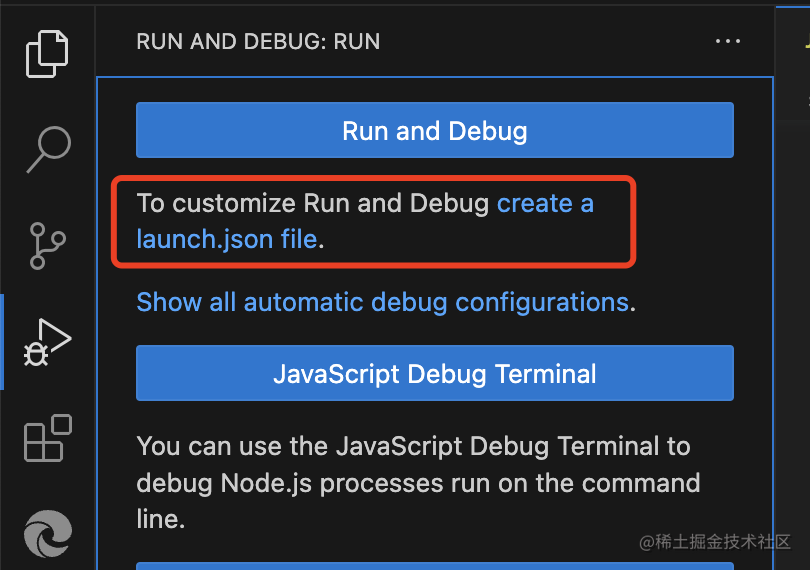
創(chuàng)建調(diào)試配置文件 launch.json,然后創(chuàng)建 chrome 類型的調(diào)試配置:
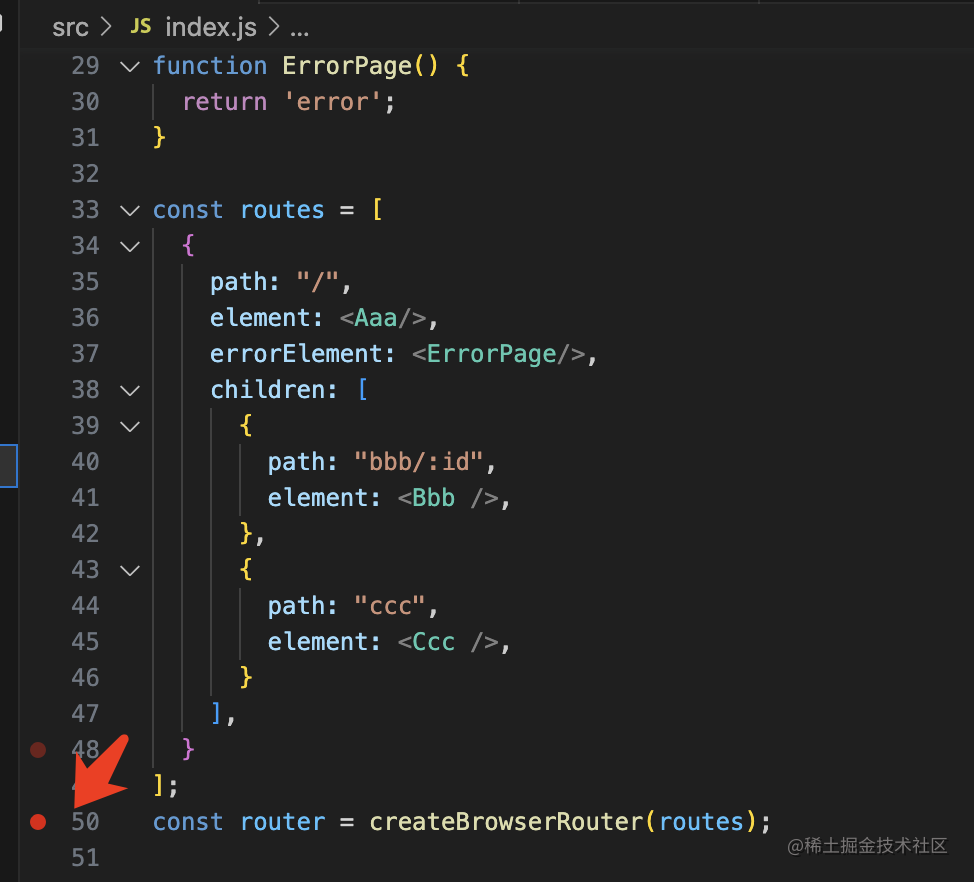
在 createBrowserRouter 的地方打個斷點(diǎn):
點(diǎn)擊 debug:

代碼會在這里斷住:
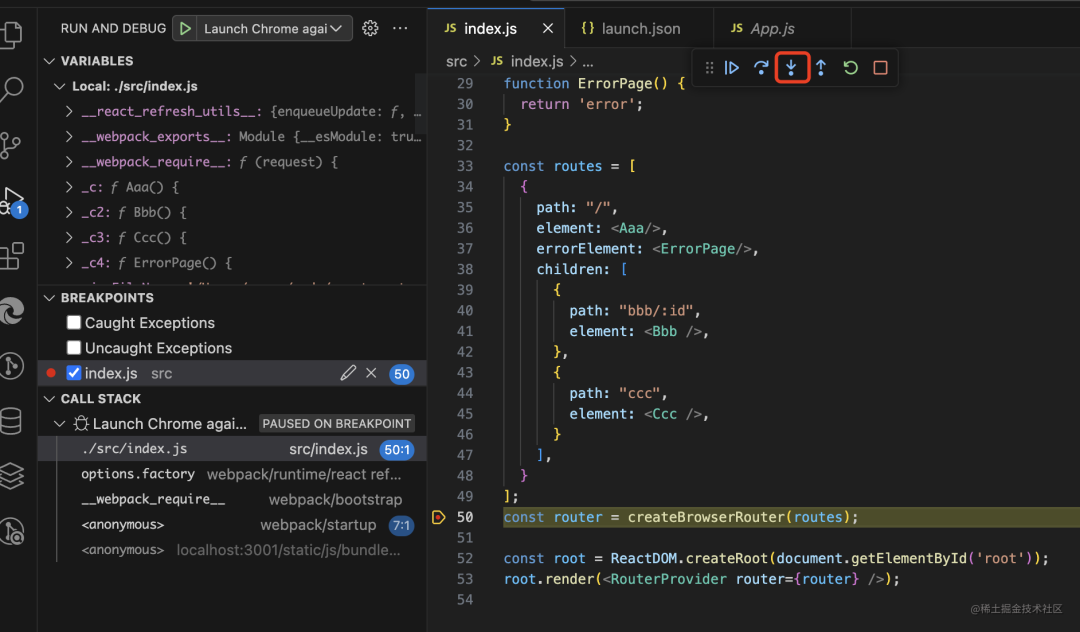
點(diǎn)擊 step into 進(jìn)入函數(shù)內(nèi)部:
它調(diào)用了 createRouter:
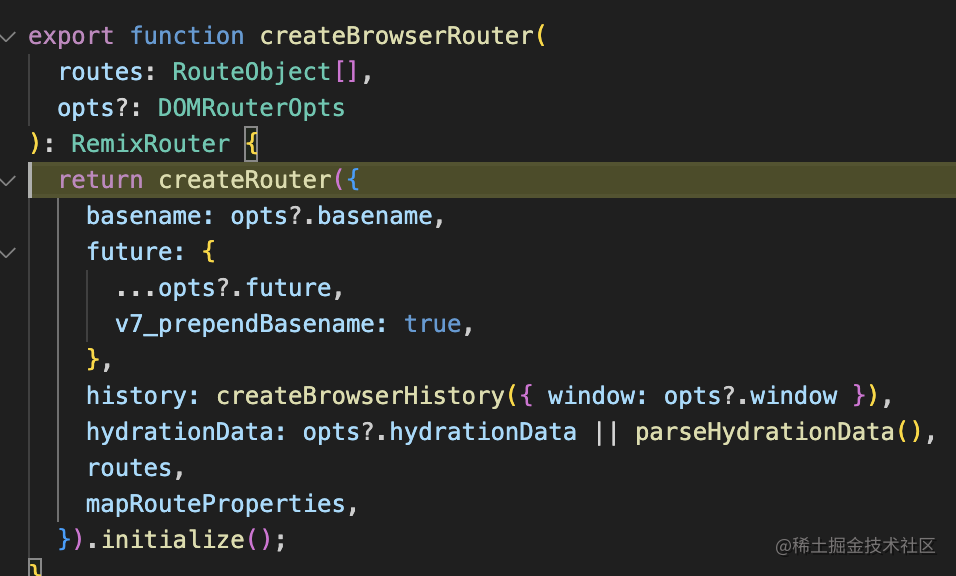
這里傳入了 history。
這個不是原生的 history api,而是包裝了一層之后的:
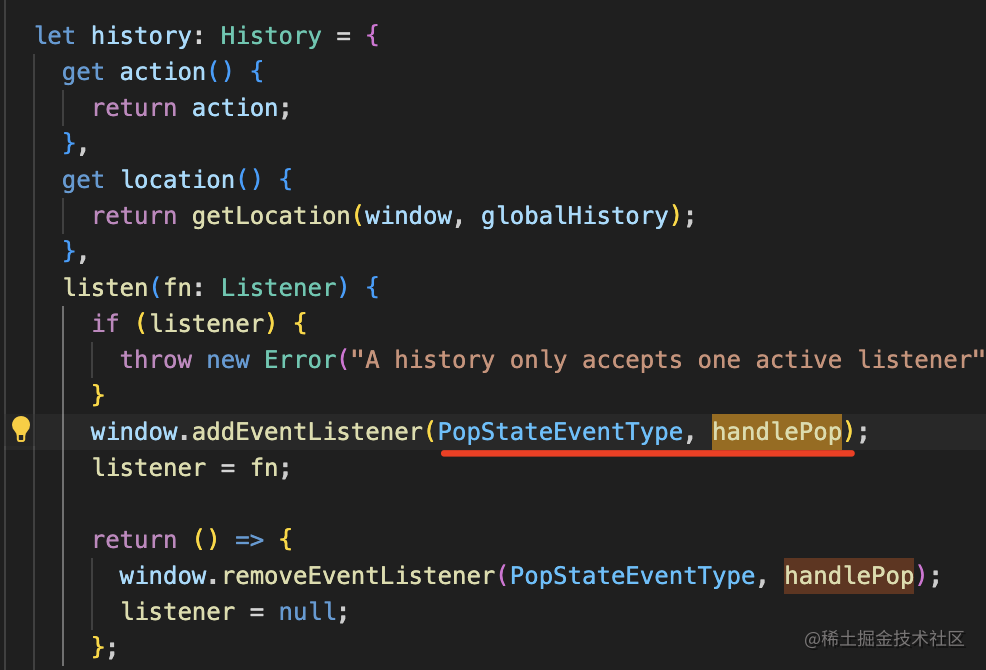
關(guān)注 listen、push、replace、go 這 4 個方法就好了:
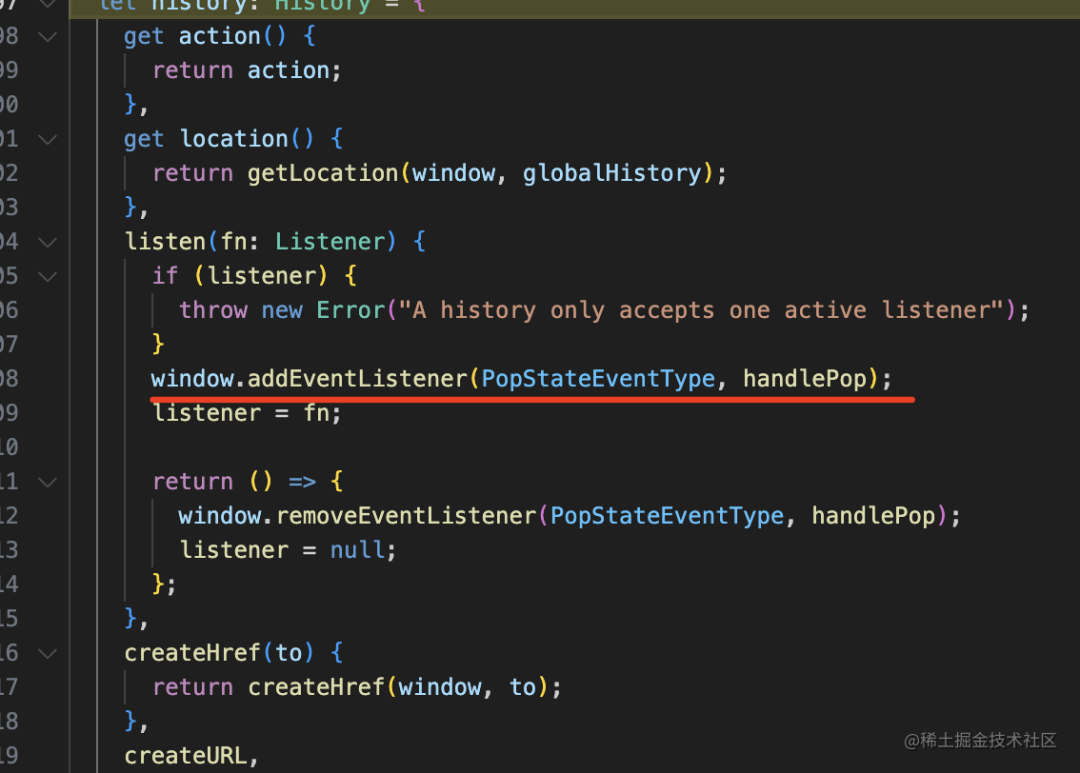
listen 就是監(jiān)聽 popstate 事件。
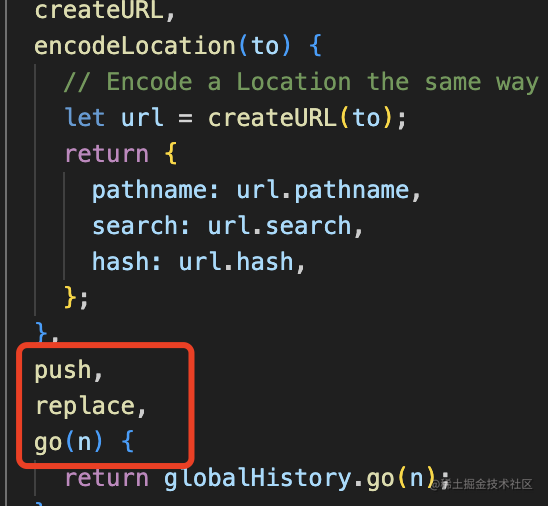
而 push、replace、go 都是對 history 的 api 的封裝:
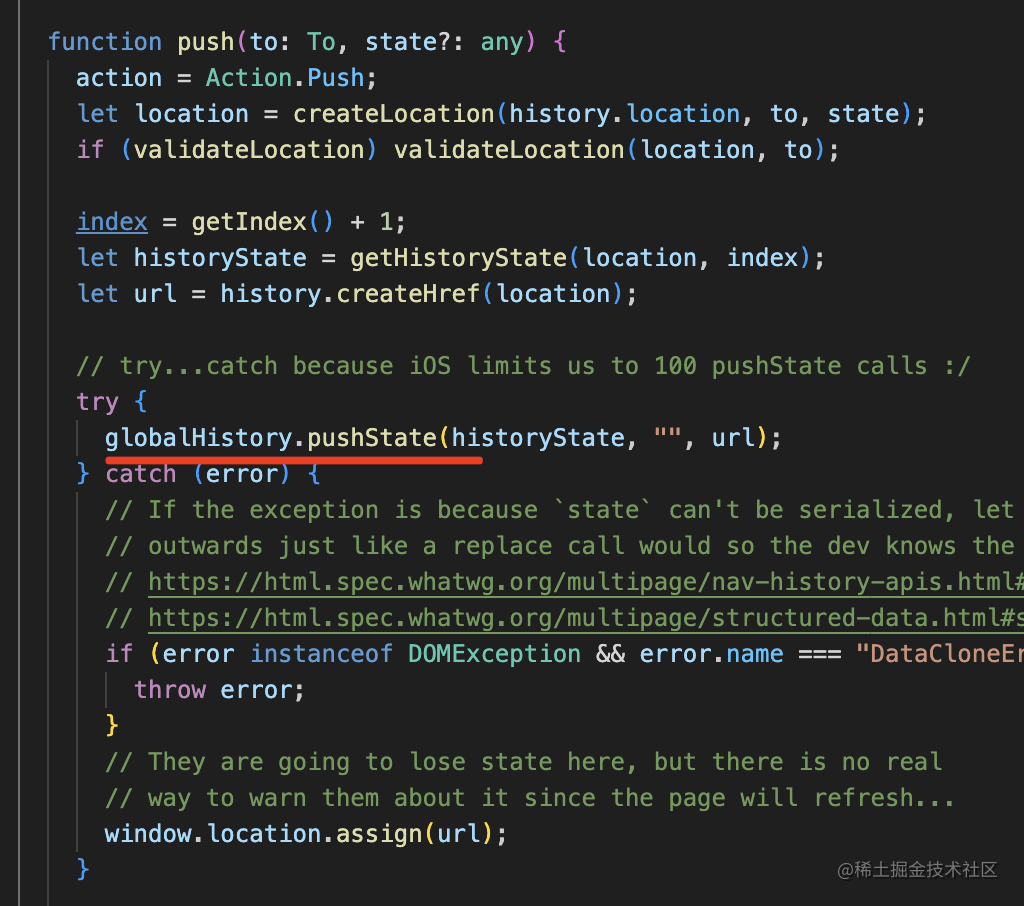
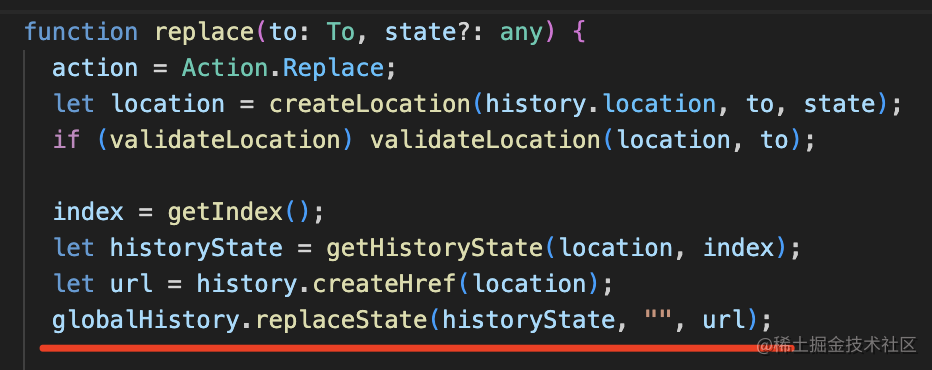
此外,history 還封裝了 location 屬性,不用自己從 window 取了。
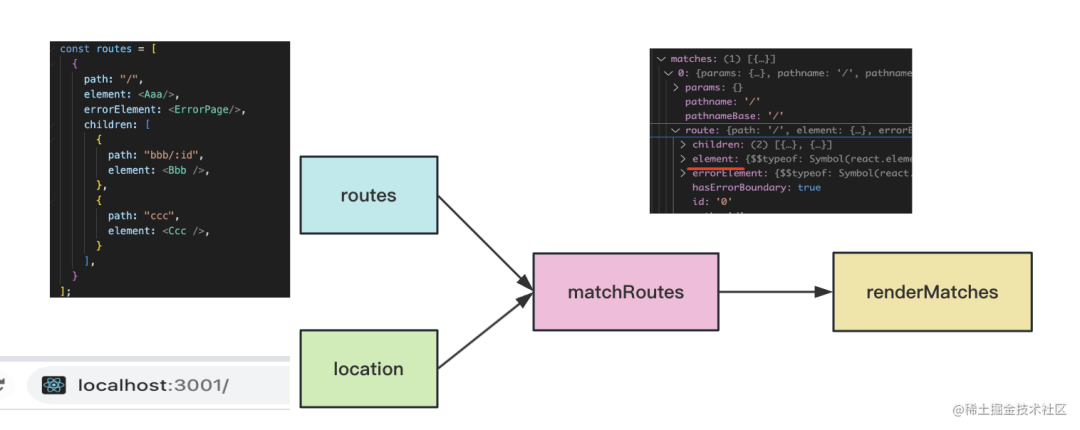
然后 createRouter 里會對 routes 配置和當(dāng)前的 location 做一次 match:
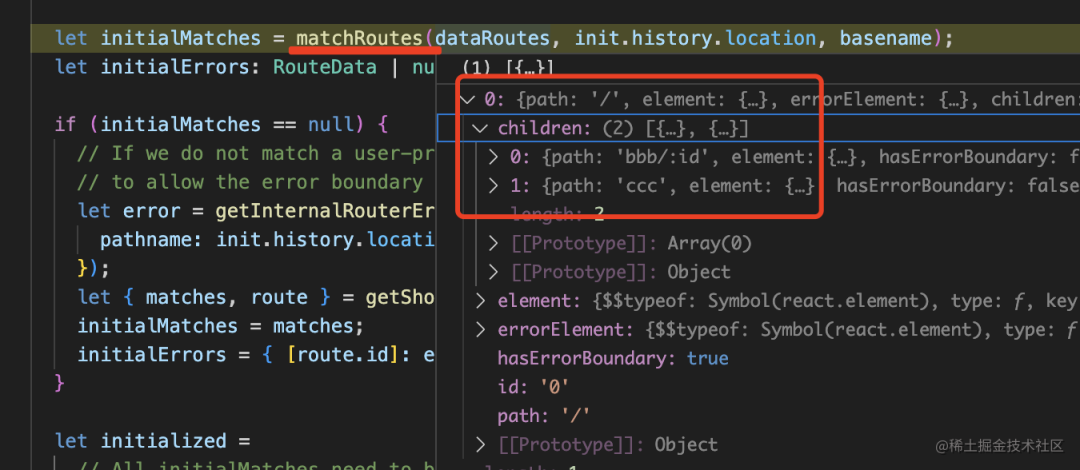
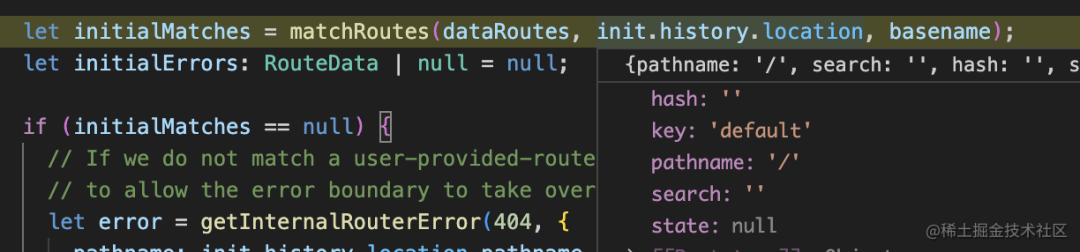
matchRoutes 會把嵌套路由拍平,然后和 location 匹配:

然后就匹配到了要渲染的組件以及它包含的子路由:
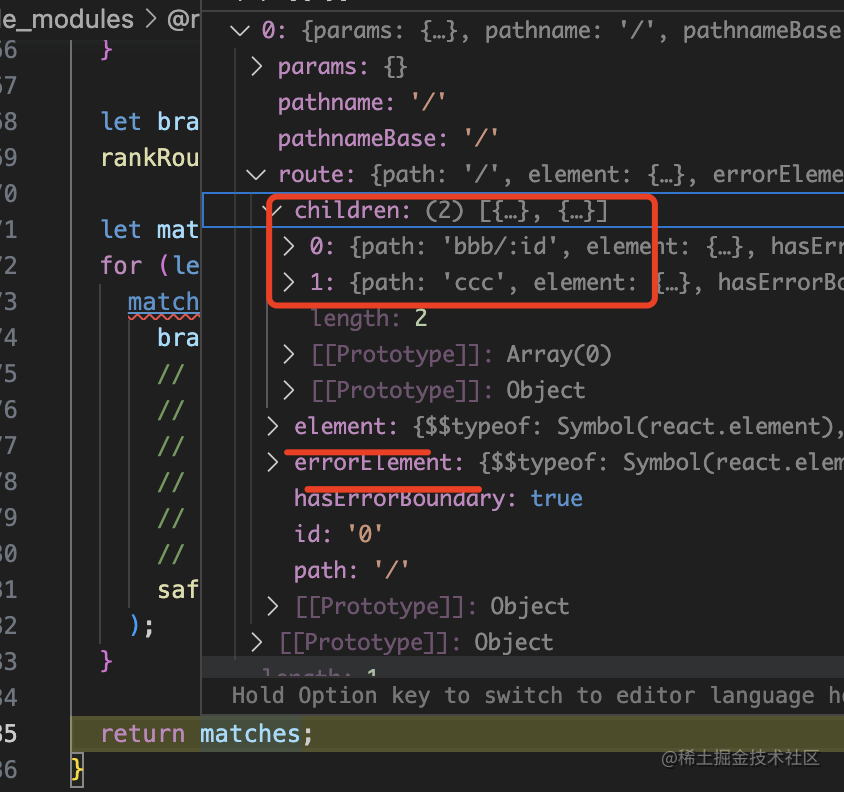
這樣當(dāng)組件樹渲染的時候,就知道渲染什么組件了:

就是把 match 的這個結(jié)果渲染出來。
這樣就完成了路由對應(yīng)的組件渲染:
也就是這樣的流程:
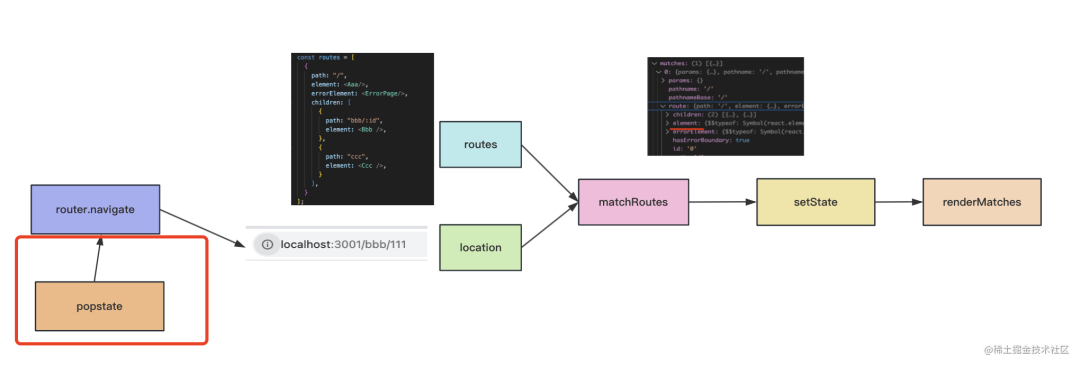
當(dāng)點(diǎn)擊 link 切換路由的時候:
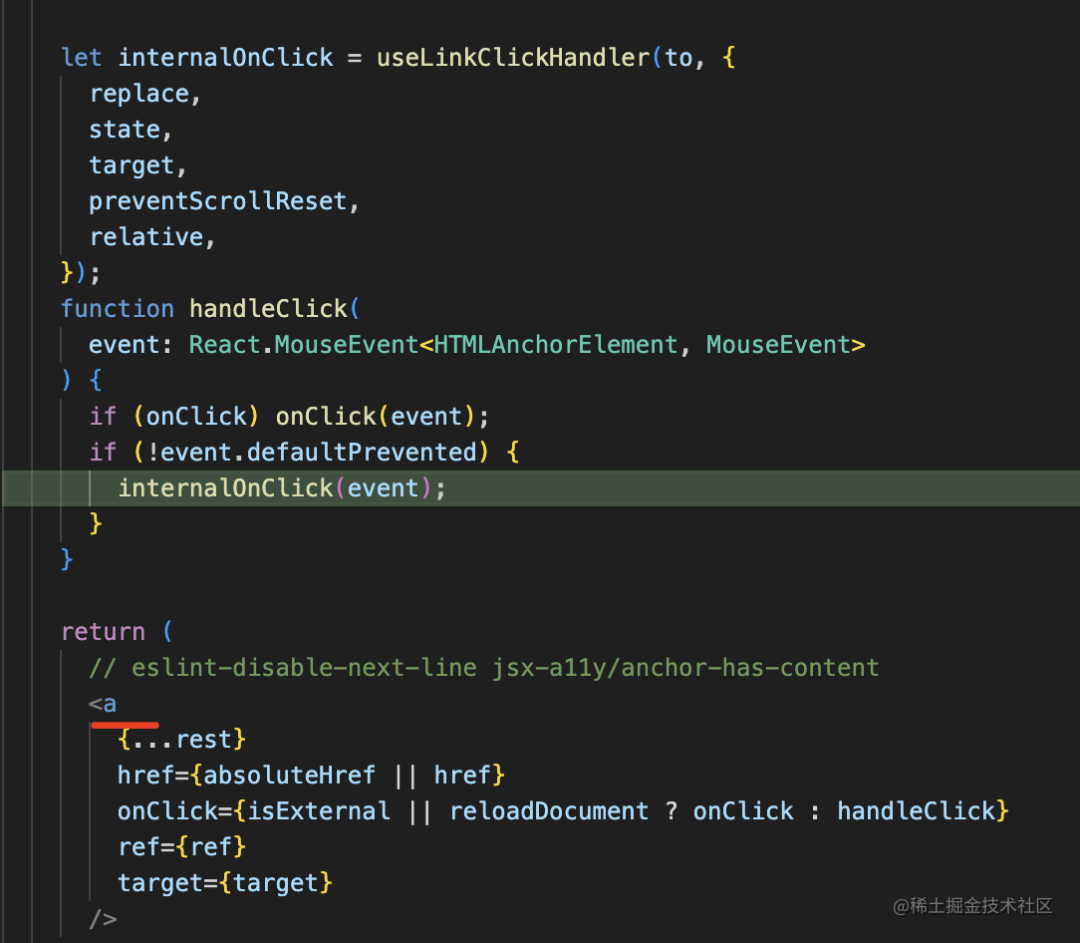
會執(zhí)行 navigate 方法:

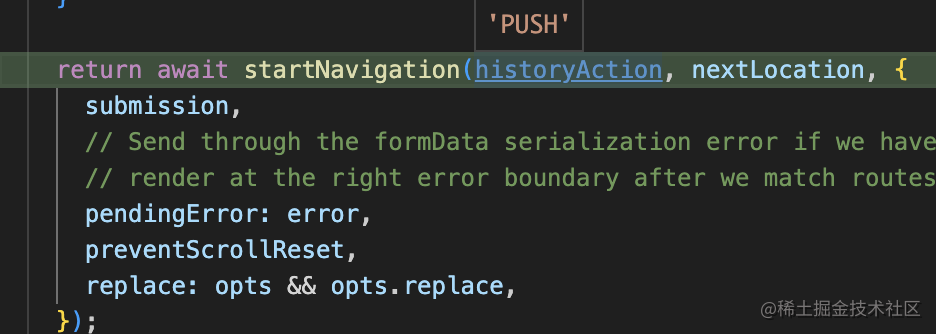
然后又到了 matchRoutes 的流程:

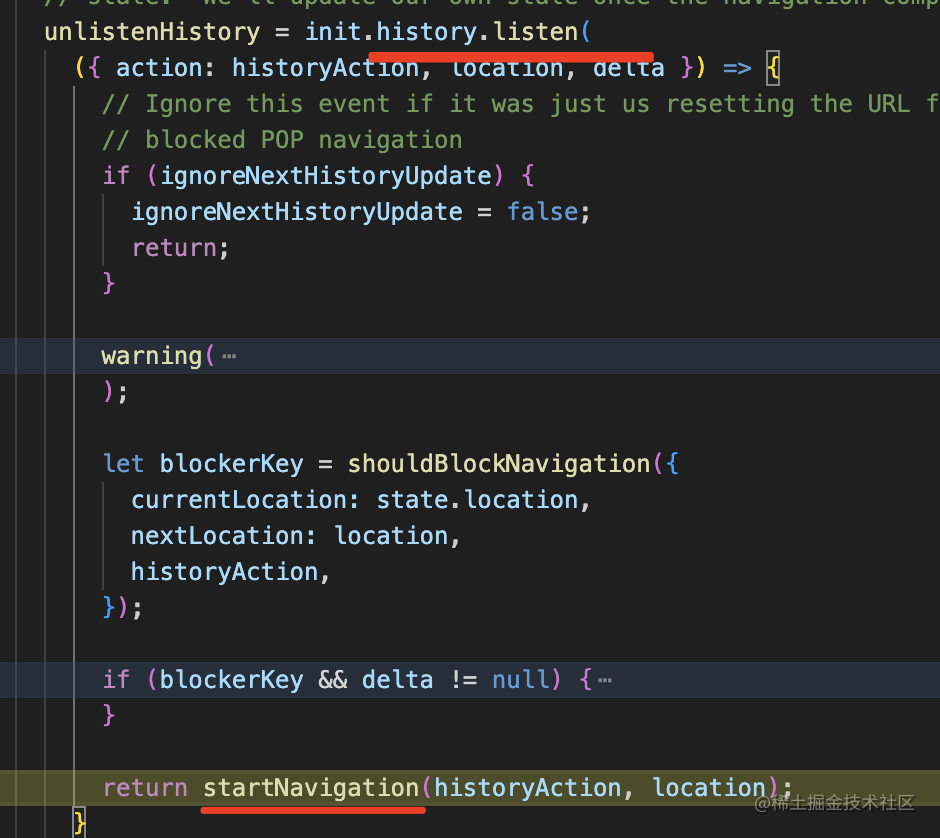
match 完會 pushState 或者 replaceState 修改 history,然后更新 state:
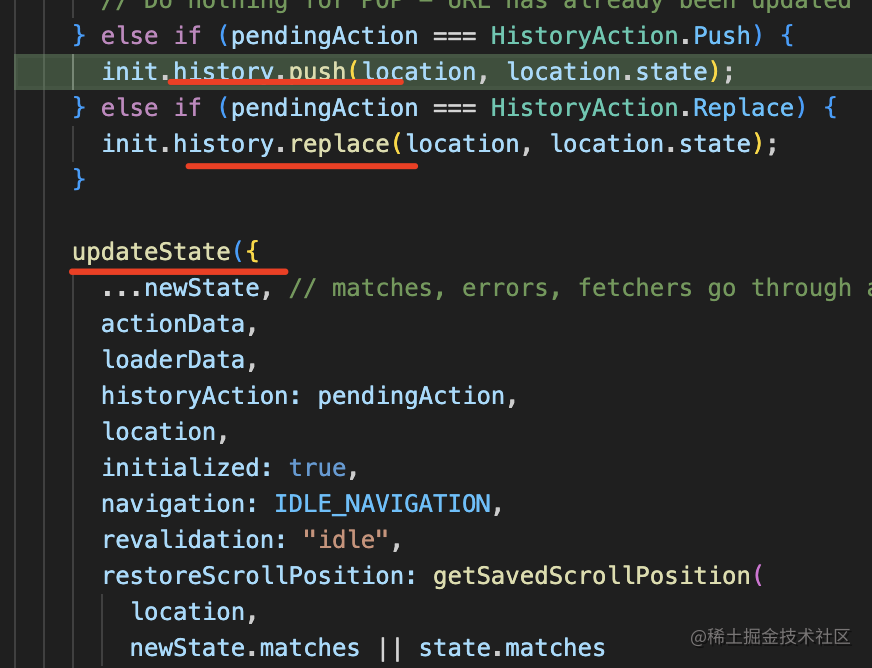
然后觸發(fā)了 setState,組件樹會重新渲染:
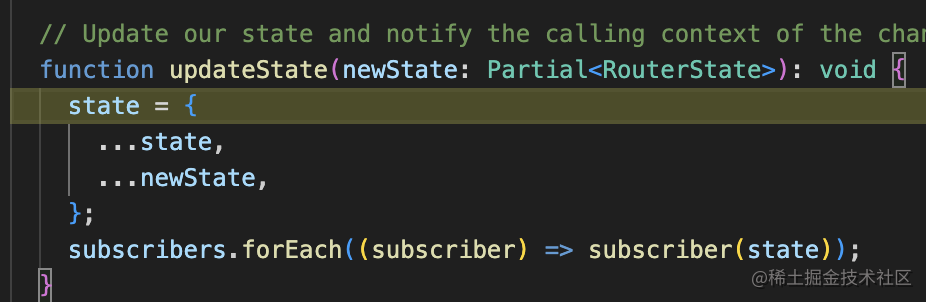
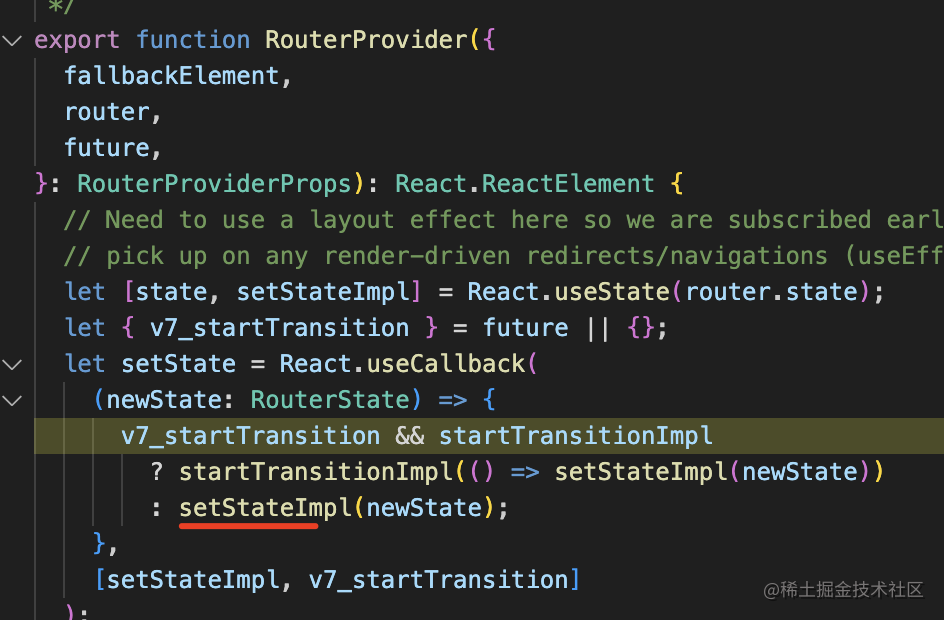
也就是這樣的流程:
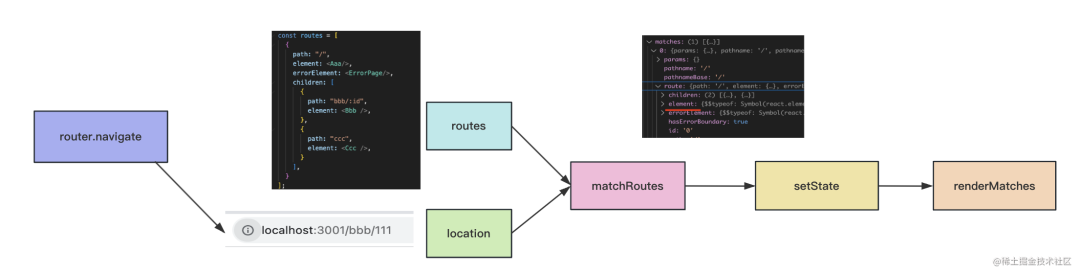
router.navigate 會傳入新的 location,然后和 routes 做 match,找到匹配的路由。
之后會 pushState 修改 history,并且觸發(fā) react 的 setState 來重新渲染,重新渲染的時候通過 renderMatches 把當(dāng)前 match 的組件渲染出來。
而渲染到 Outlet 的時候,會從 context 中取出當(dāng)前需要渲染的組件來渲染:
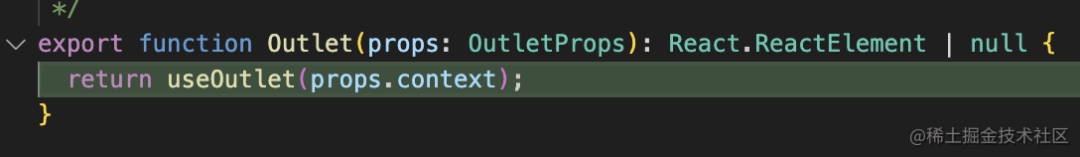

這就是 router 初次渲染和點(diǎn)擊 link 時的渲染流程。
那點(diǎn)擊前進(jìn)后退按鈕的時候呢?
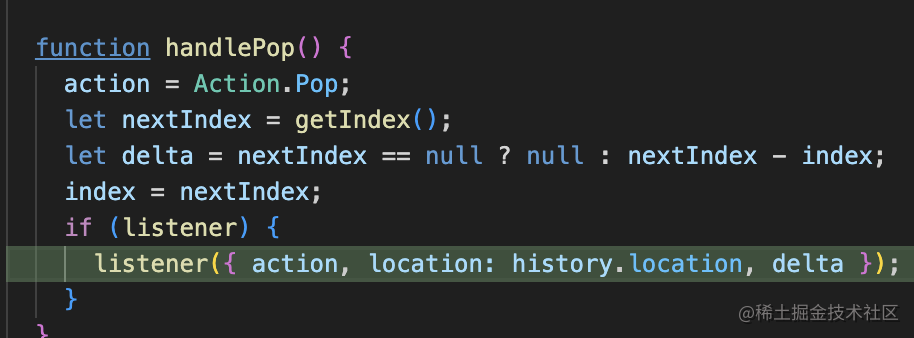
這個就是監(jiān)聽 popstate,然后也做一次 navigate 就好了:
后續(xù)流程一樣。
回過頭來,其實(shí) react router 的 routes 其實(shí)支持這兩種配置方式:

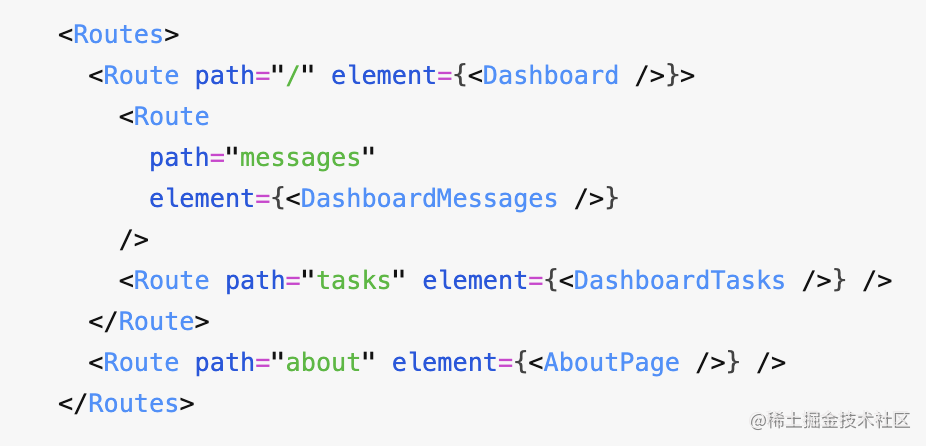
效果一樣。
看下源碼就知道為什么了:
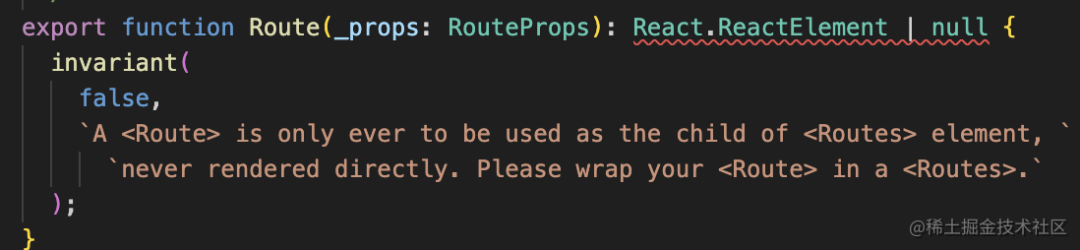
首先,這個 Route 組件就是個空組件,啥也沒:
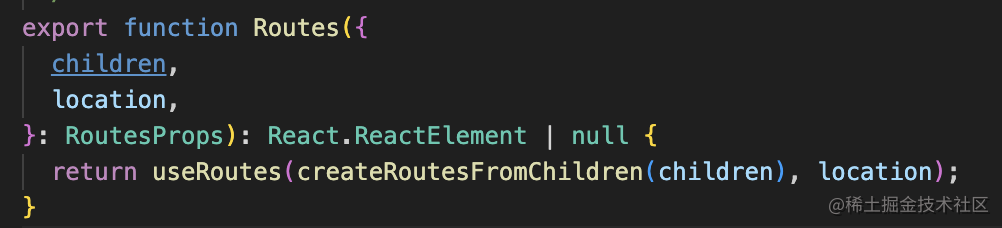
而 Routes 組件里會從把所有子組件的參數(shù)取出來,變成一個個 route 配置:
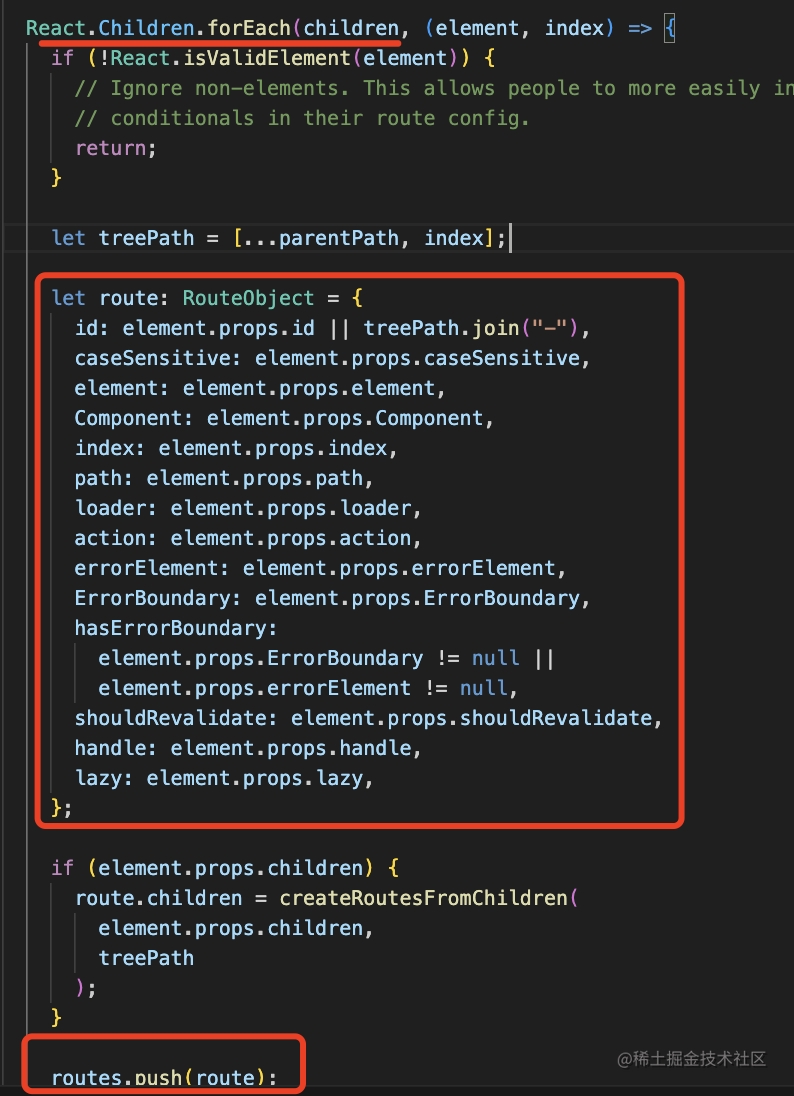
結(jié)果不就是和對象的配置方式一樣么?
總結(jié)
我們學(xué)習(xí)了 history api 和 React Router 的實(shí)現(xiàn)原理。
history api 有這些:
-
length:history 的條數(shù) -
forward:前進(jìn)一個 -
back:后退一個 -
go:前進(jìn)或者后退 n 個 -
pushState:添加一個 history -
replaceState:替換當(dāng)前 history -
scrollRestoration:保存 scroll 位置,取值為 auto 或者 manual,manual 的話就要自己設(shè)置 scroll 位置了
而且還有 popstate 事件可以監(jiān)聽到 history.go、history.back、history.forward 的導(dǎo)航,拿到最新的 location。
這里要注意 pushState、replaceState 并不能觸發(fā) popstate 事件。也就是 history 之間導(dǎo)航(go、back、forward)可以觸發(fā) popstate,而修改 history (push、replace)不能觸發(fā)。
React Router 就是基于這些 history api 實(shí)現(xiàn)的。
首次渲染的時候,會根據(jù) location 和配置的 routes 做匹配,渲染匹配的組件。
之后點(diǎn)擊 link 鏈接也會進(jìn)行 location 和 routes 的匹配,然后 history.pushState 修改 history,之后通過 react 的 setState 觸發(fā)重新渲染。
前進(jìn)后退的時候,也就是執(zhí)行 history.go、history.back、history.forward 的時候,會觸發(fā) popstate,這時候也是同樣的處理,location 和 routes 的匹配,然后 history.pushState 修改 history,之后通過 react 的 setState 觸發(fā)重新渲染。
渲染時會用到 Outlet組件 渲染子路由,用到 useXxx 來取一些匹配信息,這些都是通過 context 來傳遞的。
這就是 React Router 的實(shí)現(xiàn)原理,它和 history api 是密不可分的。
下方加 Nealyang 好友回復(fù)「 加群」即可。
如果你覺得這篇內(nèi)容對你有幫助,我想請你幫我2個小忙:
